Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class X Bat ! - 1ST 50% CHEM WS
Class X Bat ! - 1ST 50% CHEM WS
Uploaded by
physicsbooks.store0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pages1. The document contains questions about chemical reactions and equations involving metals and non-metals. It asks about the properties of metals, alloys, reactivity series, and chemical reactions including displacement and decomposition.
2. It also contains questions testing understanding of concepts like leaching, oxidation states, exothermic reactions, and uses of chemicals like quicklime, zinc, and platinum.
3. Multiple choice and true/false questions are asked about chemical properties and reactions of substances like copper, silver, iron, aluminium, zinc, lead nitrate and acids.
Original Description:
CHEM
Original Title
Class X bat !_1ST 50% CHEM WS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document contains questions about chemical reactions and equations involving metals and non-metals. It asks about the properties of metals, alloys, reactivity series, and chemical reactions including displacement and decomposition.
2. It also contains questions testing understanding of concepts like leaching, oxidation states, exothermic reactions, and uses of chemicals like quicklime, zinc, and platinum.
3. Multiple choice and true/false questions are asked about chemical properties and reactions of substances like copper, silver, iron, aluminium, zinc, lead nitrate and acids.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesClass X Bat ! - 1ST 50% CHEM WS
Class X Bat ! - 1ST 50% CHEM WS
Uploaded by
physicsbooks.store1. The document contains questions about chemical reactions and equations involving metals and non-metals. It asks about the properties of metals, alloys, reactivity series, and chemical reactions including displacement and decomposition.
2. It also contains questions testing understanding of concepts like leaching, oxidation states, exothermic reactions, and uses of chemicals like quicklime, zinc, and platinum.
3. Multiple choice and true/false questions are asked about chemical properties and reactions of substances like copper, silver, iron, aluminium, zinc, lead nitrate and acids.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Class: X FIRST 50% PORTIONS TEST Subject: Chemistry
CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS / METALS AND NON METALS
I ANSWER TH EFOLLOWING QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following metal has highest melting point?
(a) Copper (b) Silver (c) Sodium (d) Tungsten
2. The composition of aqua-regia is
(a) Dil.HCl : Conc. HNO3 :: 3 : 1 (b) Conc. HCl : Dil. HNO3 :: 3 : 1
(c) Conc. HCl : Conc. HNO3 :: 3:1
3. Which of the following is a characteristic of metals?
(a) They have one to three valence electrons
(b) They have 4 to 8 valence electrons
(c) They are brittle (d) They are capable to form anions easily
4. An alloy is
(a) an element (b) a compound
(c) a homogeneous mixture (d) a heterogeneous mixture
5. Beakers A B, and C contain zinc sulphate, silver nitrate and iron (II) sulphate
solutions respectively. Copper pieces are added to each beaker. Blue colour will
appear in case of
(a) beaker A (b) beaker B (c) beaker C (d) all the beakers
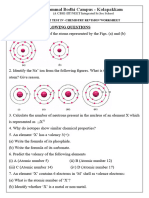
6. In each test tubes A B, ,C and D, 2mL of solution of Al2 43 ( ) SO in water
was filled. Clean pieces of zinc was placed in test tube A, clean iron nail was put
in test tube B , silver (Ag) was placed in test tube C and a clean copper wire was
placed in test tube D. Which of the following option (s) is/are correct about
above experiment?
(a) Zinc is more reactive than aluminium
(b) Copper is more reactive than aluminium
(c) Zinc is more reactive than copper
(d) Zinc, iron, silver and copper are less reactive than aluminium
7. Hydrogen gas is not widely used as a reducing agent because
(a) hydrogen decomposes to atomic hydrogen at higher temperature
(b) risk of explosion with water
(c) hydrogen isomerises to ortho hydrogen at higher temperature.
(d) many metals form hydrides at lower temperatures.
8. Froth floatation method is used for the concentration of-
(a) oxide ores (b) sulphide ores (c) sulphate ors (d) halide ores
9. Removal of impurities from ore is known as-
(a) crushing and grinding (b) concentration of ore (c) calcinations (d) roasting
10. Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions?
(a) ZnSO4 solution and Aluminium metal
(b) MgCl2 Solution and aluminium metal
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal
11. Which of the following is a physical change?
(a) Formation of curd from milk (b) Ripening of fruits
(c) Getting salt from sea water (d) Burning of wood
12. What happens when copper rod is dipped in iron sulphate solution?
(a) Copper displaces iron (b) Blue colour of copper sulphate solution is obtained
(c) No reaction takes place (d) Reaction is exothermic
13. Black and white photography uses-
(a) decomposition of silver chloride (b) decomposition of silver bromide
(c) both (d) none of these
14. A reddish brown coloured metal used in electric wires, when powdered and
heated strongly in an open China dish, its colour turns black. When hydrogen gas
is passed over this black substances, it regain its original colour. Based on this
information, the metal and black coloured substances are
(a) copper and copper nitrate (b) silver and silver oxide
(c) copper and copper oxide (d) aluminium and aluminium oxide
15. When copper powder is heated it gets coated with-
(a) black copper oxide (b) yellow copper oxide
(c) red copper oxide (d) None of these
16. A student added dilute HCl to a test tube containing zinc granules and made
following observations :
(a) the zinc surface became dull and black
(b) a gas evolved which burnt with a pop sound
(c) the solution remained colourless
(d) the solution becomes green in colour
17. A substance which oxidises itself and reduces other is known as –
(a) oxidising agent (b) reducing agent (c) both of these (d) none of these
18. Which one of the following involve a chemical reaction?
(a) Evaporation of water (b) Storing on nitrogen gas under pressure
(c) Keeping petrol in a China dish in open
(d) Heating magnesium wire in the presence of air at high temperature
19. When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper
sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid
so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of-
(a) a combination reaction (b) a displacement reaction
(c) a decomposition reaction (d) a double decomposition reaction
20. A dilute solution of sodium carbonate was added to two test tubes - one
containing dil HCl
(a) and the other containing dilute NaOH(b). The correct observation was-
(a) a brown coloured gas liberated in test tube A
(b) a brown coloured gas liberated in test tube B
(c) a colourless gas liberated in test tube A
(d) a colourless gas liberated in test tube B
II DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is
followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct
explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct
explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
1. Assertion : Different metals have different reactivities with water and dilute
acids.
Reason : Reactivity of a metal depends on its position in the reactivity series.
2. Assertion : Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to
dilute hydrochloric acid
Reason : Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction
3. Assertion : Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
Reason : Platinum, gold and silver are least reactive metals
4. Assertion : Zinc is used in the galvanisation of iron.
Reason : Its coating on iron articles increases their life by protecting them
from rusting.
5. Assertion : Leaching is a process of reduction.
Reason : Leaching involves treatment of the ore with a suitable reagent so as
to make it soluble while impurities remains insoluble.
6. Assertion(A) : Brown fumes are produced when lead nitrate is heated.
Reason (R) : Nitrogen dioxide gas is produced as a by product due to the
decomposition of lead nitrate.
7. Assertion : Quicklime reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount
of heat.
Reason : The above chemical reaction is an exothermic reaction.
8. Assertion : Stannous chloride is a powerful oxidising agent which oxidises
mercuric chloride to mercury.
Reason : Stannous chloride gives grey precipitate with mercuric chloride, but
stannic chloride does not do so.
9. Assertion (A) : Carbon dioxide turns lime water milky.
Reason (R) : Carbon dioxide sullies the water.
10. Assertion (A) : To dilute sulphuric acid, acid is added to water and not
water to acid.
Reason (R) : Specific heat of water is quite large.
You might also like
- Investment Casting - Vijay RathodDocument92 pagesInvestment Casting - Vijay Rathoddikurock100% (3)
- PPCHEM B.Dooley Oxide Growth and Exfoliation PDFDocument22 pagesPPCHEM B.Dooley Oxide Growth and Exfoliation PDFekrem turan100% (1)
- Science BookletDocument132 pagesScience BookletPiyush kumar86% (7)
- MIG Welding ManualDocument26 pagesMIG Welding ManualAmjad Mehmood100% (2)
- Chapetr 1 Chemical ReactionsDocument23 pagesChapetr 1 Chemical ReactionsmadhubalagangapureNo ratings yet
- MCQ TypeDocument3 pagesMCQ TypePuja DhawanNo ratings yet
- 5 A 9 e 8700 e 4 B 07 Ae 4 B 60 BD 59 DDocument36 pages5 A 9 e 8700 e 4 B 07 Ae 4 B 60 BD 59 DVKNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and Salt MCQDocument13 pagesAcid Bases and Salt MCQSisodia's World of scienceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations-Revision WorksheetDocument6 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations-Revision WorksheetFrederic Francois ChopinNo ratings yet
- ACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Document23 pagesACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions QuestionsZeeshan AhmadNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Metals and Non-Metals MCQDocument9 pagesCH 3 Metals and Non-Metals MCQStebin John stanlyNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Questions - Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument21 pagesTerm 1 Questions - Chemical Reactions and EquationsAmbitious StudentNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument180 pagesQuestion BankLVAM GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For Chemical Reactions and Equationspmishra029No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument7 pagesChemical Reactions and Equationstritium325No ratings yet
- Recap Worksheet 3Document2 pagesRecap Worksheet 3Divyansh Jain KingNo ratings yet
- ICSE Paper 2009Document11 pagesICSE Paper 2009CGPSC - P&P TutorialNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1Document9 pagesChemistry Chapter 1Princy Merin JoseNo ratings yet
- Workbk 10Document177 pagesWorkbk 10Manushree NayakNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals (Grand Test)Document10 pagesMetals and Non Metals (Grand Test)amit mongiaNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Questions With Answer.Document12 pagesExemplar - Questions With Answer.Liveen .S100% (1)
- CLASS - X CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsDocument17 pagesCLASS - X CHEMISTRY Important Questionsvt654009No ratings yet
- Class 10 MCQ For PracticeDocument4 pagesClass 10 MCQ For PracticeAbirami SathishNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet - SolutionDocument15 pagesScience Worksheet - SolutionZainul ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations.Document8 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations.Vivek Earnest NathNo ratings yet
- Science & Technology Chapter 1 18-APR-2024 Tv2xL524fT-2Document5 pagesScience & Technology Chapter 1 18-APR-2024 Tv2xL524fT-2siyavkhemaniNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument23 pagesChemistrySwanik BathamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations and ReactionsDocument4 pagesChemical Equations and ReactionsGauravNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 3Document22 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 3Dhwani ShahNo ratings yet
- Learn PracticallyDocument55 pagesLearn Practicallyprincethakan9No ratings yet
- Chemistry PaperDocument12 pagesChemistry PaperRitambhara BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet-1 Chapter-1Document3 pagesWork Sheet-1 Chapter-1Saisanman DhalNo ratings yet
- Abhimnyu Metal and Non Metal - AsignmentDocument3 pagesAbhimnyu Metal and Non Metal - Asignmentaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- 10th MCQ-QP AnswersDocument5 pages10th MCQ-QP AnswersNARENDRAN S0% (1)
- Chem Science Sample PaperDocument8 pagesChem Science Sample PaperskluckyskashifNo ratings yet
- Chem RXN and EqnDocument5 pagesChem RXN and EqnVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1Document21 pagesImportant Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1Darshuram DudheNo ratings yet
- 10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument12 pages10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Metalsand Non MetalsDocument2 pagesAssignment - Metalsand Non MetalsAkshita KambojNo ratings yet
- 10th Chem MCQ FullDocument24 pages10th Chem MCQ Fulltauheedbarkati65No ratings yet
- Review Exercise (1) 1. Which The Following Is The Net Ionic Equation For The Reaction Between Hydrochloric Acid and Potassium Hydroxide?Document8 pagesReview Exercise (1) 1. Which The Following Is The Net Ionic Equation For The Reaction Between Hydrochloric Acid and Potassium Hydroxide?Juma BwaiNo ratings yet
- G10 Sem 1 Chem QP 24 08Document8 pagesG10 Sem 1 Chem QP 24 08iamperoplayer19No ratings yet
- Class X Chemistry Asm Term IiDocument10 pagesClass X Chemistry Asm Term IiAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Document VithiDocument4 pagesDocument VithikshivamstarkNo ratings yet
- Ch-3: Metals and Non-Metals Question BankDocument4 pagesCh-3: Metals and Non-Metals Question BankvratNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationDocument12 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationaaravNo ratings yet
- ICSEBoardPaper X Chemistry Questions 20090Document10 pagesICSEBoardPaper X Chemistry Questions 20090Aditya SuswalNo ratings yet
- Class 9 2020Document9 pagesClass 9 2020Mariha MunirNo ratings yet
- Class 9 2020Document9 pagesClass 9 2020Mariha MunirNo ratings yet
- TP03 ChemicalDocument6 pagesTP03 Chemicalkamaldwivedi99No ratings yet
- D and F Block DPPDocument4 pagesD and F Block DPPKalyan ReddtNo ratings yet
- Chem PaperDocument4 pagesChem PaperKeertana SN100% (1)
- Set A Multiple Choice Questions Metals and Non-MetalsDocument7 pagesSet A Multiple Choice Questions Metals and Non-MetalsskandhaNo ratings yet
- Science X Case Study Question 22Document7 pagesScience X Case Study Question 22Bhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Holiday HW 24-25Document50 pagesClass 10 Holiday HW 24-25suyashvijay1No ratings yet
- CHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Document8 pagesCHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Arsh KhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Class X (SCIENCE)Document42 pagesQuestion Bank For Class X (SCIENCE)kanit8713No ratings yet
- Dca Chemistry QuestionsDocument3 pagesDca Chemistry Questionsadegoke ademolaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Ch-1 - CLASS XDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 Ch-1 - CLASS XPRVLNo ratings yet
- 1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradDocument12 pages1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradKshitiz sharma100% (1)
- Chemical Reaction and EquationDocument6 pagesChemical Reaction and EquationamitNo ratings yet
- Tissues - NotesDocument14 pagesTissues - Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- ELectricity ws-2Document1 pageELectricity ws-2physicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Cell Olympiad BitsDocument5 pagesCell Olympiad Bitsphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Motion Class 9 W.SDocument7 pagesMotion Class 9 W.Sphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Light Printed NotesDocument6 pagesLight Printed Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Lecture 04Document41 pagesAlternating Current Lecture 04physicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Psg-Qp-Body MovementsDocument2 pagesPsg-Qp-Body Movementsphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Plants and Animals ws-1Document2 pagesConservation of Plants and Animals ws-1physicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Force and PressureDocument2 pagesForce and Pressurephysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Class IX UT4-CHEM WSDocument4 pagesClass IX UT4-CHEM WSphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument2 pagesHEATphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Ws-2-Why Do We Fall IllDocument6 pagesWs-2-Why Do We Fall Illphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Class IX UT4-CHEM RT2Document2 pagesClass IX UT4-CHEM RT2physicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Class X BAT 1 - CHEM 2ND 50% SLIP TEST-1Document2 pagesClass X BAT 1 - CHEM 2ND 50% SLIP TEST-1physicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Refining of CooperDocument2 pagesElectrolytic Refining of CooperAslam PANo ratings yet
- Flanges EN 1092Document7 pagesFlanges EN 1092GagrigoreNo ratings yet
- Casting Forming & Casting, Forming &: Welding WeldingDocument25 pagesCasting Forming & Casting, Forming &: Welding WeldingJordArt GRNo ratings yet
- Astm G58.25944Document8 pagesAstm G58.25944Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Metric BoltsDocument52 pagesMetric BoltsDGW100% (1)
- Modified Jominy Test For Determining The Critical Cooling Rate For Intercritically Annealed Dual Phase SteelsDocument18 pagesModified Jominy Test For Determining The Critical Cooling Rate For Intercritically Annealed Dual Phase Steelsbmcpitt0% (1)
- HSP - As - 01Document10 pagesHSP - As - 01lokelooksNo ratings yet
- Process of Percussion Welding (With Diagram)Document5 pagesProcess of Percussion Welding (With Diagram)Karthik SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Stainless Slit StripsDocument3 pagesStainless Slit Stripscheng_cheng1234No ratings yet
- Specification For Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Extruded Bars, Rods, and ProfilesDocument10 pagesSpecification For Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Extruded Bars, Rods, and ProfilesShradha SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- 1-Fasa Dan Diagram FasaDocument20 pages1-Fasa Dan Diagram FasaWirahadi KrisnaNo ratings yet
- 42 Crmo 4 (Germany / Din) : Material PropertiesDocument4 pages42 Crmo 4 (Germany / Din) : Material PropertiesmiladrahimianNo ratings yet
- Bolt Astm A193Document2 pagesBolt Astm A193Nuzuliana EnuzNo ratings yet
- Bunkers Hill MAP WREXHAM AREADocument1 pageBunkers Hill MAP WREXHAM AREAAnnette EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials: Sonali Verma 251656009 I&PDocument20 pagesEngineering Materials: Sonali Verma 251656009 I&Psanjay kajalNo ratings yet
- Model 172 Maintenance Manual Safetying - Maintenance Practices 1. GeneralDocument3 pagesModel 172 Maintenance Manual Safetying - Maintenance Practices 1. Generalraj mohanNo ratings yet
- A Micro Project On: Industrial Components Which Are Produced Through Non Conventional Machining ProcessesDocument26 pagesA Micro Project On: Industrial Components Which Are Produced Through Non Conventional Machining Processesrajnish patilNo ratings yet
- TDS A183n 750 EngDocument3 pagesTDS A183n 750 EngVigneswaranNo ratings yet
- Jis 3445Document4 pagesJis 3445Marcos Verissimo Juca de PaulaNo ratings yet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet I PDFDocument3 pagesNaming Ionic Compounds Worksheet I PDFgowrimanohar1975No ratings yet
- Material Product Data Sheet Tin and Tin Alloy (Babbit) Thermal Spray WiresDocument3 pagesMaterial Product Data Sheet Tin and Tin Alloy (Babbit) Thermal Spray WiresKhalid M. HafezNo ratings yet
- B686B686M 14Document11 pagesB686B686M 14payamNo ratings yet
- Katalog ArcelorDocument14 pagesKatalog Arcelor666bigboy666No ratings yet
- NASA Process Specification For Nickel PlatingDocument10 pagesNASA Process Specification For Nickel PlatingRam ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Copper PRDocument17 pagesCopper PRSaadAminNo ratings yet
- Note 2 Essential and Non Essential Variables Rev1Document21 pagesNote 2 Essential and Non Essential Variables Rev1Mohamad Yusuf HelmiNo ratings yet
- British Gas Painting NotesDocument40 pagesBritish Gas Painting Notes9440864459No ratings yet