Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Allysa Megan OrpillaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Allysa Megan OrpillaCopyright:
Available Formats
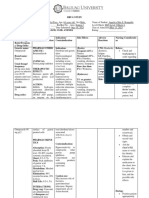
Drug name Mechanism of Indication/contraindication Adverse effects Nursing
action responsibilities
Ceftriaxone Ceftriaxone Indication: Ceftriaxone is used Injection site •monitor vital
works by for the treatment of the inflammation, rash, signs.
Brand name: inhibiting the infections (respiratory, skin, pruritus, fever,
Rocephin mucopeptide soft tissue, UTI, ENT) caused by eosinophilia, •instruct patient
synthesis in susceptible organisms. urticaria, or family to
Dosage: the bacterial anaphylaxis, colitis, report other side
•1g/50mL cell wall. is diarrhea, nausea, effects such as
•2g/50mL used to treat a Contraindication: Ceftriaxone and vomiting, severe or
wide variety is contraindicated in patients pseudomembranous prolonged fever.
Class: of bacterial with known allergy to the colitis.
cephalosporin infections. cephalosporin group of •monitor for
antibiotics Ceftriaxone antibiotics. signs of allergic
belongs to a reaction.
Route: class of drugs
• IV known as •instruct to
cephalosporin report any signs
antibiotics. It or symptoms.
works by
stopping the
growth of
bacteria.
Drug name Mechanism of Indication/contraindication Adverse effects Nursing
action responsibilities
Generic name: Paracetamol Indication:Paracetamol Allergic •Advise pt. that
paracetamol has a central (Panadol, Calpol, Alvedon) reactions, the drug is only
analgesic effect is an analgesic and which may be for short term
Brand name: that is mediated antipyretic drug that is severe and use.
Panadol, Calpol, through used to temporarily relieve include:
Tylenol, activation of mild-to-moderate pain and •Skin rashes, •Monitor vs.
descending fever. It is commonly itching or hives Give drug w/
Class: serotonergic included as an ingredient •Swelling of food if
Analgesics and pathways. in cold and flu medications the throat,
antipyretics Debate exists and is also used on its own. tongue or face •GI upset
about its •Shortness of occurs. Take the
Route: primary site of Contraindication: have breath or drug only
•IV action, which ever had an allergic wheezing
may be reaction to paracetamol or •Liver •For complaints
inhibition of any other medicine. have problems. indicated.
prostaglandin liver or kidney problems. Nausea, Report rash,
(PG) synthesis regularly drink more than sudden weight unusual bleeding
or through an the maximum amount of loss, loss of or bruising,
active alcohol recommended (14 appetite and yellowing of skin
metabolite units a week). yellowing of /eyes, changes
influencing the eyes and in voiding
cannabinoid skin can occur. pattern.
receptors.
Drug name Mechanism of Indication/contraindication Adverse effects Nursing
action responsibilities
Generic name: Hydrochloric Indication: omeprazole is a •headache • advise patient
Omeprazole acid (HCl) proton-pump inhibitor, •abdominal to avoid alcohol
secretion into used to treat gastric acid- pain and foods that
Brand the gastric related disorders. These •diarrhea make cause in
name:Prilosec lumen is a disorders may include •nausea increase
process gastroesophageal reflux •vomiting gastrointestinal
Dosage: regulated disease (GERD), peptic gas (flatulence) irritation.
•2.5mg mainly by the ulcer disease, and other •dizziness
•10mg H(+)/K(+)- diseases characterized by •upper •monitor chest
ATPase of the the oversecretion of respiratory pain and attempt
proton pump gastric acid. infection to determine if
Route: 10, expressed in •acid reflux pain is dry
•Oral high quantities Contraindication: •constipation induced
by the parietal Contraindicated in patients •rash
cells of the with known •cough •instruct patient
stomach. hypersensitivity to any to report
component of the prolonged side
formulation. Treatment effects including
with Omeprazole may skin problem
mask the symptoms of (rashes, itchingl
other gastric diseases.
Caution should be
exercised in patients with
hepatic impairment.
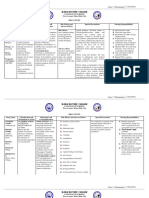
Drug name Mechanism of Indication/Contraindication Adverse Nursing
action effects responsibilities
Generic name: Salbutamol is a Indication: Salbutamol is •Dizziness •Assess lung
Salbutamol direct – acting indicated for the •insomnia sound, PR, Rr
sympathomimetic symptomatic relief and •headache before drug
Brand name: that acts on y, - prevention of •malaise administration
Proventil receptors to bronchospasm due to •palpitations and during
repay bronchial bronchial asthma, chronic •tachycardia peak of
Class: smooth muscle bronchitis, reversible •heartburn medication.
Bronchodilator mil, less obstructive airway disease.
prominent effed •Assess pulse
Obstructive on the heart. It Contraindication: Known for rhythm.
airway dose. activates adeny| sensitivity to salbutamol Instruct client
cyclase, the and/or propellant mixture. to rise slowly
enzyme that from bed /
stimulates the •Caution in infants with when
production of hypertension, changing
cyclic adenosine- hyperthyroidism, position from
3-5’- hypokalaemia. lying to
monophopale. sitting /
standing.
• Relaxes
bronchial, uterine •Advise client
I vascular smooth to have small
muscle by frequent
stimulating feeding to
bela,receptors. avoid
increasing risk
of vomiting >
heartburn.
Increase oral
fluid intake to
facilitate drug
excretion.
Drug name Mechanism of Indication/contraindication Adverse Nursing
action effects responsibilities
Generic name: Enoxaparin Indication: is indicated for •Bleeding •Monitor the
Enoxaparin binds to the prevention of ischemic gums. patient’s vital
antithrombin complications in unstable •coughing signs,
Brand name: III, a serine angina and in non Q-wave up blood. including
Lovenox protease myocardial infarction. difficulty blood
inhibitor, with pressure,
Class: forming a Contraindication: Known breathing or pulse, and
Low molecular complex that hypersensitivity to swallowing. oxygen
weight irreversibly enoxaparin (urticaria, •increased saturation,
heparins. inactivates anaphylactoid reactions, menstrual before and
factor Xa, anaphylaxis) or any flow or after
•Anticoagulant which is heparin products. vaginal administering
frequently bleeding. Lovenox.
used to •Active major bleeding •nosebleeds.
monitor such as gastrointestinal •paralysis. •Observe the
anticoagulation bleed. •prolonged injection site
in the clinical bleeding for signs of
setting. from cuts. bleeding, such
•red or as bruising,
black, tarry redness, or
stools. swelling.
•Instruct the
patient not to
rub the
injection site
and to report
any bleeding,
bruising, or
pain
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudyjoanneNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis: Case Presentation Related To Clients With Upper Respiratory ProblemsDocument54 pagesTonsillitis: Case Presentation Related To Clients With Upper Respiratory ProblemskdfhjfhfNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - EsomeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug Study - Esomeprazolechriscustodio100% (1)
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug StudyJC LumayaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drugs, Classification, Dosage & Route Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesName of Drugs, Classification, Dosage & Route Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesAiramCeszDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Copd Drug StudyDocument9 pagesCopd Drug StudyJoegie Ario100% (1)
- Drug Ana Surgery WardDocument11 pagesDrug Ana Surgery WardJames QuilingNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesGeneric Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilityorhocelo6908No ratings yet
- NCP DS Patient 2020Document13 pagesNCP DS Patient 2020Silvestre SanchezNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument9 pagesDrug NameJonathan MangawiliNo ratings yet
- AntigoutDocument21 pagesAntigoutareebwaheedNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyyyySophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- JM Drug Study CaseDocument4 pagesJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NameShainaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHoney BeeNo ratings yet
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocument3 pagesDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- NLM Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNLM Drug Studyamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocument4 pagesDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- Ward6 Drug StudyDocument6 pagesWard6 Drug StudyMichael Lloyd T. SabijonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NotesDocument3 pagesDrug Study NotesCristoper BodionganNo ratings yet
- Drugs 2Document6 pagesDrugs 2Elyse Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug Studyapi-3757116100% (4)
- DrugsssDocument3 pagesDrugsssLindy JaneNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study PharmacologyDocument11 pagesDrug-Study PharmacologyEmmanuel CaracalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Document3 pagesDrug Study (Katrina Jean B. TaniajuraNo ratings yet
- Classification: Cefditoren, As This Agent May CauseDocument3 pagesClassification: Cefditoren, As This Agent May CauseHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing DiseaseDocument8 pagesDrug Study Cushing DiseaseRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Vii. Medical Management: Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument15 pagesVii. Medical Management: Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJenny Juniora AjocNo ratings yet
- HI Drug Study - v.3Document13 pagesHI Drug Study - v.3Mary Claire AbenidoNo ratings yet
- Phinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Sciences Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Sciences Drug Studylhie cabanlitNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy and SoapieDocument17 pagesDrugstudy and SoapieYasi EcheniqueNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole P. A. P.Document1 pageOmeprazole P. A. P.cen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Case 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimDocument8 pagesCase 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimJemy Tamaño MorongNo ratings yet
- Case 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimDocument8 pagesCase 1: Pneumonia: 1st Sem:PrelimJemy Tamaño MorongNo ratings yet
- Cefradime, Paracetamol, KetorolacDocument10 pagesCefradime, Paracetamol, KetorolacMae_Sheryn_Lip_1795No ratings yet
- Omeprazole - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOmeprazole - Drug Studyjean19.goNo ratings yet
- Drugs ..Document8 pagesDrugs ..zayarosspadillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaguraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug Study Omeprazoleelmer.platiljrNo ratings yet
- Ma. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMa. Patricia R. de Leon Bsn-Iv: Drug Indications Contraindicatio Ns Action Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesTricia_De_Leon_6494No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Jam (Drug Study)Document11 pagesJam (Drug Study)Vincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Augmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Document2 pagesAugmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study orDocument4 pagesDrug Study orChristine Katherine LibuitNo ratings yet
- Invanz (Ertapenem)Document2 pagesInvanz (Ertapenem)E100% (1)
- Drug Study Anemia PTDocument3 pagesDrug Study Anemia PTLex CatNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Yuji HahahaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Yuji HahahaGabriel Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug StuyDocument23 pagesDrug StuynycaNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument5 pagesOMEPRAZOLEAngela QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studyanne009No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Generic NameJohn Edward EscoteNo ratings yet
- Prophylaxis Action: Tetanus: Injection: 5 To 10 LF Units ofDocument10 pagesProphylaxis Action: Tetanus: Injection: 5 To 10 LF Units ofElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- MICROSCOPEDocument6 pagesMICROSCOPEAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- 2023 EpidemiologyDocument55 pages2023 EpidemiologyAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LifeDocument23 pagesChemistry of LifeAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- 13 AreasDocument3 pages13 AreasAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Nurse and StatisticsDocument8 pagesNurse and StatisticsAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Protozoology ParasitologyDocument5 pagesProtozoology ParasitologyAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Handout 6 CardioVascular DisordersDocument15 pagesHandout 6 CardioVascular DisordersAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Medical AbbreviationsDocument9 pagesMedical AbbreviationsAllysa Megan OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Amclav Susp Range (CSH)Document2 pagesLeaflet Amclav Susp Range (CSH)Pak MedicoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Ward Drug StudyDocument23 pagesSurgical Ward Drug StudyKatherine May F. LloritoNo ratings yet
- Case ScenarioDocument9 pagesCase ScenarioteuuuuNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Antibiotic AgentsDocument13 pagesAntibacterial Antibiotic AgentsEmmanuel coleteNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic PolicyDocument4 pagesAntibiotic PolicyAchmad Faiz SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CompilationDocument9 pagesDrug Study CompilationRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 14 Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Untuk IskDocument40 pages14 Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Untuk IskSintaKleoNo ratings yet
- A Group Case Study 2nd Sem 1Document46 pagesA Group Case Study 2nd Sem 1Shermaigne Ananayo BuyaNo ratings yet
- Review: Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospitals: How Concerned Should We Be?Document8 pagesReview: Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospitals: How Concerned Should We Be?Victor GodwinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLouise NTFNo ratings yet
- PiperacillinDocument3 pagesPiperacillinmyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - Beta-Lactam Antibiotics & Amp Other Cell Wall - & Amp Membrane-Active AntibioticsDocument9 pagesChapter 43 - Beta-Lactam Antibiotics & Amp Other Cell Wall - & Amp Membrane-Active AntibioticsSara OchoaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument16 pagesAntibioticsaattaa100% (2)
- Name and Classification of DrugDocument3 pagesName and Classification of DrugAnicas, Ralph Joshua V.No ratings yet
- Rejano Case Scenario 2 - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRejano Case Scenario 2 - Drug StudyBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- Cephalothin SodiumDocument6 pagesCephalothin SodiumBeans JohnNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Generations of CephalosporinsDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Generations of CephalosporinsAnkan PalNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument604 pagesChemotherapyBirhanu GetaNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaDocument16 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaVhugala AudreyNo ratings yet
- CeftazidimeDocument2 pagesCeftazidimeSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ListDocument14 pagesAntibiotics ListBrenda LiawNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument18 pagesAntibioticsAhnaf Muttaqi Spondan 1716No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Cefu and Keto and SummaryDocument8 pagesDRUG STUDY Cefu and Keto and SummaryAmanie Usman AmanoddinNo ratings yet
- Cephalosporins Pharmacology and ChemistryDocument5 pagesCephalosporins Pharmacology and ChemistryIrfan QaisarNo ratings yet
- Feline Inflammatory Bowel Disease: How I Treat Feline IBDDocument4 pagesFeline Inflammatory Bowel Disease: How I Treat Feline IBDsigario hutamaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics and Antibacterial DrugsDocument69 pagesAntibiotics and Antibacterial DrugsJames PerianayagamNo ratings yet
- Role of Antibiotics in EndodonticsDocument45 pagesRole of Antibiotics in EndodonticsAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefuroxime Drug StudyEmIsme Badawi-Baggins100% (9)
























































![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)








































