Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer
Reviewer
Uploaded by
Marion Pooten0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the history and models of the atom. It describes how Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus and proposed that atoms have particles at their center. Neil Bohr then improved Rutherford's model by proposing that electrons move around the nucleus in specific orbits. Later models include the quantum mechanical model where electrons orbit in random ways and surround the atom as an electron cloud. The document also outlines the subatomic particles that make up atoms as well as their properties.
Original Description:
fte
Original Title
reviewer (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the history and models of the atom. It describes how Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus and proposed that atoms have particles at their center. Neil Bohr then improved Rutherford's model by proposing that electrons move around the nucleus in specific orbits. Later models include the quantum mechanical model where electrons orbit in random ways and surround the atom as an electron cloud. The document also outlines the subatomic particles that make up atoms as well as their properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesReviewer
Reviewer
Uploaded by
Marion PootenThe document summarizes the history and models of the atom. It describes how Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus and proposed that atoms have particles at their center. Neil Bohr then improved Rutherford's model by proposing that electrons move around the nucleus in specific orbits. Later models include the quantum mechanical model where electrons orbit in random ways and surround the atom as an electron cloud. The document also outlines the subatomic particles that make up atoms as well as their properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
SCIENCE 8 1907
Quarter 3 Module 5 Ernest Rutherford discovered protons
and nucleus and showed atoms have
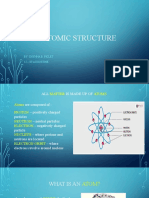
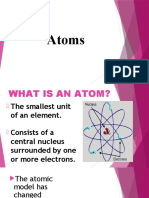
ATOM- smallest unit of matter particles in the center.
Proposed the idea that an atom contains a
PARTS OF AN ATOM: dense nucleus
Nucleus (+ charge): Contains Protons
and Neutrons 1913
Electron Cloud (- charge): Contains Neil Bohr improved Rutherford’s model
Electrons and proposed that electrons move around
the nucleus.
SUBATMOMIC PARTICLES
MODELS OF ATOM
Protons – Positive Charge,
Electrons- Negative Charge
SOLID SPHERE MODEL
Neutrons- Neutral Charge
John Dalton
States that all objects are made of
PROPERTIES OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
particles called atoms and that they are
solid spheres that cannot be divided
further into smaller particles.
PLUM PUDDING MODEL
Joseph J Thomson
LIGHTEST: Electron First one to include electrons
HEAVIEST: Neutron It shows the atom as composed of
electrons scattered throughout a spherical
NUCLEON cloud of positive charge.
- collective term for protons and neutrons
NUCLEAR MODEL
HISTORY OF ATOM Ernest Rutherford
Atom is mostly empty space, with nearly
400 BCE all of its mass concentrated in a tiny
Democritus proposed that matter could central nucleus. The nucleus is positively
not be divided into smaller pieces. charged and surrounded by the negatively
He coined the term atomos which means charged electrons.
indivisible or uncuttable.
PLANETARY MODEL
1803 Neil Bohr
John Dalton created the very first atomic Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that
theory and stated that all elements are have a set size and energy. The energy of
made of atoms. the orbit is related to its size. The lowest
energy is found in the smallest orbit.
DALTON’S ATOMIC THEORY Smaller size & lower energy: Closer to
Nucleus
1. All matter consists of tiny particles called Bigger size & higher energy: Farther
atoms. from Nucleus.
2. Atoms are indestructible and unchangeable.
3. Elements are characterized by the weight of QUANTUM MODEL/ QUANTUM MECHANICAL
their atoms. MODEL
4. When elements react, it is their atoms that Erwin Schrodinger
have combined to form new compounds. Tells electrons orbit the atom in random
ways and pictures the atom as being
1897 surrounded by an electron cloud.
Joseph J Thomson conducted cathode
ray experiment and showed that the atom OTHER TERMS:
was made of even smaller things and Orbital- region where an electron is most likely to
made the raisin bun model. be found.
Gold Foil Experiment: used by Ernest
Rutherford in his study for atomic model.
ATOMIC NUMBER
The number of protons in the nucleus of
each atom of a specific element.
MASS NUMBER
The number of protons plus the number
neutrons combined.
SYMBOLS
Z= atomic number
A = mass number
e- = number of electrons
p+ = number of protons
n°= number of neutrons
amu = atomic mass unit
FORMULAS
Z= e- = p+
A= p+ + n°
n° = A– p
“An element is a neutral atom”
- Element is a neutral atom because there
is an equal number of protons and
electrons present in it.
ION
- A charged atom. The number of electrons
do not equal the number of protons in the
atom
To obtain the mass number of an atom
Add the number of protons and
number of neutrons
Atomic number is equal to ______.
Number of protons/electrons
How to determine identity of an atom?
Number of Protons
You might also like
- Science Year 8 Term 1 NotesDocument10 pagesScience Year 8 Term 1 NotesIshaan NudurupatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 "Structure of Atom" Concept Details Key ConceptsDocument11 pagesChapter - 4 "Structure of Atom" Concept Details Key ConceptsKishlay AnandNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Atomic Structure - 7th STDDocument29 pagesUnit - 4 Atomic Structure - 7th STDthangamuthu baskarNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument50 pagesAtomRomina Mae FernandezNo ratings yet
- Block 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityDocument70 pagesBlock 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit FDocument16 pagesUnit FVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Atoms and Atomic Theory)Document47 pagesChapter 4 (Atoms and Atomic Theory)Raynan TabaldoNo ratings yet
- "The Development of Atomic Theory": "Nothing Exists Except Atoms and Empty Space: Everything Else Is Opinion."Document2 pages"The Development of Atomic Theory": "Nothing Exists Except Atoms and Empty Space: Everything Else Is Opinion."Caryl SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and IonsEugene MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom and The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesStructure of An Atom and The Periodic TableErika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument55 pagesAtomic StructureNikolai Matthew BaltazarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ix: Chapter 4: Structure of The AtomDocument6 pagesChemistry-Ix: Chapter 4: Structure of The AtomShreyashkar JhaNo ratings yet
- Unit4 - Matter and EenergyDocument21 pagesUnit4 - Matter and EenergyMiguel VintimillaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of Atomnajaf_shaanNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument29 pagesSci9 Q2 Lesson 1 Atomic Model, Sub Atomic ParticlesFlorenze GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 AtomDocument48 pagesLesson 1 Atom12 John Paolo DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure, Structure of Atom: Submitted To: Tanya Nagpal Submitted By: Rohit DasDocument23 pagesAtomic Structure, Structure of Atom: Submitted To: Tanya Nagpal Submitted By: Rohit DasAnubha RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Second PreDocument15 pagesGen Chem Second PreShayne Herrera IINo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesDocument14 pagesLESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-VDocument18 pagesUnit Iv-VIvy Marie ToyonganNo ratings yet
- Atomic Particles, Atomic Mass and Weight, and Atomic ModelsDocument17 pagesAtomic Particles, Atomic Mass and Weight, and Atomic ModelshhahahahaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. The AtomDocument26 pagesUnit 2. The Atomgarciaortegajulia5No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument91 pagesAtomic StructureUmmu juraijNo ratings yet
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 pagesPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- Week5Q3 LAS Science8 FinalDocument8 pagesWeek5Q3 LAS Science8 FinalFrances Datuin100% (1)
- عائلة نيتروجينDocument9 pagesعائلة نيتروجينzahrakerim21No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument17 pagesAtomic StructureVandana Khator100% (1)
- Chemistry Note-1Document27 pagesChemistry Note-1mematugoldahmunu21No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument20 pagesAtomic StructureshinNo ratings yet
- LB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesLB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryPhoebe BironNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: By: Chynna B. Piclet 12 - ST AugustineDocument23 pagesAtomic Structure: By: Chynna B. Piclet 12 - ST AugustineZhel TomoroNo ratings yet
- De Up of Three Particles: Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. ProtonsDocument5 pagesDe Up of Three Particles: Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. ProtonsAngelita13 ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Atoms: NucleusDocument6 pagesAtoms: Nucleusヒルデガルダ HILDEGARDENo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument26 pagesAtomsJhul Mhel SonioNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument21 pagesStructure of Atomcelineanne.maglalang.nicdaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document99 pagesChapter 3JayTooSwaggyNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument21 pagesStructure of Atomcelineanne.maglalang.nicdaoNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC HISTORY AND MODEL LlectureDocument2 pagesATOMIC HISTORY AND MODEL LlectureSherchen Antonio-CortesNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec ReviewerDocument42 pagesChem Lec ReviewerMaryashlyn NableaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For FreshmenDocument9 pagesChemistry For FreshmenMeo Angelo AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 01 3 Cont.Document52 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 01 3 Cont.Think Before You ClickNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Chem 1Document2 pagesReviewer in Chem 1MARY ZIANNE GABRIELLE QUINTONo ratings yet
- l2.1 Evolution of Atomic ModelDocument33 pagesl2.1 Evolution of Atomic ModelZeke WilliamNo ratings yet
- Atomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Document16 pagesAtomicstructurepresentation 170510013215Nilimoy Choudhury100% (1)
- Lecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawDocument32 pagesLecture 3. Atomic Structure and Periodic LawВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument13 pagesPhysical Science Reviewerjus jusNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory and ModelsDocument42 pagesAtomic Theory and ModelsJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesPhysical ScienceJazz AddNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TimelineDocument5 pagesChemistry TimelineLyncell Martin VillarNo ratings yet
- Physics - Physics of The AtomDocument7 pagesPhysics - Physics of The AtomAyden StewartNo ratings yet
- 1 Format - Eng-What Is An AtomDocument6 pages1 Format - Eng-What Is An AtomImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- 1.5 History of An Atom - OdpDocument1 page1.5 History of An Atom - OdpZaynab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Atom Stations 19-20 Answer SheetDocument6 pagesAtom Stations 19-20 Answer SheetАбдурахман ПсиксNo ratings yet
- Foundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructureDocument34 pagesFoundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructurePiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Ap 8Document30 pagesAp 8Marion PootenNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Genres of ViewingDocument24 pagesWeek 2 Genres of ViewingMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- LAST PETA Electrical HazardsDocument1 pageLAST PETA Electrical HazardsMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- InvitationDocument1 pageInvitationMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Soft Blue Word Meaning Definition Instagram Post (148 × 210 MM)Document25 pagesSoft Blue Word Meaning Definition Instagram Post (148 × 210 MM)Marion PootenNo ratings yet
- Week 3 8 Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesWeek 3 8 Parts of SpeechMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Esq1w2 3Document23 pagesEsq1w2 3Marion PootenNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Supplyings Words or Expressions That Complete The AnalogyDocument27 pagesWeek 1 Supplyings Words or Expressions That Complete The AnalogyMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Peta MapehDocument8 pagesPeta MapehMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Green Blue English Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument13 pagesGreen Blue English Reading Comprehension WorksheetMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variability: Grouped DataDocument13 pagesMeasures of Variability: Grouped DataMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Bonus PointsDocument1 pageBonus PointsMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Distant Breast CancerDocument10 pagesDistant Breast CancerMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document 9Document3 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document 9Marion PootenNo ratings yet
- ProcreateMasks IntermediateSeriesDocument27 pagesProcreateMasks IntermediateSeriesMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Performance Task MusicallyDocument1 pagePerformance Task MusicallyMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Effects of Changes in Abiotic FactorsDocument1 pageEffects of Changes in Abiotic FactorsMarion PootenNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Aluminium-Boron Carbide CompositesDocument4 pagesFabrication and Mechanical Properties of Aluminium-Boron Carbide CompositesUMA MAHESHNo ratings yet
- Imes-Icore Technologieprospekt EN 2013Document45 pagesImes-Icore Technologieprospekt EN 2013Liviu BirtNo ratings yet
- Boyles Law and Charles LawDocument7 pagesBoyles Law and Charles Lawᜃᜒᜋ᜔ ᜊᜒᜎ᜔ᜌᜈ᜔ᜆᜒNo ratings yet
- BionutrisiDocument21 pagesBionutrisiEnina Eninta SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Mandela Effect & Déjà Vu: Are We Living in A Simulated Reality?Document4 pagesMandela Effect & Déjà Vu: Are We Living in A Simulated Reality?Andy AccardoNo ratings yet
- P6 Home AssignmentDocument5 pagesP6 Home AssignmentMemoona GullNo ratings yet
- MR 341 Laguna 2Document81 pagesMR 341 Laguna 2Piotr BystryNo ratings yet
- Yield (Chemistry) - WikipediaDocument6 pagesYield (Chemistry) - WikipediakamaalNo ratings yet
- Exercises Organic Redox Plus SolutionDocument6 pagesExercises Organic Redox Plus SolutionandreeatalosNo ratings yet
- Nota 6.1Document5 pagesNota 6.1ONG JUN YAO MoeNo ratings yet
- (SHARON, 2012) Studies On Biodegradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate - A Synthetic Polymer PDFDocument10 pages(SHARON, 2012) Studies On Biodegradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate - A Synthetic Polymer PDFLeonardo LopesNo ratings yet
- Separation Biodiesel ReviewDocument7 pagesSeparation Biodiesel ReviewAdi permadiNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Engr. Usman Muhammad B.Sc. Civil Engineering (UET Taxila) M.Sc. Structural Engineering (UET Taxila)Document56 pagesInstructor: Engr. Usman Muhammad B.Sc. Civil Engineering (UET Taxila) M.Sc. Structural Engineering (UET Taxila)nauman100% (1)
- Damage of Monolithic Refractory Linings in Steel LadlesDocument20 pagesDamage of Monolithic Refractory Linings in Steel LadlesKhaled BOUALINo ratings yet
- Hughes 1997Document11 pagesHughes 1997Areaya mahetemNo ratings yet
- Control System SY DFEE: Projecting Guidelines and Commissioning InstructionsDocument26 pagesControl System SY DFEE: Projecting Guidelines and Commissioning InstructionsMustapha AlaouiNo ratings yet
- Chem Piyush THIS IS THE CHEM PROJECT OF LCASS 12TH CBSEDocument16 pagesChem Piyush THIS IS THE CHEM PROJECT OF LCASS 12TH CBSEanu870906No ratings yet
- Collection: Activity 1: Arrange The Jumbled Words Below To Form The Processes in The WaterDocument2 pagesCollection: Activity 1: Arrange The Jumbled Words Below To Form The Processes in The WaterETHEL WENCESLAO100% (1)
- Thermal Analysis of Continuous Casting Process (Maryeling)Document10 pagesThermal Analysis of Continuous Casting Process (Maryeling)Marko's Brazon'No ratings yet
- Infrared Focal Plane Array TechnologyDocument20 pagesInfrared Focal Plane Array TechnologybjsimardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument35 pagesChapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutionnicole.lippolisNo ratings yet
- Flexible ConnectionDocument8 pagesFlexible Connectionsachin sabaleNo ratings yet
- Quantum Wave MechanicsDocument75 pagesQuantum Wave MechanicsBen KnightonNo ratings yet
- Ecw567-Wastewater SedimentationDocument34 pagesEcw567-Wastewater Sedimentationhanif aiyadNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al2024-B4C-hBN Reinforced Metal Matrix CompositesDocument5 pagesMicrostructure and Mechanical Properties of Al2024-B4C-hBN Reinforced Metal Matrix CompositesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Camel: Sand Textured Paint Ma478 - SeriesDocument2 pagesCamel: Sand Textured Paint Ma478 - Seriessfwclau24No ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument9 pagesAcid Bases and SaltsSwapna's GaamingNo ratings yet
- Msds (Sodium Hydrochlorite) PDFDocument6 pagesMsds (Sodium Hydrochlorite) PDFAyman Medaney100% (1)
- Taller Quimica IDocument35 pagesTaller Quimica IZantiiagoo TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year Test (4) 1Document2 pagesChemistry 1st Year Test (4) 1Rashid JalalNo ratings yet