Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vectors
Vectors
Uploaded by
Nayeem MD AnisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vectors
Vectors
Uploaded by
Nayeem MD AnisCopyright:
Available Formats
Vectors
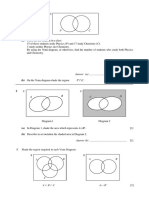
5 (a)
y
5
A
4
3
2
B
1
x
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
(i) Write down the position vector of A.
Answer(a)(i) f p [1]
(ii) Find ì ì , the magnitude of .
Answer(a)(ii) ................................................ [2]
(b)
S
NOT TO
Q SCALE
O p P R
O is the origin, = p and = q.
OP is extended to R so that OP = PR.
OQ is extended to S so that OQ = QS.
(i) Write down in terms of p and q.
Answer(b)(i) = ................................................ [1]
(ii) PS and RQ intersect at M and RM = 2MQ.
Use vectors to find the ratio PM : PS, showing all your working.
Answer(b)(ii) PM : PS = ....................... : ....................... [4]
__________________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2014 0580/43/M/J/14
7
For
16 Examiner′s
y Use
B
7
NOT TO
SCALE
A
1
x
0
–1 8
A is the point (–1, 1) and B is the point (8, 7).
(a) Write as a column vector.
Answer(a) = f p [1]
(b) Find | |.
Answer(b) | | = ............................................... [2]
(c) =2 .
Write down the co-ordinates of C.
Answer(c) (................ , ................) [1]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
17 Factorise completely.
(a) a + b + at + bt
Answer(a) ............................................... [2]
(b) x2 – 2x – 24
Answer(b) ............................................... [2]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2013 0580/21/O/N/13 [Turn over
10
⎛ 3⎞ For
6 (a) Calculate the magnitude of the vector ⎜ ⎟. Examiner's
⎝ − 5⎠ Use
Answer(a) [2]
(b)
y
16
14
12
10
8
R P
6
x
0
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
(i) The points Pand Rare marked on the grid above.
⎛ 3⎞
=⎜ ⎟ . Draw the vector on the grid above. [1]
⎝ − 5⎠
(ii) Draw the image of vector after rotation by 90° anticlockwise about R. [2]
(c) = 2a + b and = 3b O a.
Find in terms of a and b. Write your answer in its simplest form.
Answer(c) = [2]
© UCLES 2012 0580/42/O/N/12
9
20 For
D Examiner's
Use
E NOT TO
d SCALE
O c C
In the diagram, O is the origin.
= c and = d.
E is on CD so that CE = 2ED.
Find, in terms of c and d, in their simplest forms,
(a) ,
Answer(a) = [2]
(b) the position vector of E.
Answer(b) [2]
© UCLES 2012 0580/23/O/N/12 [Turn over
9
For
(b) Examiner′s
P Q Use
NOT TO
SCALE
p R
O s S
In the pentagon OPQRS, OP is parallel to RQ and OS is parallel to PQ.
PQ = 2OS and OP = 2RQ.
O is the origin, = p and = s.
Find, in terms of p and s, in their simplest form,
(i) the position vector of Q,
Answer(b)(i) ............................................... [2]
(ii) .
Answer(b)(ii) = ............................................... [2]
(c) Explain what your answers in part (b) tell you about the lines OQ and SR.
Answer(c) .................................................................................................................................. [1]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2013 0580/41/O/N/13 [Turn over
11
24
A
b
B
a NOT TO
SCALE
O
c C
In the diagram, O is the origin, OA = a, OC = c and AB = b.
P is on the line AB so that AP : PB = 2 : 1.
Q is the midpoint of BC.
Find, in terms of a, b and c, in its simplest form
(a) CB,
CB = ................................................. [1]
(b) the position vector of Q,
.................................................. [2]
(c) PQ.
PQ = ................................................. [2]
© UCLES 2016 0580/22/M/J/16
11
⎛ − 2⎞ ⎛ 5⎞ For
(d) =⎜ ⎟ and =⎜ ⎟. Examiner's
⎝ 5⎠ ⎝ − 1⎠ Use
Write as a column vector.
⎛ ⎞
⎜ ⎟
Answer(d) = ⎜ ⎟ [2]
⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠
(e)
A
NOT TO
M SCALE
X
C
= b and = c.
(i) Find in terms of b and c.
Answer(e)(i) = [1]
(ii) Xdivides CB in the ratio 1 : 3 .
M is the midpoint of AB.
Find in terms of b and c.
Show all your working and write your answer in its simplest form.
Answer(e)(ii) = [4]
© UCLES 2012 0580/42/O/N/12 [Turn over
6
14
Q b R NOT TO
SCALE
P M S
PQRS is a quadrilateral and M is the midpoint of PS.
PQ = a, QR = b and SQ = a – 2b.
(a) Show that PS = 2b.
Answer(a)
[1]
(b) Write down the mathematical name for the quadrilateral PQRM, giving reasons for your answer.
Answer(b) .............................................................. because ...............................................................
............................................................................................................................................................. [2]
__________________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2015 0580/21/M/J/15
14
7
R M Q
r NOT TO
SCALE
O p P
OPQR is a rectangle and O is the origin.
M is the midpoint of RQ and PT : TQ = 2 : 1.
OP = p and OR = r.
(a) Find, in terms of p and/or r, in its simplest form
(i) MQ,
MQ = .................................................. [1]
(ii) MT ,
MT = .................................................. [1]
(iii) OT .
OT = .................................................. [1]
(b) RQ and OT are extended to meet at U.
Find the position vector of U in terms of p and r.
Give your answer in its simplest form.
................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2016 0580/41/M/J/16
15
2k
(c) MT = c m and MT = 180 .
-k
Find the positive value of k.
k = .................................................. [3]
© UCLES 2016 0580/41/M/J/16 [Turn over
16
-2
(a) m = c m n =c m
3
9
2 3
(i) Work out 2m – 3n.
f p [2]
(ii) Calculate 2m - 3n .
................................................... [2]
(b) (i)
A
a NOT TO
M SCALE
O B
b
In the diagram, O is the origin, OA = a and OB = b.
The point M lies on AB such that AM : MB = 3 : 2.
Find, in terms of a and b, in its simplest form
(a) AB,
AB = .................................................. [1]
(b) AM ,
AM = .................................................. [1]
© UCLES 2016 0580/43/O/N/16
17
(c) the position vector of M.
................................................... [2]
(ii) OM is extended to the point C.
The position vector of C is a + kb.
Find the value of k.
k = .................................................. [1]
© UCLES 2016 0580/43/O/N/16 [Turn over
11
19
B M P
NOT TO
X SCALE
b
O a A
OAPB is a parallelogram.
O is the origin, OA = a and OB = b.
M is the midpoint of BP.
(a) Find, in terms of a and b, giving your answer in its simplest form,
(i) BA,
Answer(a)(i) BA = ................................................ [1]
(ii) the position vector of M.
Answer(a)(ii) ................................................ [1]
(b) X is on BA so that BX : XA = 1 : 2.
Show that X lies on OM.
Answer(b)
[4]
Question 20 is printed on the next page.
© UCLES 2015 0580/23/M/J/15 [Turn over
18
5
10 (a) =c m
-8
(i) Find the value of ! !.
Answer(a)(i) ! ! = ................................................ [2]
(ii) Q is the point (2, –3).
Find the co-ordinates of the point P.
Answer(a)(ii) (...................... , ......................) [1]
(b)
A
NOT TO
a M SCALE
O N B
b
In the diagram, M is the midpoint of AB and L is the midpoint of OM.
The lines OM and AN intersect at L and ON = 13 OB.
= a and = b.
(i) Find, in terms of a and b, in its simplest form,
(a) ,
Answer(b)(i)(a) = ................................................ [2]
(b) ,
Answer(b)(i)(b) = ................................................ [1]
(c) .
Answer(b)(i)(c) = ................................................ [2]
© UCLES 2015 0580/42/M/J/15
16
10
C
NOT TO
b
SCALE
M
a
A
BC = a and AC = b.
(a) Find AB in terms of a and b.
Answer(a) AB = ................................................ [1]
(b) M is the midpoint of BC.
X divides AB in the ratio 1 : 4.
Find XM in terms of a and b.
Show all your working and write your answer in its simplest form.
Answer(b) XM = ................................................ [4]
Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable
effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will
be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity.
To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced online in the Cambridge International
Examinations Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download at www.cie.org.uk after
the live examination series.
Cambridge International Examinations is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group. Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local
Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge.
© UCLES 2015 0580/41/O/N/15
19
(b)
C
Y
NOT TO
A SCALE
N
a
B
b
O
OACB is a parallelogram.
= a and = b.
2
AN : NB = 2 : 3 and AY = 5 AC.
(i) Write each of the following in terms of a and/or b.
Give your answers in their simplest form.
(a)
Answer(b)(i)(a) = ................................................ [2]
(b)
Answer(b)(i)(b) = ................................................ [2]
(ii) Write down two conclusions you can make about the line segments NY and BC.
Answer(b)(ii) ...............................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................... [2]
__________________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2014 0580/41/M/J/14 [Turn over
10
19
C B
NOT TO
c X SCALE
O a A
The diagram shows a quadrilateral OABC.
= a, = c and = 2a.
X is a point on OB such that OX : XB = 1 : 2.
(a) Find, in terms of a and c, in its simplest form
(i) ,
Answer(a)(i) = ................................................ [1]
(ii) .
Answer(a)(ii) = ................................................ [3]
(b) Explain why the vectors and show that C, X and A lie on a straight line.
Answer(b) ..................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................. [2]
__________________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2014 0580/22/O/N/14
8
For
19 t varies inversely as the square root of u. Examiner′s
t = 3 when u = 4. Use
Find t when u = 49.
Answer t = ............................................... [3]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
20
R Q
S
r M NOT TO
SCALE
O p P
OPQR is a parallelogram, with O the origin.
M is the midpoint of PQ.
OM and RQ are extended to meet at S.
= p and = r.
(a) Find, in terms of p and r, in its simplest form,
(i) ,
Answer(a)(i) = ............................................... [1]
(ii) the position vector of S.
Answer(a)(ii) ............................................... [1]
1
(b) When =– 2
p + r , what can you write down about the position of T ?
Answer(b) ................................................................................................................................. [1]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2013 0580/21/M/J/13
9
18 For
Q R Examiner's
Use
M
q X NOT TO
SCALE
O p P
O is the origin and OPRQ is a parallelogram.
The position vectors of P and Q are p and q.
X is on PR so that PX = 2XR.
Find, in terms of p and q, in their simplest forms
(a) ,
Answer(a) = [2]
(b) the position vector of M, the midpoint of QX.
Answer(b) [2]
© UCLES 2012 0580/23/M/J/12 [Turn over
10
18 For
S Examiner's
Use
X
NOT TO
SCALE
In the diagram, PQS, PMR , MXS and QXR are straight lines.
PQ = 2 QS.
M is the midpoint of PR .
QX : XR = 1 : 3.
= q and = r.
(a) Find, in terms of q and r,
(i) ,
Answer(a)(i) = [1]
(ii) .
Answer(a)(ii) = [1]
(b) By finding , show that X is the midpoint of MS.
Answer (b)
[3]
© UCLES 2011 0580/21/M/J/11
11
For
19 Examiner′s
C Use
D B
c
b
E A
OABCDE is a regular polygon.
(a) Write down the geometrical name for this polygon.
Answer(a) ............................................... [1]
(b) O is the origin. = b and = c.
Find, in terms of b and c, in their simplest form,
(i) ,
Answer(b)(i) = ............................................... [1]
(ii) ,
Answer(b)(ii) = ............................................... [2]
(iii) the position vector of E.
Answer(b)(iii) ............................................... [1]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Question 20 is printed on the next page.
© UCLES 2013 0580/23/M/J/13 [Turn over
10
For
19 Examiner′s
C Use
D B
c
O
a
E A
O is the origin.
ABCDEF is a regular hexagon and O is the midpoint of AD.
= a and = c.
Find, in terms of a and c, in their simplest form
(a) ,
Answer(a) = ............................................... [2]
(b) ,
Answer(b) = ............................................... [2]
(c) the position vector of E.
Answer(c) ............................................... [2]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2013 0580/22/O/N/13
10
19 For
S R Examiner's
Use
T Q
O p P
O is the origin and OPQRST is a regular hexagon.
= p and = t.
Find, in terms of p and t, in their simplest forms,
(a) ,
Answer(a) = [1]
(b) ,
Answer(b) = [2]
(c) the position vector of R.
Answer(c) [2]
© UCLES 2012 0580/21/M/J/12
16
8
B
P
A
NOT TO
SCALE
Q
9b
6a
3c
In the diagram, O is the origin and = 6a, = 9b and = 3c.
The point P lies on AB such that = 3b – 2a.
The point Q lies on BC such that = 2c – 6b.
(a) Find, in terms of b and c, the position vector of Q.
Give your answer in its simplest form.
Answer(a) ................................................ [2]
© UCLES 2014 0580/41/O/N/14
17
(b) Find, in terms of a and c, in its simplest form
(i) ,
Answer(b)(i) = ................................................ [1]
(ii) .
Answer(b)(ii) = ................................................ [2]
(c) Explain what your answers in part (b) tell you about PQ and AC.
Answer(c) ............................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................. [2]
__________________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2014 0580/41/O/N/14 [Turn over
15
For
(b) Examiner′s
T Use
A NOT TO
SCALE
R
4a
O 3b B
In the diagram, = 4a and = 3b.
1
R lies on AB such that = 5 (12a + 6b).
3
T is the point such that = 2 .
(i) Find the following in terms of a and b, giving each answer in its simplest form.
(a)
Answer(b)(i)(a) = ............................................... [1]
(b)
Answer(b)(i)(b) = ............................................... [2]
(c)
Answer(b)(i)(c) = ............................................... [1]
(ii) Complete the following statement.
The points O, R and T are in a straight line because ................................................................
........................................................................................................................................... [1]
(iii) Triangle OAR and triangle TBR are similar.
area of triangle TBR
Find the value of .
area of triangle OAR
Answer(b)(iii) ............................................... [2]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
© UCLES 2013 0580/43/O/N/13 [Turn over
10
⎛ ⎞ For
7 (a) Pis the point (2, 5) and = ⎜ 3⎟ . Examiner's
⎝ − 2⎠ Use
Write down the co-ordinates of Q.
Answer(a) ( , ) [1]
(b)
D
C B NOT TO
E
SCALE
c M
O 3a A
O is the origin and OABC is a parallelogram.
M is the midpoint of AB.
1
= c, = 3a and CE = CB.
3
OED is a straight line with OE : ED = 2 : 1 .
Find in terms of a and c, in their simplest forms
(i) ,
Answer(b)(i) = [1]
(ii) the position vector of M,
Answer(b)(ii) [2]
(iii) ,
Answer(b)(iii) = [1]
(iv) .
Answer(b)(iv) = [2]
(c) Write down two facts about the lines CD and OB.
Answer (c)
[2]
© UCLES 2012 0580/42/M/J/12
You might also like
- Mathematics Stage 8 Sample Paper 1 - tcm143-595673Document12 pagesMathematics Stage 8 Sample Paper 1 - tcm143-595673Eyad Mohamed100% (1)
- Laryngo Broncho EsophagologyDocument94 pagesLaryngo Broncho EsophagologyFrederick Mars UntalanNo ratings yet
- Vectors Finished 1Document29 pagesVectors Finished 1muayyaddarrasNo ratings yet
- A5 Matrices With Transformation MSDocument6 pagesA5 Matrices With Transformation MSDua LatifNo ratings yet
- 10 10 It Is Given That y (A) (B) (C) (I) (Ii) (D) (E) (I) (Ii)Document20 pages10 10 It Is Given That y (A) (B) (C) (I) (Ii) (D) (E) (I) (Ii)Rana WaleedNo ratings yet
- End of Module Assessment (Ema) : (Function) or NF (Not Function) F FDocument2 pagesEnd of Module Assessment (Ema) : (Function) or NF (Not Function) F FAxelle SeseNo ratings yet
- Transformations P1Document31 pagesTransformations P1Azaz TBGNo ratings yet
- Sets Worksheet 1Document10 pagesSets Worksheet 1johncarpusampofoNo ratings yet
- Vectors PracticeDocument8 pagesVectors PracticeDennis Junior ChorumaNo ratings yet
- Sets and Venn Diagram - P1 (Merged) PDFDocument51 pagesSets and Venn Diagram - P1 (Merged) PDFbt6dqhzj8zNo ratings yet
- TransformationDocument2 pagesTransformationKern KimbowaNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument17 pagesVectorspro.is.only.me.cause.i.am.vrindaNo ratings yet
- 3 Answer All The Questions. The Table Shows The Marks That 80 Students Scored in An ExaminationDocument12 pages3 Answer All The Questions. The Table Shows The Marks That 80 Students Scored in An ExaminationSean EGANNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument14 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionNuridahBintiZaimiNo ratings yet
- Question'sDocument31 pagesQuestion'sElie aNo ratings yet
- MTH1103T1Document2 pagesMTH1103T1OMA YHNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 0580Document600 pagesQuestion Bank 0580saisudhaNo ratings yet
- 2018f5s10ex7maths 2Document16 pages2018f5s10ex7maths 2mok lee kiauNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2016 Solution Maths PDFDocument21 pagesWBJEE 2016 Solution Maths PDFcolorado wildernessNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument8 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- National Grammar School: Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument6 pagesNational Grammar School: Cambridge Ordinary LevelAdeenaNo ratings yet
- B A A B B A: Prepared by Ms Gwee HN 1Document3 pagesB A A B B A: Prepared by Ms Gwee HN 1yeeluv99No ratings yet
- Vectors and 3DDocument34 pagesVectors and 3Dshashwat.gupta.707No ratings yet
- Line Equation IgcseDocument13 pagesLine Equation IgcseNyoman ParamarthaNo ratings yet
- VectorDocument6 pagesVectorMCHNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Entrance ExamDocument14 pagesMathematics Entrance ExamJAKE THE DOGNo ratings yet
- Circle Red SpotDocument31 pagesCircle Red SpotIrfan RanaNo ratings yet
- Vectors Past PapersDocument34 pagesVectors Past PapersF87 OperatorsNo ratings yet
- Assignment TransformationDocument9 pagesAssignment TransformationSyahirah BurhaniNo ratings yet
- College of Foundation and General Studies Putrajaya Campus Final Examination TRIMESTER 1 2015 / 2016Document5 pagesCollege of Foundation and General Studies Putrajaya Campus Final Examination TRIMESTER 1 2015 / 2016Sufian PianNo ratings yet
- Modul Add Math Kertas 1Document82 pagesModul Add Math Kertas 1Hazuriada HanafiNo ratings yet
- S6uacepure Mathematics Mock Ndejje SSS Question Paper and Marking GuideDocument16 pagesS6uacepure Mathematics Mock Ndejje SSS Question Paper and Marking GuideatabugaalexNo ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang SPM Trial Examination 2019 Mathematics Paper 2Document13 pagesSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang SPM Trial Examination 2019 Mathematics Paper 2HANNAH BINTI KAMARUDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- (A) Transformations (Rotation) 2 Marks 1: AnswerDocument2 pages(A) Transformations (Rotation) 2 Marks 1: AnswerIzzati NorNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 Vectors and 3D GeometryDocument2 pagesDPP 1 Vectors and 3D GeometryrgNo ratings yet
- VectorDocument8 pagesVectorThiri MyatnoeNo ratings yet
- EDEXCEL-linear FunctionDocument13 pagesEDEXCEL-linear Function温雅晴No ratings yet
- 2na Mye P1 2013Document10 pages2na Mye P1 2013toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- A13 Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument10 pagesA13 Co-Ordinate GeometryjamshedNo ratings yet
- Assignement (Vector & 3D)Document5 pagesAssignement (Vector & 3D)Pratham MoreNo ratings yet
- Math 4024 P2 (Midterm Practice Sheet)Document18 pagesMath 4024 P2 (Midterm Practice Sheet)Amyn WahidNo ratings yet
- (52 Marks) : Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument21 pages(52 Marks) : Answer All Questions in This SectionAndek Nor Haizurah YusofNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument28 pagesVectorsMohamed Fouad KorraNo ratings yet
- Prac 1 P1Document20 pagesPrac 1 P1Joann NgNo ratings yet
- Homework 2019 MJ 2Document6 pagesHomework 2019 MJ 2yingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Week 5 MATHS Y6Document10 pagesWeek 5 MATHS Y6Shadi AbbasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2 Test & SolutionsDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Module 2 Test & SolutionsChinaidine Petit-FrereNo ratings yet
- Basics of Compiler Design - SolutionsDocument19 pagesBasics of Compiler Design - SolutionsmanojvnvNo ratings yet
- 12 13 Solutions To This Question by Accurate Drawing Will Not Be AcceptedDocument12 pages12 13 Solutions To This Question by Accurate Drawing Will Not Be AcceptedAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Model Paper 2 SolutionDocument10 pagesClass 10 Maths Model Paper 2 SolutionArooj Yunx JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListDocument11 pagesAx bxc0 X A B B Ac: Formula ListyingwuenchanNo ratings yet
- Smis Mid Term - Add MathsDocument6 pagesSmis Mid Term - Add MathsYuanWei SiowNo ratings yet
- Homework 1: 0 0 0 N 1 2 K 1 2 M I 1 2 MDocument1 pageHomework 1: 0 0 0 N 1 2 K 1 2 M I 1 2 MbillyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper MathematicsDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper MathematicsSuperman INo ratings yet
- Vector DPP (1-10) 25.08.2018Document24 pagesVector DPP (1-10) 25.08.2018prateek amrawanshi100% (1)
- Maths - 2014Document4 pagesMaths - 2014shovongorain1002No ratings yet
- Model Test Paper II Maths ICSE Class IXDocument2 pagesModel Test Paper II Maths ICSE Class IXAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Stochastic Processes An Introduction Third Edition SolutionDocument155 pagesStochastic Processes An Introduction Third Edition SolutionLuciano VítorNo ratings yet
- Math Revision Worksheet 2 Test 1 Term 2 (2023)Document11 pagesMath Revision Worksheet 2 Test 1 Term 2 (2023)Amyn WahidNo ratings yet
- Planting & Tillage: Unflower and Hite LanterDocument20 pagesPlanting & Tillage: Unflower and Hite LanterJeremyNo ratings yet
- Cen TS 19101 (2022) (E)Document7 pagesCen TS 19101 (2022) (E)Amalia C. HuenchunaoNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking 033-DownloadDocument3 pagesCritical Thinking 033-DownloadbeneqNo ratings yet
- NFL Network ResumeDocument2 pagesNFL Network Resumeapi-314448476No ratings yet
- Bletchley & District Allotment Association - Autumn News 2010Document3 pagesBletchley & District Allotment Association - Autumn News 2010ArchenfieldNo ratings yet
- Fds Traffic Paint White YelowDocument10 pagesFds Traffic Paint White YelowMathias CoekaertsNo ratings yet
- Team Sports: Volleyball Positions and RolesDocument3 pagesTeam Sports: Volleyball Positions and RolesPATRICIA VISDA ASTORNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 2Document15 pagesLecture Week 2saneel kumarNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument10 pagesFormula SheetHuraiza AsifNo ratings yet
- 72.00.00 Engine - Fault IsolationDocument60 pages72.00.00 Engine - Fault IsolationTimoteo Molina RomeroNo ratings yet
- DLP Eugelle12Document9 pagesDLP Eugelle12Kim RusteNo ratings yet
- Fault Detection in Solar Power Plants Using Predictiveanalytic TechniquesDocument7 pagesFault Detection in Solar Power Plants Using Predictiveanalytic TechniquesRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Spoken TextsDocument4 pagesEvaluating Spoken TextsErrold SerranoNo ratings yet
- Boroneant - and - Bonsall Sahranjivanje U Mezolitu DjerdapaDocument14 pagesBoroneant - and - Bonsall Sahranjivanje U Mezolitu DjerdapaMorriganNo ratings yet
- RSER Author Checklist TableDocument3 pagesRSER Author Checklist Tablerash4344No ratings yet
- Celebration-Electric BassDocument2 pagesCelebration-Electric BassJames HenryNo ratings yet
- TSQL Coding Standards ChecklistDocument5 pagesTSQL Coding Standards ChecklistSaman AzeemNo ratings yet
- DLP IN ORAL COMMUNICATION-GRADE 11-EditedDocument6 pagesDLP IN ORAL COMMUNICATION-GRADE 11-EditedMaeann MirandoNo ratings yet
- APT NS Grout DatasheetDocument3 pagesAPT NS Grout DatasheetChit San Maung100% (1)
- Feynman's Invaluable Advice For StudentsDocument7 pagesFeynman's Invaluable Advice For StudentsJerome Rafael100% (1)
- Oando For Jevlink2Document4 pagesOando For Jevlink2Steve Bassey100% (2)
- Tarang Hearing Aids To MoH Thru DEIT - 3Document9 pagesTarang Hearing Aids To MoH Thru DEIT - 3Ravindra KumarNo ratings yet
- HAND BOOK ON Audit of WorksDocument160 pagesHAND BOOK ON Audit of WorksnathanabsNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics P3 (WMA13) RMSDocument26 pagesPure Mathematics P3 (WMA13) RMSmoona imranNo ratings yet
- Dioscorea Bulbifera: L. DioscoreaceaeDocument6 pagesDioscorea Bulbifera: L. DioscoreaceaeAlarm GuardiansNo ratings yet
- Final AdityaDocument49 pagesFinal AdityaKaushik KashyapNo ratings yet
- Bible Timeline Card GameDocument18 pagesBible Timeline Card GameTully EhlersNo ratings yet
- Quiz. For Ten (10) Points Each, Answer The Following Questions BrieflyDocument2 pagesQuiz. For Ten (10) Points Each, Answer The Following Questions BrieflyJohn Phil PecadizoNo ratings yet
- LM140/LM340A/LM340/LM7800C Series 3-Terminal Positive RegulatorsDocument15 pagesLM140/LM340A/LM340/LM7800C Series 3-Terminal Positive Regulatorsvmm mNo ratings yet