Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media and Information in Communication)
Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media and Information in Communication)
Uploaded by
Jean DaclesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- How False News Can Spread SVDocument2 pagesHow False News Can Spread SVEffie VlachouNo ratings yet
- Smoke Extraction System Sample CalculationDocument5 pagesSmoke Extraction System Sample Calculationsmcsaminda100% (3)
- Definition of Fake News RRLSDocument3 pagesDefinition of Fake News RRLSABAÑO, AZHIRA MHAE HUMSS 12-ANo ratings yet
- Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument24 pagesResponsible Use of Media and InformationErich Magsisi100% (1)
- Media and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document18 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 - Module 3Erika LayogNo ratings yet
- G 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument49 pagesG 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationGedion CrossNo ratings yet
- WARDLE Understanding Information Disorder - First DraftDocument32 pagesWARDLE Understanding Information Disorder - First DraftThamara MachadoNo ratings yet
- G 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument45 pagesG 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and Informationnoeme babiaNo ratings yet
- Fake News, Misinformation and Disinformation Written Report (GRP 3)Document6 pagesFake News, Misinformation and Disinformation Written Report (GRP 3)Sheila Mae CaballaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (Types of Media)Document4 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (Types of Media)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media LiteracyDocument40 pagesMedia LiteracyChristine RomanillosNo ratings yet
- Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument20 pagesResponsible Use of Media and InformationErich MagsisiNo ratings yet
- Information DisorderDocument18 pagesInformation DisordercraccanboomNo ratings yet
- Humss 11 A Group9 Chapter 2Document17 pagesHumss 11 A Group9 Chapter 2Phyre Lei GazziniNo ratings yet
- Responsible Media User Lesson 3Document52 pagesResponsible Media User Lesson 3parconangelamarillieNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy 2 Grading Lesson 5: Media & Information SourcesDocument8 pagesMedia and Information Literacy 2 Grading Lesson 5: Media & Information SourcesJanusNo ratings yet
- Mil Handouts Module-11-18Document8 pagesMil Handouts Module-11-18Marrianne Grace MantujacNo ratings yet
- Q1 W3-4 MIL Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument6 pagesQ1 W3-4 MIL Responsible Use of Media and InformationJunrey BelandoNo ratings yet
- Issues Concerning Media and InformationDocument3 pagesIssues Concerning Media and InformationAnna Marie BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- ParisDocument2 pagesParisHanna VelnerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument66 pagesLesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationgojomylomlNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Thuy Linh - Lesson 5Document4 pagesNguyen Thuy Linh - Lesson 5Linh ThuỳNo ratings yet
- PumboDocument98 pagesPumboIan ScheuflerNo ratings yet
- Information DisorderDocument29 pagesInformation DisorderLinard MalubayNo ratings yet
- MY Template - Fake NewsDocument4 pagesMY Template - Fake NewsnajihahNo ratings yet
- Misinformation and Disinformation Worksheets SampleDocument15 pagesMisinformation and Disinformation Worksheets SampleEmma Elizabeth SteeleNo ratings yet
- Not Everything You Read Is True Fake News Detection Using Machine Learning AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesNot Everything You Read Is True Fake News Detection Using Machine Learning Algorithmssba23088No ratings yet
- Report Lesson 10Document19 pagesReport Lesson 10Milyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument17 pagesMil ReviewerHeaven Krysthel Bless R. SacsacNo ratings yet
- MIL Q3 Week 3 4 SLMDocument10 pagesMIL Q3 Week 3 4 SLMKylene JallaNo ratings yet
- Fighting Fake News in 2022Document4 pagesFighting Fake News in 2022The Mehtab ShowNo ratings yet
- HUMSS-C Practical Research 1 (Group 5)Document19 pagesHUMSS-C Practical Research 1 (Group 5)yolayolayola1111No ratings yet
- 181 Aguinaldo Highway, Lalaan I, Silang, Cavite (046) 423 - 3403Document11 pages181 Aguinaldo Highway, Lalaan I, Silang, Cavite (046) 423 - 3403katlinajuanaNo ratings yet
- Propaganda Reading PDFDocument11 pagesPropaganda Reading PDF温雪儿100% (1)
- Eng CAT Essay ResearchDocument3 pagesEng CAT Essay ResearchIsha KalyanNo ratings yet
- Mil Reviewer 1ST Q ExaminationDocument12 pagesMil Reviewer 1ST Q ExaminationChristine JacobNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument5 pagesMIL ReviewerKristine Joy DigaNo ratings yet
- Teaching About Propaganda An Examination of The HiDocument12 pagesTeaching About Propaganda An Examination of The HiOSINT UserNo ratings yet
- Responsible Use of Media and Information: LessonDocument20 pagesResponsible Use of Media and Information: LessonFil Am Tugade67% (3)
- Social Media and PoliticsDocument15 pagesSocial Media and PoliticstriandriaNo ratings yet
- A Research Report On The Negative Effects of Fake News To The Selected Grade 10 Students of PinagbuhaDocument14 pagesA Research Report On The Negative Effects of Fake News To The Selected Grade 10 Students of PinagbuhaDhilanGamersNo ratings yet
- Fake News InfographicDocument1 pageFake News InfographicLuis HcNo ratings yet
- Seminary Work FinalDocument16 pagesSeminary Work FinalStrahinja RacNo ratings yet
- "Misinformation" vs. "Disinformation" - Get Informed On The DifferenceDocument8 pages"Misinformation" vs. "Disinformation" - Get Informed On The DifferencemycaseNo ratings yet
- Handout For Media LiteracyDocument1 pageHandout For Media LiteracyChristian Joy Elandag JacobeNo ratings yet
- BARTRON - 2019 - Critical Literacy in The Post-Truth Media LandscapeDocument13 pagesBARTRON - 2019 - Critical Literacy in The Post-Truth Media LandscapeLeonardo MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument12 pagesLesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationIan Daniel RosarioNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument4 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyFATIMA FAYEA S. MEJORADANo ratings yet
- Media Ethics Lecture 2Document45 pagesMedia Ethics Lecture 2Lojina ElkadyNo ratings yet
- Combating Disinformation in A Social Media AgeDocument23 pagesCombating Disinformation in A Social Media Agenicole100% (1)
- Fake NewsDocument3 pagesFake NewsNoamNo ratings yet
- Fake NewsDocument3 pagesFake NewsNoamNo ratings yet
- Caluya Keziah Linnae T. (FPS Ramsay)Document2 pagesCaluya Keziah Linnae T. (FPS Ramsay)Zea Maize CaluyaNo ratings yet
- q1 M 1 2 Baquilar Media and Info. LitDocument8 pagesq1 M 1 2 Baquilar Media and Info. LitRea Mae Josefa TarocNo ratings yet
- Types of MediaDocument28 pagesTypes of MediaGeorgina TorresNo ratings yet
- Media LiteracyDocument5 pagesMedia LiteracyLewis A. PearlNo ratings yet
- MIL HandoutsDocument5 pagesMIL Handoutskian BesanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditDocument12 pagesGrade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditJomari BandilloNo ratings yet
- Information Disorder Digital AWDocument32 pagesInformation Disorder Digital AWAdrian Gonzalez100% (1)
- The Different Types of Mis and DisinformationDocument8 pagesThe Different Types of Mis and DisinformationPaolo Lorenzo LoraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (The Human Person in The Society)Document6 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (The Human Person in The Society)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media in The Communication Process)Document2 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (The Role of Media in The Communication Process)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Document2 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Intersubjectivity)Document4 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Intersubjectivity)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Light-Dependent Reactions)Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Light-Dependent Reactions)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Document2 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (Circulation - Transport)Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (Circulation - Transport)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Freedom of The Human Person)Document4 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Freedom of The Human Person)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (Taxonomy)Document20 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (Taxonomy)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Stratification)Document5 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Stratification)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 5Document5 pagesPerdev Reviewer 5Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Structure)Document6 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Structure)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Factors Affecting Enzymes)Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Factors Affecting Enzymes)Jean Dacles100% (1)
- General Biology 1 (Photosynthesis)Document3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Photosynthesis)Jean Dacles100% (1)
- Earth & Life Science Module 2Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 2Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 3Document4 pagesPerdev Reviewer 3Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 1Document7 pagesPerdev Reviewer 1Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 2Document5 pagesPerdev Reviewer 2Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Module 3Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 3Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 4Document7 pagesPerdev Reviewer 4Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- E Tech Assignment NotesDocument3 pagesE Tech Assignment NotesJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Module 4Document5 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 4Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Module 5Document7 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 5Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth ScieneeeeeeeeeeDocument7 pagesEarth ScieneeeeeeeeeeJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Q1 Week 3Document2 pagesPersonal Development Q1 Week 3Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer On 21ST Century Literature (Timeline)Document6 pagesReviewer On 21ST Century Literature (Timeline)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- E Tech A4Document1 pageE Tech A4Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral Communication in ContextDocument27 pagesReviewer in Oral Communication in ContextJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Pe and HealthDocument16 pagesReviewer in Pe and HealthJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- EssaDocument2 pagesEssaJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- RFP Human Resource Management SystemDocument15 pagesRFP Human Resource Management SystemMd. Mofakker Morshed Khan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Wifi LBS - CiscoDocument206 pagesWifi LBS - Cisconassr_ismailNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For MID I CNDocument14 pagesImportant Questions For MID I CN20H51A0540-NAKKA SREEKAR B.Tech CSE (2020-24)No ratings yet
- Website ErrorDocument5 pagesWebsite ErrorJosé DavidNo ratings yet
- Category:UR Madam / Sir,: Please Affix Your Recent Passport Size Colour Photograph & Sign AcrossDocument2 pagesCategory:UR Madam / Sir,: Please Affix Your Recent Passport Size Colour Photograph & Sign AcrossVasu Ram JayanthNo ratings yet
- 2021 DBaaS Security Architect and SolutionsDocument26 pages2021 DBaaS Security Architect and Solutionsluke luNo ratings yet
- End of Course World Geography: Form H0117, CORE 1Document42 pagesEnd of Course World Geography: Form H0117, CORE 1kristymadimikeNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Document5 pagesBlockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Chiraz Elhog0% (1)
- Free Bhel Transformer Book PDFDocument4 pagesFree Bhel Transformer Book PDFMilan ShahNo ratings yet
- Handel e RuspoliDocument57 pagesHandel e RuspoliAndrea100% (1)
- International Dairy Journal: D.K. Hickey, T.P. Guinee, J. Hou, M.G. WilkinsonDocument6 pagesInternational Dairy Journal: D.K. Hickey, T.P. Guinee, J. Hou, M.G. WilkinsonBianca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Cyctocyle - Care PlanDocument22 pagesCyctocyle - Care Planarchana vermaNo ratings yet
- PetretecDocument8 pagesPetretecVenkatesan KrishnachariNo ratings yet
- 22 BÀI MẪU TASK 2 TỪ ĐỀ THI THẬT 2020 BY NGOCBACHDocument101 pages22 BÀI MẪU TASK 2 TỪ ĐỀ THI THẬT 2020 BY NGOCBACHCô TốngNo ratings yet
- Yashoda Singh Indian Coins Lots 1001-1242Document29 pagesYashoda Singh Indian Coins Lots 1001-1242Ashwin SevariaNo ratings yet
- Management of Cramps During Hemodialysis: Approved By: Write Name of The Unit Nursing HeadDocument7 pagesManagement of Cramps During Hemodialysis: Approved By: Write Name of The Unit Nursing HeadSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Operating Range Recommended Applications: Mechanical Seals - Mechanical Seals For Pumps - Pusher SealsDocument3 pagesOperating Range Recommended Applications: Mechanical Seals - Mechanical Seals For Pumps - Pusher Sealsneurolepsia3790No ratings yet
- Safety Grating CatalogDocument22 pagesSafety Grating CatalogzhukeeNo ratings yet
- On Advertising A Marxist CritiqueDocument13 pagesOn Advertising A Marxist CritiqueKisholoy AntiBrahminNo ratings yet
- NI-Predictive Maintenance and Machine Health MonitoringDocument34 pagesNI-Predictive Maintenance and Machine Health Monitoringtườngt_14No ratings yet
- Topic On CC11Document3 pagesTopic On CC11Free HitNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans WK 26Document7 pagesLesson Plans WK 26api-280840865No ratings yet
- Standard DC Output: Simplified Internal Diagram of The Charger's Output ConnectionsDocument1 pageStandard DC Output: Simplified Internal Diagram of The Charger's Output ConnectionstoufikNo ratings yet
- Coconut: Donesian Export Pro IleDocument39 pagesCoconut: Donesian Export Pro Ile764fqbbnf2No ratings yet
- Class - 8 Chapter - 3 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsDocument6 pagesClass - 8 Chapter - 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics7A04Aditya MayankNo ratings yet
- BTD Course FileDocument23 pagesBTD Course FilePrashant S HadagaliNo ratings yet
- Methods-Time Measurement: MODAPTS Technique. This Technique Was Introduced in 1966 byDocument2 pagesMethods-Time Measurement: MODAPTS Technique. This Technique Was Introduced in 1966 byChisom IkengwuNo ratings yet
- Section 2 Digital OutputDocument1 pageSection 2 Digital Outputsamim_khNo ratings yet
- Semikron Datasheet SKB 30Document3 pagesSemikron Datasheet SKB 30Kleber Milton de SouzaNo ratings yet
Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media and Information in Communication)
Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media and Information in Communication)
Uploaded by
Jean DaclesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media and Information in Communication)
Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media and Information in Communication)
Uploaded by
Jean DaclesCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY
THE ROLE OF MEDIA AND INFORMATION IN COMMUNICATION
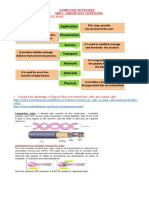
MEDIA
→ The main ways that large numbers of people receive information and
entertainment, that is television, radio, newspapers, and the internet (Oxford
Learner’s Dictionaries).
→ Refers to the combination of physical objects used to communicate or mass
communication through physical objects such as radio, television, computers, or
film, etc. (UNESCO Media and Information Literacy Curriculum for Teachers).
→ Something we use when we want to communicate with people indirectly, rather
than in person or by face-to-face contact. (David Buckingham, 2003)
→ Refers to the print medium of communication, which includes all newspapers,
periodicals, magazines, journals, and publications and all advertising therein,
and billboards, neon signs, and the like and the broadcast medium of
communication, which includes radio and television broadcasting in all their aspects
and all other cinematographic or radio promotions and advertising. (Presidential
Decree No. 1019 (1976)).
THE ROLE OF MEDIA AND INFORMATION IN COMMUNICATION
1. It makes the world a smaller place.
2. It makes communication convenient.
3. It shapes public opinion.
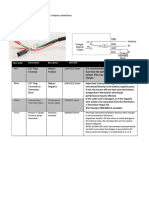
INFORMATION DISORDER
THREE (3) CATEGORIES OF INFORMATION DISORDER
1. MISINFORMATION
2. DISINFORMATION
3. MAL-INFORMATION
MISINFORMATION
→ Refers to information that is false, but the person sharing or disseminating is
unknowingly perceives it as something true.
A. FALSE CONNECTION
→ When headlines or visuals do not support the content.
B. MISLEADING CONTENT
→ By cropping photos or choosing quotes or statistics selectively.
DISINFORMATION
→ Refers to the content that contains false information with the deliberate intention
to mislead or deceive the audience.
A. FALSE CONTENT
→ When genuine content is re-circuited out of its original context.
B. IMPOSTER CONTENT
→ Persons’ bylines used alongside articles they did not write, or
organizations’ logos used in videos or images they did not create.
C. MANIPULATED CONTENT
→ When genuine content is manipulated to deceive.
D. FABRICATED CONTENT
→ Fabricated “news sites” or fabricated visuals.
MAL-INFORMATION
→ Refers to information that is based on reality but is used to inflict harm.
EXAMPLES:
1. Leaks to the press of private information for personal or corporate
interest (e.g., revenge porn).
2. Using a picture (e.g., a dead child, with no context or false context) in an
effort to ignite hatred of a particular ethnic group.
You might also like
- How False News Can Spread SVDocument2 pagesHow False News Can Spread SVEffie VlachouNo ratings yet
- Smoke Extraction System Sample CalculationDocument5 pagesSmoke Extraction System Sample Calculationsmcsaminda100% (3)
- Definition of Fake News RRLSDocument3 pagesDefinition of Fake News RRLSABAÑO, AZHIRA MHAE HUMSS 12-ANo ratings yet
- Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument24 pagesResponsible Use of Media and InformationErich Magsisi100% (1)
- Media and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document18 pagesMedia and Information Literacy: Quarter 1 - Module 3Erika LayogNo ratings yet
- G 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument49 pagesG 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationGedion CrossNo ratings yet
- WARDLE Understanding Information Disorder - First DraftDocument32 pagesWARDLE Understanding Information Disorder - First DraftThamara MachadoNo ratings yet
- G 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument45 pagesG 12 - Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and Informationnoeme babiaNo ratings yet
- Fake News, Misinformation and Disinformation Written Report (GRP 3)Document6 pagesFake News, Misinformation and Disinformation Written Report (GRP 3)Sheila Mae CaballaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (Types of Media)Document4 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (Types of Media)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media LiteracyDocument40 pagesMedia LiteracyChristine RomanillosNo ratings yet
- Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument20 pagesResponsible Use of Media and InformationErich MagsisiNo ratings yet
- Information DisorderDocument18 pagesInformation DisordercraccanboomNo ratings yet
- Humss 11 A Group9 Chapter 2Document17 pagesHumss 11 A Group9 Chapter 2Phyre Lei GazziniNo ratings yet
- Responsible Media User Lesson 3Document52 pagesResponsible Media User Lesson 3parconangelamarillieNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy 2 Grading Lesson 5: Media & Information SourcesDocument8 pagesMedia and Information Literacy 2 Grading Lesson 5: Media & Information SourcesJanusNo ratings yet
- Mil Handouts Module-11-18Document8 pagesMil Handouts Module-11-18Marrianne Grace MantujacNo ratings yet
- Q1 W3-4 MIL Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument6 pagesQ1 W3-4 MIL Responsible Use of Media and InformationJunrey BelandoNo ratings yet
- Issues Concerning Media and InformationDocument3 pagesIssues Concerning Media and InformationAnna Marie BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- ParisDocument2 pagesParisHanna VelnerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument66 pagesLesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationgojomylomlNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Thuy Linh - Lesson 5Document4 pagesNguyen Thuy Linh - Lesson 5Linh ThuỳNo ratings yet
- PumboDocument98 pagesPumboIan ScheuflerNo ratings yet
- Information DisorderDocument29 pagesInformation DisorderLinard MalubayNo ratings yet
- MY Template - Fake NewsDocument4 pagesMY Template - Fake NewsnajihahNo ratings yet
- Misinformation and Disinformation Worksheets SampleDocument15 pagesMisinformation and Disinformation Worksheets SampleEmma Elizabeth SteeleNo ratings yet
- Not Everything You Read Is True Fake News Detection Using Machine Learning AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesNot Everything You Read Is True Fake News Detection Using Machine Learning Algorithmssba23088No ratings yet
- Report Lesson 10Document19 pagesReport Lesson 10Milyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument17 pagesMil ReviewerHeaven Krysthel Bless R. SacsacNo ratings yet
- MIL Q3 Week 3 4 SLMDocument10 pagesMIL Q3 Week 3 4 SLMKylene JallaNo ratings yet
- Fighting Fake News in 2022Document4 pagesFighting Fake News in 2022The Mehtab ShowNo ratings yet
- HUMSS-C Practical Research 1 (Group 5)Document19 pagesHUMSS-C Practical Research 1 (Group 5)yolayolayola1111No ratings yet
- 181 Aguinaldo Highway, Lalaan I, Silang, Cavite (046) 423 - 3403Document11 pages181 Aguinaldo Highway, Lalaan I, Silang, Cavite (046) 423 - 3403katlinajuanaNo ratings yet
- Propaganda Reading PDFDocument11 pagesPropaganda Reading PDF温雪儿100% (1)
- Eng CAT Essay ResearchDocument3 pagesEng CAT Essay ResearchIsha KalyanNo ratings yet
- Mil Reviewer 1ST Q ExaminationDocument12 pagesMil Reviewer 1ST Q ExaminationChristine JacobNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument5 pagesMIL ReviewerKristine Joy DigaNo ratings yet
- Teaching About Propaganda An Examination of The HiDocument12 pagesTeaching About Propaganda An Examination of The HiOSINT UserNo ratings yet
- Responsible Use of Media and Information: LessonDocument20 pagesResponsible Use of Media and Information: LessonFil Am Tugade67% (3)
- Social Media and PoliticsDocument15 pagesSocial Media and PoliticstriandriaNo ratings yet
- A Research Report On The Negative Effects of Fake News To The Selected Grade 10 Students of PinagbuhaDocument14 pagesA Research Report On The Negative Effects of Fake News To The Selected Grade 10 Students of PinagbuhaDhilanGamersNo ratings yet
- Fake News InfographicDocument1 pageFake News InfographicLuis HcNo ratings yet
- Seminary Work FinalDocument16 pagesSeminary Work FinalStrahinja RacNo ratings yet
- "Misinformation" vs. "Disinformation" - Get Informed On The DifferenceDocument8 pages"Misinformation" vs. "Disinformation" - Get Informed On The DifferencemycaseNo ratings yet
- Handout For Media LiteracyDocument1 pageHandout For Media LiteracyChristian Joy Elandag JacobeNo ratings yet
- BARTRON - 2019 - Critical Literacy in The Post-Truth Media LandscapeDocument13 pagesBARTRON - 2019 - Critical Literacy in The Post-Truth Media LandscapeLeonardo MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationDocument12 pagesLesson 3 Responsible Use of Media and InformationIan Daniel RosarioNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument4 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyFATIMA FAYEA S. MEJORADANo ratings yet
- Media Ethics Lecture 2Document45 pagesMedia Ethics Lecture 2Lojina ElkadyNo ratings yet
- Combating Disinformation in A Social Media AgeDocument23 pagesCombating Disinformation in A Social Media Agenicole100% (1)
- Fake NewsDocument3 pagesFake NewsNoamNo ratings yet
- Fake NewsDocument3 pagesFake NewsNoamNo ratings yet
- Caluya Keziah Linnae T. (FPS Ramsay)Document2 pagesCaluya Keziah Linnae T. (FPS Ramsay)Zea Maize CaluyaNo ratings yet
- q1 M 1 2 Baquilar Media and Info. LitDocument8 pagesq1 M 1 2 Baquilar Media and Info. LitRea Mae Josefa TarocNo ratings yet
- Types of MediaDocument28 pagesTypes of MediaGeorgina TorresNo ratings yet
- Media LiteracyDocument5 pagesMedia LiteracyLewis A. PearlNo ratings yet
- MIL HandoutsDocument5 pagesMIL Handoutskian BesanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditDocument12 pagesGrade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week4 Final EditJomari BandilloNo ratings yet
- Information Disorder Digital AWDocument32 pagesInformation Disorder Digital AWAdrian Gonzalez100% (1)
- The Different Types of Mis and DisinformationDocument8 pagesThe Different Types of Mis and DisinformationPaolo Lorenzo LoraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (The Human Person in The Society)Document6 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (The Human Person in The Society)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (The Role of Media in The Communication Process)Document2 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (The Role of Media in The Communication Process)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Document2 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Intersubjectivity)Document4 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Intersubjectivity)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Light-Dependent Reactions)Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Light-Dependent Reactions)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Document2 pagesMedia and Information Literacy (Evolution of Traditional Media To New Media)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (Circulation - Transport)Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (Circulation - Transport)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Freedom of The Human Person)Document4 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person (Freedom of The Human Person)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (Taxonomy)Document20 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (Taxonomy)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Stratification)Document5 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Stratification)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 5Document5 pagesPerdev Reviewer 5Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Structure)Document6 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Social Structure)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 (Factors Affecting Enzymes)Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Factors Affecting Enzymes)Jean Dacles100% (1)
- General Biology 1 (Photosynthesis)Document3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (Photosynthesis)Jean Dacles100% (1)
- Earth & Life Science Module 2Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 2Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 3Document4 pagesPerdev Reviewer 3Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 1Document7 pagesPerdev Reviewer 1Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 2Document5 pagesPerdev Reviewer 2Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Module 3Document6 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 3Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Perdev Reviewer 4Document7 pagesPerdev Reviewer 4Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- E Tech Assignment NotesDocument3 pagesE Tech Assignment NotesJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Module 4Document5 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 4Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Module 5Document7 pagesEarth & Life Science Module 5Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Earth ScieneeeeeeeeeeDocument7 pagesEarth ScieneeeeeeeeeeJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Q1 Week 3Document2 pagesPersonal Development Q1 Week 3Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer On 21ST Century Literature (Timeline)Document6 pagesReviewer On 21ST Century Literature (Timeline)Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- E Tech A4Document1 pageE Tech A4Jean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral Communication in ContextDocument27 pagesReviewer in Oral Communication in ContextJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Pe and HealthDocument16 pagesReviewer in Pe and HealthJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- EssaDocument2 pagesEssaJean DaclesNo ratings yet
- RFP Human Resource Management SystemDocument15 pagesRFP Human Resource Management SystemMd. Mofakker Morshed Khan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Wifi LBS - CiscoDocument206 pagesWifi LBS - Cisconassr_ismailNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For MID I CNDocument14 pagesImportant Questions For MID I CN20H51A0540-NAKKA SREEKAR B.Tech CSE (2020-24)No ratings yet
- Website ErrorDocument5 pagesWebsite ErrorJosé DavidNo ratings yet
- Category:UR Madam / Sir,: Please Affix Your Recent Passport Size Colour Photograph & Sign AcrossDocument2 pagesCategory:UR Madam / Sir,: Please Affix Your Recent Passport Size Colour Photograph & Sign AcrossVasu Ram JayanthNo ratings yet
- 2021 DBaaS Security Architect and SolutionsDocument26 pages2021 DBaaS Security Architect and Solutionsluke luNo ratings yet
- End of Course World Geography: Form H0117, CORE 1Document42 pagesEnd of Course World Geography: Form H0117, CORE 1kristymadimikeNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Document5 pagesBlockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Chiraz Elhog0% (1)
- Free Bhel Transformer Book PDFDocument4 pagesFree Bhel Transformer Book PDFMilan ShahNo ratings yet
- Handel e RuspoliDocument57 pagesHandel e RuspoliAndrea100% (1)
- International Dairy Journal: D.K. Hickey, T.P. Guinee, J. Hou, M.G. WilkinsonDocument6 pagesInternational Dairy Journal: D.K. Hickey, T.P. Guinee, J. Hou, M.G. WilkinsonBianca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Cyctocyle - Care PlanDocument22 pagesCyctocyle - Care Planarchana vermaNo ratings yet
- PetretecDocument8 pagesPetretecVenkatesan KrishnachariNo ratings yet
- 22 BÀI MẪU TASK 2 TỪ ĐỀ THI THẬT 2020 BY NGOCBACHDocument101 pages22 BÀI MẪU TASK 2 TỪ ĐỀ THI THẬT 2020 BY NGOCBACHCô TốngNo ratings yet
- Yashoda Singh Indian Coins Lots 1001-1242Document29 pagesYashoda Singh Indian Coins Lots 1001-1242Ashwin SevariaNo ratings yet
- Management of Cramps During Hemodialysis: Approved By: Write Name of The Unit Nursing HeadDocument7 pagesManagement of Cramps During Hemodialysis: Approved By: Write Name of The Unit Nursing HeadSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Operating Range Recommended Applications: Mechanical Seals - Mechanical Seals For Pumps - Pusher SealsDocument3 pagesOperating Range Recommended Applications: Mechanical Seals - Mechanical Seals For Pumps - Pusher Sealsneurolepsia3790No ratings yet
- Safety Grating CatalogDocument22 pagesSafety Grating CatalogzhukeeNo ratings yet
- On Advertising A Marxist CritiqueDocument13 pagesOn Advertising A Marxist CritiqueKisholoy AntiBrahminNo ratings yet
- NI-Predictive Maintenance and Machine Health MonitoringDocument34 pagesNI-Predictive Maintenance and Machine Health Monitoringtườngt_14No ratings yet
- Topic On CC11Document3 pagesTopic On CC11Free HitNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans WK 26Document7 pagesLesson Plans WK 26api-280840865No ratings yet
- Standard DC Output: Simplified Internal Diagram of The Charger's Output ConnectionsDocument1 pageStandard DC Output: Simplified Internal Diagram of The Charger's Output ConnectionstoufikNo ratings yet
- Coconut: Donesian Export Pro IleDocument39 pagesCoconut: Donesian Export Pro Ile764fqbbnf2No ratings yet
- Class - 8 Chapter - 3 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsDocument6 pagesClass - 8 Chapter - 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics7A04Aditya MayankNo ratings yet
- BTD Course FileDocument23 pagesBTD Course FilePrashant S HadagaliNo ratings yet
- Methods-Time Measurement: MODAPTS Technique. This Technique Was Introduced in 1966 byDocument2 pagesMethods-Time Measurement: MODAPTS Technique. This Technique Was Introduced in 1966 byChisom IkengwuNo ratings yet
- Section 2 Digital OutputDocument1 pageSection 2 Digital Outputsamim_khNo ratings yet
- Semikron Datasheet SKB 30Document3 pagesSemikron Datasheet SKB 30Kleber Milton de SouzaNo ratings yet