Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Emmi
Emmi
Uploaded by
kartiksahni07Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ASM - Specialty Handbook, Cast IronsDocument455 pagesASM - Specialty Handbook, Cast IronsMuhammad Azlan Ibrahim100% (16)
- 4024 Mock-2 Paper-1 2022-23Document22 pages4024 Mock-2 Paper-1 2022-23niloyNo ratings yet
- High-Strength Reinforcing Bars - ETN-M-8-16 PDFDocument12 pagesHigh-Strength Reinforcing Bars - ETN-M-8-16 PDFVignesh RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument MechanicDocument58 pagesMultiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument Mechanicمصطفى شاكر محمودNo ratings yet
- Sheet IDocument7 pagesSheet IMohamed MNo ratings yet
- CHANDRADocument8 pagesCHANDRAivy agustinNo ratings yet
- Static C/cs of MeasurementsDocument3 pagesStatic C/cs of MeasurementssamadonyNo ratings yet
- Measuring CH 1 FINALDocument2 pagesMeasuring CH 1 FINALShahzaib TanoliNo ratings yet
- Measurements Mid TermDocument2 pagesMeasurements Mid TermabdallaNo ratings yet
- MTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023Document5 pagesMTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023k.ghanemNo ratings yet
- MTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023Document5 pagesMTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023k.ghanemNo ratings yet
- 1.dead Time of The Instrument Is: Span Max-MinDocument3 pages1.dead Time of The Instrument Is: Span Max-MinNaveen BhatNo ratings yet
- Metrology QBDocument16 pagesMetrology QBSubin RajNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Binders (1)Document53 pagesInstrumentation Binders (1)noelNo ratings yet
- Chandra SurveyingDocument20 pagesChandra SurveyingIvy Joy SaguranNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engr Mcqs PDFDocument23 pagesElectrical Engr Mcqs PDFFarman100% (1)
- Jr. Engineer Civil 102Document16 pagesJr. Engineer Civil 102Bindesh Chouhan100% (1)
- EJ-01-2020 Practical No.1 MCQDocument2 pagesEJ-01-2020 Practical No.1 MCQBhushan BhavarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements MCQ PDFDocument11 pagesElectronic Measurements MCQ PDFAmit Ghade67% (3)
- Eee GT - 20 PDFDocument8 pagesEee GT - 20 PDFupender raoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Long TestDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Long Testjrm.tinoyNo ratings yet
- Obj Cre PDFDocument15 pagesObj Cre PDFAyushSingh100% (1)
- RRB Junior Engineer Mechanical Model Question Paper Solved 17Document34 pagesRRB Junior Engineer Mechanical Model Question Paper Solved 17Praveen Palaniappan50% (2)
- Chapter #01Document16 pagesChapter #01Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Wa0007Document6 pagesWa0007shubham muraiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-1Document4 pagesElectronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-1chetanaNo ratings yet
- Rank Improvement Program Rank Improvement Program Rank Improvement ProgramDocument23 pagesRank Improvement Program Rank Improvement Program Rank Improvement ProgramVISHNU PRIYA BUDDANINo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-16 at 10.19.30 AMDocument96 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-16 at 10.19.30 AMRajvardhan NaikNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece Ec1104-Electronic Measurement and InstrumentationDocument3 pagesDepartment of Ece Ec1104-Electronic Measurement and InstrumentationLali ThaNo ratings yet
- EXDocument44 pagesEXLương Hồ VũNo ratings yet
- 15ee207 3 SemDocument2 pages15ee207 3 SemSarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment Error AnalysisDocument3 pagesAssignment Error Analysissingh813No ratings yet
- 2012 CSEC Physics Specimen P1Document13 pages2012 CSEC Physics Specimen P1Naps LibraryNo ratings yet
- TNEB ECE Model Question Paper 1: B) InfiniteDocument8 pagesTNEB ECE Model Question Paper 1: B) InfinitesNo ratings yet
- Quiz Test-1 Question As On 12.09.2019Document13 pagesQuiz Test-1 Question As On 12.09.2019NEELAMANI SAMALNo ratings yet
- Chhotu Ram Rural Institute of Technology Branch-Electrical Engineering M.M.45 Time 30 MinutesDocument5 pagesChhotu Ram Rural Institute of Technology Branch-Electrical Engineering M.M.45 Time 30 Minutesharish220907No ratings yet
- MCQs EC-302 EMI LNCTEDocument5 pagesMCQs EC-302 EMI LNCTEAdarsh UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cat-1Document16 pagesMCQ Cat-1vijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Units and Measurement (PG 1 - 3)Document3 pagesChapter-1 Units and Measurement (PG 1 - 3)darling deanNo ratings yet
- 2 qp2Document13 pages2 qp2JustinNo ratings yet
- QuestingDocument2 pagesQuestinganilsai56No ratings yet
- Physics - Complete Quick Revision 2021Document99 pagesPhysics - Complete Quick Revision 2021MeeraNo ratings yet
- Results Reporter: Mixed QuizDocument8 pagesResults Reporter: Mixed Quizmraza17No ratings yet
- JashuDocument204 pagesJashuPiyushsinhNo ratings yet
- DemonstratorDocument16 pagesDemonstratorswapna jeeviNo ratings yet
- 11th PCM Jee Main - 02 Sarabhai (16-07-2021)Document14 pages11th PCM Jee Main - 02 Sarabhai (16-07-2021)jdkdkdkNo ratings yet
- AMU Class 11 2010 PaperDocument6 pagesAMU Class 11 2010 Paperhacker GodNo ratings yet
- PHY 111 ExamDocument2 pagesPHY 111 ExamJoseph IsekNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Kalpit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pattern of Question, Syllabus & Probable Q & A of The Exam. For Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Through PSCDocument1 pagePattern of Question, Syllabus & Probable Q & A of The Exam. For Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Through PSCSudip MondalNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Corr1555Document16 pagesCase Study On Corr1555TarunNo ratings yet
- Emi MCQDocument27 pagesEmi MCQgautam100% (3)
- Answer: A: 1. The Measurement of A QuantityDocument15 pagesAnswer: A: 1. The Measurement of A Quantitydream breaker100% (1)
- SLO BASED MCQS AND QUESTIONS - IX PhysicsDocument60 pagesSLO BASED MCQS AND QUESTIONS - IX PhysicsWaheedkhanNo ratings yet
- S&a MCQ - SveriDocument31 pagesS&a MCQ - Sveritrail meNo ratings yet
- Measurements AnsDocument6 pagesMeasurements AnsoAeonNo ratings yet
- GATE Aerospace 2012 PaperDocument5 pagesGATE Aerospace 2012 Papermohini priya kolluriNo ratings yet
- Model Qpaper GeDocument10 pagesModel Qpaper Geसोनू जगतापNo ratings yet
- Model Qpaper GeDocument10 pagesModel Qpaper GeMr V. Phaninder ReddyNo ratings yet
- Measurements TestDocument6 pagesMeasurements TestoAeonNo ratings yet
- SAMPLEQUESTIONS COMPREXAM (ObjType)Document19 pagesSAMPLEQUESTIONS COMPREXAM (ObjType)ഹരി നീലാംബരിNo ratings yet
- Test NewDocument4 pagesTest NewKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Standard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerFrom EverandStandard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerNo ratings yet
- Corona Test ResultDocument1 pageCorona Test Resultkartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Ans. (C)Document4 pagesAns. (C)kartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Success Guaranteed..... Success Guaranteed....Document1 pageSuccess Guaranteed..... Success Guaranteed....kartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Ee+ece Scholarship Result CrritDocument1 pageEe+ece Scholarship Result Crritkartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Basic Joints & Blueprint ReadingDocument132 pagesBasic Joints & Blueprint Readingtranng100% (1)
- MANUEL Devidoir MillerDocument36 pagesMANUEL Devidoir MillerBrice DreessenNo ratings yet
- FEM Simulation of CMUT Cell For NDT ApplicationDocument7 pagesFEM Simulation of CMUT Cell For NDT ApplicationShuvam5 GuptaNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Text BookDocument111 pagesO Level Physics Text BookMatabaro BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Mechanics1 VFreadingsDocument275 pagesMechanics1 VFreadingsMohammed HachemiNo ratings yet
- EC403: Microwave & Radar EngineeringDocument70 pagesEC403: Microwave & Radar EngineeringBindu Narayanan NampoothiriNo ratings yet
- 12.2 Motion CIE IGCSE Physics Ext Theory MsDocument5 pages12.2 Motion CIE IGCSE Physics Ext Theory MsasifshahanaNo ratings yet
- WCM - Yamashina - 05 - Professional Maintenance - Chapter - 3 - ADocument100 pagesWCM - Yamashina - 05 - Professional Maintenance - Chapter - 3 - ACíceroNo ratings yet
- Model: T521 (H), T522 (H/L), T523 (L), T524 (H/HH), T525 (L/LL), T526 (H/L)Document6 pagesModel: T521 (H), T522 (H/L), T523 (L), T524 (H/HH), T525 (L/LL), T526 (H/L)firman harianjaNo ratings yet
- Fujifilm Eluxeo BL 7000Document78 pagesFujifilm Eluxeo BL 7000AngeloNo ratings yet
- JK Bose Class 12 Physics 81017 P 2013Document3 pagesJK Bose Class 12 Physics 81017 P 2013Asha BarelayNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument9 pagesShivaji University, KolhapurNiranjan PatilNo ratings yet
- WebquestDocument3 pagesWebquestanssh prajapatiNo ratings yet
- p112 Lecture2Document22 pagesp112 Lecture2Othniel SulpicoNo ratings yet
- CSE 28363 - Structural Concrete Design: Lecture 10: Shear and ServiceabilityDocument44 pagesCSE 28363 - Structural Concrete Design: Lecture 10: Shear and ServiceabilityBitch CarrieNo ratings yet
- Master SpecificationsDocument395 pagesMaster SpecificationsHaymanot BaynesagnNo ratings yet
- AIRSYS - ASPCB 2 Interconnect Guidelines Rev4 12-2-13Document5 pagesAIRSYS - ASPCB 2 Interconnect Guidelines Rev4 12-2-13mauricioNo ratings yet
- BKT2031 TDSDocument1 pageBKT2031 TDSAshutoshNo ratings yet
- s4 Physics Paper 3 Exam 5Document4 pagess4 Physics Paper 3 Exam 5MUSOKE GERALDNo ratings yet
- Disabled Systems: Customer Name Reference Product Series NoDocument17 pagesDisabled Systems: Customer Name Reference Product Series NoАлександр КачеишвилиNo ratings yet
- GEET-Small Engine Conversion PlansDocument19 pagesGEET-Small Engine Conversion PlansCristo_Alanis_8381No ratings yet
- 425ºC AHT: Ower EATDocument2 pages425ºC AHT: Ower EATSivagurunathan SpNo ratings yet
- Caledonian Railway Cables PDFDocument251 pagesCaledonian Railway Cables PDFamitvaishnav1No ratings yet
- Types of AgitatorsDocument2 pagesTypes of Agitatorsjeamnard balitaanNo ratings yet
- Very Light Aircraft Model: Sea Level Temperature K Sea Level Pressure Pa Gas Constant J/K/KG Lapse Rate K/MDocument6 pagesVery Light Aircraft Model: Sea Level Temperature K Sea Level Pressure Pa Gas Constant J/K/KG Lapse Rate K/Mrighthere201No ratings yet
- CHT307 - Ktu QbankDocument3 pagesCHT307 - Ktu QbankYuxin CasioNo ratings yet
- National Advisory Committee - For Aeronautics: Technical Note No: 1293Document56 pagesNational Advisory Committee - For Aeronautics: Technical Note No: 1293manuelq9No ratings yet
Emmi
Emmi
Uploaded by
kartiksahni07Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Emmi
Emmi
Uploaded by
kartiksahni07Copyright:
Available Formats
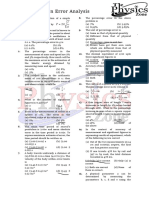
Negative-0.
33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
1. Deflection methods of direct measurements (D) ability to distinguish polarity.
are most widely used as these are 8. Hysteresis in an instrument means
(A) most simple (B) most accurate
(A) the change in same reading when
(C) least time consuming input is first increased and then
(D) most simple and least time consuming reduced.
2. Comparison methods are used (B) the reliability of the instrument.
(A) because these are most simple (C) the repeatability of the instrument.
(B) because these are inexpensive (D) the inaccuracy due to change in
(C) because these take least time in temperature.
measurement
9. An higher scale ammeter is used to
(D) when a high accuracy of measurement measure too low current. The measurement
is required. would have low
3. The main advantage of the null balance
(A) precision. (B) accuracy.
technique of measurement is that
(A) it does not load the medium. (C) resolution. (D) all of these.
(B) it gives a centre zero value at its input. 10. When reading is taken at half scale in the
instrument, the error is
(C) it gives quick measurement.
(A) exactly equal to half of full-scale
(D) it is not affected by temperature
variation error.
4. The span of a zero-centred voltmeter (B) equal to full-scale error.
having a scale from - 10 V to + 10 V is (C) less than full-scale error.
(A) 0 V (B) – 10 V (D) more than full-scale error.
(C) 10 V (D) 20 V
11. The reliability of a measuring instrument
5. If two meters X and Y require 40 mA and means
50 mA respectively, to give full scale
deflection, then (A) the life of the instrument.
(A) X is more sensitive. (B) the extent over which the
characteristics remain linear.
(B) Y is more sensitive.
(C) both X and Y are equally sensitive. (C) degree to which repeatability
continues to remain within specified
(D) it would not be possible to assess the
limits.
sensitivity on the basis of the given
data. (D) all of these.
6. The smallest change in a measured variable 12. Undesirable characteristics of a
to which an instrument will respond is measurement system are
(A) accuracy. (B) resolution. (A) accuracy and repeatability.
(C) precision. (D) sensitivity.
(B) static error.
7. Resolution of an instrument is
(C) drift and dead zone.
(A) the minimum quantity it can measure.
(D) both (b) and (c).
(B) the maximum quantity it can measure.
(C) the maximum nonlinearity.
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 1
Negative-0.33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
13. The efficiency of an instrument is defined (D) made deflection dependent.
as the ratio of the measured quantity at full 18. Which one of the following decides the
scale to the power taken by the instrument time of response of an indicating
at instrument ?
(A) one-fourth scale. (A) Deflecting system.
(B) half scale. (B) Controlling system.
(C) three-fourth scale. (C) Damping system.
(D) Pivot and jewel bearings.
(D) full scale.
19. The difference between the indicated value
14. Dead time of the instrument is and the true value of a quantity is
(A) the time required by an instrument to (A) gross error. (B) absolute error.
begin to respond to a change in the
measurand (C) dynamic error. (D) relative error.
(B) the time required by an instrument to 20. The errors introduced by an instrument fall
warm up initially. in which category ?
(C) the largest change of input quantity (A) Systematic errors.
for which there is no output of the (B) Random errors.
instrument. (C) Gross errors.
(D) none of the above. (D) Environmental errors.
15. Dead zone of an instrument is 21. To measure 5 volts, if one selects a 0-100
(A) the time required by an instrument to V range voltmeters which is accurate
warm up initially. within ± 1%, then the error in this
measurement may be up to
(B) the largest change of input quantity
for which there is no output of the (A) ±1.5% (B) ±2.5%
instrument. (C) ±7.5% (D) ±20%
(C) the time required by an instrument to 22. A 0-100 V voltmeter has an accuracy of 1
begin to respond to a change in
per cent at full-scale reading. What will be
measurand.
the error if it reads 50 V ?
(D) the unmeasured quantity which
exceeds the maximum range of the (A) 1 per cent. (B) 2 per cent.
instrument. (C) 0.5 per cent. (D) 4 per cent.
(E) none of the above. 23. A 0-250 V voltmeter has a guaranteed
16. Torque/weight ratio of an instrument accuracy of 2 per cent of full-scale reading.
indicates The voltage measured by this voltmeter is
(A) selectivity. (B) accuracy. 150 volts. The limiting error in percentage
(C) fidelity (D) sensitivity. is
17. An indicating instrument is more sensitive (A) 2.5% (B) 0.05%
if its torque to weight ratio is (C) 3.33% (D) 5.0%
(A) much larger than unity.
24. A 0 to 300 V voltmeter has an error of ±2%
(B) of the order of unity. of fsd. What is the range of readings if true
(C) much less than unity. voltage is 30 V ?
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 2
Negative-0.33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
(A) 24 V-36 V (B) 20 V-40 V (A) 1 represents greater precision than 2
and 3.
(C) 29.4 V-30.6 V (D) 20 V-30 V
(B) 2 represents greater precision but 1
25. The measured value of a capacitor is 205.5 and 3 represent same precision.
µF; whereas its true value is 202.4 µF.
(C) 2 and 3 represent greater precision
The relative error is than 1.
(A) 1.87% (B) 1.94% (D) 1, 2 and 3 represent same precision.
(C) 1.53% (D) 1.73% 30. Which one of the following statements is
correct?
26. Sensitivity of a voltmeter is given as
The application of the instrument in wrong
(A) W/V manner in the procedure of measurement
resulsts in a/an
(B) reciprocal of full-scale deflection
current. (A) systematic error. (B) random error.
(C) both (a) and (b). (D) none of these. (C) gross error. (D) instrument
error.
27. Accuracy is defined as the
31. What are the cause of gross error in the
(A) measure of the consistency or instruments ?
reproducibility of the measurement. 1. Misreading of instruments.
(B) closeness with which an instrument 2. Incorrect adjustment of instruments.
reading approaches the true value of 3. Errors due to defective instrument.
the quantity being measured.
4. Errors due to effect of environment on
(C) smallest measurable input change. the instrument.
(D) ratio of the change in output signal of (A) 1 and 2. (B) 2 and 3.
an instrument to a change in the input. (C) 3 and 1. (D) 2 and 1.
28. Which one of the following statements is 32. Systematic error are
not correct ? (A) instrumental errors.
(A) It is not possible to have precise (B) environmental errors.
measurements which are not accurate.
(C) observational errors.
(B) Correctness in measurements requires (D) all of the above.
both accuracy and precision.
33. Consider the following :
(C) Reproducibility and consistency are
expressions that best describe 1. Human errors.
precision in measurements. 2. Improper application of instruments.
(D) An instrument with 2% accuracy is 3. Error due to worn parts of an
better than another with 5% accuracy. instrument.
29. A resistance of 105 ohms is specified using 4. Errors due to effects of environment.
significant figures as indicated below :
Which of the above come under the type of
1. 105 ohms 2. 105.0 ohms systematic errors ?
3. 0.000105 MW (A) 1 and 2. (B) 2 and 3.
Among these (C) 3 and 4. (D) 1 and 4.
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 3
Negative-0.33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
34. Which of the following types of errors 39. For defining the standard metre,
come under systematic errors ? wavelength of which material is considered
1. Irregular spring tension. ?
2. Improper readings of an instrument.
(A) Neon. (B) Krypton.
3. Loading effects.
(C) Helium. (D) Xenon.
4. Error due to the presence of electric
field or magnetic field. 40. For low resistance (from few micro ohms
(A) 1 and 2. (B) 2 and 3. to one ohm) measurement, which bridge is
used ?
(C) 3 and 1. (D) 4 and 1.
35. Which one of the following statements (A) Wheatstone bridge.
correctly represents the systematic error ? (B) Kelvin bridge.
(A) These errors can be calculated from
(C) Guarded Wheatstone bridge.
the details of the instruments.
(B) These are the residual errors. (D) Maxwell bridge.
(C) These errors may occur under 41. Which one of the following bridges will be
controlled conditions. used for the measurement of very low
(D) These are the errors committed by the resistance ?
experiments.
(A) Kelvin bridge.
36. In the circuit given in the figure, the
(B) Maxwell’s bridge.
limiting error in the power dissipation ‘I 2
R’ in the resistor R is (C) Wheatstone bridge.
R = 1 0 0 ± 0 .2 % (D) Hay’s bridge.
42. The accuracy of Kelvin’s double bridge for
the measurement of low resistance is high
I = 2 + 5%
because the bridge
(A) uses two pairs of resistance arms.
(A) 1.2% (B) 5.2% (B) has medium value resistances in the
(C) 10.2% (D) 25.2%. ratio arms.
37. A set of independent current measurements (C) uses a low resistance link between
taken by four observers was recorded as : standard and test resistance.
117.02 mA, 117.11 mA, 117.08 mA and
117.03 mA. What is the range of error ? (D) uses a null indicating galvanometer.
(A) ±0.045 (B) ±0.054 43. In a Kelvin’s double bridge two sets of
(C) ±0.065 (D) ±0.056 readings are taken when measuring low
38. The unit of temperature measurement is resistance, one with current in one direction
and the other with direction of current
(A) mole. (B) Kelvin.
reversed. This is done to
(C) lumen. (D) pascal.
(A) eliminate the effect of contact
resistance. (B) eliminate the
effect of resistance of leads.
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 4
Negative-0.33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
(C) correct for the effect of changes in 48. Which one of the following is measured by
battery voltage. the loss of charge method ?
(A) Low R. (B) High R.
(D) eliminate the effect of thermoelectric
(C) Low L. (D) High L.
emfs.
49. A dc potentiometer is designed to measure
44. A Wheatstone bridge cannot be employed up to about 2 V with a slide wire of 800
for measurement of very low resistance as mm. A standard cell of emf 1.18 V obtains
it introduces error on account of balance at 600 mm. A test cell is seen to
obtain balance at 680 mm. The emf of the
(A) contact resistance.
test cell is
(B) resistance of connecting leads.
(A) 1.00 V (B) 1.34 V
(C) thermoelectric emfs.
(C) 1.50 V (D) 1.70 V
(D) all of the above.
50. In the potentiometer circuit shown in the
45. The sensitivity of a Wheatstone bridge given figure, the value of unknown voltage
depends upon ‘E’ under balanced condition will be
(A) galvanometer current sensitivity.
(B) galvanometer resistance.
(C) bridge supply voltage.
(D) all of the above.
46. A bridge is shown in the given figure. If the
resistance R5 is increased from 2 kW to 2.5
kW, the current I2 will
(A) 200 mV (B) 2.8 V
(C) 3 V (D) 3.2 V
51. The equations under conditions for balance
for a bridge measuring resistance R1 and
inductance L1 of a choke coil are
R 2R 3
(A) increase.
R1 and L1 R 2 R 3C 4
(B) decrease.
R4
(C) not change.
(D) increase or decrease depending In order to achieve convergence of balance.
47. When a capacitor was connected to the (A) R2 and R3 should be chosen as
terminal of an ohmmeter the pointer variables. (B) R2 and C4
indicated a low resistance initially and then
should be chosen as variables.
slowly came to infinity position. This
shows that the capacitor is (C) R4 and C4 should be chosen as
(A) short-circuited. (B) all right. variables.
(C) open-circuited. (D) weak. (D) R3 and C4 should be chosen as
variable.
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 5
Negative-0.33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
52. Maxwell inductance bridge is used for coils 57. Which one of the following is a frequency
of Q value sensitive bridge ?
(A) less than 1. (A) De-Sauty bridge. (B) Schering
bridge.
(B) less than 10.
(C) Wien’s bridge. (D) Maxwell’s
(C) greater than 1 and less than 10. bridge.
(D) more than 100. 58. In Wien bridge
53. In an Anderson bridge, the unknown (A) balanced conditions are independent
inductance is measured in term of known of frequency.
(B) balanced conditions are dependent on
(A) resistance.
frequency.
(B) capacitance. (C) capacitance is measured in terms of
(C) inductance and resistance. standard inductance.
(D) resistance and capacitance. (D) frequency is measured in terms of
resistance and capacitance values.
54. Hay’s bridge is suitable for the
59. Schering bridge can be used to measure
measurement of which one of the following
which one of the following ?
?
(A) Q of a coil.
(A) Inductance with Q < 10.
(B) Inductance and its Q-value.
(B) Inductance with Q > 10.
(C) Very small resistance.
(C) Capacitance with high dissipating (D) Capacitance and its power factor.
factors.
60. Dissipation factor, tan d, of a capacity
(D) Capacitance with low dissipating measured by which bridge ?
factors. (A) Anderson bridge. (B) Hay bridge.
55. Which of the following bridges can be used (C) Schering bridge. (D) Wien bridge.
for inductance measurement ?
61. The dielectric loss of a capacitor can be
1. Maxwell bridge. measured by which one of the following ?
2. Hay’s bridge. (A) Wien bridge. (B) Owen bridge.
3. Wien bridge. (C) Schering bridge. (D) Maxwell
bridge.
4. Wheatstone bridge.
62. Which one of the following bridges is used
Select the correct answer using the code
for measurement of dielectric loss and
given below :
power factor of a capacitor ?
(A) 1 and 2 (B) 2 and 3 (A) Maxwell’s bridge.
(C) 3, 4 and 5 (D) 1 and 4 (B) Anderson bridge.
56. Which bridge is used to determine (C) De Sautty’s bridge.
frequency ?
(D) Schering bridge.
(A) Anderson bridge. (B) De Sauty 63. Which of the following is used to measure
bridge. the leakage resistance of a capacitor ?
(C) Wien bridge. (D) Campell (A) Megger.
bridge.
(B) Schering bridge.
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 6
Negative-0.33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
(C) Potentiometer. (D) Vibration galvanometer, head phones
(D) Loss of charge method. and tunable amplifiers.
64. The capacitance and loss angle of a given 69. Vibration galvanometers, tuneable
capacitor specimen are best measured by amplifiers and head phones are used in
(A) Wheatstone bridge. (A) dc bridges.
(B) Maxwell bridge. (B) ac bridges.
(C) Anderson bridge. (C) both dc and ac bridges.
(D) Schering bridge. (D) Kelvin double bridge.
65. AC bridges : 70. A multimeter is used for the measurement
(A) have leakage error and eddy current of the following :
errors only.
1. Both ac and dc voltage.
(B) have residual errors, frequency errors
and wave form errors only. 2. Both ac and dc current.
(C) both (a) and (b. 3. Resistance.
(D) are free from errors. 4. Frequency.
66. Wagner Earth devices in ac bridge circuits 5. Power.
are used for Select the correct answer using the codes
(A) Shielding all the bridge elements from given
external magnetic field.
(A) 1, 2 and 4. (B) 1, 2 and 5.
(B) Eliminating the effect of stray
capacitance. (C) 1, 3 and 5. (D) 1, 2 and 3.
(C) Minimizing the effect of 71. Beam of electrons in a cathode ray tube
intercomponent capacitance. eminates because of
(D) Eliminating all the node to earth (A) secondary emission.
capacitances. (B) thermionic emission.
67. What should be the main characteristic(s) (C) diffusion.
of the null detector in a bridge
measurement ? (D) post acceleration.
1. Accuracy. 2. Precision. 72. What is the approximate input impedance
3. Sensitivity. 4. Resolution. of a CRO?
Select the correct answer using the code (A) Zero (B) 1 MW
given below : (C) 10 W (D) 10 µW
Code : 73. Which one of the following measuring
(A) Only 1 and 2. (B) Only 2 and 3. devices has minimum loading effect on the
(C) Only 3 and 4. (D) Only 3. quantity under measurement ?
68. A bridge circuit works at a frequency of 2 (A) PMMC.
kHz. Which detector can be used for (B) CRO.
detecting the null conditions in the bridge ?
(C) Hot wire.
(A) Vibration galvanometer and head
(D) Electrodynamometer.
phones.
74. In a CRO, the time-base generators supply
(B) Head phones and tunable emplifiers.
ramp voltage to
(C) Vibration galvanometer and tunable
(A) horizontal deflecting plates.
amplifiers.
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 7
Negative-0.33 Measurement Test by- Amit sinha
(B) vertical deflecting plates.
(C) both horizontal and vertical deflecting
plates.
(D) none of the above.
75. Post-deflection is required in CRO, if input
signal frequency is
(A) less than 1 kHz. (B) less than 1
MHz.
(C) below 10 MHz. (D) above 10
MHz. (A) for X and for Y.
76. The purpose of the synchronising control in (B) for X and for Y.
a CRO is to
(C) for X and for Y.
(A) focus the spot on the screen.
(D) for X and for Y.
(B) lock the display of signal.
80. In a dual beam oscilloscope
(C) adjust the amplitude of display.
(A) there are two separate vertical inputs
(D) control the intensity of the spot. and two separate horizontal inputs.
77. Which one of the following statements (B) there are two separate vertical inputs
correctly represents the post acceleration in and there is only one set of horizontal
a CRT ? deflection plates.
(A) It provides deflection of the beam. (C) there is only one vertical input but
(B) It increases the brightness of the trace there are two separate horizontal
if the signal frequency is higher than deflection plates.
10 MHz. (D) there is only one vertical and one
(C) It accelerates the beam before horizontal input.
deflection. 81. Sampling oscilloscopes are specially
(D) It increases the brightness of the trace designed to measure
of low frequency signal. (A) very low frequency.
78. The Lissajous pattern on a CRO screen is (B) very high frequency.
shown in the given figure :
(C) microwaves frequency.
The frequency ratio of the vertical signal to
the horizontal one is (D) none of the above.
(A) 3 : 2 (B) 5 : 1
(C) 1 : 5 (D) 2 : 3
79. In an oscilloscope, two Lissajous figures
(X) and (Y) are observed. This indicates
that ratio of vertical input signal frequency
to that of horizontal input frequency are
Engineers Adda,GTB Nagar,Delhi-110009 8800155821 Page 8
You might also like
- ASM - Specialty Handbook, Cast IronsDocument455 pagesASM - Specialty Handbook, Cast IronsMuhammad Azlan Ibrahim100% (16)
- 4024 Mock-2 Paper-1 2022-23Document22 pages4024 Mock-2 Paper-1 2022-23niloyNo ratings yet
- High-Strength Reinforcing Bars - ETN-M-8-16 PDFDocument12 pagesHigh-Strength Reinforcing Bars - ETN-M-8-16 PDFVignesh RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument MechanicDocument58 pagesMultiple Choice Practice Questions For Online/Omr AITT-2020 Instrument Mechanicمصطفى شاكر محمودNo ratings yet
- Sheet IDocument7 pagesSheet IMohamed MNo ratings yet
- CHANDRADocument8 pagesCHANDRAivy agustinNo ratings yet
- Static C/cs of MeasurementsDocument3 pagesStatic C/cs of MeasurementssamadonyNo ratings yet
- Measuring CH 1 FINALDocument2 pagesMeasuring CH 1 FINALShahzaib TanoliNo ratings yet
- Measurements Mid TermDocument2 pagesMeasurements Mid TermabdallaNo ratings yet
- MTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023Document5 pagesMTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023k.ghanemNo ratings yet
- MTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023Document5 pagesMTExam1 Engineering Metrology & Measurements 2022 2023k.ghanemNo ratings yet
- 1.dead Time of The Instrument Is: Span Max-MinDocument3 pages1.dead Time of The Instrument Is: Span Max-MinNaveen BhatNo ratings yet
- Metrology QBDocument16 pagesMetrology QBSubin RajNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Binders (1)Document53 pagesInstrumentation Binders (1)noelNo ratings yet
- Chandra SurveyingDocument20 pagesChandra SurveyingIvy Joy SaguranNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engr Mcqs PDFDocument23 pagesElectrical Engr Mcqs PDFFarman100% (1)
- Jr. Engineer Civil 102Document16 pagesJr. Engineer Civil 102Bindesh Chouhan100% (1)
- EJ-01-2020 Practical No.1 MCQDocument2 pagesEJ-01-2020 Practical No.1 MCQBhushan BhavarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements MCQ PDFDocument11 pagesElectronic Measurements MCQ PDFAmit Ghade67% (3)
- Eee GT - 20 PDFDocument8 pagesEee GT - 20 PDFupender raoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Long TestDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Long Testjrm.tinoyNo ratings yet
- Obj Cre PDFDocument15 pagesObj Cre PDFAyushSingh100% (1)
- RRB Junior Engineer Mechanical Model Question Paper Solved 17Document34 pagesRRB Junior Engineer Mechanical Model Question Paper Solved 17Praveen Palaniappan50% (2)
- Chapter #01Document16 pagesChapter #01Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Wa0007Document6 pagesWa0007shubham muraiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-1Document4 pagesElectronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-1chetanaNo ratings yet
- Rank Improvement Program Rank Improvement Program Rank Improvement ProgramDocument23 pagesRank Improvement Program Rank Improvement Program Rank Improvement ProgramVISHNU PRIYA BUDDANINo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-16 at 10.19.30 AMDocument96 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-16 at 10.19.30 AMRajvardhan NaikNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece Ec1104-Electronic Measurement and InstrumentationDocument3 pagesDepartment of Ece Ec1104-Electronic Measurement and InstrumentationLali ThaNo ratings yet
- EXDocument44 pagesEXLương Hồ VũNo ratings yet
- 15ee207 3 SemDocument2 pages15ee207 3 SemSarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment Error AnalysisDocument3 pagesAssignment Error Analysissingh813No ratings yet
- 2012 CSEC Physics Specimen P1Document13 pages2012 CSEC Physics Specimen P1Naps LibraryNo ratings yet
- TNEB ECE Model Question Paper 1: B) InfiniteDocument8 pagesTNEB ECE Model Question Paper 1: B) InfinitesNo ratings yet
- Quiz Test-1 Question As On 12.09.2019Document13 pagesQuiz Test-1 Question As On 12.09.2019NEELAMANI SAMALNo ratings yet
- Chhotu Ram Rural Institute of Technology Branch-Electrical Engineering M.M.45 Time 30 MinutesDocument5 pagesChhotu Ram Rural Institute of Technology Branch-Electrical Engineering M.M.45 Time 30 Minutesharish220907No ratings yet
- MCQs EC-302 EMI LNCTEDocument5 pagesMCQs EC-302 EMI LNCTEAdarsh UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cat-1Document16 pagesMCQ Cat-1vijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Units and Measurement (PG 1 - 3)Document3 pagesChapter-1 Units and Measurement (PG 1 - 3)darling deanNo ratings yet
- 2 qp2Document13 pages2 qp2JustinNo ratings yet
- QuestingDocument2 pagesQuestinganilsai56No ratings yet
- Physics - Complete Quick Revision 2021Document99 pagesPhysics - Complete Quick Revision 2021MeeraNo ratings yet
- Results Reporter: Mixed QuizDocument8 pagesResults Reporter: Mixed Quizmraza17No ratings yet
- JashuDocument204 pagesJashuPiyushsinhNo ratings yet
- DemonstratorDocument16 pagesDemonstratorswapna jeeviNo ratings yet
- 11th PCM Jee Main - 02 Sarabhai (16-07-2021)Document14 pages11th PCM Jee Main - 02 Sarabhai (16-07-2021)jdkdkdkNo ratings yet
- AMU Class 11 2010 PaperDocument6 pagesAMU Class 11 2010 Paperhacker GodNo ratings yet
- PHY 111 ExamDocument2 pagesPHY 111 ExamJoseph IsekNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Kalpit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pattern of Question, Syllabus & Probable Q & A of The Exam. For Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Through PSCDocument1 pagePattern of Question, Syllabus & Probable Q & A of The Exam. For Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Through PSCSudip MondalNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Corr1555Document16 pagesCase Study On Corr1555TarunNo ratings yet
- Emi MCQDocument27 pagesEmi MCQgautam100% (3)
- Answer: A: 1. The Measurement of A QuantityDocument15 pagesAnswer: A: 1. The Measurement of A Quantitydream breaker100% (1)
- SLO BASED MCQS AND QUESTIONS - IX PhysicsDocument60 pagesSLO BASED MCQS AND QUESTIONS - IX PhysicsWaheedkhanNo ratings yet
- S&a MCQ - SveriDocument31 pagesS&a MCQ - Sveritrail meNo ratings yet
- Measurements AnsDocument6 pagesMeasurements AnsoAeonNo ratings yet
- GATE Aerospace 2012 PaperDocument5 pagesGATE Aerospace 2012 Papermohini priya kolluriNo ratings yet
- Model Qpaper GeDocument10 pagesModel Qpaper Geसोनू जगतापNo ratings yet
- Model Qpaper GeDocument10 pagesModel Qpaper GeMr V. Phaninder ReddyNo ratings yet
- Measurements TestDocument6 pagesMeasurements TestoAeonNo ratings yet
- SAMPLEQUESTIONS COMPREXAM (ObjType)Document19 pagesSAMPLEQUESTIONS COMPREXAM (ObjType)ഹരി നീലാംബരിNo ratings yet
- Test NewDocument4 pagesTest NewKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Standard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerFrom EverandStandard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerNo ratings yet
- Corona Test ResultDocument1 pageCorona Test Resultkartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Ans. (C)Document4 pagesAns. (C)kartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Success Guaranteed..... Success Guaranteed....Document1 pageSuccess Guaranteed..... Success Guaranteed....kartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Ee+ece Scholarship Result CrritDocument1 pageEe+ece Scholarship Result Crritkartiksahni07No ratings yet
- Basic Joints & Blueprint ReadingDocument132 pagesBasic Joints & Blueprint Readingtranng100% (1)
- MANUEL Devidoir MillerDocument36 pagesMANUEL Devidoir MillerBrice DreessenNo ratings yet
- FEM Simulation of CMUT Cell For NDT ApplicationDocument7 pagesFEM Simulation of CMUT Cell For NDT ApplicationShuvam5 GuptaNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Text BookDocument111 pagesO Level Physics Text BookMatabaro BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Mechanics1 VFreadingsDocument275 pagesMechanics1 VFreadingsMohammed HachemiNo ratings yet
- EC403: Microwave & Radar EngineeringDocument70 pagesEC403: Microwave & Radar EngineeringBindu Narayanan NampoothiriNo ratings yet
- 12.2 Motion CIE IGCSE Physics Ext Theory MsDocument5 pages12.2 Motion CIE IGCSE Physics Ext Theory MsasifshahanaNo ratings yet
- WCM - Yamashina - 05 - Professional Maintenance - Chapter - 3 - ADocument100 pagesWCM - Yamashina - 05 - Professional Maintenance - Chapter - 3 - ACíceroNo ratings yet
- Model: T521 (H), T522 (H/L), T523 (L), T524 (H/HH), T525 (L/LL), T526 (H/L)Document6 pagesModel: T521 (H), T522 (H/L), T523 (L), T524 (H/HH), T525 (L/LL), T526 (H/L)firman harianjaNo ratings yet
- Fujifilm Eluxeo BL 7000Document78 pagesFujifilm Eluxeo BL 7000AngeloNo ratings yet
- JK Bose Class 12 Physics 81017 P 2013Document3 pagesJK Bose Class 12 Physics 81017 P 2013Asha BarelayNo ratings yet
- Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument9 pagesShivaji University, KolhapurNiranjan PatilNo ratings yet
- WebquestDocument3 pagesWebquestanssh prajapatiNo ratings yet
- p112 Lecture2Document22 pagesp112 Lecture2Othniel SulpicoNo ratings yet
- CSE 28363 - Structural Concrete Design: Lecture 10: Shear and ServiceabilityDocument44 pagesCSE 28363 - Structural Concrete Design: Lecture 10: Shear and ServiceabilityBitch CarrieNo ratings yet
- Master SpecificationsDocument395 pagesMaster SpecificationsHaymanot BaynesagnNo ratings yet
- AIRSYS - ASPCB 2 Interconnect Guidelines Rev4 12-2-13Document5 pagesAIRSYS - ASPCB 2 Interconnect Guidelines Rev4 12-2-13mauricioNo ratings yet
- BKT2031 TDSDocument1 pageBKT2031 TDSAshutoshNo ratings yet
- s4 Physics Paper 3 Exam 5Document4 pagess4 Physics Paper 3 Exam 5MUSOKE GERALDNo ratings yet
- Disabled Systems: Customer Name Reference Product Series NoDocument17 pagesDisabled Systems: Customer Name Reference Product Series NoАлександр КачеишвилиNo ratings yet
- GEET-Small Engine Conversion PlansDocument19 pagesGEET-Small Engine Conversion PlansCristo_Alanis_8381No ratings yet
- 425ºC AHT: Ower EATDocument2 pages425ºC AHT: Ower EATSivagurunathan SpNo ratings yet
- Caledonian Railway Cables PDFDocument251 pagesCaledonian Railway Cables PDFamitvaishnav1No ratings yet
- Types of AgitatorsDocument2 pagesTypes of Agitatorsjeamnard balitaanNo ratings yet
- Very Light Aircraft Model: Sea Level Temperature K Sea Level Pressure Pa Gas Constant J/K/KG Lapse Rate K/MDocument6 pagesVery Light Aircraft Model: Sea Level Temperature K Sea Level Pressure Pa Gas Constant J/K/KG Lapse Rate K/Mrighthere201No ratings yet
- CHT307 - Ktu QbankDocument3 pagesCHT307 - Ktu QbankYuxin CasioNo ratings yet
- National Advisory Committee - For Aeronautics: Technical Note No: 1293Document56 pagesNational Advisory Committee - For Aeronautics: Technical Note No: 1293manuelq9No ratings yet