Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Company CAU
The Company CAU
Uploaded by
ayoubbagdadkhCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- SWOT of Sasol PDFDocument6 pagesSWOT of Sasol PDFRakib TusharNo ratings yet
- The Europeische Wirtschaftsgemeinchaft Berlin 1942 PDFDocument122 pagesThe Europeische Wirtschaftsgemeinchaft Berlin 1942 PDFAlex Diam100% (1)
- DiversificationDocument41 pagesDiversificationAnamika SenguptaNo ratings yet
- The BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementFrom EverandThe BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Principles of Price and Pricing (Rowley)Document11 pagesPrinciples of Price and Pricing (Rowley)Μιχάλης ΘεοχαρόπουλοςNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management of RECKEIIT BENKSEIERDocument6 pagesSupply Chain Management of RECKEIIT BENKSEIERFuhad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Capital AllocationDocument32 pagesStrategy and Capital AllocationsonalNo ratings yet
- BCG Notes FinalDocument10 pagesBCG Notes FinalHarsora UrvilNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix (Growth Share Matrix)Document3 pagesBCG Matrix (Growth Share Matrix)Ansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bcg-Matrix SVGDocument7 pagesBcg-Matrix SVGPriyanka KansaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Winning Markets Through Market Oriented Strategic Planning - KSKDocument58 pagesChapter 4 - Winning Markets Through Market Oriented Strategic Planning - KSKWalid Ben HuseinNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument10 pagesBCG MatrixSimone BandrawalaNo ratings yet
- 1-Marketing-Chapter4and5-Product Portfolio Analysis (Including The BCG, GE Models)Document34 pages1-Marketing-Chapter4and5-Product Portfolio Analysis (Including The BCG, GE Models)WilsfunNo ratings yet
- Paper15 Solution PDFDocument22 pagesPaper15 Solution PDFDerick TanNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument6 pagesBCG MatrixSpandana AchantaNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument34 pagesBCG MatrixSaurabGhimireNo ratings yet
- Ia Bs MatrixDocument26 pagesIa Bs Matrixrscjat0% (1)
- Strategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationDocument41 pagesStrategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationSamraat SanyalNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument4 pagesBCG MatrixRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Invest in and Which Ones Should Be DivestedDocument5 pagesBCG Growth-Share Matrix: Invest in and Which Ones Should Be DivestedChanthini VinayagamNo ratings yet
- Turnaround ManagementDocument12 pagesTurnaround ManagementpriteshhegdeNo ratings yet
- BCG GrowthDocument7 pagesBCG GrowthchienNo ratings yet
- Final Theory - Marketing STRGDocument81 pagesFinal Theory - Marketing STRGkartkgala123No ratings yet
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument26 pagesGE MatrixFijo JoseNo ratings yet
- Business Portfolio AnalysisDocument20 pagesBusiness Portfolio AnalysissoumitrabehuraNo ratings yet
- Assignment of SMDocument15 pagesAssignment of SMPari KarrhaNo ratings yet
- Growth - Share - Matrix - Bahasa - Indonesia (2) enDocument6 pagesGrowth - Share - Matrix - Bahasa - Indonesia (2) enBlack EyesNo ratings yet
- Analysing Strategy (BCG Matrix)Document6 pagesAnalysing Strategy (BCG Matrix)yadavpankaj1992No ratings yet
- SM 7 PortfoliosDocument31 pagesSM 7 PortfoliosCGM MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Product Portfolio PlanningDocument35 pagesProduct Portfolio PlanningPunit BadalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Corporate Strategy and Strategic PortfolioDocument31 pagesStrategic Management: Corporate Strategy and Strategic PortfolioahlamqanabitaNo ratings yet
- Types of Marketing ModelDocument7 pagesTypes of Marketing ModelBlack EyesNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis: Definition: SWOT Analysis Is A Strategic Management Tool That Assists An Enterprise inDocument3 pagesSWOT Analysis: Definition: SWOT Analysis Is A Strategic Management Tool That Assists An Enterprise inVikram SahaNo ratings yet
- Ufa#Ed 2#Sol#Chap 06Document18 pagesUfa#Ed 2#Sol#Chap 06api-3824657No ratings yet
- Understanding The ToolDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The ToolSaratha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Genetral Electric Spot Light MatrixDocument4 pagesGenetral Electric Spot Light MatrixrajisumaNo ratings yet
- Metro 2Document7 pagesMetro 2Love SinghNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolDocument12 pagesUNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolNishath NawazNo ratings yet
- The BCG Matrix and GE9 MatrixDocument5 pagesThe BCG Matrix and GE9 MatrixAnshul MangalNo ratings yet
- PPL Viks ProjectDocument23 pagesPPL Viks ProjectVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix: Question Marks???Document6 pagesBCG Matrix: Question Marks???jagdish92No ratings yet
- Stability StrategyDocument19 pagesStability Strategyzakirno19248No ratings yet
- BCG ItcDocument92 pagesBCG Itcprachii09No ratings yet
- Strategic PlanningDocument36 pagesStrategic PlanningDinesh RaghavendraNo ratings yet
- StrengthsDocument5 pagesStrengthsMaria Christina Paredes ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- The Labyrinth Gladiator 2010Document17 pagesThe Labyrinth Gladiator 2010austermNo ratings yet
- Strategic Business UnitDocument4 pagesStrategic Business UnitRajesh WariseNo ratings yet
- Ans. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGDocument34 pagesAns. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGArti RahejaNo ratings yet
- Ans. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGDocument34 pagesAns. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGPPriyaTechNo ratings yet
- Good Returns On Capital ExpenditureDocument4 pagesGood Returns On Capital ExpenditureDe Leoz ImrNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Multi-Business Corporations Strategic ReviewDocument31 pagesStrategies For Multi-Business Corporations Strategic ReviewwordssmithNo ratings yet
- GE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsDocument15 pagesGE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsPratyay DasNo ratings yet
- DiversificationDocument27 pagesDiversificationPankaj VasudevNo ratings yet
- Strategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationDocument41 pagesStrategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationSwati JainNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Corporate Finance Fall 2011Document6 pagesAssignment # 1 Corporate Finance Fall 2011Madiha BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Boston Consulting GroupDocument6 pagesBoston Consulting GroupJaved ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument15 pagesSwot Analysistomin tominNo ratings yet
- Summary Report: RJET Task 1Document19 pagesSummary Report: RJET Task 1Hugo SolanoNo ratings yet
- BBA+LLB Question Papers Nov 2018 PDFDocument103 pagesBBA+LLB Question Papers Nov 2018 PDFSaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan: 1: Define Your BusinessDocument12 pagesMarketing Plan: 1: Define Your Businessdrken3No ratings yet
- Group3 FinalDocument10 pagesGroup3 FinalKolekarMakrandMahadeoNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document4 pagesPs 1Kevin TinNo ratings yet
- IbcmDocument11 pagesIbcmrahulhaldankarNo ratings yet
- Realistic - Constraints and Design - MethodsDocument6 pagesRealistic - Constraints and Design - MethodsAmr SamyNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions Markets and ServicesDocument2 pagesFinancial Institutions Markets and ServicesPavneet Kaur Bhatia100% (1)
- Foreign Direct Investment: Cemex'SDocument10 pagesForeign Direct Investment: Cemex'Sjacklee1918No ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument9 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPFazarizul HashidiNo ratings yet
- NELL PANTIG TRANSES CRWT-FINALSDocument5 pagesNELL PANTIG TRANSES CRWT-FINALSNELL JOSHUA PANTIGNo ratings yet
- 1994 Bart Van Steenbergen The Condition of Citizienship OCR PDFDocument94 pages1994 Bart Van Steenbergen The Condition of Citizienship OCR PDFRobinson ManilaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Productivity Theory of DistributionDocument8 pagesMarginal Productivity Theory of DistributionsamNo ratings yet
- CPAIM Couse SyllabusDocument48 pagesCPAIM Couse SyllabussajidtoshibaNo ratings yet
- Cape Economics Past Paper Solutions June 2008Document11 pagesCape Economics Past Paper Solutions June 2008Akeemjoseph50% (2)
- Alfred Sohn-Rethel 2 PDFDocument20 pagesAlfred Sohn-Rethel 2 PDFAshraf MansourNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics 1Document23 pagesManagerial Economics 1Xen Operation DPHNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economy QuizDocument2 pagesPakistan Economy QuizAmeer hamzaNo ratings yet
- Topic: DMM 3343 Assignment 1 Title: Inventory System Class: 1ZP58A Group: 3Document11 pagesTopic: DMM 3343 Assignment 1 Title: Inventory System Class: 1ZP58A Group: 3TailongKLNo ratings yet
- Elements of Cost: Expense TypesDocument17 pagesElements of Cost: Expense Typesسعيد الشوكانيNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) Stable and Unstable EquilibriumDocument29 pagesChapter (2) Stable and Unstable EquilibriumMostafa MohyNo ratings yet
- Dynamicsof Financial Intermediationand Manufacturing Outputs Growthin NigeriaDocument20 pagesDynamicsof Financial Intermediationand Manufacturing Outputs Growthin NigeriaAmeh AnyebeNo ratings yet
- Aldi AustraliaDocument435 pagesAldi AustraliaDataGroup Retailer AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - 1 Indian Economy On The Eve of IndependenceDocument33 pagesWork Sheet - 1 Indian Economy On The Eve of IndependenceAditya Shrivastava100% (1)
- I Et (Sy) 221111034123Document5 pagesI Et (Sy) 221111034123rakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- Research in Agribusiness and Value Chain (Abvm 14) : Compiled By: Milkessa Temesgen (MSC) Wondimagegn Mesfin (MSC)Document85 pagesResearch in Agribusiness and Value Chain (Abvm 14) : Compiled By: Milkessa Temesgen (MSC) Wondimagegn Mesfin (MSC)amna yousafNo ratings yet
- Workshop Distribution Channel Learning: John Orlando Moreno Instructor: Edwin Ferney Ortiz CardonaDocument3 pagesWorkshop Distribution Channel Learning: John Orlando Moreno Instructor: Edwin Ferney Ortiz CardonaJohn MorenoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Pre Board Examination in Agricultural Econonomics and MarketingDocument10 pagesSimulated Pre Board Examination in Agricultural Econonomics and MarketingMac Dwayne CarpesoNo ratings yet
The Company CAU
The Company CAU
Uploaded by
ayoubbagdadkhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Company CAU
The Company CAU
Uploaded by
ayoubbagdadkhCopyright:
Available Formats
The company CAU, specialized in turning, is located in the Arve Valley in Haute
Savoie and is facing difficulties in these times of financial crisis and highly
competitive global market. It has been suffering from a lack of investment for
several years due to insufficient financial resources. It remains a secondary
player in the turning market, known for the quality of its innovations and the
productivity of its workforce. Faced with liquidity problems, the company has
attempted to reduce all its costs, but the sources of economies of scale are
becoming limited due to the production capacities of the current equipment, which
has not been renewed for years.
To remain competitive against the competition, the company has lowered its prices,
especially in the automotive and household sectors. However, the director
emphasizes that the challenge for the company is to better understand its
environment from a strategic perspective while valuing its know-how, which is
currently underutilized due to the lack of investments allowing an upgrade. The
various strategic business areas in which the company has developed are not equally
important in terms of results and possible development paths.
At an extraordinary meeting at the end of 2010, the management controller and his
team proposed a study of the organization to address the following questions:
What are the strategic business areas on which CAU should focus?
How to plan strategic actions?
The director is well aware of the need to better control the company's activity and
the resulting performance. Therefore, he is particularly interested in an analysis
of the company's strategic business areas (SBUs) from a Boston Consulting Group
(BCG) perspective.
Intense Competition: CAU operates in a highly competitive global market,
particularly in sectors like automotive and household goods. Lowering prices to
remain competitive has put pressure on profit margins, further exacerbating
financial challenges.
Financial Constraints: The company has been experiencing financial constraints for
years, leading to a lack of investment in modernizing equipment and processes. This
has hindered its ability to improve productivity and innovate, making it difficult
to keep up with competitors.
Limited Production Capacity: Due to the lack of investment in equipment renewal,
CAU's production capacities are constrained. This limits the potential for
economies of scale and efficiency gains, making it challenging to reduce costs and
improve profitability.
Liquidity Problems: CAU is facing liquidity problems, which can impact its ability
to meet short-term financial obligations and invest in necessary upgrades and
improvements.
These problems combined poses significant challenges for CAU's sustainability and
growth. Addressing these issues will require an analysis of DAS of this company in
a point on view of BCG
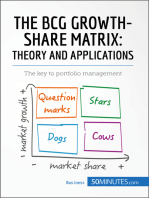
The BCG matrix is a strategic analysis tool developed by the Boston Consulting
Group in the late 1960s. Still widely used in corporate strategy, this matrix
allows companies to represent their portfolio of activities based on the growth
rate of the targeted market and the company's relative market share.
is where a company has high market share in a slow-growing industry. These units
typically generate cash in excess of the amount of cash needed to maintain the
business.
are units with low market share in a mature, slow-growing industry. These units
typically "break even", generating barely enough cash to maintain the business's
market share.
are businesses operating with a low market share in a high-growth market. They are
a starting point for most businesses. Question marks have a potential to gain
market share and become stars, and eventually cash cows when market growth slows.
are units with a high market share in a fast-growing industry. They are graduated
question marks with a market- or niche-leading trajectory
Stars require high funding to fight competitors and maintain their growth rate.
When industry growth slows, if they remain a niche leader or are amongst the market
leaders, stars become cash cows; otherwise, they become dogs due to low relative
market share.
Market Share Limitation: Market share is just one factor influencing competitive
strength, and its significance varies across industries. In some cases, market
share may not accurately reflect a company's competitive advantage or potential for
growth.
Simplistic Model: The BCG matrix oversimplifies complex business situations by
categorizing products or business units into only four quadrants based on two
dimensions. This can lead to overlooking important nuances and complexities within
the company's portfolio.
You might also like
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- SWOT of Sasol PDFDocument6 pagesSWOT of Sasol PDFRakib TusharNo ratings yet
- The Europeische Wirtschaftsgemeinchaft Berlin 1942 PDFDocument122 pagesThe Europeische Wirtschaftsgemeinchaft Berlin 1942 PDFAlex Diam100% (1)
- DiversificationDocument41 pagesDiversificationAnamika SenguptaNo ratings yet
- The BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementFrom EverandThe BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Principles of Price and Pricing (Rowley)Document11 pagesPrinciples of Price and Pricing (Rowley)Μιχάλης ΘεοχαρόπουλοςNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management of RECKEIIT BENKSEIERDocument6 pagesSupply Chain Management of RECKEIIT BENKSEIERFuhad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Capital AllocationDocument32 pagesStrategy and Capital AllocationsonalNo ratings yet
- BCG Notes FinalDocument10 pagesBCG Notes FinalHarsora UrvilNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix (Growth Share Matrix)Document3 pagesBCG Matrix (Growth Share Matrix)Ansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bcg-Matrix SVGDocument7 pagesBcg-Matrix SVGPriyanka KansaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Winning Markets Through Market Oriented Strategic Planning - KSKDocument58 pagesChapter 4 - Winning Markets Through Market Oriented Strategic Planning - KSKWalid Ben HuseinNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument10 pagesBCG MatrixSimone BandrawalaNo ratings yet
- 1-Marketing-Chapter4and5-Product Portfolio Analysis (Including The BCG, GE Models)Document34 pages1-Marketing-Chapter4and5-Product Portfolio Analysis (Including The BCG, GE Models)WilsfunNo ratings yet
- Paper15 Solution PDFDocument22 pagesPaper15 Solution PDFDerick TanNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument6 pagesBCG MatrixSpandana AchantaNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument34 pagesBCG MatrixSaurabGhimireNo ratings yet
- Ia Bs MatrixDocument26 pagesIa Bs Matrixrscjat0% (1)
- Strategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationDocument41 pagesStrategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationSamraat SanyalNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument4 pagesBCG MatrixRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Invest in and Which Ones Should Be DivestedDocument5 pagesBCG Growth-Share Matrix: Invest in and Which Ones Should Be DivestedChanthini VinayagamNo ratings yet
- Turnaround ManagementDocument12 pagesTurnaround ManagementpriteshhegdeNo ratings yet
- BCG GrowthDocument7 pagesBCG GrowthchienNo ratings yet
- Final Theory - Marketing STRGDocument81 pagesFinal Theory - Marketing STRGkartkgala123No ratings yet
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument26 pagesGE MatrixFijo JoseNo ratings yet
- Business Portfolio AnalysisDocument20 pagesBusiness Portfolio AnalysissoumitrabehuraNo ratings yet
- Assignment of SMDocument15 pagesAssignment of SMPari KarrhaNo ratings yet
- Growth - Share - Matrix - Bahasa - Indonesia (2) enDocument6 pagesGrowth - Share - Matrix - Bahasa - Indonesia (2) enBlack EyesNo ratings yet
- Analysing Strategy (BCG Matrix)Document6 pagesAnalysing Strategy (BCG Matrix)yadavpankaj1992No ratings yet
- SM 7 PortfoliosDocument31 pagesSM 7 PortfoliosCGM MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Product Portfolio PlanningDocument35 pagesProduct Portfolio PlanningPunit BadalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Corporate Strategy and Strategic PortfolioDocument31 pagesStrategic Management: Corporate Strategy and Strategic PortfolioahlamqanabitaNo ratings yet
- Types of Marketing ModelDocument7 pagesTypes of Marketing ModelBlack EyesNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis: Definition: SWOT Analysis Is A Strategic Management Tool That Assists An Enterprise inDocument3 pagesSWOT Analysis: Definition: SWOT Analysis Is A Strategic Management Tool That Assists An Enterprise inVikram SahaNo ratings yet
- Ufa#Ed 2#Sol#Chap 06Document18 pagesUfa#Ed 2#Sol#Chap 06api-3824657No ratings yet
- Understanding The ToolDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The ToolSaratha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Genetral Electric Spot Light MatrixDocument4 pagesGenetral Electric Spot Light MatrixrajisumaNo ratings yet
- Metro 2Document7 pagesMetro 2Love SinghNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolDocument12 pagesUNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolNishath NawazNo ratings yet
- The BCG Matrix and GE9 MatrixDocument5 pagesThe BCG Matrix and GE9 MatrixAnshul MangalNo ratings yet
- PPL Viks ProjectDocument23 pagesPPL Viks ProjectVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix: Question Marks???Document6 pagesBCG Matrix: Question Marks???jagdish92No ratings yet
- Stability StrategyDocument19 pagesStability Strategyzakirno19248No ratings yet
- BCG ItcDocument92 pagesBCG Itcprachii09No ratings yet
- Strategic PlanningDocument36 pagesStrategic PlanningDinesh RaghavendraNo ratings yet
- StrengthsDocument5 pagesStrengthsMaria Christina Paredes ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- The Labyrinth Gladiator 2010Document17 pagesThe Labyrinth Gladiator 2010austermNo ratings yet
- Strategic Business UnitDocument4 pagesStrategic Business UnitRajesh WariseNo ratings yet
- Ans. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGDocument34 pagesAns. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGArti RahejaNo ratings yet
- Ans. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGDocument34 pagesAns. The BCG Matrix Is A Portfolio Management Tool Used in Product Life Cycle. BCGPPriyaTechNo ratings yet
- Good Returns On Capital ExpenditureDocument4 pagesGood Returns On Capital ExpenditureDe Leoz ImrNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Multi-Business Corporations Strategic ReviewDocument31 pagesStrategies For Multi-Business Corporations Strategic ReviewwordssmithNo ratings yet
- GE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsDocument15 pagesGE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsPratyay DasNo ratings yet
- DiversificationDocument27 pagesDiversificationPankaj VasudevNo ratings yet
- Strategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationDocument41 pagesStrategy Formulation: Strategies For Growth and DiversificationSwati JainNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Corporate Finance Fall 2011Document6 pagesAssignment # 1 Corporate Finance Fall 2011Madiha BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Boston Consulting GroupDocument6 pagesBoston Consulting GroupJaved ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument15 pagesSwot Analysistomin tominNo ratings yet
- Summary Report: RJET Task 1Document19 pagesSummary Report: RJET Task 1Hugo SolanoNo ratings yet
- BBA+LLB Question Papers Nov 2018 PDFDocument103 pagesBBA+LLB Question Papers Nov 2018 PDFSaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan: 1: Define Your BusinessDocument12 pagesMarketing Plan: 1: Define Your Businessdrken3No ratings yet
- Group3 FinalDocument10 pagesGroup3 FinalKolekarMakrandMahadeoNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document4 pagesPs 1Kevin TinNo ratings yet
- IbcmDocument11 pagesIbcmrahulhaldankarNo ratings yet
- Realistic - Constraints and Design - MethodsDocument6 pagesRealistic - Constraints and Design - MethodsAmr SamyNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions Markets and ServicesDocument2 pagesFinancial Institutions Markets and ServicesPavneet Kaur Bhatia100% (1)
- Foreign Direct Investment: Cemex'SDocument10 pagesForeign Direct Investment: Cemex'Sjacklee1918No ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument9 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPFazarizul HashidiNo ratings yet
- NELL PANTIG TRANSES CRWT-FINALSDocument5 pagesNELL PANTIG TRANSES CRWT-FINALSNELL JOSHUA PANTIGNo ratings yet
- 1994 Bart Van Steenbergen The Condition of Citizienship OCR PDFDocument94 pages1994 Bart Van Steenbergen The Condition of Citizienship OCR PDFRobinson ManilaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Productivity Theory of DistributionDocument8 pagesMarginal Productivity Theory of DistributionsamNo ratings yet
- CPAIM Couse SyllabusDocument48 pagesCPAIM Couse SyllabussajidtoshibaNo ratings yet
- Cape Economics Past Paper Solutions June 2008Document11 pagesCape Economics Past Paper Solutions June 2008Akeemjoseph50% (2)
- Alfred Sohn-Rethel 2 PDFDocument20 pagesAlfred Sohn-Rethel 2 PDFAshraf MansourNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics 1Document23 pagesManagerial Economics 1Xen Operation DPHNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economy QuizDocument2 pagesPakistan Economy QuizAmeer hamzaNo ratings yet
- Topic: DMM 3343 Assignment 1 Title: Inventory System Class: 1ZP58A Group: 3Document11 pagesTopic: DMM 3343 Assignment 1 Title: Inventory System Class: 1ZP58A Group: 3TailongKLNo ratings yet
- Elements of Cost: Expense TypesDocument17 pagesElements of Cost: Expense Typesسعيد الشوكانيNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) Stable and Unstable EquilibriumDocument29 pagesChapter (2) Stable and Unstable EquilibriumMostafa MohyNo ratings yet
- Dynamicsof Financial Intermediationand Manufacturing Outputs Growthin NigeriaDocument20 pagesDynamicsof Financial Intermediationand Manufacturing Outputs Growthin NigeriaAmeh AnyebeNo ratings yet
- Aldi AustraliaDocument435 pagesAldi AustraliaDataGroup Retailer AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - 1 Indian Economy On The Eve of IndependenceDocument33 pagesWork Sheet - 1 Indian Economy On The Eve of IndependenceAditya Shrivastava100% (1)
- I Et (Sy) 221111034123Document5 pagesI Et (Sy) 221111034123rakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- Research in Agribusiness and Value Chain (Abvm 14) : Compiled By: Milkessa Temesgen (MSC) Wondimagegn Mesfin (MSC)Document85 pagesResearch in Agribusiness and Value Chain (Abvm 14) : Compiled By: Milkessa Temesgen (MSC) Wondimagegn Mesfin (MSC)amna yousafNo ratings yet
- Workshop Distribution Channel Learning: John Orlando Moreno Instructor: Edwin Ferney Ortiz CardonaDocument3 pagesWorkshop Distribution Channel Learning: John Orlando Moreno Instructor: Edwin Ferney Ortiz CardonaJohn MorenoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Pre Board Examination in Agricultural Econonomics and MarketingDocument10 pagesSimulated Pre Board Examination in Agricultural Econonomics and MarketingMac Dwayne CarpesoNo ratings yet