Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genbio 2ND
Genbio 2ND
Uploaded by
mamariljasmine03Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genbio 2ND
Genbio 2ND
Uploaded by
mamariljasmine03Copyright:
Available Formats
Some cellular activities that require energy ATP TO ADP CYCLE
are active transport, protein synthesis and
- the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP is
cell division.
reversible
Energy can exist or be stored in many forms - they are like charged and uncharged
such as light, heat, electricity and chemical forms of rechargeable battery
bonds in chemical compounds. - ATP regeneration reaction is the
reverse of hydrolysis reaction
ENERGY + ADP + P + ATP + H2O
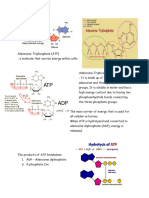
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
- when ATP is broken down energy is
- is the premier energy molecule in released and ADP is formed
most living organism - when ADP binds with another
- often referred to as the “energy phosphate group, energy is stored
currency of the cell” and ATP is formed
- an organic molecule used for short
term energy storage and transport in
the cell.
ATP IN ENERGY COUPLING
- made up of 3 parts;
1. nitrogenous base (adenine) - is the transfer of energy from one
2. sugar (ribose) chemical reaction to another
3. phosphate groups (triphosphate) - the cell can perform nearly all of the
- the 3 phosphate groups are tasks it needs to function
negatively charged, means that they
are in an unstable arrangement
- a bond between (phosphate groups) CHEMICAL REACTION
is broken through hydrolysis (water
mediated breakdown) reaction EXERGONIC
releasing energy ADP. - energy outward
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) - proceeds with a net release of free
energy
- the remaining free phosphate group - products have less energy than
and low energy molecule reactants
- spontaneous
ENDERGONIC
HYDROLYSIS REACTION OF ATP TO
ADP - energy inward
- one the absorbs free energy from its
P stands for an inorganic phosphate group
surroundings
(PO)
- products have more energy than
ATP is hydrolyzed i reactants
- not spontaneous
ATP + H2O + ADP + P + ENERGY
PHOTSYNTHESIS PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND SIDE
PRODUCTS
- a process by which autotrophic
organisms use light energy to make - solar energy is the source of
sugar and oxygen gas from carbon countless vegetable, animal etc.
dioxide and water - wood used as fuel
- occurs in plants, algae and some - paper, cotton ad other natural fibers
prokaryotes consist of cellulose
- anabolic (small molecules combined) - wool
- endergonic (stores energy)
- store as carbohydrate in their bodies
SITE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
IMPORTANCE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND SUN ENERGY
- harnesses the sun’s energy into
utilizable forms of energy on earth
- a process that most biological
organisms are unable to perform
- ATP is used to power these
processes
- converts light energy into chemical
energy in the form of glucose
PHOTOSYSNTHESIS AND CARBON
DIOXIDE REMOVAL
- converts carbon dioxide into oxygen
- during photosynthesis, carbon
dioxide leaves the atmosphere and
enters the plants and leaves as
oxygen
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND THE
ECOSYSTEM
- the energy produced by
photosynthesis forms the basis of
virtually all terrestrial and aquatic
food chains
- photosynthesis is the ultimate source
of carbon in the organic molecules
found in most organisms
You might also like
- MicrobiologyDocument99 pagesMicrobiologyYu Liang100% (1)
- Biology Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesBiology Reviewer 2nd Quarter젶레이100% (4)
- ATP ReviewerDocument5 pagesATP ReviewerDaneth Julia TuberaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Reviewer Quarter 2Document9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Reviewer Quarter 2shirleyyy.idoloNo ratings yet
- Reviwer Sa Gen BioDocument8 pagesReviwer Sa Gen Biocediebanaag10No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument17 pagesGeneral Biologydwightballes9No ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewerzoe dizonNo ratings yet
- Genbio Notes 2QL1Document5 pagesGenbio Notes 2QL1zoe dizonNo ratings yet
- Week 1 ADP & ATP CycleDocument17 pagesWeek 1 ADP & ATP Cycledenveralbarico143No ratings yet
- ATP Production: AP BiologyDocument20 pagesATP Production: AP BiologyCamille Sison-AlmirolNo ratings yet
- Bio 3Document5 pagesBio 3Jaylene Kaye CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism Overview of MetabolismDocument17 pagesCellular Metabolism Overview of MetabolismNathan Louis PalacioNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Photosynthesis 240429 180428Document60 pagesChapter-5-Photosynthesis 240429 180428kpopfandom815No ratings yet
- QTR 2 MOD 1 - ATP ProductionDocument43 pagesQTR 2 MOD 1 - ATP ProductionCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- Bio Q2 ReviewerDocument10 pagesBio Q2 Reviewerapril LomocsoNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument3 pagesGeneral Biologyjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PhotosynthesisDocument60 pagesChapter 5 Photosynthesisvijaypanwar_2000No ratings yet
- ATP-ADP CycleDocument15 pagesATP-ADP CycleMay PaviaNo ratings yet
- NatSci2 Chapter 5Document32 pagesNatSci2 Chapter 5kayNo ratings yet
- Biochem Final ReviewerDocument19 pagesBiochem Final RevieweryjllhallareNo ratings yet
- Energy and Metabolism - SimplifiedDocument17 pagesEnergy and Metabolism - SimplifiedVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis NotesAmanda Rose DalyNo ratings yet
- Overall Equation: PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesOverall Equation: PhotosynthesisEleanorNo ratings yet
- Explain The Complete Reaction For The Hydrolysis of Adenosine Triphosphat1Document15 pagesExplain The Complete Reaction For The Hydrolysis of Adenosine Triphosphat1NURAIHAN BINTI HASHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocument57 pagesCoupled Reaction ProcessesVince Paul PascualNo ratings yet
- General Biology q4 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology q4 ReviewerKean ArsenalNo ratings yet
- SolaboDocument6 pagesSolaboLoraine ChantelleNo ratings yet
- Stuvia 451056 Energy and Respiration Biology A Level Cie 9700Document12 pagesStuvia 451056 Energy and Respiration Biology A Level Cie 9700Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Energy CouplingDocument3 pagesEnergy CouplingHannah VillocenoNo ratings yet
- The Secret Behind The Power of ATP Lies in The Breaking of Chemical Bond Between Second and Third Phosphate Groups. When This Happens, Large Amount of Energy Is ReleasedDocument8 pagesThe Secret Behind The Power of ATP Lies in The Breaking of Chemical Bond Between Second and Third Phosphate Groups. When This Happens, Large Amount of Energy Is ReleasedDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- General Biology NotesDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology NotesjeayNo ratings yet
- ATP: Adenosine TriphosphateDocument3 pagesATP: Adenosine TriphosphateClaire ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument5 pagesEnergy TransformationmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Another SampleDocument7 pagesAnother SampleLuthar James JimenezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesChapter 2 PhotosynthesisTshering ChodenNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem A4Document6 pagesEcosystem A4Tristan SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Revision NotesDocument12 pagesTopic 5 Revision NotessreenitthiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: A Short Course: Metabolism: Basic Concepts and DesignDocument30 pagesBiochemistry: A Short Course: Metabolism: Basic Concepts and DesignEli JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Coupled Reaction and The Role of AtpDocument2 pagesCoupled Reaction and The Role of Atpyashikasolina07No ratings yet
- Q2W3Document3 pagesQ2W3Jihyun KimNo ratings yet
- Exam Gen Bio No HighlightsDocument6 pagesExam Gen Bio No Highlightscassyleen03No ratings yet
- Q2 Reviewer in General BiologyDocument7 pagesQ2 Reviewer in General BiologyariannealzagaNo ratings yet
- 2Q Lesson 1 ATP-ADP CycleDocument5 pages2Q Lesson 1 ATP-ADP Cycleysa padilla100% (1)
- Notes+4 +ATP,+Water+and+Inorganic+IonsDocument5 pagesNotes+4 +ATP,+Water+and+Inorganic+IonsSyeda Wardah NoorNo ratings yet
- GENBIODocument3 pagesGENBIOAngelica AbuganNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes 2016Document252 pagesA2 Biology Notes 2016MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Bot 14 Second ExamDocument7 pagesBot 14 Second ExamAnna HarietNo ratings yet
- Agricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyDocument63 pagesAgricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Atp Adp CycleDocument13 pagesAtp Adp Cycleelladomingo54No ratings yet
- Neuro ThermodynamicsDocument32 pagesNeuro ThermodynamicsNanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Metabolism - Anabolism and Catabolism & Amphibolic Reactions(1).Pdf_20240612_215137_0000Document13 pagesRegulation of Metabolism - Anabolism and Catabolism & Amphibolic Reactions(1).Pdf_20240612_215137_0000LeenaNo ratings yet
- BiologicalReview29 4 ATP PresentationDocument21 pagesBiologicalReview29 4 ATP Presentationsmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Group 3 - Atp-Adp CycleDocument1 pageGroup 3 - Atp-Adp Cycleditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- 7.1 Energy in Living Systems - Biology OpenStax 2Document1 page7.1 Energy in Living Systems - Biology OpenStax 2Althea BurgosNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation - Atp-Adp CycleDocument33 pagesEnergy Transformation - Atp-Adp CyclePrincess EscandalloNo ratings yet
- 2 ND Quarter BiologyDocument34 pages2 ND Quarter BiologyazeyhannaantonioNo ratings yet
- Objectives: 6) Light-Dependent Reactions and PhotosystemsDocument20 pagesObjectives: 6) Light-Dependent Reactions and PhotosystemsKevin ObureNo ratings yet
- Atp-Adp CycleDocument20 pagesAtp-Adp Cyclekim cchlNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Metabolism 1Document26 pagesCellular - Metabolism 1Ans JavidNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Energy MetabolismDocument7 pagesBiochemistry - Energy MetabolismProjjal SanyalNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH On EnzymesDocument3 pagesEffect of PH On EnzymesJanick MallareNo ratings yet
- Lipase Spinreact 1x24 ML, 1X48 MLDocument2 pagesLipase Spinreact 1x24 ML, 1X48 MLN. K. MandilNo ratings yet
- MembranasDocument7 pagesMembranasFrancisco GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Jute: Chapter - IIDocument10 pagesChemistry of Jute: Chapter - IIMR MimNo ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument25 pagesFood TestsPeter Hong Leong Cheah100% (5)
- Nov 2020 QPDocument20 pagesNov 2020 QPmarcoscervantes006No ratings yet
- BBL Crystal Identification Systems Enteric-Nonfermenter ID KitDocument16 pagesBBL Crystal Identification Systems Enteric-Nonfermenter ID KitWinona ShenaniNo ratings yet
- The Advances and Limitations in Biodiesel Production: Feedstocks, Oil Extraction Methods, Production, and Environmental Life Cycle AssessmentDocument21 pagesThe Advances and Limitations in Biodiesel Production: Feedstocks, Oil Extraction Methods, Production, and Environmental Life Cycle AssessmentMarkNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: BiochemistryDocument38 pagesCarbohydrates: Biochemistryhoney maxine reyNo ratings yet
- CHE 156 Acids Bases and Salt Units 1 and 9Document78 pagesCHE 156 Acids Bases and Salt Units 1 and 9NurudeenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Test For The Components of Nucleic Acid LABREPORTDocument4 pagesChemical Test For The Components of Nucleic Acid LABREPORT19 - CELENDRO ADVINNNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Color Reactions of Intact and Acid Hydrolyzed Protein CaseinDocument3 pagesQualitative Color Reactions of Intact and Acid Hydrolyzed Protein CaseinPatricia ChongNo ratings yet
- Chicken LiverDocument10 pagesChicken LiverZoran MiladinovićNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Hydrolyzation of Casein From Nonfat MilkDocument6 pagesIsolation and Hydrolyzation of Casein From Nonfat MilkKyle PanadoNo ratings yet
- Training Report.Document26 pagesTraining Report.Dikshit TomerNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Drilling FluidsDocument60 pagesPolymers in Drilling FluidsMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering AspectsDocument7 pagesColloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering AspectsThu Trang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Biotransformation 111201084539 Phpapp02Document46 pagesBiotransformation 111201084539 Phpapp02thakur1989No ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document10 pagesWa0005.samarkhatri300No ratings yet
- Guide To Practicals in Biology g10-12Document24 pagesGuide To Practicals in Biology g10-12Andrea Maluba100% (1)
- Biomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryDocument16 pagesBiomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryIshanNo ratings yet
- Atp AdpDocument27 pagesAtp AdpJanin CodillaNo ratings yet
- Solution 5: Buffer SolutionDocument24 pagesSolution 5: Buffer Solutionesi oktavia75% (4)
- Student Exploration: Dehydration SynthesisDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Dehydration SynthesisEmma AssaadNo ratings yet
- 9701 s04 QP 2 PDFDocument8 pages9701 s04 QP 2 PDFSanthi RamanNo ratings yet
- Pre Formulation Stability StudiesDocument33 pagesPre Formulation Stability StudiesDinesh Reddy50% (2)
- Bio MoleculesDocument14 pagesBio MoleculesmayashankarjhaNo ratings yet
- Biology 1401 Course OutlineDocument2 pagesBiology 1401 Course OutlinemwalalatriceNo ratings yet
- Substrate, Product of Anaerobic DigestorDocument31 pagesSubstrate, Product of Anaerobic DigestorPAVITHRA VNo ratings yet