Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 27 Notes
Lec 27 Notes
Uploaded by
Abhay MandalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lec 27 Notes
Lec 27 Notes
Uploaded by
Abhay MandalCopyright:
Available Formats
LEC-27: Segmentation | Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation
1. An important aspect of memory management that become unavoidable with paging is separation of user’s
view of memory from the actual physical memory.
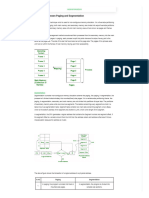
2. Segmentation is memory management technique that supports the user view of memory.
3. A logical address space is a collection of segments, these segments are based on user view of logical
memory.
4. Each segment has segment number and offset, defining a segment.
<segment-number, offset> {s,d}
5. Process is divided into variable segments based on user view.
6. Paging is closer to the Operating system rather than the User. It divides all the processes into the form of
pages although a process can have some relative parts of functions which need to be loaded in the same
page.
7. Operating system doesn't care about the User's view of the process. It may divide the same function into
different pages and those pages may or may not be loaded at the same time into the memory. It
p
decreases the efficiency of the system.
8. It is better to have segmentation which divides the process into the segments. Each segment contains the
same type of functions such as the main function can be included in one segment and the library functions
el
can be included in the other segment.
eH
od
9.
C
10. Advantages:
a. No internal fragmentation.
b. One segment has a contiguous allocation, hence efficient working within segment.
c. The size of segment table is generally less than the size of page table.
d. It results in a more efficient system because the compiler keeps the same type of functions in one
segment.
11. Disadvantages:
a. External fragmentation.
b. The different size of segment is not good that the time of swapping.
12. Modern System architecture provides both segmentation and paging implemented in some hybrid
approach.
You might also like
- Memory ManagementDocument34 pagesMemory ManagementLifeNo ratings yet
- Describe Segmentation Process and Comparison of Segmentation With Paging: Segmentation ProcessDocument5 pagesDescribe Segmentation Process and Comparison of Segmentation With Paging: Segmentation ProcessJNo ratings yet
- OS Unit-3Document13 pagesOS Unit-3Madhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- Copilot Segmentation PagingDocument4 pagesCopilot Segmentation PagingLin JeremyNo ratings yet
- CH07 - Memory ManagementDocument37 pagesCH07 - Memory ManagementTaufik Akbar WibowoNo ratings yet
- Memory ManagementDocument20 pagesMemory Managementnehavj664No ratings yet
- OS Research ReportDocument7 pagesOS Research ReportNimra ShahNo ratings yet
- Mms 1Document33 pagesMms 1Aashi NegiNo ratings yet
- Os Unit-3Document34 pagesOs Unit-3Palagani BhagyasriNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument24 pagesOperating SystemMakkapati DeepthiNo ratings yet
- Memory Management (Platform Technologies)Document43 pagesMemory Management (Platform Technologies)Luigi SeriñaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 ManagementDocument12 pagesUnit 7 ManagementCindy CortezNo ratings yet
- FragmentationDocument3 pagesFragmentationHARISHNo ratings yet
- TOPIC THREE Computer PersonelDocument4 pagesTOPIC THREE Computer PersonelOigara Onwong'aNo ratings yet
- Operating System Question With AnswersDocument57 pagesOperating System Question With AnswersPadre BhojNo ratings yet
- FocusTaskReading 13Document7 pagesFocusTaskReading 13anniebabbie77No ratings yet
- Virtual Memory: Course COMP6153 Effective Period: September 2017Document33 pagesVirtual Memory: Course COMP6153 Effective Period: September 2017Pravda CaliburNo ratings yet
- Memory ManagementDocument6 pagesMemory ManagementAgung PambudiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Paging To Thrashing)Document11 pagesUnit 3 (Paging To Thrashing)king kholiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Memory ManagementDocument60 pagesChapter 6 - Memory Managementsibhat mequanintNo ratings yet
- Segmentation and Paging & Page ReplacementDocument12 pagesSegmentation and Paging & Page ReplacementSANTOSH4176No ratings yet
- U 4 Topic 12 Virtual MemoryDocument3 pagesU 4 Topic 12 Virtual MemorySatyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Memory ManagementDocument7 pagesModule 7 Memory ManagementnatsuNo ratings yet
- Demand Paging and SegmentationDocument13 pagesDemand Paging and Segmentationmelbuela04No ratings yet
- SegmentationDocument8 pagesSegmentationSuyogNo ratings yet
- Os - Memory Management in Operating SystemDocument10 pagesOs - Memory Management in Operating Systemluckysighania93No ratings yet
- Unit-III (Memory Management)Document20 pagesUnit-III (Memory Management)Sunny ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit5 OsDocument20 pagesUnit5 Osईश्वर महालेNo ratings yet
- Os Assignment 3 AnsDocument25 pagesOs Assignment 3 AnsMuktha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Part 5Document12 pagesUnit 3 Part 5Harshita NamdevNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document8 pagesCH 08kapil_arpitaNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument44 pagesOperating SystemKunalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document2 pagesChapter 8Peter Thomas Lim100% (2)
- SegmentationDocument6 pagesSegmentationTony NakovskiNo ratings yet
- OS Assignments 3Document5 pagesOS Assignments 3humairanaz0% (1)
- 05 Handout 1 (PlatTech)Document2 pages05 Handout 1 (PlatTech)See HorseNo ratings yet
- Systematic Analysis and Simulation of Classical Page Replacement Algorithms A Proposed Novel WSClock-DerivativeDocument8 pagesSystematic Analysis and Simulation of Classical Page Replacement Algorithms A Proposed Novel WSClock-DerivativeTenma InazumaNo ratings yet
- Memory ManagementDocument17 pagesMemory ManagementAmicable YcotNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Explain Memory Management Requirements?: - The Available Memory Is Generally Shared Among ADocument10 pagesQ.1 Explain Memory Management Requirements?: - The Available Memory Is Generally Shared Among ARamesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- MITC101Document42 pagesMITC101Rapchel EstrellaNo ratings yet
- WWW Geeksforgeeks Org Difference Between Paging and Segmentation AmpDocument3 pagesWWW Geeksforgeeks Org Difference Between Paging and Segmentation AmpStock by RKNo ratings yet
- OS Unit 4Document76 pagesOS Unit 4HARSHA VINAY KOTNI HU21CSEN0100574No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Virtual Memory Part-1Document33 pagesChapter 7 Virtual Memory Part-1Ahmed Ibrahim GhnnamNo ratings yet
- Explain Paging and Segmentation in DetailDocument4 pagesExplain Paging and Segmentation in Detailimranahmedkhan42No ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Memory ManagementDocument11 pagesChapter Three: Memory ManagementmehariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document25 pagesChapter 07Fauzan PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Virtual Memory p1Document33 pagesChapter 7 Virtual Memory p1ahmedibrahimghnnam012No ratings yet
- OS Unit 6Document13 pagesOS Unit 6BHAKTI AYAREKARNo ratings yet
- Library Hour Report SE A 19Document2 pagesLibrary Hour Report SE A 19swati kaduNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Architectural DesignDocument48 pagesCh4 Architectural DesignManel MrabetNo ratings yet
- Partitioning Algorithms Operating SystemsDocument4 pagesPartitioning Algorithms Operating SystemsDIPTANU SAHANo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document8 pagesUnit 3Tejas DixitNo ratings yet
- GP - OS - Storage AllocationDocument6 pagesGP - OS - Storage AllocationRAHUL SAININo ratings yet
- Look Up in iOS - Allocation and Management of Os - Pros Internals - OptimizationsDocument19 pagesLook Up in iOS - Allocation and Management of Os - Pros Internals - OptimizationsRishabh MalikNo ratings yet
- Define Critical Section Problem?Document13 pagesDefine Critical Section Problem?Sowmya Vannala14No ratings yet
- Operating System Memory ManagementDocument7 pagesOperating System Memory ManagementNgatia SamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Memory ManagementDocument38 pagesChapter 6 Memory ManagementAhmed Ibrahim GhnnamNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Paging and Segmentation in OSDocument4 pages5.1 Paging and Segmentation in OSsamuel ceasarNo ratings yet
- Java / J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandJava / J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet