Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Joint Types, Structures and Formation
Joint Types, Structures and Formation
Uploaded by
bahadurCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAnatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetAlaka69% (16)
- Mind Map. Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageMind Map. Skeletal SystemMayeliz Urvina50% (2)
- The Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideDocument27 pagesThe Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideTiago José ReisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - JointsDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - JointsMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - KODocument1 pageSkeletal System - KOGift Munyinda (G-Man)No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Synovial JointDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - Synovial JointMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System. Assessing The MusculoskeletalDocument11 pagesMusculoskeletal System. Assessing The MusculoskeletalLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofDocument20 pages11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument27 pagesJointsJhan BencelNo ratings yet
- Joints TransesDocument19 pagesJoints TransesskidamarinkNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - FinalsDocument8 pagesAnaphy - Finalsnero.keishareignc17No ratings yet
- ArticulationsDocument36 pagesArticulationsLisaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFDocument6 pagesDynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFJorge Flores TorresNo ratings yet
- Fibrous Joint: Types: 1. Sutures 2. Syndesmoses 3. Gomphoses 4. SchindylesisDocument9 pagesFibrous Joint: Types: 1. Sutures 2. Syndesmoses 3. Gomphoses 4. SchindylesisNu Ri LeeNo ratings yet
- SEDS11 Bones Worksheet AnswersDocument13 pagesSEDS11 Bones Worksheet Answersjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- JointsDocument33 pagesJointsDeshmukh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 2006 TMJ Hylander CorrectedDocument33 pages2006 TMJ Hylander CorrectedKrupali JainNo ratings yet
- The Features of Bones and Joints: Sanae Silvera 11j Shannay Mckenzie 11jDocument10 pagesThe Features of Bones and Joints: Sanae Silvera 11j Shannay Mckenzie 11jshannay mckenzieNo ratings yet
- Sport Science NotesDocument5 pagesSport Science NotesSpicyChildrenNo ratings yet
- Muscles Anatomy-Dr - NdukuiDocument62 pagesMuscles Anatomy-Dr - Ndukuiglenian560No ratings yet
- Physical Propertes of Bone, Cartilage and Their Function Adaptation in Various ConditionsDocument15 pagesPhysical Propertes of Bone, Cartilage and Their Function Adaptation in Various ConditionsSwasti PandeyNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument5 pagesJointsSEAN JODI M. COSEPENo ratings yet
- Function Must Be Understood Before Dysfunction Can Have Any MeaningDocument47 pagesFunction Must Be Understood Before Dysfunction Can Have Any MeaningDapinder BrarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pages1.1 The Skeletal SystemPaulaNo ratings yet
- ARTICULATIONSDocument9 pagesARTICULATIONSCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument6 pagesOsteoarthritisravi ranaNo ratings yet
- SL REVISION Topic 1 & 2Document27 pagesSL REVISION Topic 1 & 2Muffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Ligament and Tendon: DR: Maryam Memon Lecturer: AbiprsDocument22 pagesBiomechanics of Ligament and Tendon: DR: Maryam Memon Lecturer: AbiprsAazeen memonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms-1Document13 pagesAnaphy Midterms-1Renz GoleNo ratings yet
- Skeleton - Movement and LocomotionDocument80 pagesSkeleton - Movement and Locomotionpreethi bharathNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The: Finals Part 3 Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The: Finals Part 3 Musculoskeletal DisordersMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument3 pagesLocomotion and MovementYouTutor PSNo ratings yet
- 4 JointsDocument47 pages4 JointsFareez HamidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5iDocument20 pagesChapter 5iMuhd HafizzudinNo ratings yet
- Joint Stability and FlexibilityDocument17 pagesJoint Stability and FlexibilityDziedzorm DZAMESINo ratings yet
- Week 5 Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesWeek 5 Skeletal SystemKimberly Faye JuevesNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument2 pagesJointsBritney MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Biomekanik Iv FDC 2020Document23 pagesBiomekanik Iv FDC 2020Nadhia FitriaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System2Document1 pageSkeletal System2Elisha DienteNo ratings yet
- Canbridge Checkpoint Grade 7Document25 pagesCanbridge Checkpoint Grade 7seema sarathNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Tendons and LigamentsDocument2 pagesDifference Between Tendons and LigamentsChristopherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- CSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesCSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemSamantha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Classificationofjoints 140413054157 Phpapp01 161023170805Document49 pagesClassificationofjoints 140413054157 Phpapp01 161023170805Adu-danquah StephenNo ratings yet
- GCSE PE Paper 1 ContentDocument18 pagesGCSE PE Paper 1 Contentshiven.solankiNo ratings yet
- Ana - Joints ClassificationsDocument12 pagesAna - Joints ClassificationsMahmoud hilmyNo ratings yet
- HAPP LEC 6 Articular SystemDocument10 pagesHAPP LEC 6 Articular SystemJomar ManalangNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inDocument19 pages2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inliefeng81100% (1)
- Joints Anatomy (Ashalatha)Document16 pagesJoints Anatomy (Ashalatha)Abdul KhadirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bones and JointsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Bones and JointsJade Karen Lingo-lingoNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Connective Tissue: Exploring Nervous Tissue and Muscle TissueDocument2 pagesCharacterizing Connective Tissue: Exploring Nervous Tissue and Muscle TissueAlbar B. SiladNo ratings yet
- 08 - Injury To Joints Dislocation and SubluxationDocument3 pages08 - Injury To Joints Dislocation and SubluxationABCDEFG HIJKLMNOPNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Skeletal SystemDocument17 pages3.1 Skeletal SystemAndriy GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Classification of BoneDocument1 pageClassification of Bonezain juttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesChapter 6 Skeletal SystemJohn Benedict Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- JOINTS HandoutDocument4 pagesJOINTS HandoutRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The AnkleDocument9 pagesBiomechanics of The AnkleSanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Joints Cliff Notes A&pDocument4 pagesJoints Cliff Notes A&pdbelmerNo ratings yet
- Joints & Their Movements001Document14 pagesJoints & Their Movements001welcome homeNo ratings yet
- SmartInvestment 17 - 23 - March-2024)Document74 pagesSmartInvestment 17 - 23 - March-2024)bahadurNo ratings yet
- Jain DigestDocument60 pagesJain DigestbahadurNo ratings yet
- JPSC 2024 Paper-1Document26 pagesJPSC 2024 Paper-1bahadurNo ratings yet
- 18 March CurrentDocument2 pages18 March CurrentbahadurNo ratings yet
- TEST SERIES【 6】Document9 pagesTEST SERIES【 6】bahadurNo ratings yet
- मौर्योत्तरDocument7 pagesमौर्योत्तरbahadurNo ratings yet
- Full ExamplarDocument16 pagesFull ExamplarbahadurNo ratings yet
- भारत पर तुर्को का आक्रमण by Rohit singhDocument4 pagesभारत पर तुर्को का आक्रमण by Rohit singhbahadurNo ratings yet
- Eco Presentation 1Document8 pagesEco Presentation 1bahadurNo ratings yet
- ExcelTwo ChapterWorkDocument2 pagesExcelTwo ChapterWorkbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision 2Document13 pagesPhysics Revision 2bahadurNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument7 pagesTime TablebahadurNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Maths ClassDocument1 pageYear 10 Maths ClassbahadurNo ratings yet
- PE Physical Education15-Feb-2024Document25 pagesPE Physical Education15-Feb-2024bahadurNo ratings yet
- Basics of APA Style Reference ListDocument2 pagesBasics of APA Style Reference ListbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics WorksheetDocument3 pagesPhysics WorksheetbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Year-10Document135 pagesPhysical Education Year-10bahadurNo ratings yet
- Skill Acquisition - Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesSkill Acquisition - Exam QuestionsbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physcial Education Lesson - 2 & 3 (Year 10 A)Document26 pagesPhyscial Education Lesson - 2 & 3 (Year 10 A)bahadurNo ratings yet
Joint Types, Structures and Formation
Joint Types, Structures and Formation
Uploaded by
bahadurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Joint Types, Structures and Formation
Joint Types, Structures and Formation
Uploaded by
bahadurCopyright:
Available Formats
IGCSE PE (0413 19-21) - Chptr 1.
2 - Joint types, structures and formation Study
Science Biology Anatomy
IGCSE PE (0413 19-21) - Chptr 1.2 - Joint types, structures and formation
Leave the first rating
Terms in this set (19)
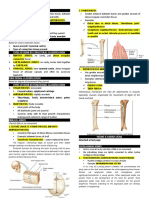
A point in the body where two or more bones are connected, but with differing degrees of movement depending
Joint
on location.
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
These bones are attached together and cannot move as
they are joined via fibrous connective tissue. For example -
Fixed or immoveable joints (fibrous joints)
the sections of the cranium.
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
The bones in these joints can move a small amount as they
are linked together by ligaments and cartilage (which
Slightly moveable joints (cartilaginous joints)
absorbs the movement). For example - The vertebral
column and the ribs.
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
These joints have the greatest amount of movement and
include the elbow, shoulder, knee and hip.
Freely moveable joints (synovial joints)
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
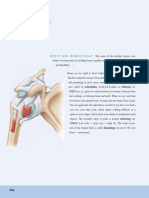
Surrounds the joint capsule with a synovial fluid.
Joint membrane
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
Acts as a lubricant that reduces friction in the joint; allows
for smoother movement and reduces wear and tear.
Synovial fluid
The structure that surrounds and protects the joint, holding the bones together; made up of an outer fibrous
Joint capsule
membrane and an inner synovial membrane.
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
The strong, elastic fibres that hold the bones together and
keep them in place.
Ligament
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
A strong but flexible material found at the end of long
bones that acts as a cushion to stop bones knocking
Cartilage
together.
Tendon A tough band of fibrous tissue that connects muscle to bone and enables joints to withstand tension.
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
These provide a large range of movement in every
direction. One bone has a bulge or ball that fits into a
Types of synovial joints: Ball and socket socket in the other bone. Found in the shoulders and the
hips. Allow actions such as an overhead clear in badminton,
bowling in cricket or all the swimming strokes.
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
These are located in the elbow and the knee and allow
movement in one direction. For example - The elbows and
Types of synovial joints: Hinge Joints
knees allow you to bend and straighten your arms and legs
when performing a jump shot in basketball.
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
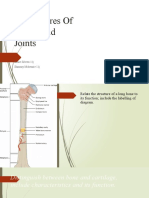
The thighbone; the longest and one of the strongest bones
in the body
Femur
TERM
IGCSE PE (0413 19-21) - Chptr 1.2 - Joint types, structures and formation
DEFINITION LOCATION
The tibia; also known as the shinbone is the larger, stronger,
and anterior of the two bones in the leg below the knee.
Tibia
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
Fibrocartilage pads that separate and cushion the
vertebrae
Intervertebral discs
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
Hyaline cartilage that covers ends of bones in synovial
joints
Articular cartilage
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
26 irregular bones that make up your backbone
Vertebrae
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
Large socket in the pelvic bone for the head of the femur
Acetabulum
TERM DEFINITION LOCATION
Articulates with the acetabulum (hip socket)
Head of the femur
You might also like
- Anatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAnatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetAlaka69% (16)
- Mind Map. Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageMind Map. Skeletal SystemMayeliz Urvina50% (2)
- The Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideDocument27 pagesThe Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideTiago José ReisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - JointsDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - JointsMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - KODocument1 pageSkeletal System - KOGift Munyinda (G-Man)No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Synovial JointDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - Synovial JointMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System. Assessing The MusculoskeletalDocument11 pagesMusculoskeletal System. Assessing The MusculoskeletalLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofDocument20 pages11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument27 pagesJointsJhan BencelNo ratings yet
- Joints TransesDocument19 pagesJoints TransesskidamarinkNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - FinalsDocument8 pagesAnaphy - Finalsnero.keishareignc17No ratings yet
- ArticulationsDocument36 pagesArticulationsLisaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFDocument6 pagesDynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFJorge Flores TorresNo ratings yet
- Fibrous Joint: Types: 1. Sutures 2. Syndesmoses 3. Gomphoses 4. SchindylesisDocument9 pagesFibrous Joint: Types: 1. Sutures 2. Syndesmoses 3. Gomphoses 4. SchindylesisNu Ri LeeNo ratings yet
- SEDS11 Bones Worksheet AnswersDocument13 pagesSEDS11 Bones Worksheet Answersjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- JointsDocument33 pagesJointsDeshmukh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 2006 TMJ Hylander CorrectedDocument33 pages2006 TMJ Hylander CorrectedKrupali JainNo ratings yet
- The Features of Bones and Joints: Sanae Silvera 11j Shannay Mckenzie 11jDocument10 pagesThe Features of Bones and Joints: Sanae Silvera 11j Shannay Mckenzie 11jshannay mckenzieNo ratings yet
- Sport Science NotesDocument5 pagesSport Science NotesSpicyChildrenNo ratings yet
- Muscles Anatomy-Dr - NdukuiDocument62 pagesMuscles Anatomy-Dr - Ndukuiglenian560No ratings yet
- Physical Propertes of Bone, Cartilage and Their Function Adaptation in Various ConditionsDocument15 pagesPhysical Propertes of Bone, Cartilage and Their Function Adaptation in Various ConditionsSwasti PandeyNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument5 pagesJointsSEAN JODI M. COSEPENo ratings yet
- Function Must Be Understood Before Dysfunction Can Have Any MeaningDocument47 pagesFunction Must Be Understood Before Dysfunction Can Have Any MeaningDapinder BrarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pages1.1 The Skeletal SystemPaulaNo ratings yet
- ARTICULATIONSDocument9 pagesARTICULATIONSCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument6 pagesOsteoarthritisravi ranaNo ratings yet
- SL REVISION Topic 1 & 2Document27 pagesSL REVISION Topic 1 & 2Muffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Ligament and Tendon: DR: Maryam Memon Lecturer: AbiprsDocument22 pagesBiomechanics of Ligament and Tendon: DR: Maryam Memon Lecturer: AbiprsAazeen memonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms-1Document13 pagesAnaphy Midterms-1Renz GoleNo ratings yet
- Skeleton - Movement and LocomotionDocument80 pagesSkeleton - Movement and Locomotionpreethi bharathNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The: Finals Part 3 Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The: Finals Part 3 Musculoskeletal DisordersMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument3 pagesLocomotion and MovementYouTutor PSNo ratings yet
- 4 JointsDocument47 pages4 JointsFareez HamidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5iDocument20 pagesChapter 5iMuhd HafizzudinNo ratings yet
- Joint Stability and FlexibilityDocument17 pagesJoint Stability and FlexibilityDziedzorm DZAMESINo ratings yet
- Week 5 Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesWeek 5 Skeletal SystemKimberly Faye JuevesNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument2 pagesJointsBritney MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Biomekanik Iv FDC 2020Document23 pagesBiomekanik Iv FDC 2020Nadhia FitriaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System2Document1 pageSkeletal System2Elisha DienteNo ratings yet
- Canbridge Checkpoint Grade 7Document25 pagesCanbridge Checkpoint Grade 7seema sarathNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Tendons and LigamentsDocument2 pagesDifference Between Tendons and LigamentsChristopherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- CSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesCSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemSamantha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Classificationofjoints 140413054157 Phpapp01 161023170805Document49 pagesClassificationofjoints 140413054157 Phpapp01 161023170805Adu-danquah StephenNo ratings yet
- GCSE PE Paper 1 ContentDocument18 pagesGCSE PE Paper 1 Contentshiven.solankiNo ratings yet
- Ana - Joints ClassificationsDocument12 pagesAna - Joints ClassificationsMahmoud hilmyNo ratings yet
- HAPP LEC 6 Articular SystemDocument10 pagesHAPP LEC 6 Articular SystemJomar ManalangNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inDocument19 pages2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inliefeng81100% (1)
- Joints Anatomy (Ashalatha)Document16 pagesJoints Anatomy (Ashalatha)Abdul KhadirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bones and JointsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Bones and JointsJade Karen Lingo-lingoNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Connective Tissue: Exploring Nervous Tissue and Muscle TissueDocument2 pagesCharacterizing Connective Tissue: Exploring Nervous Tissue and Muscle TissueAlbar B. SiladNo ratings yet
- 08 - Injury To Joints Dislocation and SubluxationDocument3 pages08 - Injury To Joints Dislocation and SubluxationABCDEFG HIJKLMNOPNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Skeletal SystemDocument17 pages3.1 Skeletal SystemAndriy GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Classification of BoneDocument1 pageClassification of Bonezain juttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesChapter 6 Skeletal SystemJohn Benedict Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- JOINTS HandoutDocument4 pagesJOINTS HandoutRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The AnkleDocument9 pagesBiomechanics of The AnkleSanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Joints Cliff Notes A&pDocument4 pagesJoints Cliff Notes A&pdbelmerNo ratings yet
- Joints & Their Movements001Document14 pagesJoints & Their Movements001welcome homeNo ratings yet
- SmartInvestment 17 - 23 - March-2024)Document74 pagesSmartInvestment 17 - 23 - March-2024)bahadurNo ratings yet
- Jain DigestDocument60 pagesJain DigestbahadurNo ratings yet
- JPSC 2024 Paper-1Document26 pagesJPSC 2024 Paper-1bahadurNo ratings yet
- 18 March CurrentDocument2 pages18 March CurrentbahadurNo ratings yet
- TEST SERIES【 6】Document9 pagesTEST SERIES【 6】bahadurNo ratings yet
- मौर्योत्तरDocument7 pagesमौर्योत्तरbahadurNo ratings yet
- Full ExamplarDocument16 pagesFull ExamplarbahadurNo ratings yet
- भारत पर तुर्को का आक्रमण by Rohit singhDocument4 pagesभारत पर तुर्को का आक्रमण by Rohit singhbahadurNo ratings yet
- Eco Presentation 1Document8 pagesEco Presentation 1bahadurNo ratings yet
- ExcelTwo ChapterWorkDocument2 pagesExcelTwo ChapterWorkbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision 2Document13 pagesPhysics Revision 2bahadurNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument7 pagesTime TablebahadurNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Maths ClassDocument1 pageYear 10 Maths ClassbahadurNo ratings yet
- PE Physical Education15-Feb-2024Document25 pagesPE Physical Education15-Feb-2024bahadurNo ratings yet
- Basics of APA Style Reference ListDocument2 pagesBasics of APA Style Reference ListbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physics WorksheetDocument3 pagesPhysics WorksheetbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Year-10Document135 pagesPhysical Education Year-10bahadurNo ratings yet
- Skill Acquisition - Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesSkill Acquisition - Exam QuestionsbahadurNo ratings yet
- Physcial Education Lesson - 2 & 3 (Year 10 A)Document26 pagesPhyscial Education Lesson - 2 & 3 (Year 10 A)bahadurNo ratings yet