Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-007
New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-007
Uploaded by
dr.kungOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-007
New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-007
Uploaded by
dr.kungCopyright:
Available Formats
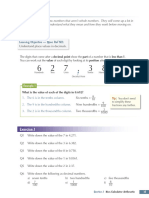
About this Book
Learning Objectives
Section 22
XX Xxxxxxxx
Area and Perimeter
Xxxxxxxxx Showing which bits of the specification
are covered in each section.
22.1 Rectangles and Triangles
You should already be familiar with area and perimeter, but for GCSE you’ll
need to work them out for all sorts of shapes, including composite shapes.
We’ll start off with the basics — squares, rectangles and triangles.
||
|| | | | | |
Prior Knowled
| | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | |
Prior Knowledge Checks
| |
Perimeter ge Check:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Be familiar with
Learning Objective — Spec Ref G17:
properties of trian
squares and rect
the
gles,
Pointing you to the parts of the book
angles.
that you should be familiar with
| | | | |
Be able to find the perimeter of rectangles and triangles. See p.242-246. | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | ||
| | | | | | | |
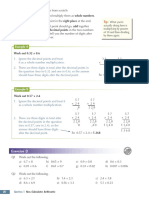
Perimeter (P) is the distance around the outside of a shape. You can work it out before moving on to this topic.
by adding up the lengths of all the sides, or by learning these formulas.
Rectangle length (l) c
a
Square length (l)
Triangle
width (w) b Explanations
P = 4l P = 2l + 2w P=a+b+c
Clear explanations of every topic.
Example 1
Find the perimeter of each of these shapes. Tip: The little lines
1. Write down a) (or ‘tick marks’) on
the formula for
the sides of the shape
Tips
10 cm
P = 4l in part a) show that
perimeter. those sides are the
= 4 × 10
2. Substitute the same length — so you
lengths of the sides
= 40 cm
know it’s a square. Lots of useful tips to help you get
into the formula. b) 5 cm
3. Simplify the
P = 2l + 2w
= (2 × 3) + (2 × 5)
your head around the tricky bits.
3 cm
answer and don’t = 6 + 10
forget to include = 16 cm
the units.
c)
6.2
Examples
m
m P=a+b+c
4.1
= 4.1 + 8.3 + 6.2
= 18.6 m
8.3 m
Plenty of step-by-step worked examples.
Section 22 Area and Perimeter 345
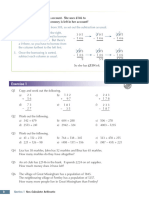
Exercise 2
In the following questions, write any repeated prime factors as powers.
Q1 a) Copy and complete the following factor trees.
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
14 33 10 25
2 ? ? 3 ? ? ? ?
b) Use your factor trees to write the following as products of prime factors.
(i) 14 (ii) 33 (iii) 10 (iv) 25
Exercises (with worked answers) Q2 Write the following numbers as the product of two prime factors.
a) 15 b) 21 c) 22
• Lots of practice for every topic, with fully d) 6 e) 14 f) 26
worked answers at the back of the book. Q3 a) Copy and complete the following factor trees.
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
30 44 24 72
• The more challenging 2 ? 2 ? 3 ? 9 8
questions are marked like this: Q1 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ?
b) Use your factor trees to write the following as the product of prime factors.
(i) 30 (ii) 44 (iii) 24 (iv) 72
70
Q4 Copy and complete the factor tree on the right
and use it to find the prime factorisation of 70. ? ?
? ?
Q5 Use factor trees to write the following numbers as the product of prime factors.
Problem Solving a) 42 b) 84 c) 190 d) 210
Q6 Write the following as the product of prime factors.
Problem solving questions involve skills a) 128 b) 168 c) 325
such as combining different areas of d) 98 e) 225 f) 1000
maths or interpreting given information Q9
Q7 Square numbers have all their prime factors raised to even powers.
For example, 36 = 22 × 32 and 64 = 26.
to identify what’s being asked for. a) Write 75 as a product of prime factors.
b) What is the smallest number you could multiply 75 by to
Questions that involve problem form a square number? Explain your answer.
solving are marked with stamps. Section 4 Multiples and Factors 57
You might also like
- A2 KEY For Schools 2 With AnswersDocument9 pagesA2 KEY For Schools 2 With Answerslana.pink.pv50% (6)
- BS EN 1295 Part 1Document38 pagesBS EN 1295 Part 1maithra333100% (2)
- BS en 12128-1998 - (2018-06-27 - 04-40-22 Am)Document16 pagesBS en 12128-1998 - (2018-06-27 - 04-40-22 Am)Rankie Choi100% (1)
- BS en 00410-1998 PDFDocument28 pagesBS en 00410-1998 PDFShan Sandaruwan AbeywardeneNo ratings yet
- En 837-1Document5 pagesEn 837-1Rodrigo Galdo Martínez50% (2)
- BS EN 1065-1999 Scaffolding AdjustableDocument38 pagesBS EN 1065-1999 Scaffolding AdjustableuchikhlikarNo ratings yet
- BS EN 524-1-1997 Steel Strip Sheaths For Prestressing Tendons - Test MethodsDocument8 pagesBS EN 524-1-1997 Steel Strip Sheaths For Prestressing Tendons - Test MethodsSanka SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- BS en 837-3-98Document26 pagesBS en 837-3-98Pablo DM100% (1)
- Math, Grade 4: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesFrom EverandMath, Grade 4: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesNo ratings yet
- Final Reflection On Curriculum DevelopmentDocument8 pagesFinal Reflection On Curriculum DevelopmentHallie Moberg Brauer100% (4)
- 933 3-97FlakinessIndex PDFDocument12 pages933 3-97FlakinessIndex PDFRed FolderNo ratings yet
- 933 5-98CrushedNBrokenSurfaces PDFDocument10 pages933 5-98CrushedNBrokenSurfaces PDFRed Folder100% (1)
- BS EN 933 P 1 Particale SizeDocument10 pagesBS EN 933 P 1 Particale SizeJack Yang100% (2)
- Quotation Summary: Item Rev Qty Description/Tags Est. DelDocument9 pagesQuotation Summary: Item Rev Qty Description/Tags Est. DelcesarerlNo ratings yet
- Insulating and Sheathing Materials For Cables ÐDocument8 pagesInsulating and Sheathing Materials For Cables ÐSamwel TarimoNo ratings yet
- ABAN Prestressing: Steel Strip Sheaths For Prestressing Tendons Ð Test MethodsDocument8 pagesABAN Prestressing: Steel Strip Sheaths For Prestressing Tendons Ð Test MethodssufyanNo ratings yet
- BS en 1652-1998 Copper and Copper AlloysÐ Plate, Sheet, Strip and Circles For General PurposesDocument42 pagesBS en 1652-1998 Copper and Copper AlloysÐ Plate, Sheet, Strip and Circles For General PurposesThao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Analisis Estructural 2Document1 pageAnalisis Estructural 2Fabio CallataNo ratings yet
- En 1514-2 1997Document14 pagesEn 1514-2 1997sbyeNo ratings yet
- BS en 1074-3-2000Document12 pagesBS en 1074-3-2000PeraNo ratings yet
- BS en 01514-3-1997Document12 pagesBS en 01514-3-1997Samwel TarimoNo ratings yet
- (BS EN 932-5 - 2000) - Tests For General Properties of Aggregates. Common Equipment and CalibrationDocument18 pages(BS EN 932-5 - 2000) - Tests For General Properties of Aggregates. Common Equipment and CalibrationAdelNo ratings yet
- BS 8221-2-2000-Code of Practice For Cleaning and Surface Repair of Buildings (Part 2)Document30 pagesBS 8221-2-2000-Code of Practice For Cleaning and Surface Repair of Buildings (Part 2)fizaNo ratings yet
- 932 1-97Document24 pages932 1-97David Morán100% (1)
- BS en 12079Document32 pagesBS en 12079مشمهندز بوسحسNo ratings yet
- BS en 1288-3-2000Document14 pagesBS en 1288-3-2000Ziyad KubbaNo ratings yet
- BS en 01810-1998Document10 pagesBS en 01810-1998Amer AmeryNo ratings yet
- Flexible Sheets For Waterproofing Bitumen Sheets For Roof Waterproofing Determination of Shear Resistance of JointsDocument1 pageFlexible Sheets For Waterproofing Bitumen Sheets For Roof Waterproofing Determination of Shear Resistance of Jointsmohammed wajidNo ratings yet
- BS 583-6 PDFDocument18 pagesBS 583-6 PDFwiNo ratings yet
- BS 255-1 AC Liquid Cooled With Heat Pump PDFDocument10 pagesBS 255-1 AC Liquid Cooled With Heat Pump PDFSam11111No ratings yet
- Flexible Sheets For Waterproofing Ð Determination of Resistance To Tearing (Nail Shank) ÐDocument10 pagesFlexible Sheets For Waterproofing Ð Determination of Resistance To Tearing (Nail Shank) ÐjovindhaNo ratings yet
- ISO 20461-2000 Determination of Uncertainty For Volume Measurements Made Using The Gravimetric MethodDocument18 pagesISO 20461-2000 Determination of Uncertainty For Volume Measurements Made Using The Gravimetric MethodByesurNo ratings yet
- BS en Iso 2064 - 2000Document12 pagesBS en Iso 2064 - 2000Diego ValentinNo ratings yet
- 480.5-97admixture - Capilary AbsorbtionDocument10 pages480.5-97admixture - Capilary AbsorbtionRed FolderNo ratings yet
- BS en 1522-1999Document8 pagesBS en 1522-1999lilyNo ratings yet
- BS en 10067-1997Document12 pagesBS en 10067-1997david13andrei100% (1)
- En 755-1 PDFDocument18 pagesEn 755-1 PDFVIJAYAKUMAR T100% (1)
- BS en 1045-1997 PDFDocument8 pagesBS en 1045-1997 PDFJorgeNo ratings yet
- BS en 10279-2000 PDFDocument10 pagesBS en 10279-2000 PDFPhạm Văn Đảng100% (1)
- BS en 1367 Part 1 2000Document16 pagesBS en 1367 Part 1 2000thoryamaraghyNo ratings yet
- BS en 00233-1999Document10 pagesBS en 00233-1999Harun ARIKNo ratings yet
- ABAN Prestressing: Steel Strip Sheaths For Prestressing Tendons Ð Test MethodsDocument8 pagesABAN Prestressing: Steel Strip Sheaths For Prestressing Tendons Ð Test MethodssufyanNo ratings yet
- BS en 10218-2-1997 Wire Diameter Tolerance StandardDocument12 pagesBS en 10218-2-1997 Wire Diameter Tolerance StandardEidrish Shaikh100% (1)
- BS EN 447-1997 Grout For Prestressing Tendons. Specification For Common GroutDocument10 pagesBS EN 447-1997 Grout For Prestressing Tendons. Specification For Common Groutkelvin.makNo ratings yet
- BS 8666Document24 pagesBS 8666Duminda AnuradhaNo ratings yet
- BS En1096 1 1999 PDFDocument14 pagesBS En1096 1 1999 PDFanalunlNo ratings yet
- BS-EN 12504-1 Cored Specimen PDFDocument12 pagesBS-EN 12504-1 Cored Specimen PDFArisan IqmaNo ratings yet
- BS EN 445 1997 Grout For Prestressing Tendons - Test MethodsDocument17 pagesBS EN 445 1997 Grout For Prestressing Tendons - Test Methodstommy' sleepNo ratings yet
- 1 00aHardenedConcrete PDFDocument14 pages1 00aHardenedConcrete PDFRed FolderNo ratings yet
- BS en 12406-1999Document18 pagesBS en 12406-1999DoicielNo ratings yet
- BS en 12543 2 1999 PDFDocument14 pagesBS en 12543 2 1999 PDFkimNo ratings yet
- Admixtures For Concrete, Mortar and Grout ÐDocument12 pagesAdmixtures For Concrete, Mortar and Grout Ðhz135874No ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Make Sure You Know How To Use Inverse Sin, Cos Etc. On Your Calc Too - You'll Need Them Here..Document2 pagesTrigonometry: Make Sure You Know How To Use Inverse Sin, Cos Etc. On Your Calc Too - You'll Need Them Here..Kareem TarekNo ratings yet
- Pei-Cheng Wu - ELP - A5 TranscriptsDocument3 pagesPei-Cheng Wu - ELP - A5 TranscriptsPei Cheng WuNo ratings yet
- BS en 00853 1997 (En)Document14 pagesBS en 00853 1997 (En)Emanuele MastrangeloNo ratings yet
- BS 91Document10 pagesBS 91Simon LawNo ratings yet
- BS en Iso 00105-J01-2000Document22 pagesBS en Iso 00105-J01-2000alfredoNo ratings yet
- Eurocode 7, Geotechnical Design, Part 3 Design Assisted by FieldtestingDocument150 pagesEurocode 7, Geotechnical Design, Part 3 Design Assisted by FieldtestingAsoka Kumarasiri JayawardanaNo ratings yet
- Ut BS en 583 1 General PrinciplesDocument13 pagesUt BS en 583 1 General PrinciplesTecnico 5 JamsandtNo ratings yet
- Math, Grade 1: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesFrom EverandMath, Grade 1: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesNo ratings yet
- Math, Grade 3: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesFrom EverandMath, Grade 3: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesNo ratings yet
- Math, Grade 2: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesFrom EverandMath, Grade 2: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesNo ratings yet
- All SetsDocument13 pagesAll Setsdr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-029Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-029dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-020Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-020dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-017Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-017dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-027Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-027dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-022Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-022dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-025Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-025dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-013Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-013dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-019Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-019dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-014Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-014dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-015Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-015dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-002Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-002dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-009Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-009dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-006Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-006dr.kungNo ratings yet
- New Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-004Document1 pageNew Grade 9-1 GCSE Maths Edexcel Student Book - Foundation-004dr.kungNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan RI Ain - OctDocument3 pagesLesson Plan RI Ain - OctNURUL AIN BINTI MOHD. DIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi Views On EducationDocument9 pagesMahatma Gandhi Views On EducationJAGROOP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Himensulan Es Sukod Files Narrativepics and Other MovsDocument33 pagesHimensulan Es Sukod Files Narrativepics and Other MovsJeverlyn Castardo LuderNo ratings yet
- Nit Goa CutoffDocument10 pagesNit Goa CutoffManu KapoorNo ratings yet
- Teachers Program: Tonga Lim Siao Sr. Integrated SchoolDocument1 pageTeachers Program: Tonga Lim Siao Sr. Integrated SchoolGemly Recto GuisihanNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt-Hesham Alshareef-UsaDocument1 pageLean Six Sigma Black Belt-Hesham Alshareef-UsaAbdulRahman AlhusseinNo ratings yet
- DEPT-HEADS-LEARNING-DELIVERY-MONITORING-TEMPLATE MarchDocument6 pagesDEPT-HEADS-LEARNING-DELIVERY-MONITORING-TEMPLATE MarchJeffreynald FranciscoNo ratings yet
- G43 de Format 2025 - Sheila - Phương UyênDocument6 pagesG43 de Format 2025 - Sheila - Phương Uyênkhanhhoi.clcNo ratings yet
- Patal Edm616 Educational System in Thailand Assignment13Document2 pagesPatal Edm616 Educational System in Thailand Assignment13api-560044360No ratings yet
- Route To ChartershipDocument18 pagesRoute To ChartershipAhmad NawwarNo ratings yet
- Professional Certificate of Competency in The Fundamentals of Process Plant Layout & Piping DesignDocument5 pagesProfessional Certificate of Competency in The Fundamentals of Process Plant Layout & Piping DesignAqil GhaffarNo ratings yet
- BRO-Ed Application FormDocument1 pageBRO-Ed Application FormVILLA NUESANo ratings yet
- Aster Prospectus WebDocument31 pagesAster Prospectus WebAkanshaNo ratings yet
- In Order of Roll Nos.: PassDocument108 pagesIn Order of Roll Nos.: PassSurajitNo ratings yet
- CERTIFICATE FinalDocument7 pagesCERTIFICATE FinalKIRK ANDREW ABELLANOSANo ratings yet
- 1 Year ResultDocument2 pages1 Year ResultVishuNo ratings yet
- Bulacan Agricultural State College: Certificate of RegistrationDocument1 pageBulacan Agricultural State College: Certificate of RegistrationKriziel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Warm Welcomes: Activity TypeDocument2 pagesWarm Welcomes: Activity Typeendah maulidaNo ratings yet
- Making The Team A Guide For Managers 6th Edition Thompson Solutions ManualDocument13 pagesMaking The Team A Guide For Managers 6th Edition Thompson Solutions Manualletitiahypatiawf76100% (24)
- Maple Walk Year 3 HomeworkDocument9 pagesMaple Walk Year 3 Homeworkcfmmpnh6100% (1)
- Book List 2024 25 I To XiiDocument22 pagesBook List 2024 25 I To XiiDeepak PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Metacognitive LearningDocument169 pagesMetacognitive LearningPsicownerNo ratings yet
- 78KDO Class SummaryDocument2 pages78KDO Class SummaryFrederick MullerNo ratings yet
- Sports ClubDocument7 pagesSports Clubhuman pandemicNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 LAS 2 - MELC 1b - 4TH QUARTERDocument11 pagesGRADE 10 LAS 2 - MELC 1b - 4TH QUARTERnorlie caneteNo ratings yet
- Bukatsudo The Educational Role of Japane PDFDocument27 pagesBukatsudo The Educational Role of Japane PDFIsaias LopezNo ratings yet
- 2021 Answer KeyDocument2 pages2021 Answer KeySumanth S CNo ratings yet
- IELTS Sample Papers General Reading Sets 1 10Document32 pagesIELTS Sample Papers General Reading Sets 1 10ds351316No ratings yet