Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Myelodysplastic Syndromes
The Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Uploaded by
Sameer PashaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Myelodysplastic Syndromes
The Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Uploaded by
Sameer PashaCopyright:
Available Formats
The myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a hetero- generous group of clonal stem-cell disorders
characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis, abnormal cellular morphology, and a propensity for progression
to acute leukemia.
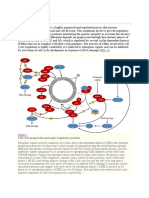
MPNs are rare hematological conditions (pre-leukemic states/disorders). Arose/occurred due to the defects
in clonal HSCs (carrying somatic mutations in leukemia prone genes) which is characterized by aberrant
proliferation/expansion of mature blood components generated from myeloid lineages ().
The MPNs categorized into two major subgroups based on the presence or absence of BCR-ABL fusion
oncogene (Ph+/-) such as Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) (BCR-ABL+) while absence of this gene in
polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET) and primary myelofibrosis (PMF) (). The latter
subtypes are well characterized by the presence of a JAK2 somatic mutation (G to T) at nucleotide 1849/exon
14 leading to the replacement of valine to phenylalanine at codon 617 (JAK2V617F) which comprises more
than 90% parts of PV and about 25-30% of ET and PMF ().
PKM is a rate-limiting glycolytic enzyme, and previous studies have shown that PKM1 is found mainly in
normal cells, whereas PKM2 is an embryonic-isoform expressed in cancer cells.
Pyruvate kinase M2 is a critical enzyme that regulates cell metabolism and growth under different
physiological conditions. In its metabolic role, pyruvate kinase M2 catalyzes the last glycolytic step which
converts phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate with the generation of ATP.
The binding leads to nuclear translocation of PKM2, where it acts as protein kinase and interacts with other
molecules to control the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), thereby promoting tumor
angiogenesis (61). Under the hypoxic condition, translocation of PKM2 and p65 to the nucleus takes place.
PKM2 expression is associated with increased glucose uptake, increased lactate production, and decreased
O2 consumption, which can be reversed by genetic manipulations that replace PKM2 expression with PKM1.
Therefore, PKM2, but not PKM1, promotes the Warburg effect.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), which catalyzes conversion of pyruvate into lactate, serves a critical role during
Warburg effect. LDH A chain (LDHA), a member of the LDH family, is upregulated in multiple types of cancer
and serves a vital role in tumor growth and progression
Myc expression was positively related to LDHA, and knock- down of c‐Myc could inhibit LDHA expression,
15 16
impairing lactate production and glucose consumption. Intriguingly, Zhang et al found that inhibition of
LDHA increased c‐Myc expression, suggesting that LDHA had a negative feedback on c‐Myc expression.
You might also like
- Original PDF Campbell Biology 11th Australian and New Zealand Edition PDFDocument22 pagesOriginal PDF Campbell Biology 11th Australian and New Zealand Edition PDFbert.roesch92897% (39)
- Bacteria Notes SketchyDocument3 pagesBacteria Notes SketchyJayNo ratings yet
- Glomerular DiseasesDocument211 pagesGlomerular DiseasesAdrián Beltrán67% (3)
- HemoglobinopathiesDocument3 pagesHemoglobinopathiesMohamed Abdullahi OsmanNo ratings yet
- MPD Target TerapiDocument6 pagesMPD Target TerapiMilka MimingNo ratings yet
- OncometabolitosDocument7 pagesOncometabolitosAinia KorrsNo ratings yet
- At Least Two Incredible Items Associated With Protease.20121203.213112Document2 pagesAt Least Two Incredible Items Associated With Protease.20121203.213112anon_916246131No ratings yet
- 976 FullDocument7 pages976 FullFirda PotterNo ratings yet
- Blood Reviews: 10.1016/j.blre.2016.11.001Document72 pagesBlood Reviews: 10.1016/j.blre.2016.11.001riybudNo ratings yet
- Abstracts of The 8th International Hematology Expert Meeting Leukemia Research 44 S1 (2016) S1-S12Document1 pageAbstracts of The 8th International Hematology Expert Meeting Leukemia Research 44 S1 (2016) S1-S12aymenNo ratings yet
- Hem 00066Document10 pagesHem 00066widweedNo ratings yet
- New Horizons in MPNs Treatment - A Review of Current and Future Therapeutic Options - 2021Document14 pagesNew Horizons in MPNs Treatment - A Review of Current and Future Therapeutic Options - 2021srowbothamNo ratings yet
- edbook_am.2012.32.85Document8 pagesedbook_am.2012.32.85Munazza RashidNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersFrom EverandThe Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersSabrina TosiNo ratings yet
- Select: Cancer MetabolismDocument2 pagesSelect: Cancer Metabolismcristian_masterNo ratings yet
- Review Article WHO Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues 4th EditionDocument8 pagesReview Article WHO Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues 4th EditionCat NhanNo ratings yet
- Describe The Molecular Basis Underlying Haematological MalignancyDocument3 pagesDescribe The Molecular Basis Underlying Haematological MalignancyAlison HinesNo ratings yet
- Classification of Adult Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument24 pagesClassification of Adult Acute Myeloid LeukemiaSusianna RismandaNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell Enzyme DisordersDocument17 pagesRed Blood Cell Enzyme DisordersGustavo GCNo ratings yet
- Blood-2014 - JAK2 Et CalreticulineDocument16 pagesBlood-2014 - JAK2 Et Calreticulineamara.ablaNo ratings yet
- WNT Signaling, A Novel Pathway For Coronary Artery Disease and Metabolic SyndromeDocument5 pagesWNT Signaling, A Novel Pathway For Coronary Artery Disease and Metabolic SyndromenamachiNo ratings yet
- 10 5772@54652 PDFDocument32 pages10 5772@54652 PDFhollNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument11 pagesAplastic AnemiaJuan Pablo CalderonNo ratings yet
- Ni Hms 862943Document38 pagesNi Hms 862943Rhinaldy DanaraNo ratings yet
- Molecular Pathogenesis of The Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Review Open AccessDocument18 pagesMolecular Pathogenesis of The Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Review Open AccesswidweedNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Cytogenetics in Acute Leukemias: Molecular DiagnosticsDocument7 pagesClinical Significance of Cytogenetics in Acute Leukemias: Molecular DiagnosticsblablalbablablablaNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics Assignment: Medha Banerjee 1660091 IMTH-7 (A)Document11 pagesBioinformatics Assignment: Medha Banerjee 1660091 IMTH-7 (A)Medha BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Ajh 25303Document11 pagesAjh 25303RaffaharianggaraNo ratings yet
- Metformin Attenuates Hyperlipidaemia-Associated Vascular Calcification Through Anti-Ferroptotic EffectsDocument14 pagesMetformin Attenuates Hyperlipidaemia-Associated Vascular Calcification Through Anti-Ferroptotic EffectsArshad AliNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Myeloproliferative NeoplasmsDocument6 pagesOverview of The Myeloproliferative NeoplasmsVitor Hugo G CorreiaNo ratings yet
- Blastic Phase of Chronic Myelogenous LeukemiaDocument11 pagesBlastic Phase of Chronic Myelogenous LeukemiaMax Linares PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Management of Essential Thrombocythemia: Philip A. Beer and Anthony R. GreenDocument8 pagesPathogenesis and Management of Essential Thrombocythemia: Philip A. Beer and Anthony R. GreenHoopmen SilaenNo ratings yet
- Gas5 Regulates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Via Mir 221 3P/P27 Axis Associated AutophagyDocument10 pagesGas5 Regulates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Via Mir 221 3P/P27 Axis Associated Autophagyvtrang0310No ratings yet
- Iub 1216Document7 pagesIub 1216Azmi FarhadiNo ratings yet
- Hypo Kale MiaDocument12 pagesHypo Kale MiadonloteNo ratings yet
- LAL Case Report3Document7 pagesLAL Case Report3hematocosas123No ratings yet
- Ahmad Sh. Silmi MSC Haematology, FIBMSDocument63 pagesAhmad Sh. Silmi MSC Haematology, FIBMSHadi AdamNo ratings yet
- Myeloid LeukemiaDocument36 pagesMyeloid LeukemiaLia pramitaNo ratings yet
- Tumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneDocument61 pagesTumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneKartthik ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Targeting PI3K - Akt - mTOR in AML - Rationale and Clinical EvidenceDocument40 pagesTargeting PI3K - Akt - mTOR in AML - Rationale and Clinical EvidenceHubertus HayuantaNo ratings yet
- Selected Time Saving Tips On Natural Compound Library.20121124.165506Document2 pagesSelected Time Saving Tips On Natural Compound Library.20121124.165506anon_513107104No ratings yet
- Genomics of Myelodysplastic Syndrome:myeloproliferative Neoplasm Overlap SyndromesDocument10 pagesGenomics of Myelodysplastic Syndrome:myeloproliferative Neoplasm Overlap Syndromesnutnut29No ratings yet
- FDocument13 pagesFAbhinav SparshNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms - Páginas 483 A 501Document38 pagesMyeloproliferative Neoplasms - Páginas 483 A 501Gabriel CohenNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis & DyslipidemiasDocument28 pagesAtherosclerosis & DyslipidemiasTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Boş 32Document2 pagesBoş 32tayibmahmad666No ratings yet
- Storti Foundation: Clinical Relevance ofDocument4 pagesStorti Foundation: Clinical Relevance ofNimra AwaisNo ratings yet
- მიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოDocument1 pageმიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოEMD GROUPNo ratings yet
- Utilizado - LiptonDocument9 pagesUtilizado - LiptondeliveryworkNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Metformin Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Drug-Resistant Leukemia CellsDocument12 pagesResearch Article: Metformin Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Drug-Resistant Leukemia Cellsnurfitriani runduNo ratings yet
- Ijms 21 09406 v2Document21 pagesIjms 21 09406 v2Shivaprakash Jagalur MuttNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument189 pagesGeneticstolgaonayNo ratings yet
- AkmxmompwodmDocument13 pagesAkmxmompwodmyour nightmareNo ratings yet
- Aspecte Patogenetice Ale Complicatiilor Cronice in Diabetul ZaharatDocument8 pagesAspecte Patogenetice Ale Complicatiilor Cronice in Diabetul ZaharatRamona PetrariuNo ratings yet
- Myeloid Leukemia: DR Budi Enoch SPPDDocument36 pagesMyeloid Leukemia: DR Budi Enoch SPPDRoby KieranNo ratings yet
- Or 22 1 215 PDFDocument7 pagesOr 22 1 215 PDFLandcel Clarence ArcedoNo ratings yet
- Sindrome MirlodisplasicoDocument2 pagesSindrome MirlodisplasicoCh LaiNo ratings yet
- PLD - Systematic ReviewDocument23 pagesPLD - Systematic ReviewCarleta StanNo ratings yet
- Concise Review: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Stem Cell Niche and Response To Pharmacologic TreatmentDocument10 pagesConcise Review: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Stem Cell Niche and Response To Pharmacologic Treatmentnurul auliaNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid LeukaemiaDocument74 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukaemiakhadija Habib100% (1)
- Biomedicines: Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Is Aggravated by Glycated Lipoproteins Novel Molecular TherapiesDocument28 pagesBiomedicines: Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Is Aggravated by Glycated Lipoproteins Novel Molecular TherapiesJaviera Paz Becerra PedrerosNo ratings yet
- Management of Myelofibrosis: Alessandro M. VannucchiDocument9 pagesManagement of Myelofibrosis: Alessandro M. VannucchifrnksusNo ratings yet
- Feline Herpes VirusDocument10 pagesFeline Herpes Viruskadek ayu ichaNo ratings yet
- En-Metabolism LipidicDocument25 pagesEn-Metabolism LipidicCristina THCSNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer: in Depth: About This WorksheetDocument8 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer: in Depth: About This WorksheetddhhdhdhdNo ratings yet
- SS3 Biology Lesson NoteDocument64 pagesSS3 Biology Lesson Notepalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Role of Chromatin in Regulating Gene Expression and Gene SilencingDocument19 pagesRole of Chromatin in Regulating Gene Expression and Gene SilencingVinod NNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesFunctions of The Nervous SystemMarion Joy GanayoNo ratings yet
- APBio-pp1 9Document66 pagesAPBio-pp1 9Kurt KleinNo ratings yet
- PPSC Biology Subject Specialist & Senior Subject Specialist Past PapersDocument8 pagesPPSC Biology Subject Specialist & Senior Subject Specialist Past PapersMaria Tahreem100% (1)
- Brock Biology of Microorganisms (11th Edn) - Michael T. Madigan, John M. Martinko (Eds)Document5 pagesBrock Biology of Microorganisms (11th Edn) - Michael T. Madigan, John M. Martinko (Eds)adhilcp83No ratings yet
- The Human Microbiome: by Unnati BhaleraoDocument14 pagesThe Human Microbiome: by Unnati BhaleraoUnnati BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- SemaxDocument7 pagesSemaxblazewindNo ratings yet
- Combined Disruption of T Cell Inflammatory RegulatorsDocument10 pagesCombined Disruption of T Cell Inflammatory RegulatorsBîkes NâçarNo ratings yet
- M LepraeDocument10 pagesM Lepraebmc microNo ratings yet
- Coccidiosis Project - Medina ShousherDocument15 pagesCoccidiosis Project - Medina ShousherMEDINA SHOUSHERNo ratings yet
- Meropenem - Drug Information - UpToDate-2Document8 pagesMeropenem - Drug Information - UpToDate-2Vh TRNo ratings yet
- Form P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDDocument2 pagesForm P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDRavi ParmarNo ratings yet
- High-Throughput Approach To Detection of Knockdown Resistance (KDR) Mutation in Mosquitoes Culex QuiDocument10 pagesHigh-Throughput Approach To Detection of Knockdown Resistance (KDR) Mutation in Mosquitoes Culex QuiManas SarkarNo ratings yet
- Alkylating AgentsDocument53 pagesAlkylating AgentsDhanya KcNo ratings yet
- Alkan Health Science Business and Technology CollegeDocument62 pagesAlkan Health Science Business and Technology CollegejibrNo ratings yet
- Chemical Periodontal TherapyDocument23 pagesChemical Periodontal Therapyneji_murniNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument15 pagesBiology ProjectArka Das56% (9)
- Covid Mask Efficacy AnalysisDocument16 pagesCovid Mask Efficacy AnalysisRamyaNo ratings yet
- De Thi HSG Tieng Anh Quang Nam 2023Document21 pagesDe Thi HSG Tieng Anh Quang Nam 2023Đặng Trí TàiNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Studying Bacteria and Fungi PDFDocument32 pagesTechniques For Studying Bacteria and Fungi PDFRoshineeNo ratings yet
- Biosintesis Dan Mekanisme Kerja Hormon Repro Wanita PDFDocument39 pagesBiosintesis Dan Mekanisme Kerja Hormon Repro Wanita PDFsallynorcelinaNo ratings yet
- Prof Nik Marzuki Data PDFDocument3 pagesProf Nik Marzuki Data PDFsue labanNo ratings yet
- English Assigmentt .Document12 pagesEnglish Assigmentt .Fareza AkbarNo ratings yet