Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ri
Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ri
Uploaded by
strawberrykate26Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesCASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de Castro86% (22)
- Hesp1A 3 Unit ActivityDocument10 pagesHesp1A 3 Unit ActivityaresthesoldierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- NCP Pneumonia May6 Ate KimDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumonia May6 Ate Kimiransevilla615No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Ineffective Airway Clearance: Arranged byDocument9 pagesNursing Care Ineffective Airway Clearance: Arranged byAlri LestariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Clinical Review QuestionsDocument1 pageChapter 23 Clinical Review QuestionsLidia DominguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Miggy EstoniloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperiencePauline GarciaNo ratings yet
- Askep DialisisDocument6 pagesAskep Dialisisvictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- NCP Discharge PlanningDocument7 pagesNCP Discharge PlanningMarcieNo ratings yet
- NCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Document4 pagesNCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Jamaica Malicdem0% (1)
- Case Study, Chapter 20, Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocument11 pagesCase Study, Chapter 20, Assessment of Respiratory FunctionMaddyNo ratings yet
- NCP of Respiratory DistressDocument3 pagesNCP of Respiratory DistressDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- NCP MiniparDocument9 pagesNCP MiniparKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: IndependentRea LynNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan # 1:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan # 1:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGj PaguidianNo ratings yet
- NCP For ICU CPDocument10 pagesNCP For ICU CPRalph Laurence TanNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasCarlito AglipayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Analysis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Analysis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluationstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Health: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Health: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Final Thyroid Storm NCPDocument6 pagesFinal Thyroid Storm NCPoguitekim1No ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianeDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- FNCP FinalDocument5 pagesFNCP FinalGewel Bardaje AmboyNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCase Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- Problem 3Document2 pagesProblem 3Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Date/Shift Focus DataDocument2 pagesDate/Shift Focus Datakuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- E LP Pneumonia Keperawatan Anak Zaii - Id.en SalinanDocument11 pagesE LP Pneumonia Keperawatan Anak Zaii - Id.en SalinanMuhammad ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Materi Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageMateri Nursing Care PlanSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Name: Zeph Age: 23 Years Old Sex: Male Room Number: 304 Hospital Number: 100921Document2 pagesName: Zeph Age: 23 Years Old Sex: Male Room Number: 304 Hospital Number: 100921kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- NCP PotentialDocument2 pagesNCP PotentialKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- Programme: High Diploma in NursingDocument7 pagesProgramme: High Diploma in NursingYeesze ChanNo ratings yet
- RLE Case PresentationDocument26 pagesRLE Case PresentationShaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGeraldine SantosNo ratings yet
- NCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Document8 pagesNCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- ABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanAndrea Abadingo100% (1)
- APOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)Document2 pagesAPOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)REYJAN APOLONIONo ratings yet
- NCP PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNCP PneumoniaMerliah LofrancoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Intervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixDocument5 pagesIntervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixRizki ArifNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 NCP Patient FDocument12 pagesGROUP 8 NCP Patient FasdasdNo ratings yet
- Efusi Pleura PPT - Id.en (Repaired)Document17 pagesEfusi Pleura PPT - Id.en (Repaired)fitriaNo ratings yet
- Example of Nursing Care Plan (Pathophysiology)Document5 pagesExample of Nursing Care Plan (Pathophysiology)Elizabeth ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Prematurity Assessment Nursing DX Scientific BG Goal/ Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesPrematurity Assessment Nursing DX Scientific BG Goal/ Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJeanne Mari CostalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Resume of Respiratory ProblemDocument5 pagesResume of Respiratory ProblemIbi Yulia SetyaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TB 1Document1 pageNursing Care Plan TB 1Blair MargauxNo ratings yet
- NCP Pagalanan PablicoDocument15 pagesNCP Pagalanan PablicoRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis G3Document12 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis G3Cuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageRisk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlantososNo ratings yet
- Piguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24Document5 pagesPiguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24kc bpNo ratings yet
- PulmonaryDocument54 pagesPulmonarytheonlinegeekhubNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis, MTB or TB (Short For TuberclesDocument4 pagesBacillus Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis, MTB or TB (Short For TuberclesLeonelyn GeromoNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Document8 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care in Lung DiseaseFrom EverandPalliative Care in Lung DiseaseKathleen O. LindellNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument4 pagesHypertensionstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument6 pagesRESEARCHstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Gen 004 Sas 9Document9 pagesGen 004 Sas 9strawberrykate26No ratings yet
- LumbosacrallllDocument6 pagesLumbosacrallllstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Sas12 - Fonbuena, Kate Ashley C.Document1 pageSas12 - Fonbuena, Kate Ashley C.strawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Gen 17Document1 pageGen 17strawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Sample of PPSC Accountant Test Preparation Notes: All Competitive Exam Mcqs & Interview QuestionDocument9 pagesSample of PPSC Accountant Test Preparation Notes: All Competitive Exam Mcqs & Interview Questionkamal sahabNo ratings yet
- Rsi 5 PDFDocument9 pagesRsi 5 PDFManoj RaiNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law ReviewDocument80 pagesCriminal Law ReviewGianna CantoriaNo ratings yet
- Box Speaker 15 Inch LapanganDocument3 pagesBox Speaker 15 Inch LapanganWilli Je WilliamNo ratings yet
- InfoDocument3 pagesInfoIonuț MoNo ratings yet
- Asbāb Al-Nuzūl: Mokrane GuezzouDocument10 pagesAsbāb Al-Nuzūl: Mokrane GuezzoubrizendineNo ratings yet
- Antenna (Radio) : TerminologyDocument9 pagesAntenna (Radio) : Terminologymikeshinoda6No ratings yet
- Bca Semester-II 2023-24 (1) 2Document49 pagesBca Semester-II 2023-24 (1) 2kimberlyeric009No ratings yet
- English Year 3 Up1 18Document15 pagesEnglish Year 3 Up1 18Nur SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Cement Industry in India - A CartelDocument35 pagesCement Industry in India - A CartelVarun NandaNo ratings yet
- Nimbly Black Lives Matter GuideDocument16 pagesNimbly Black Lives Matter GuideDaniel WuNo ratings yet
- Ed Moloney StatementDocument2 pagesEd Moloney StatementPensiveQuillNo ratings yet
- Reverse Poems LessonDocument8 pagesReverse Poems LessonVon Jezzrel Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- FormsDocument6 pagesFormsSHIELA MARIE L. DIMACULANGANNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Sastra InggrisDocument4 pagesDokumen Sastra InggrisI Gede Wisnu Adi PutrawanNo ratings yet
- Desert Magazine 1947 JuneDocument48 pagesDesert Magazine 1947 Junedm1937100% (2)
- FM 2213 Investment Analysis Portfolio ManagementDocument4 pagesFM 2213 Investment Analysis Portfolio ManagementDigit WayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Andhra PradeshDocument9 pagesChapter - Andhra PradeshindramuniNo ratings yet
- Ihrm Module 7Document18 pagesIhrm Module 7sumaiya banuNo ratings yet
- Peter Michael Quinn: EducationDocument2 pagesPeter Michael Quinn: Educationapi-407376667No ratings yet
- Egypt Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesEgypt Lesson Plan 1api-2690252530% (1)
- Memoirs of A MartyrDocument138 pagesMemoirs of A MartyrManu SarvagyaNo ratings yet
- Ashish Sahu - Software CVDocument3 pagesAshish Sahu - Software CVShubham KarnewarNo ratings yet
- Pelco by Schneider Electric Security Cameras & Surveillance SystemsDocument8 pagesPelco by Schneider Electric Security Cameras & Surveillance SystemsAnonymous MDkp0hnb3lNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Ramdhan Suwandi-N8d-360179141Document6 pagesMuhammad Ramdhan Suwandi-N8d-360179141Rija SunaNo ratings yet
- Samsung SyncMaster 932N PlusDocument51 pagesSamsung SyncMaster 932N PlusDee Jay FedeNo ratings yet
- Dse 2012 History Paper 1Document7 pagesDse 2012 History Paper 1CHEW JANICENo ratings yet
- Nama Della Agaveni Butar Butar Kelas X IIS 1: Siapakah Mereka ?Document2 pagesNama Della Agaveni Butar Butar Kelas X IIS 1: Siapakah Mereka ?Della ButarbutarNo ratings yet
- UNICEF Infant and Young Child Feeding ProgrammeDocument76 pagesUNICEF Infant and Young Child Feeding ProgrammethousanddaysNo ratings yet
Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ri
Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ri
Uploaded by
strawberrykate26Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ri
Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ri
Uploaded by
strawberrykate26Copyright:
Available Formats
PHINMA University of Pangasinan
College of Health Sciences
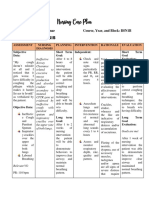
Patient’s Initials: J.D.C Age & Gender: Male Chief Complaint: shortness of breath Name of Student Nurse: Fonbuena, Kate Ashley C.
Birthday: _______________________ Admitting Diagnosis: Pneumonia Level/block/group: BSN1 - 12
Address: ________________________ Hospital/area: ________________________________
Date of Confinement: March 20, 2023 Clinical Instructor: ________________ Date: _______
ASSESSMENT NURSING ANALYSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
An inflammation of the Short-term Goals: Independent Interventions: Independent Interventions: Short-term Goal:
Subjective: lung parenchyma After 24 hours of nursing 1. Assist the patient in positioning 1. Assisting the patient in After 24 hours of nursing
“nahihirapan ako associated with alveolar intervention, the patient will and providing pursed-lip positioning and providing pursed- intervention, the patient
huminga” edema and congestion be able to: breathing and coughing lip breathing and coughing was able to:
as verbalized by the that impair gas 1. The patient will maintain a techniques to maintain airway techniques to maintain airway 1. The patient maintained a
patient. exchange. Pneumonia is patent airway patency. patency helps to ensure that the patent airway
caused by a bacterial or 2. The patient will patient’s airway remains open 2. The patient
Objective: viral infection spread by demonstrate improved lung and clear. demonstrated improved
BT- 38.5˚c droplets or by sounds and ventilation on lung sounds and ventilation
HR- 114 bpm contact and is the sixth auscultation 2. Monitor and assess the 2. Monitoring and assessing the on auscultation
BP- 110/70 mmHg leading cause of death. 3. The patient will patient’s respiratory rate, oxygen patient’s respiratory rate, oxygen 3. The patient
RR- 28 bpm demonstrate improved saturation level, and lung sounds saturation level, and lung sounds demonstrated improved
breathing pattern and at least every 4 hours. at least every 4 hours allows for breathing pattern and
Diaphoretic oxygen saturation levels early detection of any changes in oxygen saturation levels
NURSING DIAGNOSIS the patient’s condition.
Risk for Impaired Gas Long-term Goals: Long-term Goal:
Exchange related to After 1-2 weeks of nursing 3. Monitor for signs of 3. Monitoring for signs of After 1-2 weeks of nursing
reduced ventilatory intervention, the patient will complications such as pleurisy, complications such as pleurisy, intervention, the patient
capacity and increased be able to: respiratory distress, and acute respiratory distress, and acute was able to:
oxygen demand as 1. The patient will respiratory failure. respiratory failure allows for early 1. The patient
evidenced by decreased demonstrate full resolution detection and intervention. demonstrated full
oxygen saturation levels of pneumonia symptoms resolution of pneumonia
and increased respiratory 4. Monitor for signs and 4. Monitoring for signs and symptoms
rate. 2. The patient will be free of symptoms of recurrence. symptoms of recurrence allows 2. The patient was free of
complications and have for early detection and complications and had
normal oxygen saturation intervention. normal oxygen saturation
levels at discharge. levels at discharge.
3. The patient will 3. The patient
demonstrate improved demonstrated improved
knowledge of self-care Dependent Interventions: Dependent Interventions: knowledge of self-care
measures and medications 1. Administer prescribed 1. Administering prescribed measures and medications
to prevent recurrence of medications as ordered and as medications as ordered and as to prevent recurrence of
pneumonia symptoms. needed for symptom needed for symptom pneumonia symptoms.
management. management helps control
symptoms and prevent
complications.
2. Educate patient and family 2. Educating patient and family
about the disease process, about the disease process,
medications, and self-care medications, and self-care
measures. measures helps the patient and
their family to understand the
disease and how to manage it.
Collaborative Interventions: Collaborative Interventions:
1. Work with other healthcare 1. Working with other healthcare
providers to develop an providers to develop an
individualized plan of care. individualized plan of care.
2. Refer patient to pulmonary 2. Referring patient to pulmonary
rehabilitation as needed. rehabilitation as needed helps to
ensure that the patient is
receiving all the necessary care
and support, they need.
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
PROBLEM
You might also like
- CASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesCASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de Castro86% (22)
- Hesp1A 3 Unit ActivityDocument10 pagesHesp1A 3 Unit ActivityaresthesoldierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- NCP Pneumonia May6 Ate KimDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumonia May6 Ate Kimiransevilla615No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Ineffective Airway Clearance: Arranged byDocument9 pagesNursing Care Ineffective Airway Clearance: Arranged byAlri LestariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Clinical Review QuestionsDocument1 pageChapter 23 Clinical Review QuestionsLidia DominguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Miggy EstoniloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperiencePauline GarciaNo ratings yet
- Askep DialisisDocument6 pagesAskep Dialisisvictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- NCP Discharge PlanningDocument7 pagesNCP Discharge PlanningMarcieNo ratings yet
- NCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Document4 pagesNCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Jamaica Malicdem0% (1)
- Case Study, Chapter 20, Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocument11 pagesCase Study, Chapter 20, Assessment of Respiratory FunctionMaddyNo ratings yet
- NCP of Respiratory DistressDocument3 pagesNCP of Respiratory DistressDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- NCP MiniparDocument9 pagesNCP MiniparKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: IndependentRea LynNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan # 1:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan # 1:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGj PaguidianNo ratings yet
- NCP For ICU CPDocument10 pagesNCP For ICU CPRalph Laurence TanNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasCarlito AglipayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Analysis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Analysis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluationstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Health: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Health: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Final Thyroid Storm NCPDocument6 pagesFinal Thyroid Storm NCPoguitekim1No ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianeDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- FNCP FinalDocument5 pagesFNCP FinalGewel Bardaje AmboyNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCase Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- Problem 3Document2 pagesProblem 3Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Date/Shift Focus DataDocument2 pagesDate/Shift Focus Datakuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- E LP Pneumonia Keperawatan Anak Zaii - Id.en SalinanDocument11 pagesE LP Pneumonia Keperawatan Anak Zaii - Id.en SalinanMuhammad ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Materi Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageMateri Nursing Care PlanSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Name: Zeph Age: 23 Years Old Sex: Male Room Number: 304 Hospital Number: 100921Document2 pagesName: Zeph Age: 23 Years Old Sex: Male Room Number: 304 Hospital Number: 100921kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- NCP PotentialDocument2 pagesNCP PotentialKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- Programme: High Diploma in NursingDocument7 pagesProgramme: High Diploma in NursingYeesze ChanNo ratings yet
- RLE Case PresentationDocument26 pagesRLE Case PresentationShaine BalverdeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGeraldine SantosNo ratings yet
- NCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Document8 pagesNCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- ABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanAndrea Abadingo100% (1)
- APOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)Document2 pagesAPOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)REYJAN APOLONIONo ratings yet
- NCP PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNCP PneumoniaMerliah LofrancoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Intervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixDocument5 pagesIntervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixRizki ArifNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 NCP Patient FDocument12 pagesGROUP 8 NCP Patient FasdasdNo ratings yet
- Efusi Pleura PPT - Id.en (Repaired)Document17 pagesEfusi Pleura PPT - Id.en (Repaired)fitriaNo ratings yet
- Example of Nursing Care Plan (Pathophysiology)Document5 pagesExample of Nursing Care Plan (Pathophysiology)Elizabeth ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Prematurity Assessment Nursing DX Scientific BG Goal/ Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesPrematurity Assessment Nursing DX Scientific BG Goal/ Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJeanne Mari CostalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Resume of Respiratory ProblemDocument5 pagesResume of Respiratory ProblemIbi Yulia SetyaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TB 1Document1 pageNursing Care Plan TB 1Blair MargauxNo ratings yet
- NCP Pagalanan PablicoDocument15 pagesNCP Pagalanan PablicoRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis G3Document12 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis G3Cuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageRisk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlantososNo ratings yet
- Piguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24Document5 pagesPiguerra - Week 1 Activty Case Study - Ha Rle 2023to24kc bpNo ratings yet
- PulmonaryDocument54 pagesPulmonarytheonlinegeekhubNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis, MTB or TB (Short For TuberclesDocument4 pagesBacillus Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis, MTB or TB (Short For TuberclesLeonelyn GeromoNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Document8 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Hiv)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care in Lung DiseaseFrom EverandPalliative Care in Lung DiseaseKathleen O. LindellNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument4 pagesHypertensionstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument6 pagesRESEARCHstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Gen 004 Sas 9Document9 pagesGen 004 Sas 9strawberrykate26No ratings yet
- LumbosacrallllDocument6 pagesLumbosacrallllstrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Sas12 - Fonbuena, Kate Ashley C.Document1 pageSas12 - Fonbuena, Kate Ashley C.strawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Gen 17Document1 pageGen 17strawberrykate26No ratings yet
- Sample of PPSC Accountant Test Preparation Notes: All Competitive Exam Mcqs & Interview QuestionDocument9 pagesSample of PPSC Accountant Test Preparation Notes: All Competitive Exam Mcqs & Interview Questionkamal sahabNo ratings yet
- Rsi 5 PDFDocument9 pagesRsi 5 PDFManoj RaiNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law ReviewDocument80 pagesCriminal Law ReviewGianna CantoriaNo ratings yet
- Box Speaker 15 Inch LapanganDocument3 pagesBox Speaker 15 Inch LapanganWilli Je WilliamNo ratings yet
- InfoDocument3 pagesInfoIonuț MoNo ratings yet
- Asbāb Al-Nuzūl: Mokrane GuezzouDocument10 pagesAsbāb Al-Nuzūl: Mokrane GuezzoubrizendineNo ratings yet
- Antenna (Radio) : TerminologyDocument9 pagesAntenna (Radio) : Terminologymikeshinoda6No ratings yet
- Bca Semester-II 2023-24 (1) 2Document49 pagesBca Semester-II 2023-24 (1) 2kimberlyeric009No ratings yet
- English Year 3 Up1 18Document15 pagesEnglish Year 3 Up1 18Nur SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Cement Industry in India - A CartelDocument35 pagesCement Industry in India - A CartelVarun NandaNo ratings yet
- Nimbly Black Lives Matter GuideDocument16 pagesNimbly Black Lives Matter GuideDaniel WuNo ratings yet
- Ed Moloney StatementDocument2 pagesEd Moloney StatementPensiveQuillNo ratings yet
- Reverse Poems LessonDocument8 pagesReverse Poems LessonVon Jezzrel Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- FormsDocument6 pagesFormsSHIELA MARIE L. DIMACULANGANNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Sastra InggrisDocument4 pagesDokumen Sastra InggrisI Gede Wisnu Adi PutrawanNo ratings yet
- Desert Magazine 1947 JuneDocument48 pagesDesert Magazine 1947 Junedm1937100% (2)
- FM 2213 Investment Analysis Portfolio ManagementDocument4 pagesFM 2213 Investment Analysis Portfolio ManagementDigit WayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Andhra PradeshDocument9 pagesChapter - Andhra PradeshindramuniNo ratings yet
- Ihrm Module 7Document18 pagesIhrm Module 7sumaiya banuNo ratings yet
- Peter Michael Quinn: EducationDocument2 pagesPeter Michael Quinn: Educationapi-407376667No ratings yet
- Egypt Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesEgypt Lesson Plan 1api-2690252530% (1)
- Memoirs of A MartyrDocument138 pagesMemoirs of A MartyrManu SarvagyaNo ratings yet
- Ashish Sahu - Software CVDocument3 pagesAshish Sahu - Software CVShubham KarnewarNo ratings yet
- Pelco by Schneider Electric Security Cameras & Surveillance SystemsDocument8 pagesPelco by Schneider Electric Security Cameras & Surveillance SystemsAnonymous MDkp0hnb3lNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Ramdhan Suwandi-N8d-360179141Document6 pagesMuhammad Ramdhan Suwandi-N8d-360179141Rija SunaNo ratings yet
- Samsung SyncMaster 932N PlusDocument51 pagesSamsung SyncMaster 932N PlusDee Jay FedeNo ratings yet
- Dse 2012 History Paper 1Document7 pagesDse 2012 History Paper 1CHEW JANICENo ratings yet
- Nama Della Agaveni Butar Butar Kelas X IIS 1: Siapakah Mereka ?Document2 pagesNama Della Agaveni Butar Butar Kelas X IIS 1: Siapakah Mereka ?Della ButarbutarNo ratings yet
- UNICEF Infant and Young Child Feeding ProgrammeDocument76 pagesUNICEF Infant and Young Child Feeding ProgrammethousanddaysNo ratings yet