Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCM 107 (Skills)
NCM 107 (Skills)
Uploaded by
Daniela Marie GARCIA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesThis document provides information on caring for mothers, children, and adolescents. It discusses pregnancy tests, fetal development, fetal monitoring, Leopold's maneuver for determining fetal position, perineal care after birth, lactation phases, and postpartum assessment. Key points include signs of pregnancy, estimated due dates, fetal heart rate formulas, listening to the fetal heartbeat, examining the fetus' presentation, cleansing the perineum after birth, the four phases of lactogenesis from pregnancy to weaning, and assessing for complications after giving birth.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on caring for mothers, children, and adolescents. It discusses pregnancy tests, fetal development, fetal monitoring, Leopold's maneuver for determining fetal position, perineal care after birth, lactation phases, and postpartum assessment. Key points include signs of pregnancy, estimated due dates, fetal heart rate formulas, listening to the fetal heartbeat, examining the fetus' presentation, cleansing the perineum after birth, the four phases of lactogenesis from pregnancy to weaning, and assessing for complications after giving birth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesNCM 107 (Skills)
NCM 107 (Skills)
Uploaded by
Daniela Marie GARCIAThis document provides information on caring for mothers, children, and adolescents. It discusses pregnancy tests, fetal development, fetal monitoring, Leopold's maneuver for determining fetal position, perineal care after birth, lactation phases, and postpartum assessment. Key points include signs of pregnancy, estimated due dates, fetal heart rate formulas, listening to the fetal heartbeat, examining the fetus' presentation, cleansing the perineum after birth, the four phases of lactogenesis from pregnancy to weaning, and assessing for complications after giving birth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
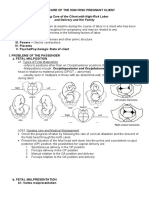
Care of Mother, Child and Adolescents
NCM 107: Lecture I to V
Lecture I: Pregnancy Test b. By 3rd lunar month (12
Signs of Pregnancy weeks), the fundus is slightly
palpated above the above the
i. Presumptive
symphysis pubis.
P Period Absent (Amenorrhea) c. By the 5th lunar month (20
R Really Tired (Fatigue)
weeks), the fundus is palpable
E Enlarged Breast
at the level of the umbilicus.
S Sore Breast
d. On the 9th lunar month, the fundus is at the level of
U Urination Increased
the xiphoid process.
M Movement of Fetus in Uterus
E Emesis and Nausea
Estimated Date of Confinement/Delivery (EDC/EDD)
ii. Probable Naegel’s Rule
P Positive Pregnancy Test for patients whose LMP falls between (April-Dec)
R Returning of the Fetus - 3mos (from LMP) + 7days (to LMP) + 1year
O Outline of the Fetus can be Palpated for patients whose LMP falls between (Jan-Mar)
B Braxton Hicks Contractions + 9mos (to LMP) + 7days (to LMP)
A Softening of Cervix (Goodell’s Sign)
B Bluish Color to the Vulva, Cervix, and Vagina Lecture III: Leopold’s Maneuver
(Chadwick’s Sign) ➢ a systematic method of observation and palpation to
L Lower Uterine Segment Becomes Soft determine fetal presentation and position
(Hegar’s Sign) ➢ methods of palpation to determine presentation and
E Enlarged Uterus position of the fetus and aid in location of fetal heart
sounds
iii. Positive
F Fetal Movements Felt by Doctor or Nurse First Maneuver: Fundal Grip
E Electronic Device Detects Fetal Heart Sounds a. Face the client’s head.
T The Delivery of the Baby b. Using both hands, palpate
U Ultrasound Detects the Fetus the fundal area, expect to
S See Visible Movement of the Baby by the palpate a soft, irregular
Doctor or Nurse mass in the upper quadrant
of the maternal abdomen.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin c. This determines the shape,
➢ The first placental hormone produced, hCG, can be size, mobility and consistency of what he/she
found in maternal blood and urine as early as the first feels. The limbs and shoulders contain little bone
missed menstrual period (shortly after implantation processes that move with the fetus’ trunk; the
has occurred) through about the 100th day of head is firm, hard, round and moves separately
pregnancy. Because this is the hormone analyzed by from the trunk; and the buttocks are symmetric
pregnancy tests, a false-negative result from a and feels soft.
pregnancy test may be obtained before or after this
period. Second Maneuver: Umbilical Grip
a. While still facing the
Lecture II: Fetal Heart Monitoring Using a patient, move hands to the
lateral sides of the
Stethoscope
abdomen. Perform this
➢ Fetal Heartbeats are audible at the 5th month or 20
maneuver by placing the
weeks.
right hand on one side of
Purpose the patient’s abdomen while using the left hand to
a. To check for the rate, rhythm, and the presence or explore the women’s uterus on the right side.
absence of accelerations and deceleration of the fetal b. Repeat this step on the opposite side using the
heartbeat. opposite hand.
c. The fetal back is smooth and form. The
Formula for Age of Gestation extremities of the fetus should feel like
protrusions and small irregularities.
McDonald’s Rule 𝐹𝐻𝑇 𝐼𝑁 𝐶𝑀 (8)
(weeks) 7 Third Maneuver: Pawlick’s Grip
McDonald’s Rule 𝐹𝐻𝑇 𝐼𝑁 𝐶𝑀 (2) a. Move hands down to the
(months) 7 lower pelvic area.
b. Palpate the area just above
Bartholomew’s Rule of Fourths the symphysis pubis to
a. This method estimates the age of gestation relative to determine the presenting
the height of the fundus of the uterus above the part.
symphysis pubis. c. Grasp the presenting part with the thumb ad
fingers of the right hand.
d. This step of the process identifies the part of the ➢ Four Phases
fetus that is above the inlet.
LACTOGENESIS I
Fourth Maneuver: Pelvic Grip ➢ Begins around 16 weeks gestation as the glandular
a. Face the client’s feet. luminal cells in the breast begin to secreting
b. Place hands on the colostrum (thin, watery pre-lactation secretion)
abdomen, and point fingers LACTOGENESIS II
toward the mother’s feet. ➢ Triggered at birth by the delivery of the placenta,
c. Gently move the fingers on when the progesterone (prolactin is no longer
both hands towards the inhibited) and other circulating pregnancy
pubis by sliding the hands hormones suddenly decrease and oxytocin sharply
over the sides of the patient’s uterus. increases as a result of the infant sucking
d. The side where the greatest resistance to the ➢ Often when mothers feel their “milk has come in”
descending fingers is the location of the brow. (engorgement) – occurs between birth to 5 to 10
days postpartum; termed as “transitional milk”
Lecture IV: Perineal Care LACTOGENESIS III
➢ cleansing of the external genitalia, perineum and ➢ Occur from day 10 until weaning postpartum
surrounding area ➢ When the “mature milk” supply is driven by the
➢ also referred to as “peri-care” or “perineal-genital” circulating lactation hormones oxytocin and
care progesterone
➢ perineal care can be provided alone or as part of the LACTOGENESIS IV
bed baths ➢ Occurs after complete weaning and the breasts
involute to their pre-lactation state
Purpose ➢ Breast milk forms in response to the decrease in
a. To prevent or eliminate infection and odor estrogen, and progesterone levels that follows
b. To promote healing delivery of the placenta
c. To remove secretions ➢ This stimulates prolactin production and milk
d. To provide client’s comfort production and an increase in prolactin and oxytocin
➢ Signs and Symptoms: Breasts become fuller, larger
Lecture 5: Post Partum Assessment and firmer as blood and lymph enter the area to
➢ The postpartum nursing assessment is an important contribute fluid to the formation of milk
aspect of care in order to identify early signs of ➢ Breast distention, engorgement with feeling of heat
complications in the woman who has just given birth. or tenderness
Following pregnancy, the woman is at risk for ➢ Engorgement Phase: The breast tissue appear
infection, hemorrhage, and the development of a reddened – 3rd or 4th day after birth – primary
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). The nurse can engorgement
remember the key points of postpartum assessment by ➢ Fades when infant begins effective latching and
learning the acronym BUBBLE-LE, which stands for begins transferring colostrum followed by milk
breast, uterus, bladder, bowels, lochia, episiotomy, from the breasts
lower extremities, and emotions.
ii. Position of the Client: Sitting or Supine Position
Purpose iii. Method of Assessment: Inspection or Palpation
a. To identify postpartum clients who are at risk after
A. Inspection
child’s delivery.
➢ Involves using the senses of vision, smell, and
b. To promote and maintain the health of the woman
hearing to observe and detect any normal or
during postpartum period
abnormal findings
➢ Used from the moment the client is seen by the nurse
The abbreviation BUBBLE-HE is used to recall the
and continues throughout the examination
components of the postpartum assessment. The
➢ Guidelines for Inspection
postpartum phase lasts from the moment of birth to
a. Make sure the room is at comfortable temperature
around 6 weeks after delivery.
b. Use good lighting: preferably sunlight
B Breasts c. Look and observe before touching. Touch can
U Uterus alter appearance and distract you from a complete,
B Bowel focused observation
B Bladder d. Completely exposed the body parts you are
L Lochia inspecting while draping the rest of the client as
E Episiorraphy appropriate
H Homan’s Sign e. Note the following characteristics: symmetry,
E Emotional Status presence of discharges from the nipple and pain
upon palpation
Breasts B. Palpation
i. Lactation ➢ Consists of using parts of the hand to touch and feel
➢ driven by hormones form the hypothalamus to the for the following characteristics:
pituitary gland in order to secrete the lactation a. Consistency: soft/hard
hormones b. Temperature: warm/cold
➢ this is identified by four phases of lactogenesis c. Tenderness upon palpation
(human milk production)
➢ Reminders: Lochia
a. Examiner’s fingernails should be short and the ➢ Lochia is a vaginal discharge after childbirth. It
hands should be at comfortable temperature consists of blood, mucus, uterine tissue and other
b. Standard precautions should be followed if materials from the uterus.
applicable Lochia Rubra
c. Proceed from light palpation, which is safest and ➢ the term for the first stage of lochia
the most comfortable for the client, to moderate ➢ 3-4 days vaginal bleeding
palpation and finally to deep palpation ➢ dark or bright red blood
➢ lasts for 3-4 days
d. Use light palpation – there should be very little or
➢ flows like a heavy period
no depression: less than 1 cm ➢ small clots are normal
➢ mild, period-like cramping
Uterus Lochia Serosa
➢ time involution is complete (6 weeks) – weight: 50g ➢ the term for the second stage of lochia
➢ the uterus of a breastfeeding mother may contract ➢ 4-6 days vaginal bleeding
more quickly because oxytocin stimulates uterine ➢ pinkish brown discharge that’s less bloody looking
contractions ➢ thinner and more watery than lochia rubra
➢ Position of the Client: Dorsal Recumbent Position ➢ lasts for 4 to 12 days
(client lies down on the examination tables or bed Lochia Alba
with the knees bent, the legs separated and the feet ➢ the last stage of lochia
flat on the table or bed) ➢ yellowish white discharge
➢ Method of Assessment: Inspection and Palpation ➢ little to no blood
A. Inspection ➢ light flow or spotting
➢ Involves using the senses of vision, smell, and ➢ lasts from about 12 days to 6 weeks
hearing to observe and detect any normal or ➢ no clots
abnormal findings
➢ Note the following characteristics: symmetry, Episiorraphy
uterine contour ➢ surgical repair of injury to the vulva by suturing
➢ Consistency of the postpartum uterus: well ➢ Episiotomy: a surgical cut made at the opening of the
contracted fundus feels so firm vagina during childbirth, to aid a difficult delivery
➢ Uterine Atony-Postpartum Bleeding: if the uterus and prevent rupture of tissues
is soft and boggy in the first hour after delivery ➢ Position of the Client: Sim’s Position (client lies on
• Nursing Mgt: assess the bladder, massage the his/her right or left side with the lower arm placed
uterus, apply cold compress over the abdomen, behind the body and the upper arm flexed at the
check the vital signs, administer Oxygen, notify shoulder and elbow with the lower leg is slightly
the physician flexed at the knee while the upper leg is flexed at a
sharper angle and pulled forward)
Bowel ➢ REEDA Scale: a tool that assesses the inflammatory
➢ digestion and absorption begin to be active again soon process and tissue healing in the perineal trauma,
after delivery unless the woman has had a cesarean through the evaluation of five items of healing:
delivery redness (hyperemia), oedema, ecchymosis,
➢ hemorrhoids (distended rectal vein) that has been discharge and approximation of the wound
pushed of the rectum during pregnancy may be edges/stitches (coaptation)
present ➢ in an episiotomy, the perineum is incised with scissors
➢ bowel sounds are active but passage of stool may be or scalpel as the infant’s head is crowning
slow because of the still-present effect of relaxin (a ➢ two types of episiotomy have been described:
hormone which softens and lengthens the cervix and midline (median) and mediolateral (see the image
pubic-symphysis for preparation of the infant’s birth) below)
➢ Management: Advice the woman to eat high fiber ➢ generally, midline episiotomies are more commonly
diet and increase fluid intake. performed in the United States, whereas
mediolateral episiotomies are more common in
Bladder other parts of the world
➢ during pregnancy: 2,000-3,000 ml of excess fluid
accumulates in the body so extensive diaphoresis Homan’s Sign
(excessive sweating) and diuresis (excess urine ➢ often used in the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis
production) begin at almost immediately after birth to of the leg
rid the body of this fluid ➢ Positive Homan’s Sign (calf pain at dorsiflexion of
➢ daily urine output: from a normal level of 1,500 to as the foot): thought to be associated with the presence
much as 3,000 ml/day during the 2nd to 5th day after of thrombosis
birth
➢ this marked increase in urine production causes the Emotional Status
bladder to fill rapidly ➢ Phases of the Puerperium
➢ Advice: a. Taking-in Phase
a. Reassure the mother that this is normal ➢ 2-3 days postpartum
b. Instruct the mother to continue to drink a healthy ➢ woman is dependent and largely passive
amount of fluids daily especially is she is b. Taking-hold Phase
breastfeeding ➢ 3 days to2 weeks
➢ woman initiates actions and makes her own Fundal Grip to check the fetal presentation
decisions Umbilical to check the fetal heart rate
Lochia Alba Grip
➢ varied time frame Pawlick’s Grip to check the fetal engagement
➢ woman redefines her new role Pelvic Grip to check the fetal habitus/attitude
Third ideal time to perform Leopold’s
Recitation Trimester Maneuver
Pregnancy Test Cephalic hard & round = fetal head
Presentation
Pregnancy a medical test can detect the presence Breech soft & glandular = fetal buttocks
Test of HCG in woman's urine blood Presentation
Missed Period/ cessation of woman's monthly How can Leopold’s Maneuver assist the healthcare
Amenorrhea menstrual period; absence of period provider in deciding if CS is necessary?
Morning term use to describe nausea and Leopold’s Maneuver assess the fetal engagement
Sickness vomiting; condition in which the Can you perform Leopold’s Maneuver at home?
pregnant woman experience nausea No, it can only be performed by a healthcare
and vomiting in the morning or provider.
common during presumptive sign of
pregnancy Perineal Care (PC)
Quickening describe the sensation of fetal
movements which can be Perinium the area located between anus and
presumptive signs of pregnancy genitalia
HCG Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Perineal Care refers to cleaning and maintenance of
Ballottement returning of the fetus the perineum
Goodell’s Sign softening of the cervix Purpose of to prevent or eliminate infection and
Chadwick’s bluish color to the vulva, cervix, and Perineal Care odor
Sign vagina to promote healing
Hegar’s Sign lower uterine segment becomes soft to remove secretions
Braxton Hicks rhythmic and false contractions to provide client's comfort
Contractions Common PC mild and scented soap, wash clothes,
Rupture of the expulsion of amniotic fluid from Products disposable gloves, warm water,
Membrane or pregnant woman’s cervix often creams/ointment to protect the skin
Amniotic occurring as a sign that labor and Dorsal the ideal position of patient before
Fluid Leakage childbirth are imminent Recumbent and during perineal care
Cervical dilatation and effacement of the From Front To technique of wiping perineal area of
Dilatation cervix as determined by the health Back the patient
Effacement care provider during a pelvic PPE Personal Protective Equipment
examination signaling the Examples Of gloves, gown, goggles, face mask,
progression of labor and impending PPE face shield
childbirth What are some additional measures that may provide
Fetal Position visual and tactile confirmation of a relieve and support perineal care after childbirth?
and developing fetus position and Using ice pack, sim bags, and pain reliver medication
Engagement engagement in the pelvis as assessed as recommended by a healthcare provider
by the healthcare provider during
pelvic examination Postpartum Assessment (PPA)
Delivery or expulsion of the baby from pregnant
Postpartum the evaluation and monitoring of
Childbirth woman of the uterus
Assessment woman's health and well-being in the
period after childbirth typically
Fetal Heart Monitoring (FHM) Using a Stethoscope
within 6 weeks after the delivery
Purpose of to identify postpartum clients who are
Purpose of to assess the well-being of the fetus PPA at risk after their child’s delivery
FHM to promote and maintain the health of
Pre-Natal FHM typically performed the woman during postpartum period
Check-Up Why Is PPA to ensure the mother's recovery,
Normal FHR 120-160 bpm Important? monitor for any potential
Why do we use stethoscope instead of Doppler’s complications and support the
Ultrasound? adjustment to mother
Avoidance of exposure to excess ultrasound Within Or the first postpartum assessment
First 24 Hours typically occur
Leopold's Maneuver (LM) Recommended frequency of postpartum assessment in
Purpose of to assess the fetal position, weeks following childbirth?
Leopold’s presentation and engagement in the 24 Hours After Birth, 1 Week Postpartum, 6 Weeks
Maneuver pregnant women's abdomen Postpartum
Purpose of patient comfort, improve palpation, Relaxin hormones that soften and lengthen the
Voiding Before reduce discomfort, enhance accuracy cervix and symphysis pubis
LM 4th Trimester other term for puerperium stage
2-3 Days or 2 postpartum blues typically manifest
Weeks
Pathogenesis unknown but it will link to hormonal
of Post Partum changes, decrease of estrogen,
Blues progesterone, and prolactin
Symptoms of crying, dysphoric affect, irritability,
Post Partum anxiety, insomnia, appetite changes
Blues
Causes of Post family history, history of depression,
Partum Blues multiparity, history of menstrual
cycle related to mood swings
Transient and How will you handle postpartum
Limited blues?
5-10 Days point during postpartum assessment
does the occurrence of transition milk
manifest
Purpose Of to assess/monitor for signs of normal
Assessing or abnormal bleeding and to gauge
Lochia During the post-partum recovery
Postpartum
How does lochia typically change in appearance and
quantity during the postpartum period?
Lochia Typically Progress through three stages:
Lochia Rubra (Dark Red), Serosa (Pink), Alba
(Yellowish White)
Offensive term used for a foul or unpleasant
Lochia odor which may indicate infection
Three Stages Taking in (2-3 days),
of Post-Natal Taking hold (3 days-2 weeks), Letting
Period go (12 weeks)
Homan's Sign often used in diagnosis of deep
Or DVT venous thrombosis of the leg
Positive calf pain at dorsiflexion of the foot
Homans's Sign
Uterine Atony- if uterus is soft and boggy in the first
Postpartum hour after delivery
Bleeding
Nursing management of uterine atony-postpartum
bleeding in the first hours of delivery?
Assess the bladder, massage the uterus, apply cold
compress over the abdomen, check the vital signs,
administer oxygen, notify the physician
Episiotomy the medical term used to describe
Repair Or medical procedure in which
Perineal healthcare provider stitches
Surgery
Sim's Position best ideal position for mother after
episiotomy
You might also like
- Physical Examination For OBDocument63 pagesPhysical Examination For OBQuolette Constante87% (77)
- FRCPath Mock 2014 Model AnswersDocument29 pagesFRCPath Mock 2014 Model Answersmonday125No ratings yet
- Nursing Procedure For Skills Lab Leopolds ManueverDocument4 pagesNursing Procedure For Skills Lab Leopolds Manueveralyza lumpodNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Fetal Assessment During LaborDocument66 pagesMaternal and Fetal Assessment During LaborHazelynne Mamucud100% (2)
- Goals of Prenatal CareDocument16 pagesGoals of Prenatal CareLhea Marie Trinidad100% (1)
- Labor RoomDocument3 pagesLabor RoomDakayu Amin LugitNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing Module 5Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing Module 5Ezekiel John GarciaNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Maneuvers Fundic Height Measurement and FHT Determination ChecklistDocument6 pagesLeopolds Maneuvers Fundic Height Measurement and FHT Determination ChecklistChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver PTTDocument23 pagesLeopold's Maneuver PTTGuila Aira GracelleNo ratings yet
- Leopolds MeasurementDocument1 pageLeopolds MeasurementCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Focus:: Canossa CollegeDocument23 pagesFocus:: Canossa CollegeZyrene RiveraNo ratings yet
- IntrapartumDocument16 pagesIntrapartumBrigitte CovarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Leopolds-Maneuver ChecklistDocument4 pagesLeopolds-Maneuver ChecklistZabelle BungarNo ratings yet
- LeopoldsDocument2 pagesLeopoldsMhianne SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver Factors Affecting Performance The ProcedureDocument5 pagesLeopold's Maneuver Factors Affecting Performance The ProcedureEmman NuelleNo ratings yet
- National College of Nursing: Procedure ONDocument6 pagesNational College of Nursing: Procedure ONSumit Yadav100% (1)
- CHN Manual - Antepartal AssessmentDocument6 pagesCHN Manual - Antepartal AssessmentInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Leopolds ManeuverDocument2 pagesLeopolds ManeuverMicah YapNo ratings yet
- MCN FinalsDocument13 pagesMCN FinalsMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Leopold ManeuverDocument4 pagesLeopold ManeuverElle100% (1)
- Antenatal Assessment ProcedureDocument3 pagesAntenatal Assessment ProcedureSANCHAYEETANo ratings yet
- 11.23b-Conduct of Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument8 pages11.23b-Conduct of Normal Labor and DeliveryJøshua Cruz100% (2)
- Leopold ManeuverDocument4 pagesLeopold ManeuverFaye MoralesNo ratings yet
- Leopolds-Maneuver StudentsDocument40 pagesLeopolds-Maneuver StudentsCarlo GacadNo ratings yet
- LEOPOLD'S MANEUVER RATIONALE&CHECKLISTDocument3 pagesLEOPOLD'S MANEUVER RATIONALE&CHECKLISTNhadzmae Asmadul IsnainNo ratings yet
- OB Return DemoDocument7 pagesOB Return DemoSophia RubiaNo ratings yet
- 4 ExamDocument7 pages4 Examjacynda linsanganNo ratings yet
- Elearning Ncm107 MidtermDocument9 pagesElearning Ncm107 MidtermHELLE AUBSNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument10 pagesAbdominal Assessmentshams100% (2)
- Procedure For Return DemonstrationDocument30 pagesProcedure For Return DemonstrationMaria Angelika BughaoNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Performing Fundal Height MeasurementDocument5 pagesRubric For Performing Fundal Height MeasurementPATRICIA JULIANNE CASTAÑETO RIVERANo ratings yet
- OB Exam 2Document14 pagesOB Exam 2Katie GermanNo ratings yet
- ' Leopold S ManaeuverDocument30 pages' Leopold S ManaeuverjamilliumNo ratings yet
- 7,2.1 Sop Antenatal CareDocument5 pages7,2.1 Sop Antenatal CarekalsumNo ratings yet
- Purpose:: Procedure: Rationale: Introduce Yourself and Inform Pregnant Woman About The ProcedureDocument5 pagesPurpose:: Procedure: Rationale: Introduce Yourself and Inform Pregnant Woman About The ProcedureArmySapphire100% (1)
- OSCE Teamwork-ObgynDocument31 pagesOSCE Teamwork-Obgynندى البركيNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Abdominal Examination and Leopolds ScriptDocument5 pagesObstetric Abdominal Examination and Leopolds ScriptNoreen Hannah GabrielNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Childbearing Client 20Document37 pagesAssessment of Childbearing Client 20Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- P-132 Leopolds-ManeuverDocument5 pagesP-132 Leopolds-ManeuverAubrey AndresNo ratings yet
- LEOPOLD's MANEUVER RATIONALEDocument3 pagesLEOPOLD's MANEUVER RATIONALEAngela AquisapNo ratings yet
- The Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument76 pagesThe Diagnosis of PregnancyCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument5 pagesAbdominal ExaminationAnuradha MauryaNo ratings yet
- Ncm33 PPT - Cabatingan, TraniDocument23 pagesNcm33 PPT - Cabatingan, TraniNicka Rubio CabatinganNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Physical ExaminationDocument7 pages5.0 Physical ExaminationJennifer Pisco LiracNo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument2 pagesMaternalqweyo yhuNo ratings yet
- NUR195 ADocument14 pagesNUR195 AJemuel DalanaNo ratings yet
- FUNDAL HEIGHT, LEOPOLDS, FHR RETDEMdocxDocument5 pagesFUNDAL HEIGHT, LEOPOLDS, FHR RETDEMdocxRenalyn Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Topic # 1 Leopold's ManueverDocument39 pagesTopic # 1 Leopold's ManueverJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Mca (107) RleDocument13 pagesMca (107) RleGulayan, Renz Bryelle T.No ratings yet
- Script For Leopold's Maneuver (Autorecovered)Document3 pagesScript For Leopold's Maneuver (Autorecovered)lea mae andoloyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor & DeliveryDocument10 pagesNursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor & DeliveryWilbert CabanbanNo ratings yet
- PARTOGRAPHDocument49 pagesPARTOGRAPHMhianne SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Walang Kwentang NotesDocument107 pagesWalang Kwentang NotesAnonymousTargetNo ratings yet
- E.Important EstimatesDocument2 pagesE.Important EstimatesJulio NazarethNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Maneuvers: Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesLeopold'S Maneuvers: Multiple ChoiceErcel ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy: Signs and Symptoms Detection of Abnormalities Diagnosis, Physio Changes, CareDocument67 pagesPregnancy: Signs and Symptoms Detection of Abnormalities Diagnosis, Physio Changes, CareJovim Cervantes LanaNo ratings yet
- MCN (Icons)Document7 pagesMCN (Icons)Angelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManeuverDocument2 pagesLeopold's ManeuverAnnaAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Leopods ManeuverDocument8 pagesLeopods ManeuverDaryl Adrian RecaidoNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL RLE ChecklistDocument3 pagesSCHOOL RLE ChecklistRafaela Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Il bambino prima e dopo il parto - Sensi, sensazioni e sensorialità del nascituroFrom EverandIl bambino prima e dopo il parto - Sensi, sensazioni e sensorialità del nascituroNo ratings yet
- Hi-Yield Notes in Ob-GyneDocument22 pagesHi-Yield Notes in Ob-GyneJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Best Pulmonologist in Velachery - Sabari Lung Care Clinic - Reasearch PaperDocument2 pagesBest Pulmonologist in Velachery - Sabari Lung Care Clinic - Reasearch PaperSabari Lung Care ClinicNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sourav Chowdhury Senior ResidentDocument79 pagesDr. Sourav Chowdhury Senior ResidentBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- FTC Vs HCG Diet Direct, Clint EthingtonDocument40 pagesFTC Vs HCG Diet Direct, Clint Ethingtontheskeptic21No ratings yet
- The Complete HCG Diet Manual: ForwardDocument8 pagesThe Complete HCG Diet Manual: ForwardCrystal RelfordNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document28 pagesChapter 10iMaibelle BelleNo ratings yet
- Sample IVF Calendar ScheduleDocument3 pagesSample IVF Calendar Schedule24x7emarketingNo ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument67 pagesPrenatal CareAllurie Umel100% (3)
- P099Document50 pagesP099Iqbal SayedNo ratings yet
- Sample Obstetrics Orders: By: Mitra Ahmad SoltaniDocument62 pagesSample Obstetrics Orders: By: Mitra Ahmad Soltanialmslmani9524100% (2)
- Practice 1 How Do Pregnancy Tests Work?Document2 pagesPractice 1 How Do Pregnancy Tests Work?ChennulNo ratings yet
- Drugs The Straight Facts, Body Enhancement Products OptimizedDocument121 pagesDrugs The Straight Facts, Body Enhancement Products OptimizedDeathbedeli100% (3)
- Biology Mod 5 Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesBiology Mod 5 Practice QuestionsLilyNo ratings yet
- Package Insert 13695 - HCG D - en - 30405-01 PDFDocument10 pagesPackage Insert 13695 - HCG D - en - 30405-01 PDFadybaila4680No ratings yet
- OB - TransesDocument112 pagesOB - TransesAldwin BagtasNo ratings yet
- Ovulation Induction and Intra Uterine InseminationDocument4 pagesOvulation Induction and Intra Uterine InseminationmasdipoNo ratings yet
- Aborsion: Spontaneou SDocument214 pagesAborsion: Spontaneou Sorkaido berisha (Addisu)No ratings yet
- Predictors For Response To Letrozole As An Ovulation Induction in Anovulatory Infertile Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome WomenDocument23 pagesPredictors For Response To Letrozole As An Ovulation Induction in Anovulatory Infertile Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome WomenAndre OpaNo ratings yet
- Flu Ore CareDocument6 pagesFlu Ore CareerielxhNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hipertiroid KehamilanDocument5 pagesJurnal Hipertiroid KehamilanAbdurrohman IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- The Vaxx ReportDocument115 pagesThe Vaxx ReportStef Dimi100% (3)
- Obstetrics MCQsDocument12 pagesObstetrics MCQsDeeksha BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument28 pagesHydatidiform MoleRitamaria100% (7)
- ABNORMALDocument33 pagesABNORMALJc Mae CuadrilleroNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document54 pagesDocument 1narayanasamy30No ratings yet
- B29061KDocument13 pagesB29061KMeethuanNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Document32 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Anitha SNo ratings yet
- Blighted Ovum - Treatment, Symptoms, Causes, and OutlookDocument14 pagesBlighted Ovum - Treatment, Symptoms, Causes, and OutlookTomiwa AdeshinaNo ratings yet
- 02 Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument8 pages02 Gestational Trophoblastic Diseasemisakichan FrandoNo ratings yet