Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA
DNA
Uploaded by
jeffersonmanalo7870 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesDNA contains the genetic instructions to build and maintain an organism. It is made up of four bases - adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. DNA takes the form of a double helix, with the bases on one strand pairing with complementary bases on the other strand. DNA is replicated prior to cell division in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, although the processes differ between the two. DNA can be damaged by lesions, but cells have repair mechanisms to identify and correct such damage. Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that cap and protect the ends of chromosomes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA contains the genetic instructions to build and maintain an organism. It is made up of four bases - adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. DNA takes the form of a double helix, with the bases on one strand pairing with complementary bases on the other strand. DNA is replicated prior to cell division in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, although the processes differ between the two. DNA can be damaged by lesions, but cells have repair mechanisms to identify and correct such damage. Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that cap and protect the ends of chromosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesDNA
DNA
Uploaded by
jeffersonmanalo787DNA contains the genetic instructions to build and maintain an organism. It is made up of four bases - adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. DNA takes the form of a double helix, with the bases on one strand pairing with complementary bases on the other strand. DNA is replicated prior to cell division in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, although the processes differ between the two. DNA can be damaged by lesions, but cells have repair mechanisms to identify and correct such damage. Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that cap and protect the ends of chromosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
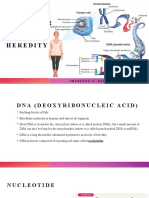
DNA
•Deoxyribonucleic acid, more commonly known as DNA, is
a complex molecule that contains all of the information
necessary to build and maintain an organism.
• Genome is made of a chemical called deoxyribonucleic acid,
or DNA for short.
• DNA contains four basic building blocks or ‘bases' :
adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
• DNA is a two-stranded molecule.
• The bases on one strand of the DNA molecule pair together
with complementary bases on the opposite strand of DNA to
form the ‘rungs’ of the DNA ‘ladder’.
• Each base pair is joined together by hydrogen bonds.
•This double helix structure was first discovered by Francis
Crick and James Watson with the help of Rosalind Franklin
and Maurice Wilkins.
•The human genome is made of 3.2 billion bases of DNA but
other organisms have different genome sizes.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
DNA Replication
• Prokaryotic DNA Replication: Prokaryotic
DNA replication is the process by which a
prokaryotic organism duplicates its entire
genome in order to pass the second copy to
a daughter cell.
• Eukaryotic DNA Replication: Eukaryotic
DNA replication is the process by which the
eukaryotic genome duplicates prior to cell
division.
• The prokaryotic
cells have a very
simple structure.
They do not have any
nucleus and
organelles.
• Eukaryotic
cells contain a
nucleus, numerous
organelles and more
DNA.
DNA LESSION
• DNA lesion refers
to a section of a DNA
molecule containing a
primary damaged
site.
• a base alteration, a
base deletion, a sugar
alteration or a strand
break
DNA REPAIR
• DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell
identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that
encode its genome.
• The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors : the
cell type, the age of the cell and the extracellular
environment.
What is Telomeres?
• Telomeres are
distinctive structures
found at the ends of
our chromosomes.
• Telomeres are
sections
of DNA found at the
ends of each of
our chromosomes.
What is Telomeres?
• They consist of the
same sequence
of bases repeated
over and over.
What do telomeres do?
1. They help to organize each of our 46
chromosomes in the nucleus (control
center) of our cells.
2. They protect the ends of our
chromosomes by forming a cap, much
like the plastic tip on shoelaces.
3. They allow the chromosome to be
replicated properly during cell division.
Prokaryotic and
Eukaryotic Transcription
Eukaryotic Transcription
• The process of transcription in Eukaryotes initiates in the Nucleus.
The mRNA travels out of the nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm,
where the process of translation takes place. The process of
Eukaryotic transcription includes three stages. These stages are-
initiation, elongation, and termination. The initiation stage of the
Eukaryotic transcription is complex, compared to other stages of
transcription
Prokaryotic and
Eukaryotic Transcription
Prokaryotic Transcription
• The process of transcription in Prokaryotes initiates in the
Cytoplasm. RNA processing is not required in Prokaryotes. This
is because the structural gene in prokaryotes is polycistronic in
nature. This process of transcription is also known as Bacterial
transcription.
You might also like
- Questions Bank For Molecular Biology Answer SheetDocument51 pagesQuestions Bank For Molecular Biology Answer Sheetmartynapet85% (39)
- DNA Replication and Mutation Concept MapDocument1 pageDNA Replication and Mutation Concept MapVibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Nucleic Acids IBDP HL NotesDocument27 pagesTopic 7 Nucleic Acids IBDP HL NotesKathryn BrandwoodNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument48 pagesDNA ReplicationAamir MumtazNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument28 pagesGenetics NotesjasNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Packaging: Fatih EREN Medical Biology Department Fatiheren@marmara - Edu.trDocument52 pagesChromosomal Packaging: Fatih EREN Medical Biology Department Fatiheren@marmara - Edu.trErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Topic: Variation and InheritanceDocument19 pagesTopic: Variation and Inheritancerediona zaimiNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyB SC Biochemistry SEM IIIDocument61 pagesMolecular BiologyB SC Biochemistry SEM IIINnleinomNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - DNA Structure and FunctionDocument47 pagesModule 7 - DNA Structure and FunctionAllan SigangaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-15, DNA Replication-II (New)Document37 pagesLecture-15, DNA Replication-II (New)Vayshnave MuniandyNo ratings yet
- PptingeneticsDocument22 pagesPptingeneticsglennbenjiepNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Structural Organization of ChromosomesDocument105 pagesUnit 1 - Structural Organization of ChromosomesSurya Prabha DNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Principles of Genetics.: January 2006Document34 pagesLecture Notes: Principles of Genetics.: January 2006Alliah SidicNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument61 pagesMolecular BiologyRaghuvar TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Mira Molecular Biology Part1Document63 pagesMira Molecular Biology Part1Ranim MiraNo ratings yet
- Physiology BIPRS 5th BatchDocument27 pagesPhysiology BIPRS 5th BatchDr Tahira NihalNo ratings yet
- What Is Genome ?Document9 pagesWhat Is Genome ?Bhumi Gameti100% (1)
- GeneticsDocument65 pagesGeneticsShaghulNo ratings yet
- ProkariatesDocument24 pagesProkariatesteja prasadNo ratings yet
- Genome Organization and ControlDocument32 pagesGenome Organization and Controllmiguel92100% (1)
- Nome Organization in Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument22 pagesNome Organization in Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesastrogeniusthreeNo ratings yet
- The Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument154 pagesThe Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeAnnisNo ratings yet
- Stage 2 Sace Biology: TOPIC 1: DNA and Proteins Chapter 1.1 DNA StructureDocument41 pagesStage 2 Sace Biology: TOPIC 1: DNA and Proteins Chapter 1.1 DNA StructureKassyKasNo ratings yet
- 8-DNA and ChromosomesDocument42 pages8-DNA and Chromosomesصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- L 6 Organization of GenomeDocument25 pagesL 6 Organization of GenomeArchana BhartiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell 1Document50 pagesChapter 6 Cell 1janardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- 5 Cell-CycleDocument13 pages5 Cell-CycleKyzenNo ratings yet
- 1 GeneticsDocument41 pages1 GeneticsFeigh AimNo ratings yet
- Molecular and Mendelian Genetics - 202203202253Document7 pagesMolecular and Mendelian Genetics - 202203202253Ej AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionADocument62 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionAimensah22No ratings yet
- Chromosomes, Genes and DNA: First Chapter in Unit 5: Variation and SelectionDocument14 pagesChromosomes, Genes and DNA: First Chapter in Unit 5: Variation and SelectionZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Topic 7 BiologyDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Topic 7 BiologySana SyedNo ratings yet
- L7.8.9.Cell BiologyDocument81 pagesL7.8.9.Cell BiologyGeethanjali SivakumarNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Notes-2Document49 pagesBIO 101 Notes-2fmukuka12No ratings yet
- PBC101 Lec3 24Document20 pagesPBC101 Lec3 24Marium ElbablyNo ratings yet
- Pbe Module 1Document38 pagesPbe Module 1MythriNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument39 pagesChromosomesSuresh Kannan100% (1)
- 3.1 Cell Reproduction BiologyDocument53 pages3.1 Cell Reproduction BiologySean CatapangNo ratings yet
- DNA JA NewDocument41 pagesDNA JA NewHamza TahaNo ratings yet
- Biology of The Cell: BIO 103-L7Document26 pagesBiology of The Cell: BIO 103-L7Nahid Sagar 1812889042No ratings yet
- Introduction To Bacterial GeneticsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Bacterial GeneticseyoelNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 6. Cell, Chromosome and Genetic Materials (Oke)Document34 pagesKuliah 6. Cell, Chromosome and Genetic Materials (Oke)Sinta DosiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis OF Heredity: Shereena V. Opiniano, RMT, MSMTDocument26 pagesMolecular Basis OF Heredity: Shereena V. Opiniano, RMT, MSMTNicole Ongbit ManogNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument28 pagesCentral DogmaBryant Villarin BaldivicioNo ratings yet
- 3 The Cell CycleDocument7 pages3 The Cell CycleHermina AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Copia Di Cell 4Document37 pagesCopia Di Cell 4dc8mypycmdNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument62 pagesMolecular GeneticsOpheliaNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Organization: AkamandalDocument24 pagesChromosome Organization: AkamandalnaomiNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument16 pagesMitosisAnahita SuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document67 pagesChapter 5علوم طبية AUG 2020No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid-Based Cellular ActivitiesDocument30 pagesNucleic Acid-Based Cellular ActivitiesTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Perform Different FunctionsDocument16 pagesDNA and RNA Perform Different FunctionsTamanda SekarNo ratings yet
- Physiology of ProkaryotesDocument19 pagesPhysiology of ProkaryotesErizka RivaniNo ratings yet
- NUCLEUSDocument2 pagesNUCLEUSSalma AslamNo ratings yet
- Zuhad by Rida Saleem CompleteDocument38 pagesZuhad by Rida Saleem CompleteAfrah NajeebNo ratings yet
- 4 Basic ConceptsDocument17 pages4 Basic ConceptsIkram sarwar MughalNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Mod IIDocument61 pagesDNA Replication Mod IIAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Organization and Structure: Instructor: Wynli F. Ancog RMT, RN, LLBDocument11 pagesChromosome Organization and Structure: Instructor: Wynli F. Ancog RMT, RN, LLBWynli.AncogNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Molecular BiologyDocument94 pagesLecture Notes On Molecular BiologykoyewubrhanuNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument24 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritanceharsh shirsatNo ratings yet
- 2 Genetics Lecture - DNA PackagingDocument45 pages2 Genetics Lecture - DNA PackagingAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Genes and GenomesDocument66 pagesGenes and Genomesselowest100% (1)
- CBRC Facilitating Learning Notes Handouts 1Document4 pagesCBRC Facilitating Learning Notes Handouts 1jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- CBRC Free Let Review For All General Education For BeedDocument9 pagesCBRC Free Let Review For All General Education For Beedjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Sample Weekend Greeting Convo.Document1 pageSample Weekend Greeting Convo.jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 4 ActivityDocument1 pageChapter 1 Lesson 4 Activityjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reaction Worksheet Practice AnswersDocument1 pageTypes of Chemical Reaction Worksheet Practice Answersjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- 7th Grade - Chemical ReactionsDocument18 pages7th Grade - Chemical Reactionsjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- WordDocument10 pagesWordjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Activity RPDocument1 pageActivity RPjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- THE EARTH IN SPACE ReportDocument21 pagesTHE EARTH IN SPACE Reportjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Performance Task Number 1Document2 pagesPerformance Task Number 1jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- 1122-Article Text-2199-1-10-20210803Document4 pages1122-Article Text-2199-1-10-20210803jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument2 pagesActivitiesjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Group 4Document29 pagesGroup 4jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Data PrivacyDocument7 pagesData Privacyjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Regulation ReportDocument14 pagesRegulation Reportjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Software and Mobile Application by Group 4Document20 pagesSoftware and Mobile Application by Group 4jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Physics Meachanics Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesPhysics Meachanics Lecture Notesjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Rizal in Nation BuildingDocument11 pagesRizal in Nation Buildingjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Pink Bright Fun Easter Bingo CardDocument16 pagesPink Bright Fun Easter Bingo Cardjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Newtonian FluidDocument16 pagesNewtonian Fluidjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Conwo Midterm ReviewerDocument6 pagesConwo Midterm Reviewerjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Long Exam in Seds15Document7 pagesLong Exam in Seds15jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- CHROMOSOMAL MUTATION LectureDocument5 pagesCHROMOSOMAL MUTATION Lecturejeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Jointsworkbook Answers - CompressDocument21 pagesTopic 1 Jointsworkbook Answers - Compressjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Long Quiz in Therodynamics 2023Document6 pagesLong Quiz in Therodynamics 2023jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Cot 3 DNA Replication 2Document56 pagesCot 3 DNA Replication 2jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- SEDS11 Bones Worksheet AnswersDocument13 pagesSEDS11 Bones Worksheet Answersjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- The Globalization of World EconomicDocument17 pagesThe Globalization of World Economicjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Group 2Document19 pagesGroup 2jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument6 pagesREVIEWERjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- IB - Biology 2009 Syllabus (Almost Complete Set of Notes)Document117 pagesIB - Biology 2009 Syllabus (Almost Complete Set of Notes)Cristen100% (24)
- M2 - L3. DNA - The Genetic MateriaDocument3 pagesM2 - L3. DNA - The Genetic MateriaPrincess Paula ArguidasNo ratings yet
- Biology 101Document72 pagesBiology 101Omar Sawas100% (1)
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument55 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritancearyan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- 07-DNA Replication II Detailed MecanismsDocument14 pages07-DNA Replication II Detailed Mecanismsفقوش عبودNo ratings yet
- Annotated-Kami Export - DNA WorksheetDocument6 pagesAnnotated-Kami Export - DNA WorksheetFredrick DanielsNo ratings yet
- Holt BiologyDocument30 pagesHolt BiologyKiro RemonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 01 BIO (Grade 9)Document78 pagesLesson Plan 01 BIO (Grade 9)حزیفہ بھٹیNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Cycle WorksheetRyan NegadNo ratings yet
- State Eligibility Test: (Original Question Paper With Answer Key)Document16 pagesState Eligibility Test: (Original Question Paper With Answer Key)Roopa ZakkamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance - PPT Slides 2022Document59 pagesChapter 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance - PPT Slides 2022aruzhan begaliyevaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentDocument4 pagesModule 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentFelix BrockmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Day 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan Day 1Stephanie Ngooi Ming MingNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma AND Concept of Genetic CodeDocument12 pagesCentral Dogma AND Concept of Genetic CodePrincyNo ratings yet
- Bioscience Jamia Malia IslamiaDocument20 pagesBioscience Jamia Malia IslamiaRahul MohantyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/01Document18 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/01Raphael JosephNo ratings yet
- TAKS Science Study GuideDocument127 pagesTAKS Science Study Guideaehsgo2collegeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Document44 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Stephanie FoleyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology The Human Experience 1St Edition Zarrintaj Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesMicrobiology The Human Experience 1St Edition Zarrintaj Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlloydkieran71epfi100% (14)
- Expand High Fidelity PCR System Roche PDFDocument2 pagesExpand High Fidelity PCR System Roche PDFTeresaNo ratings yet
- 9700 Topic QuestionsDocument137 pages9700 Topic QuestionsBrownsonNo ratings yet
- USMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideDocument137 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- Properties: GeneticDocument24 pagesProperties: Geneticpalak singhNo ratings yet
- Final Exam National Board of Examinations JUNE 2020Document2 pagesFinal Exam National Board of Examinations JUNE 2020narasimhahanNo ratings yet
- BS BiotechDocument47 pagesBS BiotechSyed Sheraz ArshadNo ratings yet
- Nucliec Acid Introductory Test in BiochemistryDocument9 pagesNucliec Acid Introductory Test in Biochemistrysghani100% (1)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Not meNo ratings yet