Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2 Learning Journal
Unit 2 Learning Journal
Uploaded by
Ben ObiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 16 Lippincott BiochemistryDocument57 pagesChapter 16 Lippincott BiochemistryMeysam SajjadiNo ratings yet
- chemistry-technical-document-CHTD 500 v1 revAA 07jul2016-AnyDocument42 pageschemistry-technical-document-CHTD 500 v1 revAA 07jul2016-AnyErikk DangNo ratings yet
- "Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)Document1 page"Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)SusanAngDíaz0% (2)
- SIMILARSDocument1 pageSIMILARSdamian pNo ratings yet
- Crosswordanswers 19Document1 pageCrosswordanswers 19ivanNo ratings yet
- Food Chain Food Web Wordsearch Answer KeyDocument1 pageFood Chain Food Web Wordsearch Answer KeyAlexander RussellNo ratings yet
- Part 1 & 2 Submission of Learning Journal Unit 2Document4 pagesPart 1 & 2 Submission of Learning Journal Unit 2simru98No ratings yet
- C869BB1C-1C27-4429-AA4F-86F9AD97496ADocument3 pagesC869BB1C-1C27-4429-AA4F-86F9AD97496AMary Louise MadariagaNo ratings yet
- Chart OrganizationDocument40 pagesChart OrganizationDhayane RedoquerioNo ratings yet
- CW-carbo Puzzle LLENARESDocument4 pagesCW-carbo Puzzle LLENARESJanica Janica Janica Janica Janica Janica JanicaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Life (Biology Exercises)Document1 pageCells and Life (Biology Exercises)Sebastian AguirreNo ratings yet
- Final Examination in IT22: S B A I A CDocument8 pagesFinal Examination in IT22: S B A I A CJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- Yokingco - Lesson 3.3 LTDocument1 pageYokingco - Lesson 3.3 LTHeart YokingcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.2: Across DownDocument1 pageActivity 2.2: Across DownThabang LeseleNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2roanjapayNo ratings yet
- Crossword PuzzleDocument1 pageCrossword PuzzleOLIN JAY HONRUBIANo ratings yet
- TTS RespiDocument1 pageTTS RespiDinda BenitaNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle AnswersDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle AnswersKristiane Reyes De VillaNo ratings yet
- T.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Document15 pagesT.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Eleonor DistrajoNo ratings yet
- Puzzle Quiz - Quezon, Camelle Ann A.Document1 pagePuzzle Quiz - Quezon, Camelle Ann A.Camelle Ann QuezonNo ratings yet
- Module On Ethical Legal AspectsDocument5 pagesModule On Ethical Legal AspectsLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Activity No.10 - Madariaga, Mary Louise - Bsn2eDocument3 pagesActivity No.10 - Madariaga, Mary Louise - Bsn2eMary Louise MadariagaNo ratings yet
- Bonafide CertificateDocument3 pagesBonafide CertificateIIT HelpNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersDocument6 pagesCrossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersNur Irdhina AkhtariNo ratings yet
- TKT Module 1: Describing Language: Grammar Participant's Worksheet 1Document1 pageTKT Module 1: Describing Language: Grammar Participant's Worksheet 1fabrizio.solerNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle - ActivityDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle - ActivityCarlo Jay BasulNo ratings yet
- Songs I Can Sing A Rainbow Worksheet 2017Document2 pagesSongs I Can Sing A Rainbow Worksheet 2017MargaritaNahuelpánAntilén.No ratings yet
- Crossword Present SimpleDocument2 pagesCrossword Present SimpleLizeth MoralesNo ratings yet
- Connectors WsDocument2 pagesConnectors WsshanNo ratings yet
- Sophia Santos - ACTIVITY 3 - Boys To MenDocument3 pagesSophia Santos - ACTIVITY 3 - Boys To MenSophia SantosNo ratings yet
- The Ten CommandmentsDocument1 pageThe Ten Commandmentsapi-408992493No ratings yet
- Past Simple (Irregular Verbs) : Grammar CrosswordDocument2 pagesPast Simple (Irregular Verbs) : Grammar CrosswordMarco67% (3)
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2Tricia Maxine DomingoNo ratings yet
- Sistema Genital Vacío CrucigramaDocument1 pageSistema Genital Vacío CrucigramaSaul NicondNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Crossword Puzzle Answer Key 40238 6162ed83Document1 pageCell Organelle Crossword Puzzle Answer Key 40238 6162ed83B0% (1)
- Actividad 5 Evidencia 5Document9 pagesActividad 5 Evidencia 5Camilo VillamilNo ratings yet
- Rizal and The Crossword of HistoryDocument2 pagesRizal and The Crossword of HistoryRyan Christian BalanquitNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet MapehDocument4 pagesActivity Sheet Mapehedward surtidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Suggested AnswersDocument20 pagesChapter Three Suggested AnswersChristine Joy OriginalNo ratings yet
- (A) Four Pics One WordDocument9 pages(A) Four Pics One WordElla May PondaraNo ratings yet
- (Answers) Part 1 Nervous SystemDocument2 pages(Answers) Part 1 Nervous SystemFranc BlancNo ratings yet
- Naming of Inorganic Compounds: Across DownDocument1 pageNaming of Inorganic Compounds: Across DownArebeeJayBelloNo ratings yet
- T o R T o I S e W L FDocument2 pagesT o R T o I S e W L FYamile NasiraNo ratings yet
- Part I. Puzzle Word. Find The Answer in The BoxDocument1 pagePart I. Puzzle Word. Find The Answer in The BoxDeana Gabato Camama-PormaderNo ratings yet
- Q1W4 Performance Task 3Document2 pagesQ1W4 Performance Task 3Leilanie SantosNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading IDocument14 pagesJournal Reading IAhmad AbqariNo ratings yet
- 74363bos60276 cp7Document1 page74363bos60276 cp7prajnesh hegdeNo ratings yet
- (Potential Cause Disease) of Pathogenic BacteriaDocument23 pages(Potential Cause Disease) of Pathogenic BacteriaAli YassinNo ratings yet
- Graella AcrosticsDocument6 pagesGraella AcrosticslourdespvNo ratings yet
- 1) Living Things and Non-Living Things: DifferencesDocument9 pages1) Living Things and Non-Living Things: DifferencescoloNo ratings yet
- A Word - Health Activity-Q1Document1 pageA Word - Health Activity-Q1jocelyn c. siarezNo ratings yet
- Crossword 1Document1 pageCrossword 1Luz karine florez DuarteNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Money and Finance: © Brian Titley 2012: This May Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteDocument1 page3.1 Money and Finance: © Brian Titley 2012: This May Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteNadine ZalfaNo ratings yet
- Act 1 - Social Science-Culture, Society & PoliticsDocument5 pagesAct 1 - Social Science-Culture, Society & Politicsfe janduganNo ratings yet
- Crucigrama Relacion HuespedDocument2 pagesCrucigrama Relacion HuespedMariaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 - AolDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 - AolFebbie Angela Dazo100% (1)
- CRUCIGRAMADocument1 pageCRUCIGRAMAPatricia BeltranNo ratings yet
- Math Terms: Across DownDocument2 pagesMath Terms: Across DownTejaNo ratings yet
- Short Stories Teddys Adventure AnswerdDocument2 pagesShort Stories Teddys Adventure AnswerdPaucarmon MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Sumatif Kelas 4Document1 pagePenilaian Sumatif Kelas 4ImaheeNo ratings yet
- DCS C01 Quiz TeacherDocument2 pagesDCS C01 Quiz TeacherMonalisaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Protein Chemistry on the Biomedical SciencesFrom EverandThe Impact of Protein Chemistry on the Biomedical SciencesAlan SchechterNo ratings yet
- Writing 2Document6 pagesWriting 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 WADocument4 pagesUnit 2 WABen ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Assignment Unit 2 StatisticsDocument2 pagesDiscussion Assignment Unit 2 StatisticsBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CS Discussion AssignmentDocument1 pageUnit 4 CS Discussion AssignmentBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 7Document2 pagesDiscussion Forum Unit 7Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 1 Phil 1402Document2 pagesDiscussion Forum Unit 1 Phil 1402Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- ENGL1102.U6.Abstract and Conclusion - JSDocument7 pagesENGL1102.U6.Abstract and Conclusion - JSBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Writing Assignment Unit 2Document4 pagesWriting Assignment Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- MethodologiesDocument6 pagesMethodologiesBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Envs 1301 DF Unit 1Document2 pagesEnvs 1301 DF Unit 1Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- 44002671Document2 pages44002671Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- LJ Unit 2Document5 pagesLJ Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- BIO 1121 Unit 2 AssignmentDocument4 pagesBIO 1121 Unit 2 AssignmentBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Unit 2Document1 pageWritten Assignment Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Math LJ Unit 1Document2 pagesMath LJ Unit 1Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- ENGL1102 - U4 - Expanded Methods - UpdatedDocument20 pagesENGL1102 - U4 - Expanded Methods - UpdatedBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Math LJ Unit 2Document3 pagesMath LJ Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 4Document1 pageDiscussion Forum Unit 4Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- ENGL1002 Lit ReviewDocument12 pagesENGL1002 Lit ReviewBen ObiNo ratings yet
- DF Unit 1 CS 1102Document2 pagesDF Unit 1 CS 1102Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Unit 7Document1 pageWritten Assignment Unit 7Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- CS Journal Unit 5Document1 pageCS Journal Unit 5Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- WA Unit 22Document7 pagesWA Unit 22Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Leaning Into LearningDocument5 pagesLeaning Into LearningBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 OutputDocument1 pageUnit 7 OutputBen ObiNo ratings yet
- LJ Unit 6Document2 pagesLJ Unit 6Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- UNIV1001 Unit 8 LJDocument2 pagesUNIV1001 Unit 8 LJBen ObiNo ratings yet
- LJ Unit 2Document2 pagesLJ Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- PHIL 1402 - Written Assign 3Document4 pagesPHIL 1402 - Written Assign 3Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- DF Unit 3Document2 pagesDF Unit 3Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code Introduction PDFDocument10 pagesGenetic Code Introduction PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: The Chemistry of Carbon, The Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pagesLesson 4: The Chemistry of Carbon, The Chemistry of LifeJGHUNGERNo ratings yet
- CLA in Milk FatDocument16 pagesCLA in Milk FatAstiari Tia LegawaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 5th EditionDocument40 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry 5th EditionkhuyenhenryzwoowNo ratings yet
- Unit 14. Biomolecules: Annual Exam - 2014Document3 pagesUnit 14. Biomolecules: Annual Exam - 2014shivanandaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ClassificationDocument8 pagesEnzyme ClassificationR.KRISHNA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Tentative Exam Questions On Food BiochemistryDocument6 pagesTentative Exam Questions On Food BiochemistryPhạm Thu ThuỷNo ratings yet
- Copyofmysteryboxquiz Docx 1Document5 pagesCopyofmysteryboxquiz Docx 1api-319863011No ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument19 pagesBiochem Midterm ReviewerERIKA ROSE ALEJONo ratings yet
- X CH 4 TestDocument2 pagesX CH 4 TestHadi BuxNo ratings yet
- Boce2626 2017 Test 3 MemoDocument7 pagesBoce2626 2017 Test 3 MemoPaleisah MoagiNo ratings yet
- Nelson Biology Answers 4Document2 pagesNelson Biology Answers 4ritaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Dna Rna No VirusDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Dna Rna No VirusLara AlbeeshyNo ratings yet
- 1901BS085 - Molecular BiologyDocument8 pages1901BS085 - Molecular BiologyThe FourNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids MetabolismDocument24 pagesAmino Acids MetabolismYeri KimNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument7 pagesPresentationfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: The Structure of DNADocument9 pagesChapter 11 Lecture Notes: The Structure of DNAKrishna VenkataNo ratings yet
- RNA InterferenceDocument26 pagesRNA InterferenceAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- PMSF Protocols Online PDFDocument2 pagesPMSF Protocols Online PDFCitra Fragrantia Theodorea Ralahalu-MailoaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Enzyme Skeleton NotesDocument8 pages2.5 Enzyme Skeleton Notesadri baigorriNo ratings yet
- Foods ReportDocument1 pageFoods ReportipinseraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Dna & RnaDocument145 pagesNucleic Acids: Dna & Rnaangelin lledoNo ratings yet
- BMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsDocument3 pagesBMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument22 pagesProteinsJeswanth NayakNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna and Protein Synthesis Homework 3Document6 pagesDna Rna and Protein Synthesis Homework 3fjn29rfk100% (1)
- Biology 111 EXAM 2 Study GuideDocument15 pagesBiology 111 EXAM 2 Study GuidecuckoofourkokoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Biology FA 4 Question and Answer - EnzymesDocument5 pagesGrade 8 Biology FA 4 Question and Answer - EnzymesdhuriprashantNo ratings yet
- Molinspiration ChembioinformaticsDocument6 pagesMolinspiration ChembioinformaticsbedibediNo ratings yet
Unit 2 Learning Journal
Unit 2 Learning Journal
Uploaded by
Ben ObiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2 Learning Journal
Unit 2 Learning Journal
Uploaded by
Ben ObiCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING JOURNAL UNIT 2
For each category of macromolecule, carbohydrate, lipid, protein and nucleic acid, select a
representative polymer and explain its function within the cell. Suggest which aspects of your chosen
molecule are characteristic of the class of macromolecules to which it belongs by identifying its
monomer subunits and describing their basic chemical structure and the manner in which the
monomers are linked together.
Carbohydrate - Lactose is a disaccharide, meaning it's made up of two smaller sugar units, called glucose
and galactose, which is are joined by a glycosidic bond. Both serve as sources of energy for cells and
provide the cell with Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The formula is C12O22H11.
Lipid - Unsaturated fats, such as oils are lipids. They consist of a hydrocarbon chain with a double bond.
They help to lower blood cholesterol. Oleic acid C18H34O2 is an example.
Protein - Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. There are 20 amino acids, each with an
amino group and a carboxyl-acid group, but with a different “r” group, they are joined by peptide bonds.
One example necessary for humans is cysteine- C3H7NO2S -because it plays a major role in protein
rigidity therefore aids in collagen production, giving the skin its well-deserved elasticity.
Nucleic Acid - An important nucleic acid is deoxyribonucleic acid. It is important to the cell as it carries
the genetic information for protein reproduction. Nucleic acids are made of monomers called
nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar,
and a phosphate group. Each nitrogenous base in a nucleotide is attached to a sugar molecule, which is
attached to one or more phosphate groups. The pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose. DNA has a double
helix structure.
Reference:
Kirstin Hendrickson. LiveStrong.Com, What Are the Functions of Lactose? Retrieved from
https://www.livestrong.com/article/367146-what-are-the-functions-of-lactose/
OpenStax College, Biology. OpenStax College (30May2013). Retrieved from
http://cnx.org/content/col11448/latest/>
Simple English Wikipedia. Adenosine triphosphate. Retrieved from
https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_triphosphate
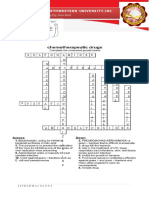
E N Z Y M E
O
N
O
S M C G
E E E L
G L Y C O R O L C A R B O X Y L
I O L C
P N F R U C T O S E C O
I D L T R A N S
D A M I N O A C I D R I
R S E B D
Y E P H O S P H O L I P I D
X H C E
Y Y H P
S A T U R A T E D Y U
I R D R
B A U R A C I L
O T A N
S E T E
E P E P T I D E
O
T W E N T Y
Across Down
1. protein that acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions 2. single unit of a polymer
6. component of fat molecule 3. structure of polypeptide chain that contains beta sheets
8. acidic group in amino acids 4. provides structural support in plant cells
9. monosaccharide commonly found in fruit 5. type of bond between monosaccharides in a chain
11. fatty acid with hydrogens in different planes 7. used for long term energy storage
12. monomer subunit of protein 10. biological macromolecule with a ratio of 1 C:2 H:1 O
14. major constituent of plasma membrane 13. sugar backbone of DNA
17. fatty acid containing no double bonds 15. type of reaction used to form polymers
18. nucleic acid found only in RNA 16. adenine and guanine are this type of nucleotide
19. bond formed between two amino acids
20. number of amino acids
You might also like
- Chapter 16 Lippincott BiochemistryDocument57 pagesChapter 16 Lippincott BiochemistryMeysam SajjadiNo ratings yet
- chemistry-technical-document-CHTD 500 v1 revAA 07jul2016-AnyDocument42 pageschemistry-technical-document-CHTD 500 v1 revAA 07jul2016-AnyErikk DangNo ratings yet
- "Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)Document1 page"Food Chain and Food Web" Crossword Puzzle (Answer Key)SusanAngDíaz0% (2)
- SIMILARSDocument1 pageSIMILARSdamian pNo ratings yet
- Crosswordanswers 19Document1 pageCrosswordanswers 19ivanNo ratings yet
- Food Chain Food Web Wordsearch Answer KeyDocument1 pageFood Chain Food Web Wordsearch Answer KeyAlexander RussellNo ratings yet
- Part 1 & 2 Submission of Learning Journal Unit 2Document4 pagesPart 1 & 2 Submission of Learning Journal Unit 2simru98No ratings yet
- C869BB1C-1C27-4429-AA4F-86F9AD97496ADocument3 pagesC869BB1C-1C27-4429-AA4F-86F9AD97496AMary Louise MadariagaNo ratings yet
- Chart OrganizationDocument40 pagesChart OrganizationDhayane RedoquerioNo ratings yet
- CW-carbo Puzzle LLENARESDocument4 pagesCW-carbo Puzzle LLENARESJanica Janica Janica Janica Janica Janica JanicaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Life (Biology Exercises)Document1 pageCells and Life (Biology Exercises)Sebastian AguirreNo ratings yet
- Final Examination in IT22: S B A I A CDocument8 pagesFinal Examination in IT22: S B A I A CJb MejiaNo ratings yet
- Yokingco - Lesson 3.3 LTDocument1 pageYokingco - Lesson 3.3 LTHeart YokingcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.2: Across DownDocument1 pageActivity 2.2: Across DownThabang LeseleNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2roanjapayNo ratings yet
- Crossword PuzzleDocument1 pageCrossword PuzzleOLIN JAY HONRUBIANo ratings yet
- TTS RespiDocument1 pageTTS RespiDinda BenitaNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle AnswersDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle AnswersKristiane Reyes De VillaNo ratings yet
- T.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Document15 pagesT.L.E 7 and 8 Week 5Eleonor DistrajoNo ratings yet
- Puzzle Quiz - Quezon, Camelle Ann A.Document1 pagePuzzle Quiz - Quezon, Camelle Ann A.Camelle Ann QuezonNo ratings yet
- Module On Ethical Legal AspectsDocument5 pagesModule On Ethical Legal AspectsLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Activity No.10 - Madariaga, Mary Louise - Bsn2eDocument3 pagesActivity No.10 - Madariaga, Mary Louise - Bsn2eMary Louise MadariagaNo ratings yet
- Bonafide CertificateDocument3 pagesBonafide CertificateIIT HelpNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersDocument6 pagesCrossword Puzzle Form 3 AnswersNur Irdhina AkhtariNo ratings yet
- TKT Module 1: Describing Language: Grammar Participant's Worksheet 1Document1 pageTKT Module 1: Describing Language: Grammar Participant's Worksheet 1fabrizio.solerNo ratings yet
- Crossword Puzzle - ActivityDocument1 pageCrossword Puzzle - ActivityCarlo Jay BasulNo ratings yet
- Songs I Can Sing A Rainbow Worksheet 2017Document2 pagesSongs I Can Sing A Rainbow Worksheet 2017MargaritaNahuelpánAntilén.No ratings yet
- Crossword Present SimpleDocument2 pagesCrossword Present SimpleLizeth MoralesNo ratings yet
- Connectors WsDocument2 pagesConnectors WsshanNo ratings yet
- Sophia Santos - ACTIVITY 3 - Boys To MenDocument3 pagesSophia Santos - ACTIVITY 3 - Boys To MenSophia SantosNo ratings yet
- The Ten CommandmentsDocument1 pageThe Ten Commandmentsapi-408992493No ratings yet
- Past Simple (Irregular Verbs) : Grammar CrosswordDocument2 pagesPast Simple (Irregular Verbs) : Grammar CrosswordMarco67% (3)
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2Tricia Maxine DomingoNo ratings yet
- Sistema Genital Vacío CrucigramaDocument1 pageSistema Genital Vacío CrucigramaSaul NicondNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Crossword Puzzle Answer Key 40238 6162ed83Document1 pageCell Organelle Crossword Puzzle Answer Key 40238 6162ed83B0% (1)
- Actividad 5 Evidencia 5Document9 pagesActividad 5 Evidencia 5Camilo VillamilNo ratings yet
- Rizal and The Crossword of HistoryDocument2 pagesRizal and The Crossword of HistoryRyan Christian BalanquitNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet MapehDocument4 pagesActivity Sheet Mapehedward surtidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Suggested AnswersDocument20 pagesChapter Three Suggested AnswersChristine Joy OriginalNo ratings yet
- (A) Four Pics One WordDocument9 pages(A) Four Pics One WordElla May PondaraNo ratings yet
- (Answers) Part 1 Nervous SystemDocument2 pages(Answers) Part 1 Nervous SystemFranc BlancNo ratings yet
- Naming of Inorganic Compounds: Across DownDocument1 pageNaming of Inorganic Compounds: Across DownArebeeJayBelloNo ratings yet
- T o R T o I S e W L FDocument2 pagesT o R T o I S e W L FYamile NasiraNo ratings yet
- Part I. Puzzle Word. Find The Answer in The BoxDocument1 pagePart I. Puzzle Word. Find The Answer in The BoxDeana Gabato Camama-PormaderNo ratings yet
- Q1W4 Performance Task 3Document2 pagesQ1W4 Performance Task 3Leilanie SantosNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading IDocument14 pagesJournal Reading IAhmad AbqariNo ratings yet
- 74363bos60276 cp7Document1 page74363bos60276 cp7prajnesh hegdeNo ratings yet
- (Potential Cause Disease) of Pathogenic BacteriaDocument23 pages(Potential Cause Disease) of Pathogenic BacteriaAli YassinNo ratings yet
- Graella AcrosticsDocument6 pagesGraella AcrosticslourdespvNo ratings yet
- 1) Living Things and Non-Living Things: DifferencesDocument9 pages1) Living Things and Non-Living Things: DifferencescoloNo ratings yet
- A Word - Health Activity-Q1Document1 pageA Word - Health Activity-Q1jocelyn c. siarezNo ratings yet
- Crossword 1Document1 pageCrossword 1Luz karine florez DuarteNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Money and Finance: © Brian Titley 2012: This May Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteDocument1 page3.1 Money and Finance: © Brian Titley 2012: This May Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteNadine ZalfaNo ratings yet
- Act 1 - Social Science-Culture, Society & PoliticsDocument5 pagesAct 1 - Social Science-Culture, Society & Politicsfe janduganNo ratings yet
- Crucigrama Relacion HuespedDocument2 pagesCrucigrama Relacion HuespedMariaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 - AolDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 - AolFebbie Angela Dazo100% (1)
- CRUCIGRAMADocument1 pageCRUCIGRAMAPatricia BeltranNo ratings yet
- Math Terms: Across DownDocument2 pagesMath Terms: Across DownTejaNo ratings yet
- Short Stories Teddys Adventure AnswerdDocument2 pagesShort Stories Teddys Adventure AnswerdPaucarmon MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Sumatif Kelas 4Document1 pagePenilaian Sumatif Kelas 4ImaheeNo ratings yet
- DCS C01 Quiz TeacherDocument2 pagesDCS C01 Quiz TeacherMonalisaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Protein Chemistry on the Biomedical SciencesFrom EverandThe Impact of Protein Chemistry on the Biomedical SciencesAlan SchechterNo ratings yet
- Writing 2Document6 pagesWriting 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 WADocument4 pagesUnit 2 WABen ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Assignment Unit 2 StatisticsDocument2 pagesDiscussion Assignment Unit 2 StatisticsBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CS Discussion AssignmentDocument1 pageUnit 4 CS Discussion AssignmentBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 7Document2 pagesDiscussion Forum Unit 7Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 1 Phil 1402Document2 pagesDiscussion Forum Unit 1 Phil 1402Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- ENGL1102.U6.Abstract and Conclusion - JSDocument7 pagesENGL1102.U6.Abstract and Conclusion - JSBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Writing Assignment Unit 2Document4 pagesWriting Assignment Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- MethodologiesDocument6 pagesMethodologiesBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Envs 1301 DF Unit 1Document2 pagesEnvs 1301 DF Unit 1Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- 44002671Document2 pages44002671Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- LJ Unit 2Document5 pagesLJ Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- BIO 1121 Unit 2 AssignmentDocument4 pagesBIO 1121 Unit 2 AssignmentBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Unit 2Document1 pageWritten Assignment Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Math LJ Unit 1Document2 pagesMath LJ Unit 1Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- ENGL1102 - U4 - Expanded Methods - UpdatedDocument20 pagesENGL1102 - U4 - Expanded Methods - UpdatedBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Math LJ Unit 2Document3 pagesMath LJ Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 4Document1 pageDiscussion Forum Unit 4Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- ENGL1002 Lit ReviewDocument12 pagesENGL1002 Lit ReviewBen ObiNo ratings yet
- DF Unit 1 CS 1102Document2 pagesDF Unit 1 CS 1102Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Unit 7Document1 pageWritten Assignment Unit 7Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- CS Journal Unit 5Document1 pageCS Journal Unit 5Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- WA Unit 22Document7 pagesWA Unit 22Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Leaning Into LearningDocument5 pagesLeaning Into LearningBen ObiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 OutputDocument1 pageUnit 7 OutputBen ObiNo ratings yet
- LJ Unit 6Document2 pagesLJ Unit 6Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- UNIV1001 Unit 8 LJDocument2 pagesUNIV1001 Unit 8 LJBen ObiNo ratings yet
- LJ Unit 2Document2 pagesLJ Unit 2Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- PHIL 1402 - Written Assign 3Document4 pagesPHIL 1402 - Written Assign 3Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- DF Unit 3Document2 pagesDF Unit 3Ben ObiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code Introduction PDFDocument10 pagesGenetic Code Introduction PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: The Chemistry of Carbon, The Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pagesLesson 4: The Chemistry of Carbon, The Chemistry of LifeJGHUNGERNo ratings yet
- CLA in Milk FatDocument16 pagesCLA in Milk FatAstiari Tia LegawaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 5th EditionDocument40 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry 5th EditionkhuyenhenryzwoowNo ratings yet
- Unit 14. Biomolecules: Annual Exam - 2014Document3 pagesUnit 14. Biomolecules: Annual Exam - 2014shivanandaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ClassificationDocument8 pagesEnzyme ClassificationR.KRISHNA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Tentative Exam Questions On Food BiochemistryDocument6 pagesTentative Exam Questions On Food BiochemistryPhạm Thu ThuỷNo ratings yet
- Copyofmysteryboxquiz Docx 1Document5 pagesCopyofmysteryboxquiz Docx 1api-319863011No ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument19 pagesBiochem Midterm ReviewerERIKA ROSE ALEJONo ratings yet
- X CH 4 TestDocument2 pagesX CH 4 TestHadi BuxNo ratings yet
- Boce2626 2017 Test 3 MemoDocument7 pagesBoce2626 2017 Test 3 MemoPaleisah MoagiNo ratings yet
- Nelson Biology Answers 4Document2 pagesNelson Biology Answers 4ritaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Dna Rna No VirusDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Dna Rna No VirusLara AlbeeshyNo ratings yet
- 1901BS085 - Molecular BiologyDocument8 pages1901BS085 - Molecular BiologyThe FourNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids MetabolismDocument24 pagesAmino Acids MetabolismYeri KimNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument7 pagesPresentationfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: The Structure of DNADocument9 pagesChapter 11 Lecture Notes: The Structure of DNAKrishna VenkataNo ratings yet
- RNA InterferenceDocument26 pagesRNA InterferenceAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- PMSF Protocols Online PDFDocument2 pagesPMSF Protocols Online PDFCitra Fragrantia Theodorea Ralahalu-MailoaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Enzyme Skeleton NotesDocument8 pages2.5 Enzyme Skeleton Notesadri baigorriNo ratings yet
- Foods ReportDocument1 pageFoods ReportipinseraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Dna & RnaDocument145 pagesNucleic Acids: Dna & Rnaangelin lledoNo ratings yet
- BMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsDocument3 pagesBMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument22 pagesProteinsJeswanth NayakNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna and Protein Synthesis Homework 3Document6 pagesDna Rna and Protein Synthesis Homework 3fjn29rfk100% (1)
- Biology 111 EXAM 2 Study GuideDocument15 pagesBiology 111 EXAM 2 Study GuidecuckoofourkokoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Biology FA 4 Question and Answer - EnzymesDocument5 pagesGrade 8 Biology FA 4 Question and Answer - EnzymesdhuriprashantNo ratings yet
- Molinspiration ChembioinformaticsDocument6 pagesMolinspiration ChembioinformaticsbedibediNo ratings yet