Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsConcept Paper Outline
Concept Paper Outline
Uploaded by
stardustmoonlight18The document outlines the Haber process for synthesizing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases. It involves reacting nitrogen and hydrogen over an iron catalyst under high pressures and temperatures. Fritz Haber developed this process in 1908, allowing for large-scale production of ammonia which can then be used to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers. The process is important industrially as it provides a vital raw material for agriculture and other industries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Taller ContaminantesDocument11 pagesTaller ContaminantesDaniel F Amado0% (1)
- 32642892-PL WelcomeLetterDocument4 pages32642892-PL WelcomeLetterMohan ChandraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2 Combined-1Document14 pagesUnit 2 Module 2 Combined-1api-2930012170% (2)
- Life 2e BrE Inter SB U01AB Day-1Document29 pagesLife 2e BrE Inter SB U01AB Day-1Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- Pink and Beige Flat Graphic Sugar Chemistry ReportDocument2 pagesPink and Beige Flat Graphic Sugar Chemistry ReportടHՕՕꝄedкƲȠNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2farah.syafiqah.asNo ratings yet
- Feasibilty For The ProjectDocument18 pagesFeasibilty For The ProjectRana UzairNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Formation ProjectDocument14 pagesAmmonia Formation ProjectNebyu DanielNo ratings yet
- 1صناعاتDocument15 pages1صناعاتroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Synthesis Gas Production and Derived ChemicalsDocument78 pagesChapter 3: Synthesis Gas Production and Derived ChemicalsFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- Modak 2002Document9 pagesModak 2002许凉发No ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument10 pagesHaber ProcessTon5698No ratings yet
- Development and Recent Progress On Ammonia Synthesis Catalysts For Haber-Bosch ProcessDocument23 pagesDevelopment and Recent Progress On Ammonia Synthesis Catalysts For Haber-Bosch ProcessEzgi GeyikNo ratings yet
- Energy BalanceDocument10 pagesEnergy Balanceazzatul amiraNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production From SyDocument11 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production From SyAlexey DoroginNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia at Relatively Low P, T: Aspen Process Economic AnalysisDocument6 pagesProduction of Ammonia at Relatively Low P, T: Aspen Process Economic Analysisroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 22Document7 pagesHSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 22Ali HaidarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plant Design For The Production of Ammonia Through Haldor Topsoe Process Route: Simulation Using Plant Design Management SystemDocument9 pagesChemical Plant Design For The Production of Ammonia Through Haldor Topsoe Process Route: Simulation Using Plant Design Management Systemmagdy salehNo ratings yet
- HaberDocument4 pagesHaberamber psycheNo ratings yet
- Haber-Bosch Process PaperDocument15 pagesHaber-Bosch Process Paperapi-529628802No ratings yet
- Assignment BNFDocument3 pagesAssignment BNFhassan aliNo ratings yet
- Haber Process For AmmoniaDocument9 pagesHaber Process For AmmoniarafcobosNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Energy 1Document20 pagesHydrogen Energy 1Yash ChorariaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Mohammad Hasan Khademi, Mohammad Lotfi-VarnoosfaderaniDocument16 pagesJournal of Cleaner Production: Mohammad Hasan Khademi, Mohammad Lotfi-VarnoosfaderaniCinthia Sierra LgarsNo ratings yet
- Amoníaco A Partir de H2 VerdeDocument10 pagesAmoníaco A Partir de H2 VerdeMariangel RicciardiNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ConversionDocument24 pagesAmmonia ConversionKashan AslamNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production Using HYSYS SoftwareDocument9 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production Using HYSYS SoftwareAkhmad MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Haber Process For Ammonia Synthesis: Resonance September 2002Document10 pagesHaber Process For Ammonia Synthesis: Resonance September 2002ctzy86No ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis GaDocument12 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis GaMr RobotNo ratings yet
- Haber Process NotesDocument2 pagesHaber Process NotesTaha GhaderiNo ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument59 pagesAmmoniavcoolkrazy0% (3)
- Haber ProcessDocument6 pagesHaber ProcessLuis Daniel Gil PachecoNo ratings yet
- Description of Ammonia Manufacturing ProcessesDocument4 pagesDescription of Ammonia Manufacturing ProcessesSameer PandeyNo ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument19 pagesHaber ProcessLauren CaseNo ratings yet
- Habers Bosch Process: Submitted byDocument10 pagesHabers Bosch Process: Submitted byHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Ammonia Using The Haber Process: BSC IllDocument8 pagesManufacturing Ammonia Using The Haber Process: BSC Illdigukharade9848No ratings yet
- Haber Process For Ammonia SynthesisDocument10 pagesHaber Process For Ammonia Synthesisbhawnagaur1189No ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis GaDocument12 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis Gasagar dasguptaNo ratings yet
- Obt AmoniacoDocument16 pagesObt AmoniacoNatalia ParedesNo ratings yet
- Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Antonio Tripodi, Matteo Compagnoni, Elnaz Bahadori, Ilenia RossettiDocument11 pagesJournal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Antonio Tripodi, Matteo Compagnoni, Elnaz Bahadori, Ilenia RossettiDarwin Alejandro Velasquez CastroNo ratings yet
- Review of Electrochemical Ammonia Production Technologies and MaterialsDocument19 pagesReview of Electrochemical Ammonia Production Technologies and MaterialsAlejandro Duvan Lopez RojasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technology Production of Ammonia: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicDocument3 pagesChemical Technology Production of Ammonia: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Fixation Via Nitride Formation and Reduction of Dinitrogen To AmmoniaDocument2 pagesNitrogen Fixation Via Nitride Formation and Reduction of Dinitrogen To AmmoniavaishuchemipsNo ratings yet
- 5 - - 懶人包 - Production of FertilizerDocument7 pages5 - - 懶人包 - Production of Fertilizer1126playpubgNo ratings yet
- 5.3. Dynamic EquilibriaDocument3 pages5.3. Dynamic Equilibriasanjay.vullisNo ratings yet
- 7 Urea Synthesis Using Chemical Looping ProcessDocument10 pages7 Urea Synthesis Using Chemical Looping ProcessandiesNo ratings yet
- Haber AmmoniaDocument22 pagesHaber AmmoniaKabilanNo ratings yet
- Haber Process and AmmoniaDocument2 pagesHaber Process and AmmoniaAaron HongNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and UreaDocument33 pagesAmmonia and UreaPRAJWAL RASTOGINo ratings yet
- Ammonia PDFDocument49 pagesAmmonia PDFmfruge7No ratings yet
- Biomass Gasification For Synthesis Gas Production and Applications of The SyngasDocument21 pagesBiomass Gasification For Synthesis Gas Production and Applications of The SyngasYacineBenguerbaNo ratings yet
- Gilbert 2010Document9 pagesGilbert 2010Maria PaulaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia (NH3) Synthesis Simulation Manual.Document39 pagesAmmonia (NH3) Synthesis Simulation Manual.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0360319919340479 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0360319919340479 MainReviana RevitasariNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ProductionDocument7 pagesAmmonia ProductionPanchdev Kumar0% (1)
- Rapid Pressure Swing Adsorption For Small Scale Ammonia Separation A Proof-Of-ConceptDocument15 pagesRapid Pressure Swing Adsorption For Small Scale Ammonia Separation A Proof-Of-ConceptKhai Q TranNo ratings yet
- Rauch Et Al.Document20 pagesRauch Et Al.Bilal KazmiNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen IndustriesDocument22 pagesNitrogen IndustriesKarla Joy P. SucgangNo ratings yet
- Suschem 03 00011Document23 pagesSuschem 03 00011Eduardo TamargoNo ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument33 pagesAmmoniaWilly ChandraNo ratings yet
- Thesis ReportDocument106 pagesThesis ReportMuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsFrom EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerNo ratings yet
- Thermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerFrom EverandThermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerNo ratings yet
- What Is Intranet?: Document & Content ManagementDocument4 pagesWhat Is Intranet?: Document & Content Managementali muhdorNo ratings yet
- Aquafine DW Series ManualDocument19 pagesAquafine DW Series Manualjorman GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Resume - Nicholas SkorinDocument1 pageResume - Nicholas Skorinapi-582665545No ratings yet
- PERDEV 3rd Summative TestDocument2 pagesPERDEV 3rd Summative TestPrincess Maiva ValleNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab-Water QualityDocument7 pagesVirtual Lab-Water Qualityapi-268159571No ratings yet
- RV A. Paler: Technical SkillsDocument5 pagesRV A. Paler: Technical SkillsRv PalerNo ratings yet
- TDAE Product Tank: HSD Storage Tank HSD Storage TankDocument7 pagesTDAE Product Tank: HSD Storage Tank HSD Storage TankAnonymous p0iwBoNo ratings yet
- Crusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolDocument7 pagesCrusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolMatt ThielNo ratings yet
- 951 SignedDocument21 pages951 SignedDany GunawanNo ratings yet
- Deliver Simplified Clinical Solu On Anywhere: VINNO Technology (Suzhou) Co,. LTDDocument6 pagesDeliver Simplified Clinical Solu On Anywhere: VINNO Technology (Suzhou) Co,. LTDelom djadoo-ananiNo ratings yet
- Learning Delivery Modalities Course 2 (Ldm2) For Instructional CoachesDocument4 pagesLearning Delivery Modalities Course 2 (Ldm2) For Instructional CoachesMAILENE SALES100% (1)
- Aurora 3800 Especificaciones PDFDocument8 pagesAurora 3800 Especificaciones PDFCarlos PalmaNo ratings yet
- Junior Agronomist - On Contract: Gujarat State Fertilizers and Chemicals LTDDocument2 pagesJunior Agronomist - On Contract: Gujarat State Fertilizers and Chemicals LTDZayn AliNo ratings yet
- Book Abstracts CORMVDocument171 pagesBook Abstracts CORMVthamizh555No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToKathleen BorjaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics Specialist Doctor List of DhakaDocument14 pagesOrthopedics Specialist Doctor List of DhakaSultanaQuaderNo ratings yet
- When Key Employees ClashDocument4 pagesWhen Key Employees ClashRowell DizonNo ratings yet
- Writing An ArticleDocument11 pagesWriting An ArticleNozima ToirovaNo ratings yet
- Excel Basics RoadmapDocument3 pagesExcel Basics RoadmapLalatenduNo ratings yet
- Power ResourcesDocument14 pagesPower ResourcesDawoodNo ratings yet
- Ebook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolDocument45 pagesEbook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolmariaNo ratings yet
- 6 Speed Automatic Gearbox 09g EngDocument241 pages6 Speed Automatic Gearbox 09g EngGime PedrozaNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties: Cryoscopy & EbulliosDocument30 pagesColligative Properties: Cryoscopy & EbulliosRSL100% (1)
- MAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02Document4 pagesMAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02manuel canas nunezNo ratings yet
- PR'S A-ZDocument65 pagesPR'S A-ZJesusNo ratings yet
- Science Subject For Middle School - 7th Grade - DNA in Biology by SlidesgoDocument55 pagesScience Subject For Middle School - 7th Grade - DNA in Biology by SlidesgoJenniferNo ratings yet
Concept Paper Outline
Concept Paper Outline
Uploaded by
stardustmoonlight180 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThe document outlines the Haber process for synthesizing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases. It involves reacting nitrogen and hydrogen over an iron catalyst under high pressures and temperatures. Fritz Haber developed this process in 1908, allowing for large-scale production of ammonia which can then be used to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers. The process is important industrially as it provides a vital raw material for agriculture and other industries.
Original Description:
Original Title
CONCEPT PAPER OUTLINE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the Haber process for synthesizing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases. It involves reacting nitrogen and hydrogen over an iron catalyst under high pressures and temperatures. Fritz Haber developed this process in 1908, allowing for large-scale production of ammonia which can then be used to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers. The process is important industrially as it provides a vital raw material for agriculture and other industries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesConcept Paper Outline
Concept Paper Outline
Uploaded by
stardustmoonlight18The document outlines the Haber process for synthesizing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases. It involves reacting nitrogen and hydrogen over an iron catalyst under high pressures and temperatures. Fritz Haber developed this process in 1908, allowing for large-scale production of ammonia which can then be used to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers. The process is important industrially as it provides a vital raw material for agriculture and other industries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
CONCEPT PAPER OUTLINE
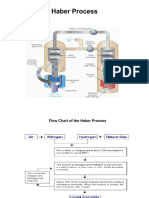
I. Title - Haber Process for Synthesis of Ammonia
II. Introduction - Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound made up of
hydrogen and nitrogen. It is usually used as a refrigerant gas, also in
explosives, fabrics, dyes, and about 80% of it as a fertilizer because of its high
nitrogen content. In 1908, Fritz Haber, a German chemist, developed a chemical
method-now known as Haber process-for producing large amounts of ammonia
that could easily be converted to nitrogen based fertilizers. The Haber process
uses hydrogen gas and nitrogen gas to synthesize ammonia.It involves the
reaction of three hydrogen molecules with one nitrogen molecule in the
presence of iron catalyst N 2 ( g ) + 3 H 2 g ⇌ 2 N H 3 ( g ) .
III. Purpose
The Haber Process is used in the manufacturing of ammonia from nitrogen and
hydrogen, and then goes on to explain the reasons for the conditions used in
the process.
IV. Project Description
The Haber Process, developed by Fritz Haber, is a fundamental technique in
industrial chemistry for creating ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen (N2) and
hydrogen (H2) gasses. Ammonia is synthesized industrially through the Haber
process, which involves reacting a nitrogen molecule with three hydrogen
molecules over a bed of silver catalyst. The reaction takes place at high
pressures and relatively low temperatures to maximize the ammonia yield to
15-20%. The benefits of this process are manifold, with ammonia serving as a
vital element in fertilizers, improving agricultural productivity, and acting as a
precursor for diverse industrial compounds like pharmaceuticals and plastics.
V. Goals & Objectives
Converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with
hydrogen (H2) using an iron metal catalyst under high temperatures and
pressures. This reaction is slightly exothermic (i.e. it releases energy), meaning
that the reaction is favored at lower temperatures and higher pressures.
VI. Methodology
The process combines nitrogen from the air with hydrogen derived mainly from
natural gas (methane) into ammonia. The reaction is reversible and the
production of ammonia is exothermic.
VII. Outcomes
The Haber Process, employed in the production of ammonia from nitrogen and
hydrogen gases, endeavors to optimize output and efficiency by adjusting
parameters like temperature, pressure, and catalysts. Economically, it serves as
a vital supplier of raw materials for agriculture and industry, aiding in crop
enhancement and sustaining various industrial sectors. Despite environmental
concerns like energy usage and emissions, ongoing initiatives aim to harmonize
sustainability with the process's advantages across economic, agricultural,
industrial, and environmental domains.
VIII. References
● Libretexts. “The Haber Process.” Chemistry LibreTexts, January 30, 2023.
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_
Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/
Equilibria/Le_Chateliers_Principle/The_Haber_Process.
● "Ammonia Synthesis: Production & Reaction." Study.com. Accessed
[2/11/24].https://study.com/learn/lesson/ammonia-synthesis-production-rea
ction.html
● Admin. “Haber’s Process for the Manufacture of Ammonia &Amp;Amp; Its
Uses.” BYJUS, May 18, 2022. https://byjus.com/chemistry/haber-process/.
● “The Haber Process.” Chemistry LibreTexts, January 30, 2023.
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_
Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/
Equilibria/Le_Chateliers_Principle/The_Haber_Process.
You might also like
- Taller ContaminantesDocument11 pagesTaller ContaminantesDaniel F Amado0% (1)
- 32642892-PL WelcomeLetterDocument4 pages32642892-PL WelcomeLetterMohan ChandraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2 Combined-1Document14 pagesUnit 2 Module 2 Combined-1api-2930012170% (2)
- Life 2e BrE Inter SB U01AB Day-1Document29 pagesLife 2e BrE Inter SB U01AB Day-1Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- Pink and Beige Flat Graphic Sugar Chemistry ReportDocument2 pagesPink and Beige Flat Graphic Sugar Chemistry ReportടHՕՕꝄedкƲȠNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2farah.syafiqah.asNo ratings yet
- Feasibilty For The ProjectDocument18 pagesFeasibilty For The ProjectRana UzairNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Formation ProjectDocument14 pagesAmmonia Formation ProjectNebyu DanielNo ratings yet
- 1صناعاتDocument15 pages1صناعاتroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Synthesis Gas Production and Derived ChemicalsDocument78 pagesChapter 3: Synthesis Gas Production and Derived ChemicalsFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- Modak 2002Document9 pagesModak 2002许凉发No ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument10 pagesHaber ProcessTon5698No ratings yet
- Development and Recent Progress On Ammonia Synthesis Catalysts For Haber-Bosch ProcessDocument23 pagesDevelopment and Recent Progress On Ammonia Synthesis Catalysts For Haber-Bosch ProcessEzgi GeyikNo ratings yet
- Energy BalanceDocument10 pagesEnergy Balanceazzatul amiraNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production From SyDocument11 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production From SyAlexey DoroginNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia at Relatively Low P, T: Aspen Process Economic AnalysisDocument6 pagesProduction of Ammonia at Relatively Low P, T: Aspen Process Economic Analysisroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 22Document7 pagesHSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 22Ali HaidarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plant Design For The Production of Ammonia Through Haldor Topsoe Process Route: Simulation Using Plant Design Management SystemDocument9 pagesChemical Plant Design For The Production of Ammonia Through Haldor Topsoe Process Route: Simulation Using Plant Design Management Systemmagdy salehNo ratings yet
- HaberDocument4 pagesHaberamber psycheNo ratings yet
- Haber-Bosch Process PaperDocument15 pagesHaber-Bosch Process Paperapi-529628802No ratings yet
- Assignment BNFDocument3 pagesAssignment BNFhassan aliNo ratings yet
- Haber Process For AmmoniaDocument9 pagesHaber Process For AmmoniarafcobosNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Energy 1Document20 pagesHydrogen Energy 1Yash ChorariaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Mohammad Hasan Khademi, Mohammad Lotfi-VarnoosfaderaniDocument16 pagesJournal of Cleaner Production: Mohammad Hasan Khademi, Mohammad Lotfi-VarnoosfaderaniCinthia Sierra LgarsNo ratings yet
- Amoníaco A Partir de H2 VerdeDocument10 pagesAmoníaco A Partir de H2 VerdeMariangel RicciardiNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ConversionDocument24 pagesAmmonia ConversionKashan AslamNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production Using HYSYS SoftwareDocument9 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production Using HYSYS SoftwareAkhmad MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Haber Process For Ammonia Synthesis: Resonance September 2002Document10 pagesHaber Process For Ammonia Synthesis: Resonance September 2002ctzy86No ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis GaDocument12 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis GaMr RobotNo ratings yet
- Haber Process NotesDocument2 pagesHaber Process NotesTaha GhaderiNo ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument59 pagesAmmoniavcoolkrazy0% (3)
- Haber ProcessDocument6 pagesHaber ProcessLuis Daniel Gil PachecoNo ratings yet
- Description of Ammonia Manufacturing ProcessesDocument4 pagesDescription of Ammonia Manufacturing ProcessesSameer PandeyNo ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument19 pagesHaber ProcessLauren CaseNo ratings yet
- Habers Bosch Process: Submitted byDocument10 pagesHabers Bosch Process: Submitted byHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Ammonia Using The Haber Process: BSC IllDocument8 pagesManufacturing Ammonia Using The Haber Process: BSC Illdigukharade9848No ratings yet
- Haber Process For Ammonia SynthesisDocument10 pagesHaber Process For Ammonia Synthesisbhawnagaur1189No ratings yet
- Simulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis GaDocument12 pagesSimulation of Ammonia Production From Synthesis Gasagar dasguptaNo ratings yet
- Obt AmoniacoDocument16 pagesObt AmoniacoNatalia ParedesNo ratings yet
- Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Antonio Tripodi, Matteo Compagnoni, Elnaz Bahadori, Ilenia RossettiDocument11 pagesJournal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Antonio Tripodi, Matteo Compagnoni, Elnaz Bahadori, Ilenia RossettiDarwin Alejandro Velasquez CastroNo ratings yet
- Review of Electrochemical Ammonia Production Technologies and MaterialsDocument19 pagesReview of Electrochemical Ammonia Production Technologies and MaterialsAlejandro Duvan Lopez RojasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technology Production of Ammonia: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicDocument3 pagesChemical Technology Production of Ammonia: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Fixation Via Nitride Formation and Reduction of Dinitrogen To AmmoniaDocument2 pagesNitrogen Fixation Via Nitride Formation and Reduction of Dinitrogen To AmmoniavaishuchemipsNo ratings yet
- 5 - - 懶人包 - Production of FertilizerDocument7 pages5 - - 懶人包 - Production of Fertilizer1126playpubgNo ratings yet
- 5.3. Dynamic EquilibriaDocument3 pages5.3. Dynamic Equilibriasanjay.vullisNo ratings yet
- 7 Urea Synthesis Using Chemical Looping ProcessDocument10 pages7 Urea Synthesis Using Chemical Looping ProcessandiesNo ratings yet
- Haber AmmoniaDocument22 pagesHaber AmmoniaKabilanNo ratings yet
- Haber Process and AmmoniaDocument2 pagesHaber Process and AmmoniaAaron HongNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and UreaDocument33 pagesAmmonia and UreaPRAJWAL RASTOGINo ratings yet
- Ammonia PDFDocument49 pagesAmmonia PDFmfruge7No ratings yet
- Biomass Gasification For Synthesis Gas Production and Applications of The SyngasDocument21 pagesBiomass Gasification For Synthesis Gas Production and Applications of The SyngasYacineBenguerbaNo ratings yet
- Gilbert 2010Document9 pagesGilbert 2010Maria PaulaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia (NH3) Synthesis Simulation Manual.Document39 pagesAmmonia (NH3) Synthesis Simulation Manual.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0360319919340479 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0360319919340479 MainReviana RevitasariNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ProductionDocument7 pagesAmmonia ProductionPanchdev Kumar0% (1)
- Rapid Pressure Swing Adsorption For Small Scale Ammonia Separation A Proof-Of-ConceptDocument15 pagesRapid Pressure Swing Adsorption For Small Scale Ammonia Separation A Proof-Of-ConceptKhai Q TranNo ratings yet
- Rauch Et Al.Document20 pagesRauch Et Al.Bilal KazmiNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen IndustriesDocument22 pagesNitrogen IndustriesKarla Joy P. SucgangNo ratings yet
- Suschem 03 00011Document23 pagesSuschem 03 00011Eduardo TamargoNo ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument33 pagesAmmoniaWilly ChandraNo ratings yet
- Thesis ReportDocument106 pagesThesis ReportMuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsFrom EverandSynthetic Natural Gas: From Coal, Dry Biomass, and Power-to-Gas ApplicationsTilman J. SchildhauerNo ratings yet
- Thermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerFrom EverandThermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerNo ratings yet
- What Is Intranet?: Document & Content ManagementDocument4 pagesWhat Is Intranet?: Document & Content Managementali muhdorNo ratings yet
- Aquafine DW Series ManualDocument19 pagesAquafine DW Series Manualjorman GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Resume - Nicholas SkorinDocument1 pageResume - Nicholas Skorinapi-582665545No ratings yet
- PERDEV 3rd Summative TestDocument2 pagesPERDEV 3rd Summative TestPrincess Maiva ValleNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab-Water QualityDocument7 pagesVirtual Lab-Water Qualityapi-268159571No ratings yet
- RV A. Paler: Technical SkillsDocument5 pagesRV A. Paler: Technical SkillsRv PalerNo ratings yet
- TDAE Product Tank: HSD Storage Tank HSD Storage TankDocument7 pagesTDAE Product Tank: HSD Storage Tank HSD Storage TankAnonymous p0iwBoNo ratings yet
- Crusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolDocument7 pagesCrusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolMatt ThielNo ratings yet
- 951 SignedDocument21 pages951 SignedDany GunawanNo ratings yet
- Deliver Simplified Clinical Solu On Anywhere: VINNO Technology (Suzhou) Co,. LTDDocument6 pagesDeliver Simplified Clinical Solu On Anywhere: VINNO Technology (Suzhou) Co,. LTDelom djadoo-ananiNo ratings yet
- Learning Delivery Modalities Course 2 (Ldm2) For Instructional CoachesDocument4 pagesLearning Delivery Modalities Course 2 (Ldm2) For Instructional CoachesMAILENE SALES100% (1)
- Aurora 3800 Especificaciones PDFDocument8 pagesAurora 3800 Especificaciones PDFCarlos PalmaNo ratings yet
- Junior Agronomist - On Contract: Gujarat State Fertilizers and Chemicals LTDDocument2 pagesJunior Agronomist - On Contract: Gujarat State Fertilizers and Chemicals LTDZayn AliNo ratings yet
- Book Abstracts CORMVDocument171 pagesBook Abstracts CORMVthamizh555No ratings yet
- Introduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToKathleen BorjaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics Specialist Doctor List of DhakaDocument14 pagesOrthopedics Specialist Doctor List of DhakaSultanaQuaderNo ratings yet
- When Key Employees ClashDocument4 pagesWhen Key Employees ClashRowell DizonNo ratings yet
- Writing An ArticleDocument11 pagesWriting An ArticleNozima ToirovaNo ratings yet
- Excel Basics RoadmapDocument3 pagesExcel Basics RoadmapLalatenduNo ratings yet
- Power ResourcesDocument14 pagesPower ResourcesDawoodNo ratings yet
- Ebook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolDocument45 pagesEbook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolmariaNo ratings yet
- 6 Speed Automatic Gearbox 09g EngDocument241 pages6 Speed Automatic Gearbox 09g EngGime PedrozaNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties: Cryoscopy & EbulliosDocument30 pagesColligative Properties: Cryoscopy & EbulliosRSL100% (1)
- MAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02Document4 pagesMAN Diesel: Tools For Reconditioning 52001-02manuel canas nunezNo ratings yet
- PR'S A-ZDocument65 pagesPR'S A-ZJesusNo ratings yet
- Science Subject For Middle School - 7th Grade - DNA in Biology by SlidesgoDocument55 pagesScience Subject For Middle School - 7th Grade - DNA in Biology by SlidesgoJenniferNo ratings yet