Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSP
Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSP
Uploaded by
engabd345Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Teste Ingles TecnologiaDocument5 pagesTeste Ingles TecnologiaMeninaDuMarNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Definition of The Derivative Lab 5: GraphicallyDocument22 pagesExploring The Definition of The Derivative Lab 5: GraphicallyJill GoughNo ratings yet
- English II Merchant of Venice Notes Compiled by Nilay Kumar Das PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish II Merchant of Venice Notes Compiled by Nilay Kumar Das PDFSubhadip RoyNo ratings yet
- Using Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7Document2 pagesUsing Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Using Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7Document2 pagesUsing Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 0402 gdc08 XXTNSPDocument3 pagesBks MaiHL 0402 gdc08 XXTNSPMark ChangNo ratings yet
- Daa Module2Document83 pagesDaa Module2sreekanthpyatagoudaNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84Document5 pagesBks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84W SNo ratings yet
- Exercises 4Document3 pagesExercises 4Madrid MadridNo ratings yet
- GCD HL CH6 Example11Document4 pagesGCD HL CH6 Example11Mark ChangNo ratings yet
- De The Only GDC That I Hademdekmdekmekmve Used Is The TI 83 (+) and Thus The Comments Below Are Restricted To ThisDocument16 pagesDe The Only GDC That I Hademdekmdekmekmve Used Is The TI 83 (+) and Thus The Comments Below Are Restricted To ThisSarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 BBA1 SundayDocument18 pagesLec 8 BBA1 SundaySYED HASHIM ALI BUKHARINo ratings yet
- Area Under A Curve - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityDocument8 pagesArea Under A Curve - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Modelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Document4 pagesModelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Sophie HoltusNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Evaluating LimitsDocument27 pagesTechniques For Evaluating LimitsRaven MercadoNo ratings yet
- Linear and Multiobjective Programming With Fuzzy Stochastic ExtensionsDocument103 pagesLinear and Multiobjective Programming With Fuzzy Stochastic ExtensionsKharolin MauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document16 pagesChapter 01sameh esmatNo ratings yet
- Practical Work 2Document1 pagePractical Work 2dalila bourasNo ratings yet
- Mathcad and Matlab Instruction Guide: by Breneman Whitfield (gth782h)Document26 pagesMathcad and Matlab Instruction Guide: by Breneman Whitfield (gth782h)Puspal GhoshNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Econ 217 PDFDocument3 pagesProblem Set 1 - Econ 217 PDFmiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Linear ProgrammingDocument77 pagesLesson 1 Linear Programmingasra010110No ratings yet
- Vanessa-Linear ProgrammingDocument13 pagesVanessa-Linear ProgrammingVanessa PallarNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration: Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsDocument75 pagesMaster of Business Administration: Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsDawit TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Intro LabDocument3 pagesIntro LabmojeebmashalNo ratings yet
- Part A: Texas A&M University MEEN 683 Multidisciplinary System Design Optimization (MSADO) Spring 2021 Assignment 2Document5 pagesPart A: Texas A&M University MEEN 683 Multidisciplinary System Design Optimization (MSADO) Spring 2021 Assignment 2BobaNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus 7th Edition Stewart Solutions ManualDocument60 pagesMultivariable Calculus 7th Edition Stewart Solutions Manualdecardbudgerowhln100% (25)
- Multivariable Calculus 7Th Edition Stewart Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesMultivariable Calculus 7Th Edition Stewart Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFheadmostzooenule.s8hta6100% (11)
- Using Mathcad To Plot Graph1 PDFDocument12 pagesUsing Mathcad To Plot Graph1 PDFFickriJokyalitNo ratings yet
- Integration ProblemsDocument5 pagesIntegration ProblemsMartin Alejandro Arredondo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Sample Linear ProgrammingDocument37 pagesSample Linear ProgrammingmarianaNo ratings yet
- Math 21 Written Homework Chapter 5 ReviewDocument3 pagesMath 21 Written Homework Chapter 5 ReviewDavidsLockNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: F X X XDocument2 pagesInstructions:: F X X XPranshu DixitNo ratings yet
- 3 Sensitivity Analysis PDFDocument45 pages3 Sensitivity Analysis PDFajay meenaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programmin G: by Nagendra Bahadur Amatya Head of DepartmentDocument29 pagesLinear Programmin G: by Nagendra Bahadur Amatya Head of DepartmentMuhhamed NuuraniNo ratings yet
- 2 ModelingDocument8 pages2 ModelingAgarwal HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Local Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8Document2 pagesLocal Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Application of IntegrationDocument52 pagesApplication of IntegrationrafiiiiidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Linear ProgrammingDocument8 pagesChapter 5 - Linear ProgrammingKhabib moginiNo ratings yet
- GRADE 4 Test 1Document2 pagesGRADE 4 Test 1akio haruNo ratings yet
- 14 BBMP1103 T10Document18 pages14 BBMP1103 T10elizabeth lizNo ratings yet
- Linaer Programming NotedDocument13 pagesLinaer Programming NotedTäð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- VCE Math Quest - Specialist Maths - Year 11Document96 pagesVCE Math Quest - Specialist Maths - Year 11Anila Jayaraj100% (1)
- Graphing TechniquesDocument26 pagesGraphing TechniquesTrí VũNo ratings yet
- CG ManualDocument33 pagesCG ManualpoojadoreyNo ratings yet
- OR ReportDocument49 pagesOR ReportAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument24 pagesExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsMary Jane PLNo ratings yet
- OQM Lecture Note - Part 1 Introduction To Mathematical OptimisationDocument10 pagesOQM Lecture Note - Part 1 Introduction To Mathematical OptimisationdanNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 4Document2 pagesMaths Grade 4akio haruNo ratings yet
- 15.1. To 15.3 Multiple IntegralsDocument65 pages15.1. To 15.3 Multiple IntegralsChiến QuangNo ratings yet
- 9231 s20 QP 21 PDFDocument16 pages9231 s20 QP 21 PDFShehzad QureshiNo ratings yet
- Integration by Substitution and Using Partial FractionsDocument8 pagesIntegration by Substitution and Using Partial FractionsDaniel SolhNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-19 at 21.19.20Document2 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-19 at 21.19.20olliewright63No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Kanak DhotreNo ratings yet
- The - Fundamental - Theorem - of - Calculus Part 2Document3 pagesThe - Fundamental - Theorem - of - Calculus Part 2demiNo ratings yet
- O.R Unit 2Document29 pagesO.R Unit 2Saif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- 2.parcial2 AreaDocument1 page2.parcial2 AreaMarc Velasco PujolNo ratings yet
- Operations Research: Chapter 3 (Ii)Document27 pagesOperations Research: Chapter 3 (Ii)Ashish BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming: 1.1 FormulationsDocument33 pagesLinear Programming: 1.1 FormulationsStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linear ProgrammingDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Linear ProgrammingMohammad Faizal Azwar Annas100% (2)
- 1 Plotting Complex Quantities in Matlab: ECE 298JA NS #1 - Fall 2017Document2 pages1 Plotting Complex Quantities in Matlab: ECE 298JA NS #1 - Fall 2017ahmed kamalNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Lesson 1 TrigonometryDocument11 pagesLesson 1 Trigonometryengabd345No ratings yet
- G9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked AnswersDocument8 pagesG9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked Answersengabd345No ratings yet
- Extra Practice Answer KeyDocument4 pagesExtra Practice Answer Keyengabd345No ratings yet
- Section 4.6 SolutionsDocument7 pagesSection 4.6 Solutionsengabd345No ratings yet
- Perimeter ProblemsDocument2 pagesPerimeter Problemsengabd345No ratings yet
- Example of ProjectDocument6 pagesExample of Projectengabd345No ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Unit 1 and 2 ProjectDocument2 pagesProbability and Statistics Unit 1 and 2 Projectengabd345No ratings yet
- UKMTDocument20 pagesUKMTengabd345No ratings yet
- Game 2Document6 pagesGame 2engabd345No ratings yet
- 555R-01 Removal and Reuse of Hardened ConcreteDocument27 pages555R-01 Removal and Reuse of Hardened ConcreteJORAMNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledDocument2 pagesTutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledJohn LionelNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Parliamentary ProceduresDocument9 pagesModule 3 Parliamentary ProceduresRonJen VlogsNo ratings yet
- HemoptysisDocument30 pagesHemoptysisTAUFIK RAMADHAN BIYANo ratings yet
- Part I - SemanticsDocument59 pagesPart I - SemanticsQuân KhảNo ratings yet
- Productbrochure Dd22 Dd24 en 22b1004022Document4 pagesProductbrochure Dd22 Dd24 en 22b1004022Bruno MasieroNo ratings yet
- Small-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutionDocument81 pagesSmall-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutiondibudkNo ratings yet
- Auvinet State of The Art 0Document7 pagesAuvinet State of The Art 0khernandez6491No ratings yet
- Psychology and AdvertisingDocument59 pagesPsychology and AdvertisingEMMA SHAFFU EL CHACARNo ratings yet
- Summer Training in Lucknow - AUTOCADDocument14 pagesSummer Training in Lucknow - AUTOCADArshit RaiNo ratings yet
- Research Survey QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesResearch Survey QuestionnaireReshane SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Serva Cementing 113015 LR Pages PDFDocument16 pagesServa Cementing 113015 LR Pages PDFAnonymous uKoNmLxkNo ratings yet
- Bearing Pad 400 X 400 X 52 MM (Ss400 Yield 235 Mpa)Document3 pagesBearing Pad 400 X 400 X 52 MM (Ss400 Yield 235 Mpa)AlvinbriliantNo ratings yet
- (J25) Joomla! 2.5 - Beginner's Guide PDFDocument259 pages(J25) Joomla! 2.5 - Beginner's Guide PDFPaco FernándezNo ratings yet
- Seismic Retrofitting of Mani Mandir Complex at Morbi, Gujarat, IndiaDocument15 pagesSeismic Retrofitting of Mani Mandir Complex at Morbi, Gujarat, IndiaShubhaNo ratings yet
- Linearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear: Standard Test Method ForDocument9 pagesLinearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear: Standard Test Method Forvuqar0979No ratings yet
- Affective Assessment ToolsDocument18 pagesAffective Assessment ToolsAlicia Pangilinan Francisco0% (1)
- Escuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facultad de Ciencias Pecuarias Carrera de Zootecnia NombreDocument15 pagesEscuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facultad de Ciencias Pecuarias Carrera de Zootecnia NombreJoselyn Vallejo PizanánNo ratings yet
- Twisted Pair, Coaxial Cable, Optical FiberDocument34 pagesTwisted Pair, Coaxial Cable, Optical Fiber7t854s6wd2No ratings yet
- Download full ebook of Google Cloud Platform Gcp Professional Cloud Network Engineer Certification Companion Learn And Apply Network Design Concepts To Prepare For The Exam 1St Edition Dario Cabianca online pdf all chapter docxDocument70 pagesDownload full ebook of Google Cloud Platform Gcp Professional Cloud Network Engineer Certification Companion Learn And Apply Network Design Concepts To Prepare For The Exam 1St Edition Dario Cabianca online pdf all chapter docxoufireny100% (11)
- Alignment PDFDocument12 pagesAlignment PDFVictor Nunez100% (1)
- Common Nail Disorders J.clindermatol.2013.06.015Document9 pagesCommon Nail Disorders J.clindermatol.2013.06.015Vita BūdvytėNo ratings yet
- Panriang County Profile - March - 2021Document9 pagesPanriang County Profile - March - 2021Stephen NzimaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Physical Activity: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesMental Health and Physical Activity: SciencedirectKAMYA SRIDHARAN 20214044No ratings yet
- Caustinerf ForteDocument5 pagesCaustinerf Fortefadli_nugraha6109No ratings yet
- A170566 Study Report BodyDocument79 pagesA170566 Study Report BodyAnonymous yqRB5cVMeNo ratings yet
- C MAMI Tool OverviewDocument4 pagesC MAMI Tool OverviewAbebe TilahunNo ratings yet
- ACK NAK EnhancementDocument15 pagesACK NAK Enhancementbasit_engineerNo ratings yet
Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSP
Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSP
Uploaded by
engabd345Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSP
Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSP
Uploaded by
engabd345Copyright:
Available Formats
GDC skills: TI-Nspire CX
Chapter 13 / Example 7
Using Numerical Solve to find an integral limit
Occasionally Numerical Solve provides a unique method for providing the answer to a
problem that cannot easily be solved otherwise. It should always, however, be used with
caution.
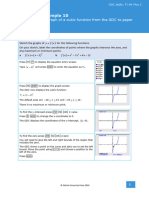
The area of the region bounded by the graph of f ( x=
) x 2 + 3 , the x-axis and the vertical
lines x = −1 and x = a with a > −1 is equal to 12. Find the value of a.
It is helpful to draw the graph before attempting to solve the
problem.
Open a new document and add a Graphs page.
The entry line is displayed at the top of the work area.
The default graph type is function, so ‘f1(x)=’ is displayed.
The default axes are 10 x 10 and 6.67 y 6.67 .
Type x 2 3 and press ·.
The GDC displays the function f 1 x x 2 1 with the default
axes.
Press b 4:Window/Zoom | 1:Window Settings…
Set the axes to show 4 x 4 with a scale of 1 and
0 y 20 with scale of 2.
Press · when you have finished.
The GDC now displays the quadratic function in a suitable
window.
© Oxford University Press 2019 1
GDC skills: TI-Nspire CX
Chapter 13 / Example 7
Using Numerical Solve to find an integral limit
We want to find the value of a for which
a
1
x 2 3 d x 12 .
Add a new Calculator page to your document by pressing
/ ~ (¿) 1:Add Calculator.
b 3:Algebra | 1: Numerical Solve
Press t and select with the trackpad.
The template shows places for the limits, the function and the
variable that you are integrating with respect to.
Enter the limits –1 and X, the function X2 + 3, the variable X.
Type = 12 , X
Press · to obtain a solution to the problem.
The Solver has found that a = 2.
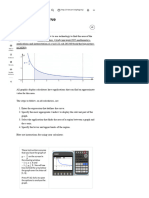
Check this result with the graph integral function.
Press / ¡ to return to the graph.
To find the integral press b 6:Analyze Graph | 6:Integral
You need to give the lower and upper bounds of the region that
includes the intersection.
The GDC shows a line and asks you to set the lower bound.
Do not use the line to set the lower bound as you need to enter
an exact value.
Type 1 and press ·.
The GDC asks you to set the upper bound.
© Oxford University Press 2019 2
GDC skills: TI-Nspire CX
Chapter 13 / Example 7
Using Numerical Solve to find an integral limit
Type 2, the upper bound, and press ·.
The GDC shows the area defined by the integral and its value.
2
1
x 2 3 d x 12 as required.
© Oxford University Press 2019 3
You might also like
- Teste Ingles TecnologiaDocument5 pagesTeste Ingles TecnologiaMeninaDuMarNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Definition of The Derivative Lab 5: GraphicallyDocument22 pagesExploring The Definition of The Derivative Lab 5: GraphicallyJill GoughNo ratings yet
- English II Merchant of Venice Notes Compiled by Nilay Kumar Das PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish II Merchant of Venice Notes Compiled by Nilay Kumar Das PDFSubhadip RoyNo ratings yet
- Using Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7Document2 pagesUsing Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Using Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7Document2 pagesUsing Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 0402 gdc08 XXTNSPDocument3 pagesBks MaiHL 0402 gdc08 XXTNSPMark ChangNo ratings yet
- Daa Module2Document83 pagesDaa Module2sreekanthpyatagoudaNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84Document5 pagesBks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84W SNo ratings yet
- Exercises 4Document3 pagesExercises 4Madrid MadridNo ratings yet
- GCD HL CH6 Example11Document4 pagesGCD HL CH6 Example11Mark ChangNo ratings yet
- De The Only GDC That I Hademdekmdekmekmve Used Is The TI 83 (+) and Thus The Comments Below Are Restricted To ThisDocument16 pagesDe The Only GDC That I Hademdekmdekmekmve Used Is The TI 83 (+) and Thus The Comments Below Are Restricted To ThisSarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 BBA1 SundayDocument18 pagesLec 8 BBA1 SundaySYED HASHIM ALI BUKHARINo ratings yet
- Area Under A Curve - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityDocument8 pagesArea Under A Curve - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Modelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Document4 pagesModelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Sophie HoltusNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Evaluating LimitsDocument27 pagesTechniques For Evaluating LimitsRaven MercadoNo ratings yet
- Linear and Multiobjective Programming With Fuzzy Stochastic ExtensionsDocument103 pagesLinear and Multiobjective Programming With Fuzzy Stochastic ExtensionsKharolin MauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document16 pagesChapter 01sameh esmatNo ratings yet
- Practical Work 2Document1 pagePractical Work 2dalila bourasNo ratings yet
- Mathcad and Matlab Instruction Guide: by Breneman Whitfield (gth782h)Document26 pagesMathcad and Matlab Instruction Guide: by Breneman Whitfield (gth782h)Puspal GhoshNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 - Econ 217 PDFDocument3 pagesProblem Set 1 - Econ 217 PDFmiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Linear ProgrammingDocument77 pagesLesson 1 Linear Programmingasra010110No ratings yet
- Vanessa-Linear ProgrammingDocument13 pagesVanessa-Linear ProgrammingVanessa PallarNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration: Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsDocument75 pagesMaster of Business Administration: Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsDawit TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Intro LabDocument3 pagesIntro LabmojeebmashalNo ratings yet
- Part A: Texas A&M University MEEN 683 Multidisciplinary System Design Optimization (MSADO) Spring 2021 Assignment 2Document5 pagesPart A: Texas A&M University MEEN 683 Multidisciplinary System Design Optimization (MSADO) Spring 2021 Assignment 2BobaNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus 7th Edition Stewart Solutions ManualDocument60 pagesMultivariable Calculus 7th Edition Stewart Solutions Manualdecardbudgerowhln100% (25)
- Multivariable Calculus 7Th Edition Stewart Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesMultivariable Calculus 7Th Edition Stewart Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFheadmostzooenule.s8hta6100% (11)
- Using Mathcad To Plot Graph1 PDFDocument12 pagesUsing Mathcad To Plot Graph1 PDFFickriJokyalitNo ratings yet
- Integration ProblemsDocument5 pagesIntegration ProblemsMartin Alejandro Arredondo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Sample Linear ProgrammingDocument37 pagesSample Linear ProgrammingmarianaNo ratings yet
- Math 21 Written Homework Chapter 5 ReviewDocument3 pagesMath 21 Written Homework Chapter 5 ReviewDavidsLockNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: F X X XDocument2 pagesInstructions:: F X X XPranshu DixitNo ratings yet
- 3 Sensitivity Analysis PDFDocument45 pages3 Sensitivity Analysis PDFajay meenaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programmin G: by Nagendra Bahadur Amatya Head of DepartmentDocument29 pagesLinear Programmin G: by Nagendra Bahadur Amatya Head of DepartmentMuhhamed NuuraniNo ratings yet
- 2 ModelingDocument8 pages2 ModelingAgarwal HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Local Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8Document2 pagesLocal Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Application of IntegrationDocument52 pagesApplication of IntegrationrafiiiiidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Linear ProgrammingDocument8 pagesChapter 5 - Linear ProgrammingKhabib moginiNo ratings yet
- GRADE 4 Test 1Document2 pagesGRADE 4 Test 1akio haruNo ratings yet
- 14 BBMP1103 T10Document18 pages14 BBMP1103 T10elizabeth lizNo ratings yet
- Linaer Programming NotedDocument13 pagesLinaer Programming NotedTäð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- VCE Math Quest - Specialist Maths - Year 11Document96 pagesVCE Math Quest - Specialist Maths - Year 11Anila Jayaraj100% (1)
- Graphing TechniquesDocument26 pagesGraphing TechniquesTrí VũNo ratings yet
- CG ManualDocument33 pagesCG ManualpoojadoreyNo ratings yet
- OR ReportDocument49 pagesOR ReportAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument24 pagesExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsMary Jane PLNo ratings yet
- OQM Lecture Note - Part 1 Introduction To Mathematical OptimisationDocument10 pagesOQM Lecture Note - Part 1 Introduction To Mathematical OptimisationdanNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 4Document2 pagesMaths Grade 4akio haruNo ratings yet
- 15.1. To 15.3 Multiple IntegralsDocument65 pages15.1. To 15.3 Multiple IntegralsChiến QuangNo ratings yet
- 9231 s20 QP 21 PDFDocument16 pages9231 s20 QP 21 PDFShehzad QureshiNo ratings yet
- Integration by Substitution and Using Partial FractionsDocument8 pagesIntegration by Substitution and Using Partial FractionsDaniel SolhNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-19 at 21.19.20Document2 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-19 at 21.19.20olliewright63No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Kanak DhotreNo ratings yet
- The - Fundamental - Theorem - of - Calculus Part 2Document3 pagesThe - Fundamental - Theorem - of - Calculus Part 2demiNo ratings yet
- O.R Unit 2Document29 pagesO.R Unit 2Saif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- 2.parcial2 AreaDocument1 page2.parcial2 AreaMarc Velasco PujolNo ratings yet
- Operations Research: Chapter 3 (Ii)Document27 pagesOperations Research: Chapter 3 (Ii)Ashish BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming: 1.1 FormulationsDocument33 pagesLinear Programming: 1.1 FormulationsStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linear ProgrammingDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Linear ProgrammingMohammad Faizal Azwar Annas100% (2)
- 1 Plotting Complex Quantities in Matlab: ECE 298JA NS #1 - Fall 2017Document2 pages1 Plotting Complex Quantities in Matlab: ECE 298JA NS #1 - Fall 2017ahmed kamalNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Lesson 1 TrigonometryDocument11 pagesLesson 1 Trigonometryengabd345No ratings yet
- G9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked AnswersDocument8 pagesG9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked Answersengabd345No ratings yet
- Extra Practice Answer KeyDocument4 pagesExtra Practice Answer Keyengabd345No ratings yet
- Section 4.6 SolutionsDocument7 pagesSection 4.6 Solutionsengabd345No ratings yet
- Perimeter ProblemsDocument2 pagesPerimeter Problemsengabd345No ratings yet
- Example of ProjectDocument6 pagesExample of Projectengabd345No ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Unit 1 and 2 ProjectDocument2 pagesProbability and Statistics Unit 1 and 2 Projectengabd345No ratings yet
- UKMTDocument20 pagesUKMTengabd345No ratings yet
- Game 2Document6 pagesGame 2engabd345No ratings yet
- 555R-01 Removal and Reuse of Hardened ConcreteDocument27 pages555R-01 Removal and Reuse of Hardened ConcreteJORAMNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledDocument2 pagesTutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledJohn LionelNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Parliamentary ProceduresDocument9 pagesModule 3 Parliamentary ProceduresRonJen VlogsNo ratings yet
- HemoptysisDocument30 pagesHemoptysisTAUFIK RAMADHAN BIYANo ratings yet
- Part I - SemanticsDocument59 pagesPart I - SemanticsQuân KhảNo ratings yet
- Productbrochure Dd22 Dd24 en 22b1004022Document4 pagesProductbrochure Dd22 Dd24 en 22b1004022Bruno MasieroNo ratings yet
- Small-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutionDocument81 pagesSmall-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutiondibudkNo ratings yet
- Auvinet State of The Art 0Document7 pagesAuvinet State of The Art 0khernandez6491No ratings yet
- Psychology and AdvertisingDocument59 pagesPsychology and AdvertisingEMMA SHAFFU EL CHACARNo ratings yet
- Summer Training in Lucknow - AUTOCADDocument14 pagesSummer Training in Lucknow - AUTOCADArshit RaiNo ratings yet
- Research Survey QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesResearch Survey QuestionnaireReshane SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Serva Cementing 113015 LR Pages PDFDocument16 pagesServa Cementing 113015 LR Pages PDFAnonymous uKoNmLxkNo ratings yet
- Bearing Pad 400 X 400 X 52 MM (Ss400 Yield 235 Mpa)Document3 pagesBearing Pad 400 X 400 X 52 MM (Ss400 Yield 235 Mpa)AlvinbriliantNo ratings yet
- (J25) Joomla! 2.5 - Beginner's Guide PDFDocument259 pages(J25) Joomla! 2.5 - Beginner's Guide PDFPaco FernándezNo ratings yet
- Seismic Retrofitting of Mani Mandir Complex at Morbi, Gujarat, IndiaDocument15 pagesSeismic Retrofitting of Mani Mandir Complex at Morbi, Gujarat, IndiaShubhaNo ratings yet
- Linearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear: Standard Test Method ForDocument9 pagesLinearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear: Standard Test Method Forvuqar0979No ratings yet
- Affective Assessment ToolsDocument18 pagesAffective Assessment ToolsAlicia Pangilinan Francisco0% (1)
- Escuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facultad de Ciencias Pecuarias Carrera de Zootecnia NombreDocument15 pagesEscuela Superior Politécnica de Chimborazo Facultad de Ciencias Pecuarias Carrera de Zootecnia NombreJoselyn Vallejo PizanánNo ratings yet
- Twisted Pair, Coaxial Cable, Optical FiberDocument34 pagesTwisted Pair, Coaxial Cable, Optical Fiber7t854s6wd2No ratings yet
- Download full ebook of Google Cloud Platform Gcp Professional Cloud Network Engineer Certification Companion Learn And Apply Network Design Concepts To Prepare For The Exam 1St Edition Dario Cabianca online pdf all chapter docxDocument70 pagesDownload full ebook of Google Cloud Platform Gcp Professional Cloud Network Engineer Certification Companion Learn And Apply Network Design Concepts To Prepare For The Exam 1St Edition Dario Cabianca online pdf all chapter docxoufireny100% (11)
- Alignment PDFDocument12 pagesAlignment PDFVictor Nunez100% (1)
- Common Nail Disorders J.clindermatol.2013.06.015Document9 pagesCommon Nail Disorders J.clindermatol.2013.06.015Vita BūdvytėNo ratings yet
- Panriang County Profile - March - 2021Document9 pagesPanriang County Profile - March - 2021Stephen NzimaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Physical Activity: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesMental Health and Physical Activity: SciencedirectKAMYA SRIDHARAN 20214044No ratings yet
- Caustinerf ForteDocument5 pagesCaustinerf Fortefadli_nugraha6109No ratings yet
- A170566 Study Report BodyDocument79 pagesA170566 Study Report BodyAnonymous yqRB5cVMeNo ratings yet
- C MAMI Tool OverviewDocument4 pagesC MAMI Tool OverviewAbebe TilahunNo ratings yet
- ACK NAK EnhancementDocument15 pagesACK NAK Enhancementbasit_engineerNo ratings yet