Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Micro Insurance
Micro Insurance
Uploaded by
Gundupagi ManjunathCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- (Customer) Gauge Panel RebuildDocument9 pages(Customer) Gauge Panel RebuildLidetu DemissieNo ratings yet
- Screening Test - Grade 7Document5 pagesScreening Test - Grade 7Hosain Said Usman Jr.100% (17)
- Problems and Prospects of General Insurance in BangladeshDocument56 pagesProblems and Prospects of General Insurance in BangladeshAmirul Islam75% (4)
- Customer LoyaltyDocument39 pagesCustomer LoyaltyGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- IndiaHikes PDFDocument5 pagesIndiaHikes PDFAAMOD KHARB PGP 2018-20 BatchNo ratings yet
- Micro Insurance HDocument46 pagesMicro Insurance HNirupa KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument17 pagesMicro InsurancerishipathNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii-Theoretical View: Credit Unions MicrofinanceDocument15 pagesChapter Iii-Theoretical View: Credit Unions MicrofinanceMrudula M NairNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument37 pagesMicro InsuranceBhavna Advani100% (2)
- Microinsurance ProjectDocument59 pagesMicroinsurance Projectmayur9664501232No ratings yet
- Insurance Ii Assignment On The Topic "MICROINSURANCE - TRENDS & Strategies"Document7 pagesInsurance Ii Assignment On The Topic "MICROINSURANCE - TRENDS & Strategies"Sumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Kamlesh - Micro InsuranceDocument33 pagesKamlesh - Micro InsuranceKrishna PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Micro Takaful Vs MicroinsuranceDocument5 pagesMicro Takaful Vs MicroinsuranceSiful Islam AnikNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document19 pagesUnit 6ChandrakantBangarNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance - Executive Summary (English)Document4 pagesMicroinsurance - Executive Summary (English)IPS Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- 7 Youseph AsefaDocument15 pages7 Youseph AsefamohamedfisalNo ratings yet
- Micro Insurance ProjectDocument56 pagesMicro Insurance ProjectParag More50% (4)
- Micro Insurance in India: A Powerful Tool To Empower Poor: June 2020Document21 pagesMicro Insurance in India: A Powerful Tool To Empower Poor: June 2020Naina BaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Micro-Insurance Augmenting The Poverty Alleviation Role of Micro-Finance: A Case Study of BangladeshDocument17 pagesContribution of Micro-Insurance Augmenting The Poverty Alleviation Role of Micro-Finance: A Case Study of BangladeshSaif Hasan JyotiNo ratings yet
- Awareness of Micro Insurance Product in Patan District: Mr. Mitul M. Deliya Dr. Karshanbhai N. PatelDocument21 pagesAwareness of Micro Insurance Product in Patan District: Mr. Mitul M. Deliya Dr. Karshanbhai N. PatelAnonymous 6x5cTCmNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To ReferDocument11 pagesMicroinsurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To ReferKush TiwariNo ratings yet
- Dec08 138 Microfinance en FINAL2Document4 pagesDec08 138 Microfinance en FINAL2Hedato M DatuNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils inDocument5 pagesMicroinsurance Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils inSanjay SmartNo ratings yet
- Insurance For Small BusinessesDocument2 pagesInsurance For Small BusinessesTheodorah Gaelle MadzyNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance Term Paper RevisedDocument25 pagesMicroinsurance Term Paper RevisedAnish S.MenonNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument1 pageConclusionAjeet YadavNo ratings yet
- Aka SH Bang ADocument63 pagesAka SH Bang AakashbangaNo ratings yet
- MICRO INSURANCE PttsDocument21 pagesMICRO INSURANCE PttsSushil PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Insurance in BangladeshDocument37 pagesInsurance in BangladeshNahidRahman100% (1)
- ECODEVDocument2 pagesECODEVEena Viamae PinpinNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument56 pagesExecutive Summaryshwetachalke21No ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument4 pagesMicro InsuranceBasil V JamesNo ratings yet
- IIA Word ReportDocument5 pagesIIA Word Reportshiva sambhawiNo ratings yet
- A Microinsurance Compendium - Vol I - Part 3Document190 pagesA Microinsurance Compendium - Vol I - Part 3charlesdaud395No ratings yet
- Notes Irt04205Document24 pagesNotes Irt04205shabanzuhura706No ratings yet
- Advantages of Life InsuranceDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Life Insurancekeyur5689No ratings yet
- Background Bangladesh Is Highly Vulnerable To Tropical Cyclones and Floods1 Due To Its Geographical Location and Very Low Land ElevationDocument4 pagesBackground Bangladesh Is Highly Vulnerable To Tropical Cyclones and Floods1 Due To Its Geographical Location and Very Low Land ElevationSikder Insurance [Gmail.com]No ratings yet
- Community Based Insurance-MicroinsuranceDocument33 pagesCommunity Based Insurance-MicroinsuranceRanjusha AshokNo ratings yet
- File TushaDocument5 pagesFile Tushahiru jariwalaNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Microinsurance: Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils in ExchangeDocument4 pagesDefinitions of Microinsurance: Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils in ExchangeDinesh GodhaniNo ratings yet
- Indian Insurance SectorDocument32 pagesIndian Insurance Sectorbanirumi100% (2)
- Summer Internship Project ON A Study On Consumer Perception About Insurance CompanyDocument13 pagesSummer Internship Project ON A Study On Consumer Perception About Insurance CompanySHARMA TECHNo ratings yet
- Insurance Company AnalysisDocument13 pagesInsurance Company AnalysisAyon ImtiazNo ratings yet
- "Mdicleaim": Mamta Ashok GuptaDocument50 pages"Mdicleaim": Mamta Ashok GuptaKarishma Dharmesh SoohindaNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance in IndiaDocument6 pagesMicroinsurance in IndiaPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument13 pagesMicro Insurancedhiraj1No ratings yet
- Micro Insurance Scenario in India: Group - 5Document21 pagesMicro Insurance Scenario in India: Group - 5Shivank PantNo ratings yet
- Insurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To Refer ToDocument16 pagesInsurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To Refer ToNupur Gangurde0% (1)
- Article 1Document2 pagesArticle 1lvprasad3125No ratings yet
- Micro Health Insurance - A Way of Ensuring Financial Security To The Poor. By. Dr.N.JeyaseelanDocument12 pagesMicro Health Insurance - A Way of Ensuring Financial Security To The Poor. By. Dr.N.JeyaseelanvijayjeyaseelanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1 IntroductionPrerana AroraNo ratings yet
- Q3. Micro Insurance Relationship With Life InsuranceDocument19 pagesQ3. Micro Insurance Relationship With Life InsuranceSomnath DashNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument14 pagesMicro Insuranceshalini shaluNo ratings yet
- Mi Final CCDocument52 pagesMi Final CCHomework PingNo ratings yet
- Microfinance CommunityDocument19 pagesMicrofinance CommunityrahulskullNo ratings yet
- A Summer Training Project Report On Tata Aig 2010-11 MuzaffarnagarDocument105 pagesA Summer Training Project Report On Tata Aig 2010-11 Muzaffarnagarghanshyam1988No ratings yet
- Problems of Insurance Company in Bangladesh: Religious SuperstitionDocument6 pagesProblems of Insurance Company in Bangladesh: Religious Superstitionboishakh38512No ratings yet
- Special Report: Micro - InsuranceDocument36 pagesSpecial Report: Micro - InsuranceShasha HarrietNo ratings yet
- Daffodil International University Journal of Business and Economics, Vol. 2Document17 pagesDaffodil International University Journal of Business and Economics, Vol. 2hannan000No ratings yet
- Indian Insurance SectorDocument59 pagesIndian Insurance Sectorsidhu008100% (2)
- Risk Management: How to Use Different Insurance to Your BenefitFrom EverandRisk Management: How to Use Different Insurance to Your BenefitNo ratings yet
- Vanijya SammelanaDocument2 pagesVanijya SammelanaGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- A Report On Consumer Behaviour Towards Colgate Colgate Palmolive (I) LTDDocument22 pagesA Report On Consumer Behaviour Towards Colgate Colgate Palmolive (I) LTDGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- GPM Abstract FiDocument2 pagesGPM Abstract FiGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Summer CaMP Participants Application FormDocument1 pageSummer CaMP Participants Application Formjoshua gaspadoNo ratings yet
- If Installing A New Clutch Go To Step 19. 2. Install The Special Tool in A ViseDocument18 pagesIf Installing A New Clutch Go To Step 19. 2. Install The Special Tool in A Viserolly abantoNo ratings yet
- VISCOpvt Reference Manual Rev CDocument15 pagesVISCOpvt Reference Manual Rev ClgustavolucaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument2 pagesFoundations of EducationJoan BayanganNo ratings yet
- NeoCryl A 1127 - en - 50016095 23666669 23488781Document2 pagesNeoCryl A 1127 - en - 50016095 23666669 23488781Jhonny DávilaNo ratings yet
- Ehs M1 KtuDocument39 pagesEhs M1 KtuMEBIN ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Tax FBTDocument9 pagesTax FBTJames GuiruelaNo ratings yet
- First Article Inspection 001ADocument21 pagesFirst Article Inspection 001AWalt PrystajNo ratings yet
- Co-Parenting After DivorceDocument6 pagesCo-Parenting After DivorceSam Hasler100% (5)
- Approaches of Community DevelopmentDocument26 pagesApproaches of Community DevelopmentWasafAliAzmatNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations 31 PDFDocument5 pagesBalancing Equations 31 PDFIgnacio Jr. PaguyoNo ratings yet
- Failures in FPDDocument15 pagesFailures in FPDAnkita Piplani DuaNo ratings yet
- WSH Guidelines Commercial DivingDocument151 pagesWSH Guidelines Commercial Divingyassentaha20000No ratings yet
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument3 pagesComparatives and SuperlativesJulia TinocoNo ratings yet
- NDT Certi JaydeepDocument5 pagesNDT Certi JaydeepDarshanRavalNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Business Plan RevisedDocument56 pagesGROUP 3 Business Plan RevisedJwhll Mae50% (2)
- ABB Make TTF200 Basic TransmitterDocument10 pagesABB Make TTF200 Basic TransmitterRushil H SevakNo ratings yet
- Nokia Case StudyDocument12 pagesNokia Case Studysatyam basaiyeNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFDocument6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFTanUeiHorngNo ratings yet
- Mast MaterialDocument1 pageMast MaterialShankar SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- The Hindu 22nd DecemberDocument25 pagesThe Hindu 22nd DecemberLikhitha YerraNo ratings yet
- Clean Agent Fire Protection SystemDocument9 pagesClean Agent Fire Protection Systemjkhan_724384No ratings yet
- I Want It AllDocument25 pagesI Want It AllEmanuelle OliveiraNo ratings yet
- A163282 Ais PCDocument3 pagesA163282 Ais PCIZZAD FAIZ BIN HASSANNo ratings yet
- Arthur Leroy Horton v. Joseph R. Blalock, M.D., Supreintendent, Southwestern State Hospital, Marion, Virginia, 282 F.2d 782, 4th Cir. (1960)Document2 pagesArthur Leroy Horton v. Joseph R. Blalock, M.D., Supreintendent, Southwestern State Hospital, Marion, Virginia, 282 F.2d 782, 4th Cir. (1960)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- DS PNSSDocument3 pagesDS PNSSKathryne May JinonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Stability DataDocument21 pagesEvaluation of Stability DataMartin Celestino100% (2)
Micro Insurance
Micro Insurance
Uploaded by
Gundupagi ManjunathOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Micro Insurance
Micro Insurance
Uploaded by
Gundupagi ManjunathCopyright:
Available Formats
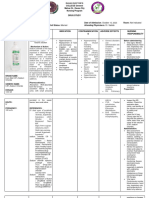
MICRO INSURANCE IS NOW A MACRO BUSINESS Now microinsurance is not a charity moreover it is a macro business for the insurers
and service providers. Now reducing the poverty is not only the social objective of Government. Private sector has taken this as an opportunity as business rather than corporate social responsibility.Insurers now they have to change their mind set in selling a micro insurance product who has never heard of the concept itself. How insurers adjust claims in remote areas and inaccesible parts of the country. When micro insurance is considered as a macro business then how insurers will make money from the micro insurance policy where the isurers are charging very low premium. Insurers now they have taken this as an opportunity to tap the excluded poor people by going back to find the quick, cheap and simple ways to cover for the poor people who have little money. What is microinsurance? Microinsurance defined as protection of low income people against specific perills in exchange for regular premium payments proportionate to the likelihood and cost of the risk involved International Association of Insurance Supervisors Differences between traditional insurance and microinsurance: Traditional Insurance Clients Premium Calculation Microinsurance
- Low risk environment. - High risk exposure. - Established insurance culture. - Weak insurance culture. - Good statistical data. - Pricing based on individual risk - Sold by licensed intermediaries. - Complex policy documentation. - Monthly, quaterly or yearly payments. - Less historical data. - Group pricing, price senstive market and higher premium to cover ratios. - Sold by non traditional intermediaries. - Simple documentation & few exclusions. - Frequent, irregular payments adapted to volatile cash flows of clients. - Often linked with other transactions. - Broad eligibility. - Limited controls. - Risk included in premiums. - Link to other services. - Simple and fast procedures for small sums. - Efficient fraud control.
Distribution Models Policies Premium collection
Risk control
-Limited eligibility. - Significant documentation required. Screenings, such as medical tests, may be required. - Complicated processes. Extensive verification documentation.
Claims handling
It is very difficult to reach the poor people through microinsurance as they don't understand the basic concept of microinsurance. Insurance education is very low among the household heads of the poor. It is very difficult to insurers to market the product to the poor. Poor understand the microinsurance product is like savings and they can get money back if they are not claiming. This is the understanding level of the poor people on the microinsurance product. Insurers now they have to educate and bring awareness among the poor people about the insurance principle, risk management and cost before they rollout the microinsurance products in the market. The definition of microinsurance products according to IRDA is shown in the table below: Type Sum Assured Term (Years) Age (Years) Term Life Endowment Health (Individual) Health (Family) Accident Rider Livestock/Assets Accident(Non-Life) Source: Microsave Sources & References: Lloyd's 360 Risk insight, Insurance in developing countries: Exploring opportunities in microinsurance, Pg. No. 06, Microinsurance Centre, available at www.lloyds.com David M. Dror, Can we assume that people understand insurance principles, Reaching people through Microinsurance: The case of India & Nepal, Pg. No. 50, MMS Bulletin 120, 2011. Premasis Mukherjee, Trends of Microinsurance in India, Microsave India Focus Note 49, August 2010, available at www.microsave.org. 5000 50,000 5,000 30,000 5,000 30,000 10,000 30,000 10,000 50,000 5000 30,000 10,000 30,000 5 to 15 5 to 15 1 to 7 1 to 7 5 to 15 1 1 18 - 60 18 60 Insurers Discretion Insurers Discretion 18 - 60 NA 01/05/70
You might also like
- (Customer) Gauge Panel RebuildDocument9 pages(Customer) Gauge Panel RebuildLidetu DemissieNo ratings yet
- Screening Test - Grade 7Document5 pagesScreening Test - Grade 7Hosain Said Usman Jr.100% (17)
- Problems and Prospects of General Insurance in BangladeshDocument56 pagesProblems and Prospects of General Insurance in BangladeshAmirul Islam75% (4)
- Customer LoyaltyDocument39 pagesCustomer LoyaltyGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- IndiaHikes PDFDocument5 pagesIndiaHikes PDFAAMOD KHARB PGP 2018-20 BatchNo ratings yet
- Micro Insurance HDocument46 pagesMicro Insurance HNirupa KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument17 pagesMicro InsurancerishipathNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii-Theoretical View: Credit Unions MicrofinanceDocument15 pagesChapter Iii-Theoretical View: Credit Unions MicrofinanceMrudula M NairNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument37 pagesMicro InsuranceBhavna Advani100% (2)
- Microinsurance ProjectDocument59 pagesMicroinsurance Projectmayur9664501232No ratings yet
- Insurance Ii Assignment On The Topic "MICROINSURANCE - TRENDS & Strategies"Document7 pagesInsurance Ii Assignment On The Topic "MICROINSURANCE - TRENDS & Strategies"Sumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Kamlesh - Micro InsuranceDocument33 pagesKamlesh - Micro InsuranceKrishna PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Micro Takaful Vs MicroinsuranceDocument5 pagesMicro Takaful Vs MicroinsuranceSiful Islam AnikNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document19 pagesUnit 6ChandrakantBangarNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance - Executive Summary (English)Document4 pagesMicroinsurance - Executive Summary (English)IPS Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- 7 Youseph AsefaDocument15 pages7 Youseph AsefamohamedfisalNo ratings yet
- Micro Insurance ProjectDocument56 pagesMicro Insurance ProjectParag More50% (4)
- Micro Insurance in India: A Powerful Tool To Empower Poor: June 2020Document21 pagesMicro Insurance in India: A Powerful Tool To Empower Poor: June 2020Naina BaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Micro-Insurance Augmenting The Poverty Alleviation Role of Micro-Finance: A Case Study of BangladeshDocument17 pagesContribution of Micro-Insurance Augmenting The Poverty Alleviation Role of Micro-Finance: A Case Study of BangladeshSaif Hasan JyotiNo ratings yet
- Awareness of Micro Insurance Product in Patan District: Mr. Mitul M. Deliya Dr. Karshanbhai N. PatelDocument21 pagesAwareness of Micro Insurance Product in Patan District: Mr. Mitul M. Deliya Dr. Karshanbhai N. PatelAnonymous 6x5cTCmNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To ReferDocument11 pagesMicroinsurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To ReferKush TiwariNo ratings yet
- Dec08 138 Microfinance en FINAL2Document4 pagesDec08 138 Microfinance en FINAL2Hedato M DatuNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils inDocument5 pagesMicroinsurance Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils inSanjay SmartNo ratings yet
- Insurance For Small BusinessesDocument2 pagesInsurance For Small BusinessesTheodorah Gaelle MadzyNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance Term Paper RevisedDocument25 pagesMicroinsurance Term Paper RevisedAnish S.MenonNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument1 pageConclusionAjeet YadavNo ratings yet
- Aka SH Bang ADocument63 pagesAka SH Bang AakashbangaNo ratings yet
- MICRO INSURANCE PttsDocument21 pagesMICRO INSURANCE PttsSushil PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Insurance in BangladeshDocument37 pagesInsurance in BangladeshNahidRahman100% (1)
- ECODEVDocument2 pagesECODEVEena Viamae PinpinNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument56 pagesExecutive Summaryshwetachalke21No ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument4 pagesMicro InsuranceBasil V JamesNo ratings yet
- IIA Word ReportDocument5 pagesIIA Word Reportshiva sambhawiNo ratings yet
- A Microinsurance Compendium - Vol I - Part 3Document190 pagesA Microinsurance Compendium - Vol I - Part 3charlesdaud395No ratings yet
- Notes Irt04205Document24 pagesNotes Irt04205shabanzuhura706No ratings yet
- Advantages of Life InsuranceDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Life Insurancekeyur5689No ratings yet
- Background Bangladesh Is Highly Vulnerable To Tropical Cyclones and Floods1 Due To Its Geographical Location and Very Low Land ElevationDocument4 pagesBackground Bangladesh Is Highly Vulnerable To Tropical Cyclones and Floods1 Due To Its Geographical Location and Very Low Land ElevationSikder Insurance [Gmail.com]No ratings yet
- Community Based Insurance-MicroinsuranceDocument33 pagesCommunity Based Insurance-MicroinsuranceRanjusha AshokNo ratings yet
- File TushaDocument5 pagesFile Tushahiru jariwalaNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Microinsurance: Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils in ExchangeDocument4 pagesDefinitions of Microinsurance: Microinsurance Is The Protection of Low-Income People Against Specific Perils in ExchangeDinesh GodhaniNo ratings yet
- Indian Insurance SectorDocument32 pagesIndian Insurance Sectorbanirumi100% (2)
- Summer Internship Project ON A Study On Consumer Perception About Insurance CompanyDocument13 pagesSummer Internship Project ON A Study On Consumer Perception About Insurance CompanySHARMA TECHNo ratings yet
- Insurance Company AnalysisDocument13 pagesInsurance Company AnalysisAyon ImtiazNo ratings yet
- "Mdicleaim": Mamta Ashok GuptaDocument50 pages"Mdicleaim": Mamta Ashok GuptaKarishma Dharmesh SoohindaNo ratings yet
- Microinsurance in IndiaDocument6 pagesMicroinsurance in IndiaPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument13 pagesMicro Insurancedhiraj1No ratings yet
- Micro Insurance Scenario in India: Group - 5Document21 pagesMicro Insurance Scenario in India: Group - 5Shivank PantNo ratings yet
- Insurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To Refer ToDocument16 pagesInsurance: Microinsurance Is A Term Increasingly Used To Refer ToNupur Gangurde0% (1)
- Article 1Document2 pagesArticle 1lvprasad3125No ratings yet
- Micro Health Insurance - A Way of Ensuring Financial Security To The Poor. By. Dr.N.JeyaseelanDocument12 pagesMicro Health Insurance - A Way of Ensuring Financial Security To The Poor. By. Dr.N.JeyaseelanvijayjeyaseelanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1 IntroductionPrerana AroraNo ratings yet
- Q3. Micro Insurance Relationship With Life InsuranceDocument19 pagesQ3. Micro Insurance Relationship With Life InsuranceSomnath DashNo ratings yet
- Micro InsuranceDocument14 pagesMicro Insuranceshalini shaluNo ratings yet
- Mi Final CCDocument52 pagesMi Final CCHomework PingNo ratings yet
- Microfinance CommunityDocument19 pagesMicrofinance CommunityrahulskullNo ratings yet
- A Summer Training Project Report On Tata Aig 2010-11 MuzaffarnagarDocument105 pagesA Summer Training Project Report On Tata Aig 2010-11 Muzaffarnagarghanshyam1988No ratings yet
- Problems of Insurance Company in Bangladesh: Religious SuperstitionDocument6 pagesProblems of Insurance Company in Bangladesh: Religious Superstitionboishakh38512No ratings yet
- Special Report: Micro - InsuranceDocument36 pagesSpecial Report: Micro - InsuranceShasha HarrietNo ratings yet
- Daffodil International University Journal of Business and Economics, Vol. 2Document17 pagesDaffodil International University Journal of Business and Economics, Vol. 2hannan000No ratings yet
- Indian Insurance SectorDocument59 pagesIndian Insurance Sectorsidhu008100% (2)
- Risk Management: How to Use Different Insurance to Your BenefitFrom EverandRisk Management: How to Use Different Insurance to Your BenefitNo ratings yet
- Vanijya SammelanaDocument2 pagesVanijya SammelanaGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- A Report On Consumer Behaviour Towards Colgate Colgate Palmolive (I) LTDDocument22 pagesA Report On Consumer Behaviour Towards Colgate Colgate Palmolive (I) LTDGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- GPM Abstract FiDocument2 pagesGPM Abstract FiGundupagi ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Summer CaMP Participants Application FormDocument1 pageSummer CaMP Participants Application Formjoshua gaspadoNo ratings yet
- If Installing A New Clutch Go To Step 19. 2. Install The Special Tool in A ViseDocument18 pagesIf Installing A New Clutch Go To Step 19. 2. Install The Special Tool in A Viserolly abantoNo ratings yet
- VISCOpvt Reference Manual Rev CDocument15 pagesVISCOpvt Reference Manual Rev ClgustavolucaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument2 pagesFoundations of EducationJoan BayanganNo ratings yet
- NeoCryl A 1127 - en - 50016095 23666669 23488781Document2 pagesNeoCryl A 1127 - en - 50016095 23666669 23488781Jhonny DávilaNo ratings yet
- Ehs M1 KtuDocument39 pagesEhs M1 KtuMEBIN ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Tax FBTDocument9 pagesTax FBTJames GuiruelaNo ratings yet
- First Article Inspection 001ADocument21 pagesFirst Article Inspection 001AWalt PrystajNo ratings yet
- Co-Parenting After DivorceDocument6 pagesCo-Parenting After DivorceSam Hasler100% (5)
- Approaches of Community DevelopmentDocument26 pagesApproaches of Community DevelopmentWasafAliAzmatNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations 31 PDFDocument5 pagesBalancing Equations 31 PDFIgnacio Jr. PaguyoNo ratings yet
- Failures in FPDDocument15 pagesFailures in FPDAnkita Piplani DuaNo ratings yet
- WSH Guidelines Commercial DivingDocument151 pagesWSH Guidelines Commercial Divingyassentaha20000No ratings yet
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument3 pagesComparatives and SuperlativesJulia TinocoNo ratings yet
- NDT Certi JaydeepDocument5 pagesNDT Certi JaydeepDarshanRavalNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Business Plan RevisedDocument56 pagesGROUP 3 Business Plan RevisedJwhll Mae50% (2)
- ABB Make TTF200 Basic TransmitterDocument10 pagesABB Make TTF200 Basic TransmitterRushil H SevakNo ratings yet
- Nokia Case StudyDocument12 pagesNokia Case Studysatyam basaiyeNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFDocument6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology Chapter 1 4 PDFTanUeiHorngNo ratings yet
- Mast MaterialDocument1 pageMast MaterialShankar SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- The Hindu 22nd DecemberDocument25 pagesThe Hindu 22nd DecemberLikhitha YerraNo ratings yet
- Clean Agent Fire Protection SystemDocument9 pagesClean Agent Fire Protection Systemjkhan_724384No ratings yet
- I Want It AllDocument25 pagesI Want It AllEmanuelle OliveiraNo ratings yet
- A163282 Ais PCDocument3 pagesA163282 Ais PCIZZAD FAIZ BIN HASSANNo ratings yet
- Arthur Leroy Horton v. Joseph R. Blalock, M.D., Supreintendent, Southwestern State Hospital, Marion, Virginia, 282 F.2d 782, 4th Cir. (1960)Document2 pagesArthur Leroy Horton v. Joseph R. Blalock, M.D., Supreintendent, Southwestern State Hospital, Marion, Virginia, 282 F.2d 782, 4th Cir. (1960)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- DS PNSSDocument3 pagesDS PNSSKathryne May JinonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Stability DataDocument21 pagesEvaluation of Stability DataMartin Celestino100% (2)