Professional Documents
Culture Documents
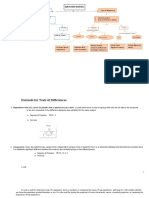
Assumptions For Different Kinds of Statistics
Assumptions For Different Kinds of Statistics
Uploaded by
Erika ToralbaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assumptions For Different Kinds of Statistics
Assumptions For Different Kinds of Statistics
Uploaded by
Erika ToralbaCopyright:
Available Formats
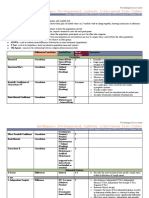
Sta�s�cal Distribu�on Data Variables or Number of Value of Level of Parametric
Tool Type Gathering data Groups being variance Measurement or Non
Method involved compared (scale) Parametric Purpose
t-test Normal Random Con�nuous 2 groups Each group Interval and -t-test is a sta�s�cal tool use to
Distribu�on Sampling variable and (shouldn’t being compared ra�o compare the means
( shape: independent exceed) should have the of two groups.
symmetrical data ( result same value of P -It is o�en used in hypothesis tes�ng
) from one variance to determine
sample is (homogeneity of whether a process or treatment
independent variance) actually has an
from other effect on the popula�on of interest
sample) -rela�onship between independent
and dependent variable.
Pearson’s Normal Random Con�nuous 2 Con�nuous _____ Interval and P -Iden�fies the degree of linear
r distribu�on Sampling variable group/ ra�o rela�onship that exist between two
( shape: variables ( 1 variables or two sets of scores
symmetrical independent, -Pearson r is usually used when you
) 1 dependent want to evaluate whether two
or 2 quan�ta�ve variables, X and Y, are
independent linearly related
variables) rela�onship between an individual’s
loca�on in the X distribu�on and his
or her loca�on in the Y distribu�on.
Spearman Either _______ Con�nuous Degree of _______ Ordinal ( also NP -It measure the strength and
rho skewed or or ordinal monotonic: can be raw direc�on of rela�onship of two
not normal variables consistent score, interval variables (X and Y) when both
distribu�on one- and nominal as variables are measured in ordinal
( shape: direc�onal long as it can scales (ranks)
asymmetric rela�onship be ranked) -The difference between Pearson’s R
al) of 2 paired and Spearman is, PR concerns with
variable with the strength and direc�on of “linear
other 2 rela�onship” while SR concerns
paired with the strength and direc�on of
variable or “monotonic rela�onship”
what we call -You can only use Spearman a�er
bivariate) using Pearson’s if the variables used
In Pearson’s can be ranked.
-Spearman correla�on measures
consistency, rather than form,
comes from a simple observa�on:
When two variables are
consistently related, their ranks are
linearly related. (monotonic)
Skewed Random Variable are 2 or more Nominal ( I NP -Chi-square is designed to analyze
Chi- distribu�on Sampling categorical groups/ think, since it’s categorical variables that can be
square (posi�ve) and the popula�on categorical nominal or ordinal.
(shape: observa�on hehe) and Data should be in frequency or by
asymmetric data is ordinal count.
al) independent -chi-square (χ2) sta�s�c is a measure
of the difference between the
observed and expected frequencies
of the outcomes of a set of events or
variables.
-Chi-square is useful for analyzing
such differences in categorical
variables, especially those nominal
in nature.
Anuba Normal Parang Con�nuous 3 or more Each group the dependent P -One-way Analysis of variance
(Analysis Distribu�on random and groups or 3 being compared variable must compares the means between the
of ( shape: sampling categorical or more should have the be a groups you are
Variance) symmetrical din? Pero variable, independent same value of con�nuous interested in and determines
one way ) di naman independent variable variance (interval or whether any of those means
or yan data (homogeneity of ra�o) while are sta�s�cally significantly different
another, kasama sa (observa�on variance independent from each other.
im gona exam so result from variables -Used to determine whether there
get yah im kerii lang one sample is categorical are any sta�s�cally
gonna get independent (nominal or significant differences between the
yah get from other ordinal) means of three or
yah get sample) variables more independent (unrelated)
yah get groups.
yah get - One-way ANOVA is an omnibus test
yah~ sta�s�c and cannot
tell you which specific groups were
sta�s�cally
significantly different from each
other, only that at least
two groups were. To determine
which specific groups
differed from each other, you need
to use a post hoc test.
z-test Normal random Con�nuous One or two Homogeneity of ra�o P -sta�s�cal test use to determine
Distribu�on sampling variable/data groups ( one variance whether two popula�on means are
( shape: sample z test different when
symmetrical use only one the variances and standard devia�on
) group) are known
and the sample size is large (30 or
more).
-One-sample z-test is use to
determine whether
a popula�on mean is different from
a
hypothesized value.
-Two-sample z-test is use to
determine whether
two popula�on means differ.
Phi Skewed Binary 2 groups nominal NP -The phi-coefficient is one of a
coeffficien distribu�on variables (Two number of correla�on
t (shape: (only 2 independent sta�s�cs developed to measure the
asymmetric possible variables OR strength of
al) values per one associa�on/rela�onship between
variable, e.g. independent two variables.
“yes/no” variable -used in cross-tabulated table
“true/false” and the data where both (two) variables are
“sya o ako?” other is dichotomous. Dichotomous means
dependent that there are
variable) only two possible values for a
variable.
You might also like
- Project - Time Series Forecasting - Rajendra M BhatDocument33 pagesProject - Time Series Forecasting - Rajendra M BhatRajendra Bhat82% (11)
- Choice of The Test To DoDocument1 pageChoice of The Test To DoAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Correlation Regression - Summary NotesDocument4 pagesCorrelation Regression - Summary NotesRockyNo ratings yet
- 2.correlation Regression Summary Notes by Pranav Popat 1Document4 pages2.correlation Regression Summary Notes by Pranav Popat 1Finu x FinuNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics: IdentifyDocument7 pagesInferential Statistics: Identifysean michael leomoNo ratings yet
- Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient - WikipediaDocument10 pagesSpearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient - WikipediaHin HuchNo ratings yet
- Spearman's Rank Correlation CoefficientDocument11 pagesSpearman's Rank Correlation Coefficientdev414No ratings yet
- Correlation Coefficients Appropriate Use And.50Document6 pagesCorrelation Coefficients Appropriate Use And.50Sheena Marie Falcatan-RoblesNo ratings yet
- PsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsDocument7 pagesPsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsMaricrise FernandezNo ratings yet
- Q2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONDocument12 pagesQ2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONmacristinaisabel.talladorNo ratings yet
- PsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsDocument6 pagesPsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsWinona JardinelNo ratings yet
- ResumenDocument10 pagesResumencwdfcvqfsvNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Correlation CorrelationDocument6 pagesLECTURE 1 - Correlation CorrelationJANISCHAJEAN RECTONo ratings yet
- Cream and Brown Simple Modern Creative Mind Map BrainstormDocument1 pageCream and Brown Simple Modern Creative Mind Map BrainstormKaren tovarNo ratings yet
- Activity 3-Table Completion On Parametric Test-Hazel P. PatalotDocument2 pagesActivity 3-Table Completion On Parametric Test-Hazel P. PatalothazelppatalotNo ratings yet
- MMW - Midterm Notes (FINAL) PDFDocument8 pagesMMW - Midterm Notes (FINAL) PDFDhon Aldrin CastroNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Paper #6Document11 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Paper #6Precious NosaNo ratings yet
- 3 Matm111Document3 pages3 Matm111wooziwaegNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment HW #4Document8 pagesPsychological Assessment HW #4maerucelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 and 9 Regression Correlation and IndexDocument32 pagesLecture 8 and 9 Regression Correlation and Indexআসিফ বিন মনজুরNo ratings yet
- Stats Midterms Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesStats Midterms Cheat Sheetjibberish yoNo ratings yet
- 4estimation of Population MeanDocument10 pages4estimation of Population MeanHarshdeep BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Group AssignmentDocument3 pagesGroup AssignmentdatumNo ratings yet
- Correlation Statistics Bbe4301Document14 pagesCorrelation Statistics Bbe4301Kyoshu delabajanNo ratings yet
- MKT500 - Week 11 - Winter 2023 - D2LDocument81 pagesMKT500 - Week 11 - Winter 2023 - D2Lsyrolin123No ratings yet
- Which Statistical Tests To UseDocument2 pagesWhich Statistical Tests To Useian1231No ratings yet
- Biostat Handouts Lesson 10 PDFDocument45 pagesBiostat Handouts Lesson 10 PDFheyyymeeeNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning - White BGDocument5 pagesMachine Learning - White BGDang VH100% (1)
- Cba101 FTDocument3 pagesCba101 FTservanezrmNo ratings yet
- 05 1 Correlation PDFDocument7 pages05 1 Correlation PDFKristen DiazNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument83 pagesData AnalysisLantana MedikaNo ratings yet
- Application of ANOVADocument18 pagesApplication of ANOVAUma Shankar38% (8)
- QR Midterm MemoDocument2 pagesQR Midterm MemoMarkus H.No ratings yet
- Lesson - 4.2 - Exploratory Data Analysis - Analyze - PhaseDocument50 pagesLesson - 4.2 - Exploratory Data Analysis - Analyze - PhaseHarika KalluriNo ratings yet
- Stats 4TH Quarter ReviewerDocument2 pagesStats 4TH Quarter ReviewerKhryzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- Review: Lecture 5: Bivariate Analysis 2 (Spearman and Chi)Document8 pagesReview: Lecture 5: Bivariate Analysis 2 (Spearman and Chi)Imeen flissNo ratings yet
- Parametric Versus Non Parametric StatisticsDocument19 pagesParametric Versus Non Parametric Statisticsمهنوش جوادی پورفرNo ratings yet
- Which Statistical Tests To UseDocument1 pageWhich Statistical Tests To UsePam FajardoNo ratings yet
- Application of ANOVADocument19 pagesApplication of ANOVAabhay_prakash_ranjan100% (2)
- Alagad Ni Maam Dela CruzDocument3 pagesAlagad Ni Maam Dela CruzDominique Larah EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Matriks Pemilihan Metoda StatistikDocument5 pagesMatriks Pemilihan Metoda StatistikethachappunkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Minaw BelayNo ratings yet
- CorrDocument3 pagesCorrgohchuansinNo ratings yet
- Spearman Vs KendallDocument8 pagesSpearman Vs KendallDelfa OtrNo ratings yet
- SPSS Procedures SummaryDocument1 pageSPSS Procedures SummaryMohnmad ZaitoonNo ratings yet
- 08 Introduction To Correlation and Linear Regression Analysis 2Document5 pages08 Introduction To Correlation and Linear Regression Analysis 2Angela Erish CastroNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci Sequence & Golden Ratio: Truth of SentencesDocument6 pagesFibonacci Sequence & Golden Ratio: Truth of SentencesCheyenne Mari RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CanonicalDocument8 pagesCanonicalkrishnamurari9No ratings yet
- Correlation 180511133644Document12 pagesCorrelation 180511133644Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Correlation 180511133644Document12 pagesCorrelation 180511133644Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Common Statistical Tools For AnalysisDocument9 pagesCommon Statistical Tools For AnalysisCyeonjNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression: Yandell - Econ 216 Chap 13-1Document70 pagesSimple Linear Regression: Yandell - Econ 216 Chap 13-1Mr. Raghunath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Correlation AnalysisDocument25 pagesCorrelation AnalysisAJ PatricioNo ratings yet
- Spearman Rank Correlation:, Y, - . - , Y) R (Y) R (X)Document6 pagesSpearman Rank Correlation:, Y, - . - , Y) R (Y) R (X)Andrés ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- 9 Hypothesis Testing in The GWN ModelDocument58 pages9 Hypothesis Testing in The GWN ModelJ.i. LopezNo ratings yet
- Example Writing SPSS ResultsDocument3 pagesExample Writing SPSS ResultsSamerNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Test For Normal Distribution - A CaseDocument5 pagesChi Square Test For Normal Distribution - A CaseRicky SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Multivariate Analysis MPU2263Document14 pagesIntroduction To Multivariate Analysis MPU2263Schahyda ArleyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in SP (CO)Document11 pagesLesson Plan in SP (CO)CIELA LAVESARESNo ratings yet
- MindTap - Chapter7-18Document7 pagesMindTap - Chapter7-18Estefania FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 Topics: Sampling Distributions and Central Limit TheoremDocument4 pagesProblem Set 2 Topics: Sampling Distributions and Central Limit TheoremSravya Tummala100% (1)
- Ujian Tengah Semester 1 Biostatistika Magister Kesehatan MasyarakatDocument2 pagesUjian Tengah Semester 1 Biostatistika Magister Kesehatan MasyarakatYogama SuryaNo ratings yet
- AS-Statistics-Facts-and-Definitions-Quiz Answers PT 1Document2 pagesAS-Statistics-Facts-and-Definitions-Quiz Answers PT 1cokonkwoNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing and Confidence IntervalsDocument3 pagesHypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervalsdreamydamsel0% (1)
- Solutions To Problems: X 0 ZX X yDocument19 pagesSolutions To Problems: X 0 ZX X yrohitvanNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Multinomial Logit Models in R: The Mlogit PackagesDocument73 pagesEstimation of Multinomial Logit Models in R: The Mlogit PackagesCarlos Eduardo Melo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Instant download pdf Elementary Statistics 3rd Edition Navidi Solutions Manual full chapterDocument54 pagesInstant download pdf Elementary Statistics 3rd Edition Navidi Solutions Manual full chapteraszaeuda100% (9)
- Fourth Quarter ExaminationDocument7 pagesFourth Quarter ExaminationWilliam SorianoNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Provide The Most Powerful Information?Document10 pagesWhich of The Following Provide The Most Powerful Information?Media TeamNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument14 pagesForecastingHisokaNo ratings yet
- 4 Pretest and Posttest AnalysisDocument6 pages4 Pretest and Posttest AnalysisRonnie NaagNo ratings yet
- STA 114 SPECIAL TEST 2 - Questions Solution 11 May 2021Document10 pagesSTA 114 SPECIAL TEST 2 - Questions Solution 11 May 2021Monowalehippie MangaNo ratings yet
- Lampiran SPSS Pengetahuan Dan Status GiziDocument2 pagesLampiran SPSS Pengetahuan Dan Status GiziJorge Davis0% (1)
- Statistics and Probability - q4 - Mod 5 - Identifying The Appropriate Rejection Region For A Given Level of Significance - V2Document25 pagesStatistics and Probability - q4 - Mod 5 - Identifying The Appropriate Rejection Region For A Given Level of Significance - V2Moreal QazNo ratings yet
- Final Paul BourgadeDocument2 pagesFinal Paul BourgadeaqszaqszNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Final - ExamDocument1 pageFormula Sheet For Final - ExamFlávia PedrosaNo ratings yet
- MGMT 222 Ch. V-1Document30 pagesMGMT 222 Ch. V-1Asteway Mesfin100% (1)
- Using AMOS To Estimate Composite Reliability McDonald's OmegaDocument18 pagesUsing AMOS To Estimate Composite Reliability McDonald's OmegaGeletaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 14 Confidence IntervalsDocument26 pagesMODULE 14 Confidence IntervalsSajath SabryNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii - Part IDocument43 pagesChapter Iii - Part ILuna AnNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Methods Statistical AnalysisDocument697 pagesBayesian Methods Statistical AnalysisPriscilla Wessels100% (7)
- How To Calculate Stats in ExcelxxDocument6 pagesHow To Calculate Stats in ExcelxxCarooNo ratings yet
- Latihan Regresi SederhanaDocument7 pagesLatihan Regresi Sederhanafhj77thnm9No ratings yet