Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nsejs 2016 SOLUtION
Nsejs 2016 SOLUtION
Uploaded by
Anindita GhoshSatpathiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nsejs 2016 SOLUtION
Nsejs 2016 SOLUtION
Uploaded by
Anindita GhoshSatpathiCopyright:
Available Formats
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
1. Two bodies A and B are charged with equal magnitude of charge but A with positive charge and B
with negative. If MA and MB are masses before charging and MA1 and MB1 are the masses after
charging, then (mo is some constant mass)
a) MA1 = MA + mo and MB1 = MB – mo b) MA1 = MA - mo and MB1 = MB + mo
c) MA1 = MB1 d) MA1 = MA – mo /2 and MB1 = MB + mo
Sol. A body attains positive charge by losing electrons
A body attains negative charge by gaining electrons
Mass of electron (9.11 x 10-31 kg) is negligibly small.
Object A is positively charged, so its mass decreases. (MA1 = MA - mo)
Object B is negatively charged, so its mass increases. (MB1 = MB + mo)
2. A conductor of length L has a varying cross section with area 2A at P
and A at Q as shown in figure. If it carries a steady current I, then
a) net charge per unit volume near P is more than net charge per unit volume near Q
b) net charge per unit volume near Q is less than net charge per unit volume
c) current per unit area near P is more than current per unit area near Q
d) current per unit area P is less than current per unit area near Q
Sol. The current flowing through a conductor : I = n a e vd (I/a = nevd) where
n no. of charge carriers per unit volume / a area of cross section of the conductor
e charge on the electron / vd drift velocity of the electrons
Drift velocity is inversely proportional to area of cross section.
So, current per unit area P is less than current per unit area near Q
3. Vessels A and B are made of conducting material. Both contain water. Vessel A floats in B. Vessel
B is now heated at a uniform rate, then
a) water in A boils first
b) water in A boils sometime after water in B starts boiling
c) water in both A and B start boiling simultaneously
d) water in A does not boil
Sol. As heat is supplied to vessel B, the water present in B takes the heat from which it is transferred to
water in vessel A.
The boiling point of water is 100 0C after which its temperature remains constant.
As the water in vessel in B starts boiling, it stops transferring heat to water in vessel A.
So, water in vessel A reaches 100 0C temperature, but doesn’t boil.
NSEJS – 2016 [PHYSICS] Page 1
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
4. A body thrown vertically up reaches maximum height and returns. Its acceleration is
a) downward during both ascent and descent
b) downward at all positions except at the highest point, where it is zero
c) upward during both ascent and descent
d) downward during ascent and upward during descent
Sol. Acceleration due to gravity acts always towards the centre of the earth.
For smaller heights (h<<R – radius of the earth), it can be taken to be vertically down.
It does not depend on the direction of motion of the body. Whether the body is moving vertically
down or up, acceleration due to gravity always acts downwards
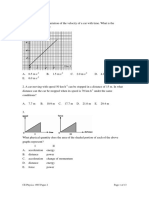
5. Velocity of a particle moving along a straight line varies with time as shown in figure. Net forces
acting on the particle are F1, F2, F3, F4 and F5 in the intervals OA, AB, BC, CD and DE
respectively. Identify the correct statement.
a) F1 increases with time b) F5 is initially positive and then becomes negative
c) F1 and F2 are in opposite directions d) F3 is negative
Sol. OA – F1 (+ve and constant) / AB – F2 (- ve and constant)
BC – F3 ( zero )
CD – F4 (+ve and constant)
DE – F5 (- ve and constant)
Slope of velocity – time graph : acceleration
Force = mass x acceleration
F1 and F2 are in opposite directions
6. A wooden block (W) is suspended by a cord from a heavy steel ball (B). The entire system is
dropped from certain height. Neglecting air resistance, the tension in the cord
a) zero b) the difference in mass of B and W
c) the difference in weight of B and W d) the weight of B
Sol. Acceleration due to gravity is same for every freely falling body
The wooden block and the steel ball are falling under gravity with same acceleration (g).
So the tension in the cord connecting them is zero.
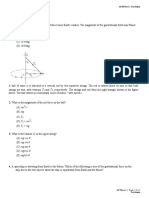
7. A circus performer of weight W is standing on a wire as shown in figure. The tension in the wire is
a) approximately w/4 b) approximately w/2
c) much more than w/2 d) much less than w/2
Sol. As seen in the diagram, tension in the string can be resolved into two rectangular components.
T cos components on either side cancel each other.
NSEJS – 2016 [PHYSICS] Page 2
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
T sin components on either side act in upward direction to support the weight (W) of the person.
𝑊 𝑊/2
2T sin = W T = 2 sin 𝜃 = sin 𝜃
As is small, sin is very small, the tension in the wire is much greater than W/2.
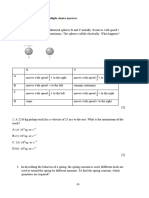
8. In the following diagram, O is a point object and I is the image formed by a concave mirror.
Identify the diagram in which, position of image I is nearly correct.
a) b)
c) d)
Sol. In the options, the object is represented with black dot and the image with circle
The object is placed between focal point (F) and pole of the mirror.
So, it’s image should be formed behind the mirror and it should be magnified.
9. Following diagram shows refraction of parallel beam of light through a spherical surface. Identify
the correct ray diagram.
a) b)
c) d)
NSEJS – 2016 [PHYSICS] Page 3
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
Sol. As light travels from denser medium to rarer medium, it bends away from normal
As light travels from rarer medium to denser medium, it bends towards normal
In the second diagram, as the light rays are entering the denser medium, they are bending away
from normal. So, second one is the correct diagram.
10. In the diagram, M1 and M2 are two plane mirrors at right angles to each other. O is a luminous point
object. Consider two images formed due to first reflection at M1 and M2. The area of the triangle
formed by the object and two images is
a) 4 cm2 b) 2 cm2 c) 8 cm2 d) 16 cm2
Sol. Image distance = object distance for plane mirror
The object and the two images formed by both mirrors M1 and M2 form isosceles triangle.
1
Area of the triangle : 2 x base x height
1
Area = 2 x 4 x 4 = 8 cm2
11. A fisherman of height h is standing on the bank of a lake. A fish in the water perceives his height as
h1 , then
a) h1 > h b) h1 < h c) h1 = h d) a or b depending on position of fist
Sol. A fisher man of height h is standing in rarer medium (air).
The fish is looking at him from denser medium (water).
As the light ray travels from rarer medium to denser medium, it
bends towards the normal as shown in figure.
So, the height of the fisher man as perceived by the fish h1 is
greater than h.
12. Object A is completely immersed in water. True weight of object A is WA. Weight of water with
beaker is WB. Let B be the buoyant force. W1 and W2 are scale readings of spring balance and
weighing scale respectively
a) W1 = W A b) W1 = WA + B c) W2 = W B d) W2 = WB + B
NSEJS – 2016 [PHYSICS] Page 4
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
Sol. True weight of object A = weight in air : WA
Weight of water with beaker : WB
Reading of the spring balance :
W1 = apparent weight = true weight – buoyancy = WA – B
Reading of the weighing scale :
W2 = weight of water with beaker + buoyancy = WB + B
13. A point object O is kept at origin. When a concave mirror M1 is placed at x = 6 cm, image is
formed at infinity. When M1 is replaced by another concave mirror M2 at same position, image is
formed at x = 30 cm, then ratio of the focal length of M1 to that of M2 is
a) 3/4 b) 4/3 c) 5 d) 1/5
Sol. Image is formed at infinity for the first mirror : so focal length f1 = 6 cm
Image distance for second mirror : v = 24 cm (behind the mirror : virtual image)
Object distance for the second mirror : u = 6 cm
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Mirror formula : 𝑣 + 𝑢 = 𝑓 24 - 6 = − 𝑓 𝑓 = − 24 + 6 = 8 𝑓 = 8 𝑐𝑚
𝟑
Ratio of focal lengths: f1 / f = 6/8 =
𝟒
14. Melting point of a substance is 100 C. when does this mean?
a) the substance is a liquid at 100 C
b) the substance is a solid at 100 C
c) there is an equilibrium between solid and liquid phase at 100 C
d) the substance is 50 % solid and 50 % liquid at 100 C
Sol. Melting point is defined as the constant temperature at which the solid phase of a substance gets
converted into liquid phase.
During melting, the solid and liquid phases remain in equilibrium till the complete solid turns into
liquid.
The heat energy supplied to the substance during melting is converted into increased potential
energy of the molecules of the substance known as latent heat.
15. U tube contains some amount of mercury. Immiscible liquid X is poured in left arm and immiscible
liquid Y is poured in the right arm. Length of liquid X is 8 cm; length of liquid Y is 10 cm and
upper levels of X and Y are equal. If density of Y is 3.36 g/cc and density of mercury is13.6 g/cc,
then the density of X is
a) 0.8 g/cc b) 1.2 g/cc c) 1.4 g/cc d) 1.6 g/cc
NSEJS – 2016 [PHYSICS] Page 5
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
Sol. Length of liquid column x : 8 cm
Length of liquid column y : 10 cm
Since the upper levels of x and y are same, length of mercury
column at the common horizontal level : 2 cm
Pressure at same horizontal level is same : PA = PB
x g hx + m g hm = y g hy x hx + m hm = y hy
8 x + 13.6 x 2 = 3.36 x 10
x = (33.6 – 27.2) / 8 = 6.4 / 8 = 0.8 g/cc
16. The effective resistance between A and D in the circuit shown in the adjacent figure is
a) 5 b) 10 c) 15 d) 20
Sol. Imagine a battery connected between A and D
The current entering A divides at A1.
One part takes the path A1B1D1D. So, the resistor in this path (10 , 10 ) are in series.
Another part takes the path A1C1D1D. So the resistors in this path (10 , 10 ) are in series
Effective circuit is shown in figure.
20𝑥20
So RAD = 5 + 20+20 + 5 = 5 + 10 + 5 = 20
17. Three bulbs B1, B2 and B3 having rated powers 100 W, 60 W and 60 W at 250 V are connected in a
circuit as shown in figure. If W1, W2 and W3 are the output powers of the bulbs B1, B2 and B3
respectively, then
a) W1 > W 2 = W3 b) W1 > W2 > W3 c) W1 < W 2 = W3 d) W1 < W2 < W3
Sol. Output power of the bulb = power consumed
𝑣 2
Consumed power = ( 𝑠 ) rated power
𝑣𝑟
250 2
Output power of B3 = W3 = ( ) 60 = 60 W
250
𝑣2 250 𝑥 250
Resistance of B1 = 𝑃
= 100
= 625
𝑣2 250 𝑥 250 6250
Resistance of B2 = = 𝑃 60
= 6
As same I flows through B1 and B2 the power consumed by B2 is more
NSEJS – 2016 [PHYSICS] Page 6
Kalyan’s Physics Challenge
18. Rod AB of radius 2r is joined with rod BC of radius r. They are of same material and are of same
length. The combination carries a current I. choose the correct statement.
a) VAB = 4 VBC
b) current per unit area in AB and BC is equal
c) RAB is greater than RBC
d) VBC = 4 VAB
Sol. Both the rods are same material and same length. The rods are connected in series
(same current flows)
𝜌𝑙 𝜌𝑙 1 𝜌𝑙
Resistance of AB : RAB = = =
𝐴 𝜋 4𝑟 2 4 𝜋 𝑟2
𝜌𝑙 𝜌𝑙 𝜌𝑙
Resistance of BC : RBC = 𝐴
= 𝜋 𝑟2 = 𝜋 𝑟2 = 4 RAB
As same current is flowing through both the rods, V = I R : VAB = I RAB / VBC = I RBC
𝑉𝐴𝐵 1
𝑉𝐵𝐶
= 4 VBC = 4 VAB
19. In the figure shown, the current carrying loop is fixed whereas current carrying straight conductor
is free to move. Then straight wire will (ignore gravity)
a) remain stationary b) move towards the loop
c) move away from the loop d) rotate about the axis perpendicular to plane of paper
Sol. The magnetic field created by the loop is as shown.
x represents magnetic field into the plane of paper
. represents magnetic field out of the plane of the paper
Apply Fleming’s Left Hand rule for the straight current carrying conductor
placed in magnetic field.
The force is acting on the straight conductor towards right (towards the loop)
20. A convex mirror of focal length f produces an image of size equal to 1/n times the size of the
object. Then the object distance is
a) nf b) f/n c) (n+1) f d) (n – 1) f
Sol. Focal length of the convex mirror : f
1 𝑢
Size of the image = 1/n times the size of the object ( hi = 𝑛 ho v = 𝑛 )
1 1 1
Mirror formula : 𝑣 + 𝑢 = 𝑓 (sign convention : u – ve, v +ve and f +ve)
1 1 1 𝑛 1 1 𝑛−1 1
𝑣
-𝑢=𝑓𝑢-𝑢=𝑓 𝑢
= 𝑓 u = (n – 1) f
NSEJS – 2016 [PHYSICS] Page 7
You might also like
- Stainless Steel Handrail Structural CalculationDocument31 pagesStainless Steel Handrail Structural CalculationZaido Al Halabi100% (4)
- 1.each of The Solids Shown in The Diagram Has The Same MassDocument12 pages1.each of The Solids Shown in The Diagram Has The Same MassrehanNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFDocument7 pagesNsejs 2015 SOLUtION PDFamit kumarNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2014 SOLUtIONDocument8 pagesNsejs 2014 SOLUtIONAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2017 SOLUtIONDocument8 pagesNsejs 2017 SOLUtIONAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Physics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 10 May 2010 (Morning) 45 MinutesDocument119 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 10 May 2010 (Morning) 45 MinutesNipun RustagiNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument14 pagesSolutionsSRIJANo ratings yet
- Utkarsh Test-7.11.2022 (G-1) - PaperDocument11 pagesUtkarsh Test-7.11.2022 (G-1) - PaperDivyeh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2010 SolutionDocument7 pagesNsejs 2010 SolutionAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- G11 Rev Sheet Mar 23Document31 pagesG11 Rev Sheet Mar 23dfrydmanNo ratings yet
- Physics 8thstd Test2 3march2024Document3 pagesPhysics 8thstd Test2 3march2024ssbhattoraNo ratings yet
- Physics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 6 May 2013 (Morning) 45 MinutesDocument100 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 1 Monday 6 May 2013 (Morning) 45 MinutesTej BainsNo ratings yet
- SJPO 2015 General Round - QuestionDocument23 pagesSJPO 2015 General Round - QuestionZleepNo ratings yet
- DPP NLM 1Document3 pagesDPP NLM 1hrushikeshstudyNo ratings yet
- 2020 UEC Physics Trial Paper 1Document5 pages2020 UEC Physics Trial Paper 1Benson TanNo ratings yet
- Reshuffl Test 1Document12 pagesReshuffl Test 1PiyushNo ratings yet
- 2023 SJI Y3OP EOY P1 AnsDocument19 pages2023 SJI Y3OP EOY P1 Anscharansaip13No ratings yet
- Pan Pearl Physics Olympiad 2005Document5 pagesPan Pearl Physics Olympiad 2005Shivam100% (1)
- JEE Main, Feb - March - July, Physics, PYQ MarathonDocument320 pagesJEE Main, Feb - March - July, Physics, PYQ MarathonAneena ThasneemNo ratings yet
- Two Yr CRP 224 - B-Lot - Ph-I - Paper-1 - PhysicsDocument5 pagesTwo Yr CRP 224 - B-Lot - Ph-I - Paper-1 - Physicsjdhmyj2zchNo ratings yet
- 1.WTA 14 08-08-16 RotationDocument5 pages1.WTA 14 08-08-16 RotationRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ws 2Document49 pagesWs 2maahiNo ratings yet
- PHY (SET A) - XI 3rdTERM 80Document8 pagesPHY (SET A) - XI 3rdTERM 80fghughjjguhvjiNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 1Document10 pagesMock Test 1dawiji2491No ratings yet
- PHP NCR Z7 IDocument14 pagesPHP NCR Z7 INo SubscribesNo ratings yet
- Physics Enrich Test STPM Sem 1Document17 pagesPhysics Enrich Test STPM Sem 1雷顺开No ratings yet
- Физика 11- 2021-2022Document14 pagesФизика 11- 2021-2022Nameless RFGNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power QuestionsDocument44 pagesWork Energy Power Questionsmynameis 1609No ratings yet
- 1628687722Kiran-Written-SAT Physics Practice Test 24Document7 pages1628687722Kiran-Written-SAT Physics Practice Test 24Manish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Com and CollisionsDocument6 pagesCom and Collisionsarun2006No ratings yet
- 11 GravitationDocument24 pages11 GravitationSamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Physics 4 UpdtdDocument9 pagesMathematical Physics 4 UpdtdbiriginpeterNo ratings yet
- 03 Circular WPE QuestionsDocument7 pages03 Circular WPE Questions17swabhiNo ratings yet
- Nsejs 2013 SOLUtIONDocument7 pagesNsejs 2013 SOLUtIONAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Sat - : Multiple Correct 1Document6 pagesCumulative Sat - : Multiple Correct 1ullasagwNo ratings yet
- 2009 (DUHS-JSMU) Question Keys ResearchDocument5 pages2009 (DUHS-JSMU) Question Keys ResearchFaiza KhurramNo ratings yet
- Details: All Questions Are Compulsory. There Are 33 Questions in AllDocument6 pagesDetails: All Questions Are Compulsory. There Are 33 Questions in AllPriyanshu GehlotNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 8 April - Evening Shift MathongoDocument41 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 8 April - Evening Shift MathongoAparaNo ratings yet
- Phy XI Term 1 Set B 080Document5 pagesPhy XI Term 1 Set B 080aayankc9841No ratings yet
- Physics Class 11Document8 pagesPhysics Class 11sindhu1975nairNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type)Document6 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Iit PaceDocument19 pagesIit PaceabhishekjanjalkarNo ratings yet
- CE Physics 1985 Paper 2 Page 1 of 13Document13 pagesCE Physics 1985 Paper 2 Page 1 of 13jshfjksNo ratings yet
- PCM - (13th) Paper-1 Code-ADocument23 pagesPCM - (13th) Paper-1 Code-ARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Mechanics 1 SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 - Mechanics 1 SolutionJosé Maurício FreireNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyDocument24 pagesWork, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyChirag SinghNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument28 pagesSolutionasrikdatta12No ratings yet
- QP 1098Document10 pagesQP 1098Anshul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Rotat PDFDocument54 pagesRotat PDFSai PragathiNo ratings yet
- Q5Document14 pagesQ5Saad MohsinNo ratings yet
- End of Year Exam HL Paper 1Document22 pagesEnd of Year Exam HL Paper 1rajashreebasuNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Electrostatics (Exercise) (81-118)Document38 pages1.2 Electrostatics (Exercise) (81-118)Rohan GubbaNo ratings yet
- Yr.12 Physics Pre-Mock MCQDocument12 pagesYr.12 Physics Pre-Mock MCQ-IIIXIII- -Identity-No ratings yet
- AP Physics Unit TestDocument11 pagesAP Physics Unit TestAbdElMalek Abdo SalehNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 11Document12 pagesPhysics Set 11bijayakumal819No ratings yet
- 2024 p1 Pre - Mid Year Exam - TestDocument18 pages2024 p1 Pre - Mid Year Exam - TestYolanda WillsonNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and Magnetism ExamplerDocument6 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetism ExamplermuazNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 (Moving Charges and Magnetism)Document6 pagesUnit 4 (Moving Charges and Magnetism)Sneha Maria SunnyNo ratings yet
- C3 Physics W.P.E Concept I To 4Document29 pagesC3 Physics W.P.E Concept I To 4suryanarayana raju kalidindi100% (1)
- Rugby PhysicsDocument2 pagesRugby PhysicsToufic HageNo ratings yet
- Complex PotentialDocument2 pagesComplex PotentialAshvin Grace100% (1)
- Torsion of Multi-Cell Cross-Section - Hw7 - BDocument12 pagesTorsion of Multi-Cell Cross-Section - Hw7 - BNagaraj RamachandrappaNo ratings yet
- Effective Laminate Thickness For The Design of Laminated GlassDocument5 pagesEffective Laminate Thickness For The Design of Laminated GlassLaurence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- PHYS4652 Assignment2Document2 pagesPHYS4652 Assignment2Yang Woo SeongNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics, Aeronautics and Flight MechanicsDocument94 pagesAerodynamics, Aeronautics and Flight Mechanicsegalewing100% (1)
- UG11T4509-Heat Transfer and Marine Heat Exchangers SyllabusDocument6 pagesUG11T4509-Heat Transfer and Marine Heat Exchangers SyllabusSandeep KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - Mechanical Properties of Metals and AlloysDocument98 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Mechanical Properties of Metals and AlloysAlex HunterNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Piles Shafts PDFDocument26 pagesStructural Design of Piles Shafts PDFamanpreet_ahuja100% (1)
- STATICS OF RIGID BODIES GuideDocument7 pagesSTATICS OF RIGID BODIES GuideMichael Angelo MontebonNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems - 5 ExerciseDocument8 pagesSolved Problems - 5 ExerciseRoberto Macias NNo ratings yet
- Design of Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer For Underwater Acoustic ImagingDocument75 pagesDesign of Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer For Underwater Acoustic ImagingHehe JeansNo ratings yet
- Compressors OverviewDocument34 pagesCompressors OverviewAhmed Tariq KhalilNo ratings yet
- Material Selection For Flare TipsDocument200 pagesMaterial Selection For Flare Tipscanakyuz100% (2)
- Si 7013 Bab Iv Advanced Concept - Mixed Mode: Ivindra Pane, PHD Kantor: Lab. Rekayasa Struktur Teknik Sipil, FTSLDocument44 pagesSi 7013 Bab Iv Advanced Concept - Mixed Mode: Ivindra Pane, PHD Kantor: Lab. Rekayasa Struktur Teknik Sipil, FTSLMauvil SulinciNo ratings yet
- Velocity - Time GraphsDocument31 pagesVelocity - Time GraphsCaloykOoy Danday DueñasNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Physics Question BookDocument5 pages1st Year Physics Question BookranaateeqNo ratings yet
- R600 ADocument1 pageR600 ATrần ViệtNo ratings yet
- Thesis Bondsman - 2021Document142 pagesThesis Bondsman - 2021adnan-651358No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Module SixDocument27 pagesElectromagnetism: Module SixCameron SmytheNo ratings yet
- RCL202210180 ProjectDocument22 pagesRCL202210180 ProjectAASHISH CHANDRANo ratings yet
- CIVIL ENGINEERING Curriculum PDFDocument178 pagesCIVIL ENGINEERING Curriculum PDFChirag N PatelNo ratings yet
- Design of ChimneyDocument10 pagesDesign of ChimneyPETER PENNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set01Document7 pagesPractise Problems Set01rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Adapted Reference TablesDocument4 pagesAdapted Reference Tablesapi-327660250No ratings yet
- Ce Correl Fluid Mechanics (A) : Situation 1Document2 pagesCe Correl Fluid Mechanics (A) : Situation 1Glenn Frey LayugNo ratings yet
- C8 QuestionnairesDocument2 pagesC8 QuestionnairesCharlie SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Fluid Kinematics 3Document87 pagesFluid Kinematics 3Sunil BagadeNo ratings yet
- 04 - GR (Circular Motion - Work, Power - Energy) - Eng by AllenDocument12 pages04 - GR (Circular Motion - Work, Power - Energy) - Eng by AllenNeil ShettigarNo ratings yet