Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electron Configurations (Beyond Basics) - 1
Electron Configurations (Beyond Basics) - 1
Uploaded by
Shayla LopezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electron Configurations (Beyond Basics) - 1
Electron Configurations (Beyond Basics) - 1
Uploaded by
Shayla LopezCopyright:
Available Formats
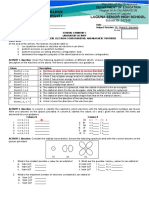
Electron Configurations (beyond the basics)
Nucleus contains ______________ + ______________
type of reactions:
Outside of nucleus contains ______________
type of reactions:
Periodic Table
Vertical columns of the periodic table known as:
Alkali metals = Halogens =
Alkaline earth metals = Noble (inert) gases =
Horizontal rows of the periodic table are known as:
What does an electron configuration indicate?
Four “quantum numbers” give each electron its “address” in the atom.
No two electrons in the same atom can have the same exact “address” (set of 4
quantum numbers)
# of electrons
1s22s22p4
principal energy level sublevel
The above configuration indicates the location of ______ electrons in an atom of
________________ .
There are _____ electrons in the “s” sublevel of the first principal energy level
There are _____ electrons in the “s” sublevel of the second principal energy level
There are _____ electrons in the “p” sublevel of the second principal energy level
Acc. Chem Atomic Structure (rev.2017) page 1
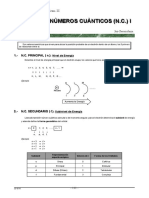
Principal energy level or shell (n = 1, 2, 3, 4.....)
What does it tell you?
valence vs. kernel
relationship to periods of the periodic table
Sublevels (s, p, d, f)
1st energy level has _____ sublevel
2nd energy level has _____ sublevels
3rd energy level has _____ sublevels
4th energy level has _____ sublevels
Orbitals
Each orbital can hold a maximum of _____ electrons
“s” sublevel has ____ orbital(s)
shape = max. number of “s” electrons =
“p” sublevel has ____ orbital(s)
shape = max. number of “p” electrons =
“d” sublevel has ____ orbital(s)
max. number of “d” electrons =
“f” sublevel has ____ orbital(s)
max. number of “f” electrons =
Spin
Each electron within an orbital has a different spin, usually described as spin “up” or
“down” and indicated by up/down arrows
Acc. Chem Atomic Structure (rev.2017) page 2
1s22s22p63s23p64s24p2
1s22s22p63s23p3
______ number of occupied energy levels
______ number of completely filled energy levels
______ number of completely filled energy levels
______ number of completely filled “p” orbitals
______ number of completely filled “s” sublevels
______ number of half-filled “p” orbitals
______ number of completely filled “p” sublevels
______ number of empty “p” orbitals
______ number of completely filled “p” orbitals
______ number of valence electrons
______ number of half-filled “p” orbitals
______ if neutral, name this element
______ number of empty “p” orbitals
______ ground or excited state
______ number of valence electrons
______ number of electrons
______ if neutral, name this element
______ ground or excited state
1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d45s1
1s22s22p63s23p63d34s24p4
______ number of electrons
______ number of occupied energy levels
______ number of occupied energy levels
______ number of completely filled energy levels
______ number of completely filled energy levels
______ number of completely filled “s” sublevels
______ number of completely filled “s” sublevels
______ number of completely filled “p” sublevels
______ number of completely filled “s” orbitals
______ number of completely filled “d” sublevels
______ number of completely filled “p” sublevels
______ number of completely filled “d” orbitals
______ number of completely filled “d” sublevels
______ number of half-filled “d” orbitals
______ number of half-filled “p” orbitals
______ number of empty “d” orbitals
______ number of empty “p” orbitals
______ total number of completely filled orbitals
______ number of valence electrons
______ total number of half-filled orbitals
______ number of electrons
______ number of valence electrons
______ if neutral, name this element
______ if neutral, name this element
______ ground or excited state
______ ground or excited state
Acc. Chem Atomic Structure (rev.2017) page 3
You might also like
- QUANTUM NUMBERS WORKSHEET A.CalvinDocument2 pagesQUANTUM NUMBERS WORKSHEET A.CalvinPrince Calvin100% (1)
- A. Readings/Discussions: Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Document7 pagesA. Readings/Discussions: Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Zeus RomeroNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q2-W 1 - SLHT-1 OkDocument9 pagesScience 9 Q2-W 1 - SLHT-1 OkNylana Cañedo del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration - QuestionsDocument5 pagesElectron Configuration - Questionslon.bar.27No ratings yet
- LAB 13 - Honors Electron Configuration0809Document4 pagesLAB 13 - Honors Electron Configuration0809John Park0% (1)
- N, L, ML, MsDocument7 pagesN, L, ML, MsclassicalcatNo ratings yet
- Chapter AssessmentDocument1 pageChapter AssessmentpututuPLNo ratings yet
- Test-03 Quantum Numbers: B. C. D. E. F. GDocument2 pagesTest-03 Quantum Numbers: B. C. D. E. F. GNishali Sam100% (1)
- AP Quantum Numbers WorksheetDocument2 pagesAP Quantum Numbers WorksheetSoumi VesaliNo ratings yet
- AP Quantum Numbers WorksheetDocument2 pagesAP Quantum Numbers WorksheetDanah Faith Vera Cruz100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1: Quarter 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quarter 2Mohammad Ryyan PumbagulNo ratings yet
- Activity-Quantum NumbersDocument2 pagesActivity-Quantum NumbersCarl GhimboNo ratings yet
- POGIL Electron Configuration and OrbitalsDocument11 pagesPOGIL Electron Configuration and OrbitalsCrumb BanditNo ratings yet
- Quantum Numbers: Name Anuj Class 11Document5 pagesQuantum Numbers: Name Anuj Class 11Anuj MorNo ratings yet
- Quantum Numbers & OrbitalsDocument3 pagesQuantum Numbers & OrbitalsAaronkim PalonNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY SHEET Quantum NumbersDocument1 pageACTIVITY SHEET Quantum NumbersElaine MagpatagNo ratings yet
- POGIL Electron Configuration and OrbitalsDocument10 pagesPOGIL Electron Configuration and Orbitals776pmsfq2fNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration of Elements:: Fourth LectureDocument43 pagesElectron Configuration of Elements:: Fourth LectureMashael 7No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Fill in Blank Notes2009 - WorksheetDocument10 pagesChapter 11 Fill in Blank Notes2009 - WorksheetKiki EdsNo ratings yet
- Quantum NUmbers - 2qtr Worksheet1Document1 pageQuantum NUmbers - 2qtr Worksheet1Isaac PiaoNo ratings yet
- Electron Config Test RevDocument4 pagesElectron Config Test RevSri HartonoNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Guided Notes SE Electron ConfigurationDocument9 pages1 6 Guided Notes SE Electron ConfigurationMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- G9 - Q2 - C1 - TQ - Derano, AbegailDocument2 pagesG9 - Q2 - C1 - TQ - Derano, AbegailChenna Rose ChanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4, Worksheet #2: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument3 pagesChapter 4, Worksheet #2: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionTarek FaramawyNo ratings yet
- Ficha 3ro Cyt 2Document32 pagesFicha 3ro Cyt 2Esika ArequipaNo ratings yet
- Week 5-P.2.3.5 - Quantum Numbers PDFDocument51 pagesWeek 5-P.2.3.5 - Quantum Numbers PDFJulchen BeilschmidtNo ratings yet
- 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science: Mit OpencoursewareDocument5 pages5.111 Principles of Chemical Science: Mit OpencoursewareAnonymous JLK6KfNo ratings yet
- Science G9 Q2 W1 ModDocument8 pagesScience G9 Q2 W1 ModRhia Mae AjocNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson 1 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 1 2nd QuarterKristine Jewel MacatiagNo ratings yet
- 5.2 General Chemistry 1. Module Lesson 5Document14 pages5.2 General Chemistry 1. Module Lesson 5Francesca BarolaNo ratings yet
- Sqe STM005Document21 pagesSqe STM005yen neyNo ratings yet
- The Quantum Theory and Its Relation To Electronic ConfigurationDocument14 pagesThe Quantum Theory and Its Relation To Electronic Configurationariinnggg onichaNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 - Electron ConfigurationDocument6 pagesActivity 5 - Electron Configurationfernanda.martinezlNo ratings yet
- ENGR 1130 Module 6 Lecture OutlineDocument7 pagesENGR 1130 Module 6 Lecture Outlineskarpo 911No ratings yet
- Element Atomic Number Electron Configuration With Spin Quantum Nos. (Arrow Up and Down) Orbital Diagram (3 Points)Document1 pageElement Atomic Number Electron Configuration With Spin Quantum Nos. (Arrow Up and Down) Orbital Diagram (3 Points)Anthony Bernard BalderamaNo ratings yet
- 16.3 G12 WorksheetDocument3 pages16.3 G12 WorksheetShafiq Ul NisaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Chem W1Document12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Chem W1Prince Dave NievesNo ratings yet
- CHEM113 Assignment No1Document3 pagesCHEM113 Assignment No1Mark Ryan TripoleNo ratings yet
- Cq11 Electrons AddressDocument3 pagesCq11 Electrons AddressAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Quantum NumbersDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Quantum NumbersJannah Mae IsioNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quantum NumbersDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quantum NumbersVienie Ramirez BadangNo ratings yet
- 2016 - Flame Test LabDocument3 pages2016 - Flame Test LabDenise SorianoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Q Gen Physics 2 ReviewerDocument2 pages3rd Q Gen Physics 2 ReviewerKit DyNo ratings yet
- Week 012-Course Module-Quantum-Numbers-CHEM - L - v23 - GTD - s1Document5 pagesWeek 012-Course Module-Quantum-Numbers-CHEM - L - v23 - GTD - s1BOY TAPANGNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - G9 - Q2Document1 pageQuiz 1 - G9 - Q2ChelleNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 2nd QuarterDocument84 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 2nd QuarterZylaNo ratings yet
- GC1 - Q2 - Week 1Document10 pagesGC1 - Q2 - Week 1Inol DuqueNo ratings yet
- GC1 - Q2 - Week 1Document10 pagesGC1 - Q2 - Week 1Inol DuqueNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Worksheet No. 1 - Melc: S9Mtiib-14Document3 pagesQuarter 2 - Worksheet No. 1 - Melc: S9Mtiib-14Adrian James S AngelesNo ratings yet
- Practice Final Exam EEL4420Document4 pagesPractice Final Exam EEL4420Thomas CaseyNo ratings yet
- 03 - Quantum Number WorksheetDocument4 pages03 - Quantum Number Worksheetkomal sheikh100% (1)
- Science8 Q3 Week7Document20 pagesScience8 Q3 Week7Kathrina De SenaNo ratings yet
- Science 8, q3Document3 pagesScience 8, q3cattleya abelloNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q2 Wk1 PDFDocument4 pagesSci9 Q2 Wk1 PDFrayanthony.tagadiadNo ratings yet
- N-This Is The Principal Quantum Number Also Known As The (Shell #)Document3 pagesN-This Is The Principal Quantum Number Also Known As The (Shell #)Josh KizitoNo ratings yet
- HUMSSABM QQuantumDocument16 pagesHUMSSABM QQuantumlokibestvillainNo ratings yet
- Nps 94 C7Document6 pagesNps 94 C7adolfo2No ratings yet
- QMM e ConfigurationDocument74 pagesQMM e ConfigurationcarlellisebacarraNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity Turnip Peroxidase Lab32Document8 pagesEnzyme Activity Turnip Peroxidase Lab32Shayla LopezNo ratings yet
- ST Ives - Google ShoppingDocument1 pageST Ives - Google ShoppingShayla LopezNo ratings yet
- PreCalc Questions With ObjectivesDocument2 pagesPreCalc Questions With ObjectivesShayla LopezNo ratings yet
- ArtsBridge Best Summer Arts Programs Our Picks For 2022! - ArtsBridgeDocument1 pageArtsBridge Best Summer Arts Programs Our Picks For 2022! - ArtsBridgeShayla LopezNo ratings yet
- Hamilton NotesDocument2 pagesHamilton NotesShayla LopezNo ratings yet
- Golden Key William BallDocument12 pagesGolden Key William BallShayla LopezNo ratings yet
- Precalc Question 23Document3 pagesPrecalc Question 23Shayla LopezNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 7: Solar Control: OrientationDocument12 pagesTOPIC 7: Solar Control: OrientationAjay PanghalNo ratings yet
- Physics Set A AKDocument3 pagesPhysics Set A AKCherry Grace Articulo Dabucon100% (1)
- Sensus WPD BrochureDocument4 pagesSensus WPD BrochureNoelNo ratings yet
- Simscape Fluids Exercise 2019Document24 pagesSimscape Fluids Exercise 2019anesaNo ratings yet
- 238 Modeling of Gas Turbines and Steam Turbines in Combined Cycle Power Plants PDFDocument119 pages238 Modeling of Gas Turbines and Steam Turbines in Combined Cycle Power Plants PDFsenthil031277100% (2)
- CFD Analysis of Steam Boiler Used in PowerDocument10 pagesCFD Analysis of Steam Boiler Used in PowermohanNo ratings yet
- Operating Problems and Glycol CareDocument17 pagesOperating Problems and Glycol CareJonathan Mike0% (1)
- Chapter 6Document33 pagesChapter 6Victor M. JakiNo ratings yet
- The Synergistic Effect of Temperature, H2S/CO2 Partial Pressure and Stress Toward Corrosion of X80 Pipeline SteelDocument11 pagesThe Synergistic Effect of Temperature, H2S/CO2 Partial Pressure and Stress Toward Corrosion of X80 Pipeline SteelRoberta VasquesNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauges PPT-2Document30 pagesStrain Gauges PPT-2Shreyas shreyuNo ratings yet
- FEA Lab Manual PDFDocument49 pagesFEA Lab Manual PDFAdithya KashyapNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modeling Techniques in MSC NASTRAN and LS DYNADocument173 pagesFinite Element Modeling Techniques in MSC NASTRAN and LS DYNAIndranil BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Friction FactorDocument79 pagesFriction FactorahmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics - DynamicsDocument108 pagesMechanics - DynamicsSherif Yehia Al Maraghy100% (1)
- Olivia S JournalDocument14 pagesOlivia S JournalSanjay Kumar SahNo ratings yet
- ColoradoDocument340 pagesColoradoBahiya Al RifaiiNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Deposition by Spray Pyrolysis and The Application PDFDocument167 pagesThin Film Deposition by Spray Pyrolysis and The Application PDFFlorin AgaiNo ratings yet
- Physics Question Set - 082544Document8 pagesPhysics Question Set - 082544Abu Syeed Md. Aurangzeb Al MasumNo ratings yet
- Types of TransducersDocument33 pagesTypes of TransducersShoSheetaNo ratings yet
- A Single-Atom Transistor PDFDocument5 pagesA Single-Atom Transistor PDFyashreyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Manual-6Document35 pagesEngineering Manual-6cengizNo ratings yet
- CircularDocument3 pagesCircularJonathan SolimanNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of 3 Storey Hospital StructureDocument13 pagesAnalysis and Design of 3 Storey Hospital StructureMicron MacronNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Measurement of Horizontal DistancesDocument8 pagesUnit 2. Measurement of Horizontal DistancesRAIZZNo ratings yet
- شركة توتال Fundamentals of Petroleum-اساسيات هندسة النفطDocument454 pagesشركة توتال Fundamentals of Petroleum-اساسيات هندسة النفطCvbcx100% (3)
- (International Series of Monographs On Physics) Walter T. Grandy Jr. - Entropy and The Time Evolution of Macroscopic Systems-Oxford University Press, USA (2008) PDFDocument224 pages(International Series of Monographs On Physics) Walter T. Grandy Jr. - Entropy and The Time Evolution of Macroscopic Systems-Oxford University Press, USA (2008) PDFAli Sholihin100% (1)
- Smokers EquationDocument8 pagesSmokers Equationbakhtyar210% (1)
- Notes On Molecular Orbital CalculationDocument170 pagesNotes On Molecular Orbital CalculationFreeWill100% (1)
- Process: Accutech Laser PVT LTD Master List of MachinesDocument11 pagesProcess: Accutech Laser PVT LTD Master List of MachinesMagesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Seismological Consideration in DesignsDocument14 pagesSeismological Consideration in DesignsIbie Scandie Shain QuimanNo ratings yet