Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Logaritmic Function: Magnitude Principle
Logaritmic Function: Magnitude Principle
Uploaded by
7pnpp6jdxmOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Logaritmic Function: Magnitude Principle
Logaritmic Function: Magnitude Principle
Uploaded by
7pnpp6jdxmCopyright:
Available Formats
Logaritmic function
So I prepared a short presentation about logaritmic scale in practical use.
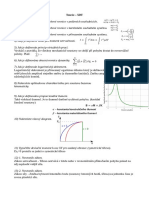
Logaritmic scale displays quantities over a range of many orders of magnitude.
Most often exponential increase, which would rise too fast in a small graph.
The disadvantage may be that in some cases the logarithmic scale only allows
to display positive numbers. There are many examples where the logarithmic
scale is used and I chose the Richter scale which describes the strength of an
earthquake. The Richter scale is a logarithmic scale with base ten. And it's
calculated from the amplitude of the largest shift from zero on the
seismograph. For explanation, amplitude is the maximum value of a
periodically varying quantity.
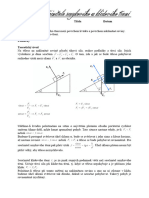
Magnitude principle
Magnitude is a quantity proportional to the amount of an earthquake that
does not depend on the distance from the source of the earthquake.
ML .....is magnitudo
A ..... Wood-Anderson seismograph deviation (odchylka)
A0 ..... is empirical function (empirická funkce)
D ..... distance from the epicentre
Logaritmická stupnice zobrazuje veličiny v rozsahu mnoha řádů. Nejčastěji
exponenciální růst, který by v malém grafu rostl příliš rychle. Nevýhodou může
být, že v některých případech logaritmická stupnice umožňuje zobrazit pouze
čísla, která jsou kladná. Existuje mnoho příkladů, kde se logaritmická stupnice
používá, a já jsem si vybral Richterovu stupnici, která popisuje sílu zemětřesení.
Richterova stupnice je logaritmická stupnice se základem deset. A počítá se z
amplitudy největšího posunu od nuly na seismografu. Pro vysvětlení amplituda
je maximální hodnota periodicky se měnící veličiny.
Princip magnitudy
Magnitudo je veličina úměrná velikosti zemětřesení, která nezávisí na
vzdálenosti od zdroje zemětřesení.
You might also like
- Příklady Z Lékařské Chemie A BiochemieDocument63 pagesPříklady Z Lékařské Chemie A BiochemieMarek MalčekNo ratings yet
- KalkulackaDocument5 pagesKalkulackamaterejjNo ratings yet
- Kinematika Hmotného Bodu - Josef PolášekDocument4 pagesKinematika Hmotného Bodu - Josef Polášekcreepy.craft.czNo ratings yet
- Teorie Fyzikálních Měření: Role Experimentu Ve FyziceDocument5 pagesTeorie Fyzikálních Měření: Role Experimentu Ve Fyzicesalcakova.martinaNo ratings yet
- Vypracované Otázky 2023Document41 pagesVypracované Otázky 2023hana.hovorkovaNo ratings yet
- TreniDocument2 pagesTreniRoman TörvenyiNo ratings yet
- 8 MAT UCEBNICE Goniometrie A TrigonometrieDocument48 pages8 MAT UCEBNICE Goniometrie A TrigonometrieSara SykorovaNo ratings yet
- 02 Měření - Úvod, Jednotky, ChybyDocument3 pages02 Měření - Úvod, Jednotky, Chybyx2vqcky5v2No ratings yet
- 2 KinematikaDocument23 pages2 KinematikaOndřej MušálekNo ratings yet
- LC 04 Navod KyvadloDocument2 pagesLC 04 Navod Kyvadlorobinbubenik2No ratings yet
- VY 32 INOVACE 19 36 PL RozÅ¡Ã Å Enã ZnalostãDocument6 pagesVY 32 INOVACE 19 36 PL RozÅ¡Ã Å Enã Znalostãydbfv97hc7No ratings yet
- 6 RocnikDocument45 pages6 Rocnikklara.faltysovaNo ratings yet
- TeorieDocument9 pagesTeorieX4NRTNNo ratings yet
- Teorie Marišek-FÓRUMDocument14 pagesTeorie Marišek-FÓRUMJan mužíkNo ratings yet
- Fyzika Příprava Na TestDocument35 pagesFyzika Příprava Na TestMatěj BarešNo ratings yet
- Chyby MereniDocument2 pagesChyby Merenimartinvanko.chessNo ratings yet
- KinematikaDocument19 pagesKinematikaOlga GalkinaNo ratings yet
- Kap 01Document11 pagesKap 01api-3702628100% (1)
- Protokol Od Dibur - X Návrh A Korekce Elektronického Voltmetru PRDocument6 pagesProtokol Od Dibur - X Návrh A Korekce Elektronického Voltmetru PRapi-3827942No ratings yet
- Základy Interpretace IČ A 1D NMR SpekterDocument164 pagesZáklady Interpretace IČ A 1D NMR SpekterCatenaneNo ratings yet
- Vypocet Hustota PDFDocument2 pagesVypocet Hustota PDFstolbovaklarkaNo ratings yet
- ACHII Otazky VypracovaneDocument44 pagesACHII Otazky Vypracovanehana.hovorkovaNo ratings yet
- Měření Digitálním Multimetrem A RLC MetremDocument3 pagesMěření Digitálním Multimetrem A RLC Metremjan.brabec24No ratings yet
- Oco 3Document1 pageOco 3Denisa KrálováNo ratings yet
- Protokol 1Document6 pagesProtokol 1kimberleea2No ratings yet