Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nsejs 2014 SOLUtION
Nsejs 2014 SOLUtION
Uploaded by
Anindita GhoshSatpathiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nsejs 2014 SOLUtION
Nsejs 2014 SOLUtION
Uploaded by
Anindita GhoshSatpathiCopyright:
Available Formats
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
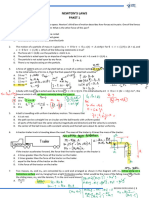
1. Three identical vessels carrying equal amount of water are placed in three lifts. Lift A is
accelerating upwards, lift B is accelerating downwards while lift C is moving up with constant
velocity. The pressure at a depth h from free surface in the three vessels is measured as PA, PB and
PC. Then which of the following is true?
a) PA = PC > PB b) PA > PC > PB c) PA > PC = PB d) PA = PC = PB
Sol. Pressure in a static liquid: P = Po + hg
Pressure in a static liquid for vertically accelerated vessel: P = Po + hgeff
geff = g + a for acceleration vertically up (lift A)
geff = g – a for acceleration vertically down (lift B)
geff = g – 0 = g for uniform velocity up/down (lift C)
2. A particle starting from rest is moving with uniform acceleration in a straight line. The percentage
increase of the displacement of the particle in 9th second compared to that in the immediate
previous second is about
a) 8.3 % b) 13.3 % c) 20.6 % d) 24.5 %
Sol. Displacement of the particle in nth second: sn = u + a (n - 1)
2
1
Displacement of the particle in 8th second: s8 = 0 + a (8 - 2) = 7.5 a
1
Displacement of the particle in 9th second: s9 = 0 + a (9 - ) = 8.5 a
2
Increase in displacement: s = 8.5 a – 7.5 a = a
∆𝑠 𝑎 100
Percentage increase in displacement: 𝑠
x 100 = 7.5𝑎 x 100 = 7.5
= 13.3 %
3. An inflated balloon with a heavy rock tied to it submerges in water. As the balloon sinks deeper
and deeper. The buoyant force acting on it
a) increases b) decreases
c) remains nearly unchanged d) initially increases and then decreases
Sol. Gravitational force: constant in magnitude and direction (downward). F = mg
Buoyancy force : Fb = Vg
(V – volume of liquid displaced, - density of liquid, g – acceleration due to gravity)
As the balloon sinks deeper and deeper, the pressure of the water above it increases (P = hg).
With increase in pressure, the volume of the balloon decreases.
As the volume of the balloon decreases, the buoyancy force acting on it decreases
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 1
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
4. A particle is moving along a straight line. Its velocity – time graph is as shown in figure. Then
match the following.
Physical Quantity Remarks
I. acceleration at 4 second p. positive
II. Velocity at 4 second q. negative
III. Direction of motion at 2 sec. r. zero
a) I is p; II is q; III is r b) I is q; II is r; III is p
c) I is r; II is q; III is p d) I is q; II is p; III is r
Sol. Slope of velocity – time graph gives acceleration. As the slope is negative, acceleration is –ve.
The straight line passes through zero at 4 sec. so the velocity is zero at t = 4 sec
From 0 to 4 sec. the particle has positive velocity, so the direction of motion of the particle is +ve
5. A rectangular parallelepiped with sides a, b and c in the ratio 3 : 2 : 1 is kept on a uniformly rough
horizontal surface as shown in figure. The value of limiting friction is
a) minimum in I b) minimum in II c) minimum in III d) same in all cases
Sol. Limiting friction: the maximum value of static friction.
limiting friction is independent of area of contact.
So, same frictional force acts in all the cases.
6. If two bodies of different masses, initially at rest are acted upon by the same force for the same
time, then both bodies acquire the same
a) velocity b) momentum c) acceleration d) kinetic energy
Sol. Force acting on both masses is same: F1 = F2 / Initially both the bodies are at rest.
Force acts on the bodies for the same time.
𝐹 𝐹 𝐹
Acceleration of the object: a = 𝑚 a1 = 𝑚 and a2 = 𝑚
1 2
Velocity after some time: v = u + at = 0 + at = at
𝑑𝑃
Force acting on a body: F = 𝑑𝑡
𝑑𝑝 = 𝐹 𝑑𝑡
As same force is acting on both the objects for same time, change in momentum is same for both.
As both the objects are initially at rest, they acquire same final momentum
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 2
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
7. It is more difficult to walk on a sandy road than on a concrete road. The most appropriate reason
for this is
a) sand is soft and concrete is hard
b) the friction between sand and feet is less than that between concrete and feet
c) the friction between sand and feet is more than that between concrete and feet
d) the sand is grainy but concrete is solid
Sol. Friction: it is a tangential force that opposes the relative motion of point of contact between two
surfaces.
As we walk, we push the floor backwards. So the frictional force acts in the forward direction thus
helping us to walk.
The frictional force between sand and feet is far less than that between concrete and feet.
So, it is relatively difficult to walk on sandy road than on a concrete road.
8. The magnetic force on a moving charged particle can change the particle’s
a) speed only b) direction only
c) both speed and direction d) neither speed nor direction
Sol. The force acting on a charged particle due to a magnetic field is given by
𝐹̅ = q (𝑣̅ 𝑥 𝐵̅) where q is charge, v is speed and B is magnetic field strength.
The magnitude of force: F = qvB sin [force is perpendicular to plane of v & B]
As the force is always perpendicular to velocity vector, it acts as centripetal force that takes the
particle into circular path. Work done by centripetal force is zero.
So, the force changes only the direction of motion of the particle
9. A ray of light is incident on system of mirrors as shown in the figure. What is the total deflection d
of the ray when it emerges out after two reflections?
a) 2200 b) 1800 c) 1400 d) 1200
Sol.
Angle between the mirrors : 700
So the angle of incidence of the ray at N1 = 200
Angle of incidence (200) = angle of reflection (200)
Angle of incidence of the ray at N2 = 500
Angle of incidence (500) = angle of reflection (500)
From the diagram: sum of the angles in a triangle is 1800.
So, the angle of deviation: d = 1400
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 3
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
10. A light source of diameter 2 cm is placed 20 cm behind a circular opaque disc of diameter 4 cm.
Shadow is formed on a screen at a distance of 80 cm. The ratio of the area of umbra and penumbra
shadow regions is equal to
a) 0.22 b) 0.18 c) 0.58 d) 0.11
Sol.
AA1 is the source (disc of radius 1 m) and BB1 is the opaque disc of radius 2 m.
Umbra is formed between ABC and A1B1C1.
Penumbra is formed between CD and C1D1.
Light rays from the source are extended to meet at point O.
𝑂𝐹 𝐹𝐴 𝑥 1
triangles OFA and OEB (similar triangles): 𝑂𝐸 = 𝐸𝐵 𝑥+20 = 2 x = 20 cm
𝑂𝐹 𝐹𝐴 20 1
Triangles OFA and OHC (similar triangles): 𝑂𝐺 = 𝐻𝐶 120 = 𝑟 r = 6 cm
𝐹𝐺 𝐹𝐴1 𝑦 1 20
Triangles FA1G and GBE (similar triangles): 𝐺𝐸 = 𝐸𝐵
20−𝑦 = 2 y = 3
cm
𝐺𝐸 𝐸𝐵 40/3 2
Triangles GEB and GHD (similar triangles): 𝐺𝐻 = 𝐻𝐷 280/3 = 𝑅 R = 14 cm
Area of umbra region: Au = r2 = 36
Area of penumbra region: Ap = (R2 – r2) = (196 – 36) = 160
𝟑𝟔𝐩
Ratio of area of umbra and penumbra: 𝟏𝟔𝟎𝐩 = 0.22
11. Consider the following two statements:
statement 1: when red light travels from air to water, for observer in water it appears to be still red
statement 2: color of light is associated with frequency and frequency does not change when it
travels in different media
choose the correct option
a) statement 1 is correct while statement 2 is wrong b) statement 1 and 2 are correct
c) statement 1 is wrong while statement 2 is correct d) statement 1 and 2 are wrong
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 4
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
Sol. Statement 1: color of light does not change as it travels from one medium to another.
Statement 2: as light travels from one medium to another, its frequency remains constant.
(color depends on frequency)
12. A spring of force constant 7600 N/m is attached to a block of mass 0.25 kg as shown in figure.
Frequency of oscillation on frictionless surface is
a) 27.76 Hz b) 39.26 Hz c) 9681.5 Hz d) 98.39 Hz
Sol. 1 𝑘
frequency of oscillation of a spring block system: f = 2𝜋 √𝑚
Where k is spring (force) constant and m is mass of the block
1 𝑘 1 7600 1 174.36
f= √ = √ = √30400 = = 27.76 Hz
2𝜋 𝑚 2𝜋 0.25 2𝜋 2𝜋
13. A wave is sent along a string by oscillating at one end. If the tension in the string is increased then
speed of the wave and wavelength of the wave
a) both increase b) speed increases, wavelength decreases
c) both decrease d) wavelength increases, speed decreases
Sol. Transverse waves travel along string. The speed of the wave is given by
𝑇
v = √ where T is tension in the string and is linear density. (v ∝ √𝑇)
𝜇
As the tension in the string is increased, the speed of the wave also increases.
Speed of a wave in any medium (in terms of wave parameters) is given by
v = f where f is frequency and is wavelength. Frequency of the wave depends on the source.
So, it remains constant as long as the source does not change. (v ∝ )
So, the wavelength of the wave increases with increase in speed.
14. Clock A based on oscillations of spring and clock B is based on pendulum motion. Both the clocks
keep the same time on earth. If they are taken to a planet having half the density of earth and twice
the radius
a) then A runs faster than B b) B runs faster than A
c) both will run at same rate as earth d) both will run at equal faster rate than earth
Sol. 𝑚
Time period of spring – block system: T = 2 √ 𝑘 (independent of g)
𝑙
Time period of simple pendulum: T = 2 √𝑔
𝐺𝑀 4
Acceleration due to gravity: g = = GR g ∝ R
𝑅2 3
𝑔𝑝 𝑅𝑝 𝜌𝑝 2𝑅 𝜌
= = = 1 𝑔𝑝 = 𝑔𝑒
𝑔𝑒 𝑅𝑒 𝜌𝑒 𝑅 2𝜌
So, the time period of simple pendulum is same on planet and earth.
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 5
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
15. In the circuit B1, B2 and B3 represent identical bulbs. Consider the case
i. with resistance R4
ii. Without resistance R4 (R4 comparable to resistance of bulb)
a) B1, B2 and B3 glow with equal brightness in both cases
b) B1 is the brightest in i and in ii, B2 and B3 becomes brighter and B1
dimmer compared to case I
c) B2, B3 brightest in case i and B1 becomes brighter in ii
d) B1 is brightest in i and B2 becomes brighter in comparison to B3 in ii
Sol. Consider the circuit without R4. It can be Consider the circuit with R4. It can be
represented as follows. represented as follows.
3𝑅 4𝑅
Effective resistance of the circuit: Effective resistance of the circuit:
2 3
𝑉 2𝑉 𝑉 3𝑉
Current in the circuit: I = = Current in the circuit: I = 𝑅 = 4𝑅
𝑅 3𝑅
2 4𝑉 2 4𝑉 2 9𝑉 2 9𝑉 2
Power consumed by B1: I R = 9𝑅2 R = 9𝑅 Power consumed by B1 = I2R = 16𝑅2 R = 16𝑅
𝐼 2 𝑽𝟐 𝐼 2 𝑽𝟐
Power consumed by B2 / B3 = (2) 𝑅 = 𝟗𝑹 Power consumed by B2 / B3 / R4 = (3) 𝑅 = 𝟏𝟔𝑹
16. Three identical resistors each of resistance R are connected in the following four configurations.
Rank the arrangement in the order of their equivalent resistors from highest to lowest.
a) I, II, III & IV b) IV, III, II & I c) I, III, IV & II d) II, IV, III & I
Sol. I : series combination : Rs = R + R + R = 3R
1 1 1 1 3 𝑅
II : parallel combination : = + + = Rp =
𝑅𝑝 𝑅 𝑅 𝑅 𝑅 3
𝑅 3
III : first one in series with parallel combination of last two : R = R + 2 = 2 R
2𝑅 𝑥 𝑅 2
IV : first two in series connected in parallel to third : R = 2𝑅+𝑅
=3R
17. A positively charged insulator is brought in contact with an uncharged conductor, then
a) conductor acquires +ve charge due to conduction
b) conductor acquires –ve charge due to induction
c) conductor acquires +ve charge due to induction
d) conductor cannot acquire any charge
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 6
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
Sol. As the charged object is placed in contact with the uncharged object, conduction of charge takes
place. Charge flow takes place from a body at high potential (charged object) to a body at low
potential (uncharged conductor).
So, some positive charge flows from charged insulator to uncharged conductor due to conduction
18. Two infinite wires carrying identical currents are placed at position A and C, normal to plane of the
paper as shown in figure. The resultant magnetic field at a point P on the perpendicular bisector is
a) along perpendicular bisector pointing towards line AC
b) along line joining PC and pointing towards C
c) along line joining PA and pointing towards A
d) along line parallel to AC and pointing towards right.
Sol. Magnetic field lines around a current carrying conductor are in the form
of concentric circles.
Tangent to this circle gives the magnetic field direction at that point.
So, fields due to wire A and B are equal in magnitude and Perpendicular
to each other at the point P.
The resultant is angular bisector. So, the resultant field is horizontal
(parallel to the line AC and towards right)
19. When an incandescent bulb is switched on and the outer glass bulb also gets heated up. This is due
to
a) conduction and convection of heat from filament to the bulb by the medium inside the bulb
at lower temperatures and by radiation of heat at higher temperature
b) convection of heat from filament to the bulb by the medium inside the bulb at all temperatures
c) radiation of heat from filament to the bulb at all temperatures
d) conduction of heat from filament to the bulb by the medium inside the bulb at higher
temperatures and by radiation of heat at lower temperature
Sol. Conduction: requires a material medium (solids). Heat is transferred through the connectors to the
glass bulb.
Convection: requires a material medium (fluids). Heat is transferred through the inert gas
(generally argon) filled in the bulb.
Radiation: does not require a material medium. Heat is transferred at high temperature according to
the Stefan – Boltzmann's law (P = AT4 where is Stefan – Boltzmann's constant)
P is rate of heat transfer, A is surface area of filament, T is absolute temperature)
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 7
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
20. We all know the sky appears to touch the ground at a distance. The distance at which we
perceive the sky to touch the ground is called horizon. The reason for the perception is due to
the fact that the earth is a sphere (almost) and not a flat surface. Which of these pictures
below accurately depict the horizon for a person standing on a high rise building like Burj
Khalifa in Dubai?
(here h represents the height of the building while line H represents horizon)
Sol. The distance at which we perceive the sky to touch the ground is called horizon.
As the person stands on a building of height h, he will be able to see a maximum distance H which
is shown by first diagram.
NSEJS – 2014 [PHYSICS] Page 8
You might also like
- NYA Review Package W24Document14 pagesNYA Review Package W24s0ph13.sushiNo ratings yet
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Document311 pagesUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- HW Chapter 7Document24 pagesHW Chapter 7maan1988No ratings yet
- Mastering Physics Chapter 13 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMastering Physics Chapter 13 Solutionsrmachado70% (1)
- Nsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFDocument7 pagesNsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2017 SOLUtIONDocument8 pagesNsejs 2017 SOLUtIONAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2016 SOLUtIONDocument7 pagesNsejs 2016 SOLUtIONAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Some Sample Conceptual Questions For Midterm OneDocument7 pagesSome Sample Conceptual Questions For Midterm Onenovegih985No ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Magnetic Field FULL 2Document27 pagesChapter 20 Magnetic Field FULL 2froyo1119No ratings yet
- Nsejs 2013 SOLUtIONDocument7 pagesNsejs 2013 SOLUtIONAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Physics 8thstd Test2 3march2024Document3 pagesPhysics 8thstd Test2 3march2024ssbhattoraNo ratings yet
- Phy 01Document212 pagesPhy 01Varsha Dange100% (1)
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Quiz I 2019 SolDocument4 pagesMechanics Quiz I 2019 SolSanskar JainNo ratings yet
- NMAT 17 Crash Course Review - PhysicsDocument64 pagesNMAT 17 Crash Course Review - PhysicsMikaela Rome BigayNo ratings yet
- DPP RotationDocument4 pagesDPP RotationVibhas SharmaNo ratings yet
- NSEP 2018 SolutionDocument23 pagesNSEP 2018 SolutionVedant TodiNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQDocument13 pagesPhysics MCQharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Physics Xi Simple Harmonic Motion Name: - : To Make The Frequency Double of An Oscillator, We Have ToDocument1 pagePhysics Xi Simple Harmonic Motion Name: - : To Make The Frequency Double of An Oscillator, We Have TolohanopiryaNo ratings yet
- 2023 SJI Y3OP EOY P1 AnsDocument19 pages2023 SJI Y3OP EOY P1 Anscharansaip13No ratings yet
- ch10 PDFDocument18 pagesch10 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- XI Ch-6 Work Energy and Power 0Document37 pagesXI Ch-6 Work Energy and Power 0debabrata09No ratings yet
- C3 Physics W.P.E Concept I To 4Document29 pagesC3 Physics W.P.E Concept I To 4suryanarayana raju kalidindi100% (1)
- 2223 Level L T3 Physics Final Revision Sheet - AKDocument26 pages2223 Level L T3 Physics Final Revision Sheet - AKfarhadkazim2008No ratings yet
- ForcesDocument17 pagesForcesMalik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Physics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 10 May 2010 (Morning) 45 MinutesDocument119 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 10 May 2010 (Morning) 45 MinutesNipun RustagiNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed HandoutDocument30 pagesProf Ed HandoutKhristine Khate Odiaman MendezNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-24-13th Paper-2 TEST-3Document5 pagesPHYSICS-24-13th Paper-2 TEST-3Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- NCERT 15may Chapter 14 OscillationsDocument26 pagesNCERT 15may Chapter 14 OscillationshaikukkkNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physics Class XiDocument6 pagesSample Paper Physics Class XiBhaskar JhaNo ratings yet
- Measurement 8Document18 pagesMeasurement 8Gaurav ShekharNo ratings yet
- 2009 (DUHS-JSMU) Question Keys ResearchDocument5 pages2009 (DUHS-JSMU) Question Keys ResearchFaiza KhurramNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyDocument24 pagesWork, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyChirag SinghNo ratings yet
- Motion in Plane AssignmentDocument3 pagesMotion in Plane Assignmentdishugirdhar08No ratings yet
- Paper V: M MG FDocument4 pagesPaper V: M MG FAka AkaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Science)Document13 pagesReviewer (Science)JonasDepaynosNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 2000Document49 pagesAipmt 2000pravinkhartadNo ratings yet
- Top 30 QuestionsDocument120 pagesTop 30 Questionssohammodi9030No ratings yet
- Matter and Interaction Chapter 05 SolutionsDocument33 pagesMatter and Interaction Chapter 05 SolutionslangemarNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2010 SolutionDocument7 pagesNsejs 2010 SolutionAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Iit PaceDocument19 pagesIit PaceabhishekjanjalkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Short Answer PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Short Answer PDFAmar SinghNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Document7 pagesSample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Sukhwinder KumarNo ratings yet
- Samplepape03022024112234 0Document7 pagesSamplepape03022024112234 0bladex605No ratings yet
- Ws 2Document49 pagesWs 2maahiNo ratings yet
- CH 05 Laws of MotionDocument38 pagesCH 05 Laws of Motionmystic.mortal.222No ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersDocument17 pagesUniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersLawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSDocument14 pages11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSharshitsharmasportsNo ratings yet
- 1979 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1. (A)Document4 pages1979 Applied Maths Higher Level Questions 1. (A)dawnNo ratings yet
- Question and Answers OscillationDocument22 pagesQuestion and Answers OscillationVishal BhanawatNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Sat - : Multiple Correct 1Document6 pagesCumulative Sat - : Multiple Correct 1ullasagwNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 OscillationsDocument24 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 Oscillationsaniruddha deshpandeNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Homework SolutionsDocument67 pagesCh06 Homework SolutionsAlex ZhangNo ratings yet
- Compre 2Document3 pagesCompre 2nknknNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: KinematicsDocument38 pagesMultiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: Kinematics张书No ratings yet
- Gravitation CircleDocument38 pagesGravitation CircleSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- Rotat PDFDocument54 pagesRotat PDFSai PragathiNo ratings yet
- Explain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorFrom EverandExplain Quantum Physics With a Single-Particle in Motion: Anharmonic OscillatorNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Ronald GarzonDocument23 pagesTask 3 Ronald GarzonRonal Enrique Garzon SanchezNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.2 - Traveling WavesDocument48 pagesTopic 4.2 - Traveling Wavesusha pittyNo ratings yet
- AcceleratorDocument27 pagesAcceleratorM Agung FatahillahNo ratings yet
- Race 1 1686742220Document3 pagesRace 1 1686742220xenonverd321No ratings yet
- IE4155 Course OverviewDocument6 pagesIE4155 Course OverviewEthan ChiaNo ratings yet
- S10Fe-Iia-B-47: The Learners Shall Be Able ToDocument8 pagesS10Fe-Iia-B-47: The Learners Shall Be Able Toxoxkakidoxox100% (4)
- Nomograph Rev.13191Document2 pagesNomograph Rev.13191Misbah NiamatNo ratings yet
- Topic 1b - Free VibrationDocument31 pagesTopic 1b - Free Vibrationnurul adilahNo ratings yet
- Lab - Manual - (Flow and Energy Loss)Document17 pagesLab - Manual - (Flow and Energy Loss)Cl SkyeNo ratings yet
- Uv SpecDocument99 pagesUv SpecAmanuel TamiruNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Exam in Science 8 2022 2023Document3 pages2nd Grading Exam in Science 8 2022 2023GRACE LABATANo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test - For ReDocument3 pagesThird Periodical Test - For ReJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1 PDFDocument1 pageTutorial Sheet 1 PDFAmish Kartik100% (1)
- Chapter 21 Nuclear Physics Exercise Short QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 21 Nuclear Physics Exercise Short Questionsmursaleen100% (2)
- Observer's Frame Is ImportantDocument17 pagesObserver's Frame Is ImportantMASUD RAIHANNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument23 pagesLectureabasNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics LectureDocument18 pagesMedical Physics LectureBahadur AliNo ratings yet
- Sci4 Q3 Module3 1Document15 pagesSci4 Q3 Module3 1Aechelle CatenzaNo ratings yet
- Mid-Sem 2020 QuestionsDocument2 pagesMid-Sem 2020 QuestionsTejaswi VykuntamNo ratings yet
- QM Unit IiDocument64 pagesQM Unit IiDHRUV RAINo ratings yet
- 9 Class Guess Paper-2022 Physics.: Unit No. 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement. Short QuestionsDocument3 pages9 Class Guess Paper-2022 Physics.: Unit No. 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement. Short QuestionsAtiq KhanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsAlzon Joseph SamboNo ratings yet
- Direct Noise Computation With A Lattice-Boltzmann Method PDFDocument49 pagesDirect Noise Computation With A Lattice-Boltzmann Method PDFMiliani AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Magnetooptic Effects MARVIS J. FREISER 1968Document10 pagesA Survey of Magnetooptic Effects MARVIS J. FREISER 1968Jose MatutesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Loads and Boundary ConditionsDocument18 pagesThermal Loads and Boundary ConditionsIslem MESSAOUDINo ratings yet
- Performance of A Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger Experiment: Group 7Document10 pagesPerformance of A Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger Experiment: Group 7RonaldNo ratings yet
- Double-Slit TeacherDocument8 pagesDouble-Slit TeacherEden MasseyNo ratings yet
- Anachem Lecture (Spectro) - FinalsDocument35 pagesAnachem Lecture (Spectro) - FinalsAldrin Patrick Galvez EstocapioNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and It: External FlowDocument23 pagesFaculty of Engineering and It: External Flowbooklover1950No ratings yet