Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PM Test C10 (Student)
PM Test C10 (Student)
Uploaded by
damonchooOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PM Test C10 (Student)
PM Test C10 (Student)
Uploaded by
damonchooCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:______________________________ ( ) Class:_________ Date:___________
TEST
Chapter 10: Transfer of Thermal Energy
25
Multiple-Choice Questions (10 marks)
1. Choose the most appropriate statement that describes thermal energy transfer.
A Heat flows from a hotter body to a colder body, and coldness flows in the
opposite direction.
B Conduction is one process of thermal energy transfer that involves the vibration
of particles.
C There is no heat flow when two bodies are in thermal equilibrium.
D Radiation refers to the process of heat transfer by the movement of fluid due to
density differences. ( )
2. Two similarly sized blocks (one made out of metal, and the other, wood) are in contact
with each other. The metal block is at a higher temperature than the wooden block.
Describe what is likely to happen to both blocks.
A The metal block transfers some of its temperature to the wooden block, causing
the wooden block to gain temperature.
B The metal block gets hotter and the wooden block gets cooler due to net thermal
energy transfer from the wooden block to the metal block.
C The metal block and the wooden block eventually reach thermal equilibrium with
each other, and there will be no net thermal energy transfer between them.
D The metal block and the wooden block cannot reach thermal equilibrium even
after a long time since they are made of different substances. ( )
3. In the early morning, Ali touches the surface of a car body and finds that it is cold. This
is because the metallic surface of the car is a good
A thermal conductor and it conducts heat from the surface to Ali’s hands.
B thermal conductor and it conducts heat from Ali’s hands to the surface.
C thermal insulator and it does not conduct heat from the surface to Ali’s hands
easily.
D thermal insulator and it does not conduct heat from Ali’s hands to the surface
easily. ( )
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1
4. Which of the following shows the correct order of the three states of matter arranged
according to their thermal conductivity?
Best conductor Worst conductor
A Solid, gas, liquid
B Gas, liquid, solid
C Liquid, gas, solid
D Solid, liquid, gas ( )
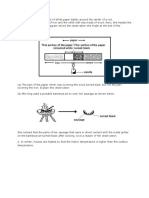
5. A metal gauze is wrapped around a piece of ice and dropped into a boiling tube
containing water. The top of the boiling tube is then heated up by a Bunsen burner until
the water near the surface begins to boil, as shown in the diagram below. During this
time, the ice is observed to remain largely un-melted. This experiment shows that
A ice is a poor conductor of heat.
B water is a good conductor of heat.
C water is a poor conductor of heat.
D metal gauze is a good conductor of heat. ( )
6. A lamp has been switched on for a while. Siti, who is sitting beside it, begins to feel its
heat. This heat transfer is largely due to
A conduction from the lamp through the air to Siti.
B convection of the air heated by the lamp.
C radiation from the lamp to Siti.
D free electron diffusion from the lamp to Siti. ( )
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 2
7. Two similarly sized metal cans have different outer casings. One is painted dull and
black, and the other is painted shiny and silver. Both cans are filled with equal amounts
of water and heated to the same temperature after which they are left to cool to room
temperature. Which of the following statements best describes the cooling process of
the water?
A Water in the dull and black can takes a shorter time to cool because dull and black
surfaces are good absorbers of radiation.
B Water in the dull and black can takes a longer time to cool because dull and black
surfaces are good emitters of radiation.
C Water in the shiny and silver can takes a shorter time to cool because shiny and
silver surfaces are bad absorbers of radiation.
D Water in the shiny and silver can takes a longer time to cool because shiny and
silver surfaces are bad emitters of radiation. ( )
8. Which of the following is the best thermal insulator?
A Still air B Wood
C Insulating plastic D Water ( )
9. Certain physical characteristics of a polar bear help it to reduce heat loss in winter.
Choose the correct characteristics from the list below.
1 Its white coat reduces heat loss by radiation.
2 A layer of fat under its skin reduces heat loss by conduction.
3 The thick fur reduces heat loss by convection.
A 1 and 2 only B 1 and 3 only
C 2 and 3 only D All of the above ( )
10. A solar panel is designed to collect heat from the Sun. Which of the following panel
designs is most appropriate for this purpose?
A A black-coloured panel is used because black surfaces are better absorbers of
heat.
B A light-coloured panel is used because white surfaces are better absorbers of heat.
C A black-coloured panel is used because black surfaces are better emitters of heat.
D A light-coloured panel is used because white surfaces are better emitters of heat.
( )
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 3
Structured Questions (15 marks)
11. (a) Describe the process of heat transfer by conduction. [3]
(b) Describe why metals are better conductors of heat than non-metals. [2]
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 4
12. Some cold liquid is placed in a vacuum flask. Describe, with a well-labelled diagram,
how the flask is able to keep the liquid inside it cold. [5]
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 5
13. A burning candle is positioned directly below a chimney in a box, as shown in the
diagram below.
(a) Indicate clearly with arrows the direction of the convection current in the air. [1]
(b) Describe how the convection current is set up. [4]
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 6
Table of Specifications
Type of Syllabus learning Assessment
Question no. No. of marks
question outcome(s) objectives*
1 9(a) K 1
2 9(a) C 1
3 9(b), 9(e) A 1
4 9(b) C 1
5 Multiple- 9(b) C 1
6 choice 9(d), 9(e) A 1
7 9(c), 9(e) A 1
8 9(d), 9(e) A 1
9 9(b), 9(c), 9(d), 9(e) A 1
10 9(d) C 1
11 9(b) C 5
12 Structured 9(d) A 5
13 9(c) C 5
*K/C: Knowledge/Comprehension
A: Application
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 7
You might also like
- Test Chapter 17Document18 pagesTest Chapter 17damonchooNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Physics Sample Paper 2Document5 pagesICSE Class 8 Physics Sample Paper 2madhumitra mohantyNo ratings yet
- p4 Science Revision MCQ - HeatDocument8 pagesp4 Science Revision MCQ - HeatfranticfoodfrenzyNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument13 pagesHeatSrirama SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- AS - PS - CB - IX - Sci - Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument7 pagesAS - PS - CB - IX - Sci - Matter in Our Surroundingsmaurya.ghanshyam101984No ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument22 pagesHeat and Temperatureziaurrehmanrizvi7No ratings yet
- 3.4_EXERCISE_(1)Document10 pages3.4_EXERCISE_(1)keishamutsakaniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Document3 pagesWorksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Random AccNo ratings yet
- Jets of Zambia Olympiads PrimaryDocument3 pagesJets of Zambia Olympiads Primarybchanda375No ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument4 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4: Back of Chapter QuestionsPugalmeena PugalmeenaNo ratings yet
- IES 1998 - I Scan PDFDocument20 pagesIES 1998 - I Scan PDFK.v.SinghNo ratings yet
- CB - IX - Sci - Ch1 Matter in Our Surroundings - Specific QsDocument2 pagesCB - IX - Sci - Ch1 Matter in Our Surroundings - Specific QsHarshikaNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry & Thermal Expansion - Fa74ca2a c2f5 4343 85b3 004b19627fc2Document16 pagesCalorimetry & Thermal Expansion - Fa74ca2a c2f5 4343 85b3 004b19627fc2veereshgajwelNo ratings yet
- Science Class X DPSBNDocument13 pagesScience Class X DPSBNhangezoe68khpNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument180 pagesScienceR. K. GoswamiNo ratings yet
- The United Republic of Tanzania National Examinations Council Certificate of Secondary Education Examination Physics 1Document7 pagesThe United Republic of Tanzania National Examinations Council Certificate of Secondary Education Examination Physics 1Alhamdu Mussa SogoleNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument108 pagesGeneral ScienceArijit MandalNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 2023: Annual ExaminationDocument5 pagesQuestion Paper 2023: Annual ExaminationUTTAM KUMBHARNo ratings yet
- Exercise Questions Page Number 45 - 47Document4 pagesExercise Questions Page Number 45 - 47Ricky 's PremiumNo ratings yet
- QP SEM 1 GR 8 2023 24 Combined Science PhysicsDocument8 pagesQP SEM 1 GR 8 2023 24 Combined Science PhysicsSansridh SridharanNo ratings yet
- Jets of Zambia Olympiads Primary (2)Document6 pagesJets of Zambia Olympiads Primary (2)bchanda375No ratings yet
- 2017 - S3 - Mid (Post) PhysicsDocument8 pages2017 - S3 - Mid (Post) Physicsasdasd1414196No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4Document4 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4Ayesha KhanNo ratings yet
- HKUGA College: S1 Science Module 2 Test (2021-22) Question & Answer BookletDocument7 pagesHKUGA College: S1 Science Module 2 Test (2021-22) Question & Answer Booklet6A 12 Nathan Leung 梁逸曦No ratings yet
- WS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetDocument8 pagesWS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetSiyaNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument4 pagesHeat TransferSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test Standard (S) : Name Class Date 1 The Drawing Below Shows A Measuring InstrumentDocument18 pagesEnd of Unit Test Standard (S) : Name Class Date 1 The Drawing Below Shows A Measuring Instrument108173No ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument17 pagesTemperature and HeatSubho BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Our Surroundings Test SolutionsDocument3 pagesMatter and Our Surroundings Test Solutionsdayanandan1No ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsnAnswers With Explanation-1 PDFDocument16 pagesPhysics QuestionsnAnswers With Explanation-1 PDFKOLLA VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Year:Iii Sem:I Subject: Heat Transfer Unit-IDocument21 pagesYear:Iii Sem:I Subject: Heat Transfer Unit-IKiran ReddyNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Easter Exam 2022Document7 pagesForm 4 Easter Exam 2022TechnixFNNo ratings yet
- ICSE Sample Papers For Class 8 Chemistry Paper 1 (2023-24)Document13 pagesICSE Sample Papers For Class 8 Chemistry Paper 1 (2023-24)kapilsaggi2526No ratings yet
- Do Nguyen Khoa - Thermal PhysicsDocument13 pagesDo Nguyen Khoa - Thermal PhysicsThanh DinhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year T-5Document3 pagesChemistry 1st Year T-5Amir HabibNo ratings yet
- Physics WE g7 s2 BPK HeatDocument3 pagesPhysics WE g7 s2 BPK HeatnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- 9th Chapter 1Document10 pages9th Chapter 1EdumaaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 March 31 Science Chapter 4 HeatDocument5 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 March 31 Science Chapter 4 Heatarunadevi30081990No ratings yet
- Physics MCQ English (Complete)Document53 pagesPhysics MCQ English (Complete)YOGA With SUNITANo ratings yet
- KS3 TestDocument6 pagesKS3 TestVytheeshwaran Vedagiri80% (5)
- 07-Elasticity + (Calor & Therma Exp) - SCDocument8 pages07-Elasticity + (Calor & Therma Exp) - SCAnujNo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document5 pages© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication Railways ALP General Science Section TestDocument7 pagesDisha Publication Railways ALP General Science Section TestKundan KrNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Basics MCQ Practice TestDocument10 pagesChemical Engineering Basics MCQ Practice TestAmir RajputtNo ratings yet
- RTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 7 2008Document8 pagesRTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 7 2008iwan93No ratings yet
- Sing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicsDocument4 pagesSing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicstestNo ratings yet
- Physics 7thDocument2 pagesPhysics 7thswathyraghavendranNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Summer Holidays Homework(B)(24 25)Document2 pagesClass 9 Summer Holidays Homework(B)(24 25)srinivas.rapakulaNo ratings yet
- Paper Test For Thermal PhysicsDocument8 pagesPaper Test For Thermal PhysicsJerrySemuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4, HEAT: 7 ScienceDocument4 pagesChapter 4, HEAT: 7 ScienceravilullaNo ratings yet
- 4 Transfer Processes: Practice 4.1 (p.109)Document6 pages4 Transfer Processes: Practice 4.1 (p.109)Oscar TSANGNo ratings yet
- Problems Based On Conduction Basic Level: Transmission of HeatDocument11 pagesProblems Based On Conduction Basic Level: Transmission of HeatApoorvNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Heat Transfer Quiz-II: D. Height of The CylinderDocument2 pagesSolutions For Heat Transfer Quiz-II: D. Height of The CylindermkvemulaNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - Practice SheetDocument3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - Practice Sheetsifivar867No ratings yet
- Heat NcertDocument5 pagesHeat NcertSagarNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : CalorimetryDocument15 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : CalorimetryHarshit100% (1)
- Post Midterm XI PHY Question PPR PhyDocument4 pagesPost Midterm XI PHY Question PPR PhyFlick OPNo ratings yet
- BM Test C20 SEDocument5 pagesBM Test C20 SEdamonchooNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument28 pagesAn Introduction To Organic ChemistrydamonchooNo ratings yet
- TPG SOW (Modular) Chapter 18Document3 pagesTPG SOW (Modular) Chapter 18damonchooNo ratings yet
- BM (Modular) Chapter 18Document6 pagesBM (Modular) Chapter 18damonchooNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 17Document18 pagesTest Chapter 17damonchooNo ratings yet
- Thermal Insulation and Corrosion Controls Coating: Kevin KimDocument37 pagesThermal Insulation and Corrosion Controls Coating: Kevin KimPuding SutraNo ratings yet
- 06 - Exhibit D - Scope of Work 26 Dec 06Document15 pages06 - Exhibit D - Scope of Work 26 Dec 06Ahmad Abd RabouNo ratings yet
- A Compilation of Laboratory ReportsDocument57 pagesA Compilation of Laboratory ReportsEli Leopoldo Geneston100% (3)
- Katalog SikaDocument112 pagesKatalog SikaSeptian Adi S75% (4)
- BiesuzDocument4 pagesBiesuzJoão Gustavo da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - EIFS - SmallerDocument89 pagesLecture 2 - EIFS - SmallertrungNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Wick Type Solar StillDocument59 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Wick Type Solar StillmktutyNo ratings yet
- Astm C 898 - 95 - Qzg5oc05nqDocument15 pagesAstm C 898 - 95 - Qzg5oc05nqsunitkghoshNo ratings yet
- Achall WebDocument85 pagesAchall WebSathish PNo ratings yet
- Fisher R 2502 Controllers: Instruction ManualDocument32 pagesFisher R 2502 Controllers: Instruction ManualCarlos RinconNo ratings yet
- ENV SPV DR B 018 Insulation Procedure Rev - ADocument6 pagesENV SPV DR B 018 Insulation Procedure Rev - AyoeyNo ratings yet
- CH2355Document9 pagesCH2355anonymousNo ratings yet
- Sagar Group of Institutes, Bhopal: Subject: Heat& Mass Transfer CODE: ME-6003 Unit-IDocument3 pagesSagar Group of Institutes, Bhopal: Subject: Heat& Mass Transfer CODE: ME-6003 Unit-IRiyasNo ratings yet
- Challenges and New Developments: Subsea and Deepwater Flow Assurance InsulationDocument23 pagesChallenges and New Developments: Subsea and Deepwater Flow Assurance InsulationFerryNo ratings yet
- Halac Sy 1958Document5 pagesHalac Sy 1958Anonymous sAmJfcVNo ratings yet
- Ambient Temperature Correction Factor TG 1-16-05 2.186191639Document32 pagesAmbient Temperature Correction Factor TG 1-16-05 2.186191639freeware freeNo ratings yet
- Foamglas Insulation System SpecificationsDocument28 pagesFoamglas Insulation System SpecificationsChristian DoriaNo ratings yet
- Basement InsulationDocument12 pagesBasement InsulationAdam RossmillerNo ratings yet
- Storage Tank Alumnuim Roof - LatestDocument22 pagesStorage Tank Alumnuim Roof - LatesthgagNo ratings yet
- Sub:-Heat TransferDocument17 pagesSub:-Heat TransferDileep Chowdary KuchipudiNo ratings yet
- KJM442 386Document8 pagesKJM442 386Amar MursyidNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hut Pakistan - Company ProfileDocument14 pagesEngineering Hut Pakistan - Company ProfilesidsaleemNo ratings yet
- Transient Molten Salt 2 Tank TS Modeling For CSPDocument18 pagesTransient Molten Salt 2 Tank TS Modeling For CSPShiva Kumar NidanampallyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ProblemsDocument9 pagesHeat Transfer ProblemsAdriane Gabrielle BautistaNo ratings yet
- List of Worked Examples: Hol29362 - Ch01 10/29/2008 14:7Document5 pagesList of Worked Examples: Hol29362 - Ch01 10/29/2008 14:7osamaahmedc7No ratings yet
- Dryer Handbook PDFDocument60 pagesDryer Handbook PDFselviraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Conduction Heat TransferDocument3 pagesTutorial - Conduction Heat TransferDayanidiNo ratings yet
- Jablite Basement BoardDocument7 pagesJablite Basement BoardalokNo ratings yet
- 6 - Conduction Through Solids in SeriesDocument16 pages6 - Conduction Through Solids in SeriesPatricia de LeonNo ratings yet