Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TUTORIAL2BCpdf 2023 08 01 22 27 49
TUTORIAL2BCpdf 2023 08 01 22 27 49
Uploaded by
mnatsu0432Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MAS3114 Project 4Document9 pagesMAS3114 Project 4Clif PottbergNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Inverse TrigoDocument3 pagesAssignment-3 Inverse Trigoanish kapoorNo ratings yet
- Complex No Class 11Document12 pagesComplex No Class 11shriganesharamaa007No ratings yet
- Sample Paper Cal-1Document3 pagesSample Paper Cal-1HuzaiFa JavedNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems of D&ICDocument2 pagesPractice Problems of D&ICSimra Shahid BawanyNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigo and Functions BansalDocument28 pagesInverse Trigo and Functions BansalYagyank ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 2-Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet 2-Differential EquationsYASHASVI -No ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document4 pagesAssignment No 1Ahmad ShahNo ratings yet
- TM1 Lista13 Derivada Definicao e RegraDocument2 pagesTM1 Lista13 Derivada Definicao e RegraCarlos Capatto da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Complex Assignment IIDocument2 pagesComplex Assignment IIranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Musune Complex AssignDocument10 pagesMusune Complex AssignMakani MusuneNo ratings yet
- IX MATHS extra questions CHAP-1,3 AND 6Document6 pagesIX MATHS extra questions CHAP-1,3 AND 6candyrame08No ratings yet
- Mb104 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry For Applied Sciences Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesMb104 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry For Applied Sciences Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Review QuestionsLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Facultad de Ingenieria Industrial Calculo Iii Práctica 2Document3 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Facultad de Ingenieria Industrial Calculo Iii Práctica 2Liliana QGNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San MarcosDocument3 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San MarcosYonatan BartoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Quadratic EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Quadratic Equationsmlb_blmNo ratings yet
- Assigment 6Document1 pageAssigment 6Fatin HananiNo ratings yet
- EcuacionesDocument1 pageEcuacioneskiararodriguez1701No ratings yet
- GMC Class 12 Sub. Assign. 3 LogDocument3 pagesGMC Class 12 Sub. Assign. 3 Logxyz641137No ratings yet
- Tutorial Manual SESH1070Document19 pagesTutorial Manual SESH1070ajajaNo ratings yet
- Eni Sarifatul P - 192153001 - Tugas Turunan ParsialDocument4 pagesEni Sarifatul P - 192153001 - Tugas Turunan ParsialVinna IsmiNo ratings yet
- Diff Eqn TutDocument2 pagesDiff Eqn TutMohamed Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- Limits and Derivatives - 02 - Class Notes - Limits CompleteDocument67 pagesLimits and Derivatives - 02 - Class Notes - Limits CompleteMohit SuaradkarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - Assignment On Complex NumbersDocument1 pageTutorial 9 - Assignment On Complex NumbersEshaan KuttikadNo ratings yet
- Lista 5Document2 pagesLista 5Gabriel MathiasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - ComplexDocument2 pagesAssignment 3 - Complexranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- K 0 P LVJ Ox VPT ZX Anzheyrn HF7 Es J1 BR 0 X MMSH Rba 3Document33 pagesK 0 P LVJ Ox VPT ZX Anzheyrn HF7 Es J1 BR 0 X MMSH Rba 3Jatin YadavNo ratings yet
- Diff Eqn TutDocument3 pagesDiff Eqn TutMohamed Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- Math Paper 2 SolutionDocument11 pagesMath Paper 2 SolutionAka NainNo ratings yet
- S3 Math - Difference of Two Squares - by GHSDocument2 pagesS3 Math - Difference of Two Squares - by GHSNathan PrayerNo ratings yet
- Final Differential and Integral CalculusDocument3 pagesFinal Differential and Integral CalculusRook LiftNo ratings yet
- Aula 2 Equações Do 1º E 2º Grau.: Licenciatura em QuimicaDocument2 pagesAula 2 Equações Do 1º E 2º Grau.: Licenciatura em QuimicaWellington Victor NevesNo ratings yet
- O Level A Maths 2016 Paper 1Document10 pagesO Level A Maths 2016 Paper 1Lawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- Math AssignmentDocument3 pagesMath Assignmentnihhaal bharathNo ratings yet
- 2011 Cambridge H2Maths Paper1 SolutionsDocument14 pages2011 Cambridge H2Maths Paper1 SolutionsLinda aiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Alternative A AnswersDocument5 pagesMathematics Alternative A Answersmoggadavid480No ratings yet
- Guía Ejerc-Exam 1er Inter-P55Document2 pagesGuía Ejerc-Exam 1er Inter-P55Jaime Andres GarzónNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Additional Mathematics Additional Mathematics Basic SkillsDocument1 pageForm 4: Additional Mathematics Additional Mathematics Basic SkillsSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- MTH 211 CivilDocument1 pageMTH 211 CivilZaid HabibuNo ratings yet
- Calculus Midterm Exam Review JensenDocument6 pagesCalculus Midterm Exam Review JensenJivan KaprielianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet For MA210 Engineering Maths 2021 COVID YearDocument4 pagesTutorial Sheet For MA210 Engineering Maths 2021 COVID YearPrinceNo ratings yet
- Actividad 3Document3 pagesActividad 3LeoNo ratings yet
- Ficha de DerivadasDocument1 pageFicha de DerivadasSilvia Pañeda GonzálezNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths Guess Paper For Annual Exam Session 23-23 by Prof. M Saqib Nauman (1) - 1Document8 pagesXI - Maths Guess Paper For Annual Exam Session 23-23 by Prof. M Saqib Nauman (1) - 1bloodygaming7879No ratings yet
- AQA A Level Further Maths Module 1 Assignment AnswersDocument4 pagesAQA A Level Further Maths Module 1 Assignment Answersjlawler69420No ratings yet
- DPP 1 PolynomialsDocument3 pagesDPP 1 Polynomialsmrmath8889No ratings yet
- FunctionDocument1 pageFunctionpravin.mepg14No ratings yet
- Homework (1) Calculus 1 First Semester 2022 2023Document2 pagesHomework (1) Calculus 1 First Semester 2022 2023Wael DemeriNo ratings yet
- Ms H.W AlgebraDocument44 pagesMs H.W Algebravqwssvd2h9No ratings yet
- CH2 Revision DerivativesDocument10 pagesCH2 Revision DerivativesH A M ONo ratings yet
- Test-IV - Class XIIDocument2 pagesTest-IV - Class XIIHarsh MandhianNo ratings yet
- M-1 (UNIT-3) (MCQS)Document19 pagesM-1 (UNIT-3) (MCQS)Aniket RupnawarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnswersDocument9 pagesChapter 7 AnswersabhijeetNo ratings yet
- Apostila MB 2013 2Document5 pagesApostila MB 2013 2jbg2005No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module Tests AnswersDocument28 pagesUnit 2 Module Tests AnswersashtigosineNo ratings yet
- Alevelh 2 Maths 2012 Paper 2Document11 pagesAlevelh 2 Maths 2012 Paper 2Ethan RiceNo ratings yet
- Material Aula 7Document3 pagesMaterial Aula 7Vitoria MirandaNo ratings yet
- QB BMS-311302 - Sem-I Ut-2 111223Document3 pagesQB BMS-311302 - Sem-I Ut-2 111223pagareaaryan.2007No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations NotesDocument36 pagesQuadratic Equations Notesfazluddinshaik96No ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesCheat SheetAkhiJarodiaNo ratings yet
- LN4 DiagonalizationDocument3 pagesLN4 DiagonalizationNikhilesh PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- LA QuestionbankDocument22 pagesLA QuestionbankK S Sadiya 1SI19CH014No ratings yet
- Calculus and Matrix AlgebraDocument64 pagesCalculus and Matrix AlgebraJEYADURGANo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra For Test and Analysis: Imac - XixDocument74 pagesLinear Algebra For Test and Analysis: Imac - XixVitor PereiraNo ratings yet
- MAN-102, Tutorial Sheet-1: Linear Algebra: (Vector SpringDocument2 pagesMAN-102, Tutorial Sheet-1: Linear Algebra: (Vector SpringSHIVAM MAANNo ratings yet
- Matrix Module 12Document54 pagesMatrix Module 12FITSUM SEID100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1lallamayandNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1Document32 pagesLecture Note 1Workineh Asmare KassieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document29 pagesUnit 4asdfgNo ratings yet
- Rajendra Higher Secondary School, Balangir Academic Session 2020-21Document19 pagesRajendra Higher Secondary School, Balangir Academic Session 2020-21aaaa100% (1)
- Matrix MCQDocument32 pagesMatrix MCQAbu Talha RongonNo ratings yet
- Matrices: 2.1 Operations With Matrices 2.2 Properties of Matrix OperationsDocument29 pagesMatrices: 2.1 Operations With Matrices 2.2 Properties of Matrix OperationscharlynNo ratings yet
- Assignment Linear Algebra 2021Document2 pagesAssignment Linear Algebra 2021Muhammad Ali100% (1)
- Determinants and Matrices - SummaryDocument11 pagesDeterminants and Matrices - Summaryaryanraj24001728No ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document15 pagesLecture 01raja hahaNo ratings yet
- The Kernels of The Hankel and Toeplitz OperatorDocument43 pagesThe Kernels of The Hankel and Toeplitz OperatorJim-Felix LobsienNo ratings yet
- Level-Up Linear Algebra 2Document89 pagesLevel-Up Linear Algebra 2hafemik287No ratings yet
- Cis515 13 sl1 C PDFDocument68 pagesCis515 13 sl1 C PDFMathSpaceNo ratings yet
- MTH641 Quiz#2 - Data 1Document2 pagesMTH641 Quiz#2 - Data 1shining star100% (2)
- Adjoint and Inverse Matrices Linear EquationsDocument9 pagesAdjoint and Inverse Matrices Linear EquationsGeraldine TimpocNo ratings yet
- CH 4 MCQDocument19 pagesCH 4 MCQANIKET ROYNo ratings yet
- Cayley Hamilton Theorem Example PDFDocument7 pagesCayley Hamilton Theorem Example PDFNaman GaurNo ratings yet
- Applied and Computational Linear AlgebraDocument504 pagesApplied and Computational Linear AlgebraSelf-Developer100% (1)
- Integral PDFDocument1 pageIntegral PDFIsaac Farfan CondorNo ratings yet
- Fast Transforms: Banded Matrices With Banded InversesDocument4 pagesFast Transforms: Banded Matrices With Banded InversesHaris KhawarNo ratings yet
- Ma8352 IqDocument17 pagesMa8352 IqBkNo ratings yet
- Sturm-Liouville TheoryDocument12 pagesSturm-Liouville TheorywaveletNo ratings yet
- Matrices That Commute With Their Conjugate and Transpose: Geoffrey GoodsonDocument4 pagesMatrices That Commute With Their Conjugate and Transpose: Geoffrey GoodsonJade Bong NatuilNo ratings yet
TUTORIAL2BCpdf 2023 08 01 22 27 49
TUTORIAL2BCpdf 2023 08 01 22 27 49
Uploaded by
mnatsu0432Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TUTORIAL2BCpdf 2023 08 01 22 27 49
TUTORIAL2BCpdf 2023 08 01 22 27 49
Uploaded by
mnatsu0432Copyright:
Available Formats
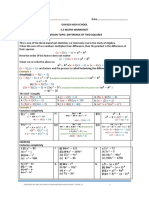
Tutorial-2 Differentiation and its Application
Q-1 Find the derivative of the following function:
i) 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥
ii) 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥
iii) 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥
iv) 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑒 𝑥
Q-2 Differentiate the following functions w.r.t x:
5
i) 𝑦 = 𝑥 −3
1 2
ii) 𝑦 = (𝑥 − 𝑥)
1
iii) 𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥 + 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥 + 𝑥
2 3
iv) 𝑦 = (𝑥 4 − 𝑥 2) (𝑥 2 − 𝑥 3 )
1 1 1
v) 𝑦 = ( √𝑥 − ) ( √𝑥 + ) (𝑥 + 𝑥)
√ 𝑥 √ 𝑥
Q-3 Using the first principles, find the derivatives of the following functions with
respect to x:
i) 𝑓 ( 𝑥 ) = √𝑥
ii) 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = sin2 𝑥
iii) 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑥𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥
Q-4 Differentiate the following w.r.t. x:
i) 𝑦 = 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥 ∙ 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥
ii) 𝑦 = 𝑒 𝑥 5𝑥
iii) 𝑦 = 𝑒 𝑥 3𝑥 𝑥 3
iv) 𝑦 = 𝑥 2 3𝑥 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥
𝑑𝑦
Q-5 Find 𝑑𝑥 for 𝑦 = 2𝑥𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 − 𝑥 3 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥.
Q-6 Differentiate the following functions w.r.t x:
𝑥 2−𝑥+1
i) 𝑦 = 𝑥 2+𝑥+1
𝑎+𝑏𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥
ii) 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥+𝑏
𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥
iii) 𝑦=
𝑥
Q-7 Differentiate the following functions w.r.t x:
2 2𝑥−1
i) (𝑥 + 𝑥+3) (𝑥 2+3𝑥+2)
1 3𝑥 2
ii) (1 + 𝑥) (𝑥 2+6𝑥+5)
Q-8 Differentiate the following functions w.r.t x:
i) 𝑦 = √𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥
ii) 𝑦 = √𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐
iii) 𝑦 = log sin 𝑥 2
𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥
iv) 𝑦 = log(1+𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 )
Q-9 𝑑𝑦
Obtain 𝑑𝑥 for the following:
𝑎+𝑥
i) 𝑦 = log √𝑎−𝑥
ii) 𝑦 = log(𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥 ) + 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥
𝑥
iii) 𝑦 = tan−1 (𝑎)
sin(𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥)
iv) 𝑦= 𝑥
𝑑𝑦
Q-10 Find 𝑑𝑥 of the following functions:
i) 𝑥 = 𝑎𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃, 𝑦 = 𝑏𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
1+𝑡 2
ii) 𝑥 = 𝑎 ∙ 1−𝑡 2
iii) 𝑥 = 𝑎𝑠𝑒𝑐𝜃𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑦 = 𝑏𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃
iv) 𝑥 = 𝑎(𝜃 + 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃)𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑦 = 𝑎(1 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃)
Q-11 𝑑𝑦
Find 𝑑𝑥 from 𝑥 = 𝑒 2𝑡 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡, 𝑦 = 𝑒 2𝑡 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡.
Q-12 Differentiate the following functions w.r.t x
i) 𝑥 2 − 𝑦 2 = 𝑥 2𝑦 2
ii) 𝑥 3 + 𝑦 3 = 3𝑎𝑥𝑦
iii) 𝑦 = sin(𝑥 + 𝑦)
𝑑𝑦 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥
Q-13 If 𝑥 𝑦 = 𝑒 𝑥−𝑦 , then prove that = (1+𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑥)2 .
𝑑𝑥
Q-14 𝑑𝑦
If 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑦 = 𝑥𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑎 + 𝑦) then prove that 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑎 𝑑𝑥 = sin2 (𝑎 + 𝑦).
Q-15 Differentiate the following functions w.r.t x
2
i) 𝑦 = 𝑥 sin 𝑥
𝑒 𝑥 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑥
ii) 𝑦= 𝑥+1
√2𝑥−3(4𝑥−3)5
iii) 𝑦= 3
√3𝑥+5
2
Q-16 Differentiate −1 √1+𝑥 −1
tan [ 𝑥 ] with respect to tan−1 𝑥.
Q-17 𝑑2 𝑦
Find for each of the following:
𝑑𝑥 2
1
i) 𝑦 = 4 𝑥 4 − 4𝑥 2 + 25
ii) 𝑦 = 𝑙𝑜𝑔3𝑥 + tan−1 𝑥
Q-18 𝑑2 𝑦
If 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑒 𝑘𝑥 + 𝑏𝑒 (−𝑘𝑥) , Prove that 𝑑𝑥 2 = 𝑘 2 𝑦.
Q-19 𝑑2 𝑦
If 𝑦 = 𝐴𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑝𝑡 + 𝐵𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑡,prove that 𝑑𝑥 2 + 𝑝2 𝑦 = 0.
Q-20 If 𝑦 = sin−1 𝑥, 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡(1 − 𝑥 2 )𝑦2 − 𝑥𝑦1 = 0.
You might also like
- MAS3114 Project 4Document9 pagesMAS3114 Project 4Clif PottbergNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Inverse TrigoDocument3 pagesAssignment-3 Inverse Trigoanish kapoorNo ratings yet
- Complex No Class 11Document12 pagesComplex No Class 11shriganesharamaa007No ratings yet
- Sample Paper Cal-1Document3 pagesSample Paper Cal-1HuzaiFa JavedNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems of D&ICDocument2 pagesPractice Problems of D&ICSimra Shahid BawanyNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigo and Functions BansalDocument28 pagesInverse Trigo and Functions BansalYagyank ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 2-Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet 2-Differential EquationsYASHASVI -No ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document4 pagesAssignment No 1Ahmad ShahNo ratings yet
- TM1 Lista13 Derivada Definicao e RegraDocument2 pagesTM1 Lista13 Derivada Definicao e RegraCarlos Capatto da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Complex Assignment IIDocument2 pagesComplex Assignment IIranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Musune Complex AssignDocument10 pagesMusune Complex AssignMakani MusuneNo ratings yet
- IX MATHS extra questions CHAP-1,3 AND 6Document6 pagesIX MATHS extra questions CHAP-1,3 AND 6candyrame08No ratings yet
- Mb104 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry For Applied Sciences Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesMb104 - Calculus and Analytical Geometry For Applied Sciences Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Review QuestionsLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Facultad de Ingenieria Industrial Calculo Iii Práctica 2Document3 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Facultad de Ingenieria Industrial Calculo Iii Práctica 2Liliana QGNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San MarcosDocument3 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San MarcosYonatan BartoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Quadratic EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Quadratic Equationsmlb_blmNo ratings yet
- Assigment 6Document1 pageAssigment 6Fatin HananiNo ratings yet
- EcuacionesDocument1 pageEcuacioneskiararodriguez1701No ratings yet
- GMC Class 12 Sub. Assign. 3 LogDocument3 pagesGMC Class 12 Sub. Assign. 3 Logxyz641137No ratings yet
- Tutorial Manual SESH1070Document19 pagesTutorial Manual SESH1070ajajaNo ratings yet
- Eni Sarifatul P - 192153001 - Tugas Turunan ParsialDocument4 pagesEni Sarifatul P - 192153001 - Tugas Turunan ParsialVinna IsmiNo ratings yet
- Diff Eqn TutDocument2 pagesDiff Eqn TutMohamed Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- Limits and Derivatives - 02 - Class Notes - Limits CompleteDocument67 pagesLimits and Derivatives - 02 - Class Notes - Limits CompleteMohit SuaradkarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - Assignment On Complex NumbersDocument1 pageTutorial 9 - Assignment On Complex NumbersEshaan KuttikadNo ratings yet
- Lista 5Document2 pagesLista 5Gabriel MathiasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - ComplexDocument2 pagesAssignment 3 - Complexranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- K 0 P LVJ Ox VPT ZX Anzheyrn HF7 Es J1 BR 0 X MMSH Rba 3Document33 pagesK 0 P LVJ Ox VPT ZX Anzheyrn HF7 Es J1 BR 0 X MMSH Rba 3Jatin YadavNo ratings yet
- Diff Eqn TutDocument3 pagesDiff Eqn TutMohamed Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- Math Paper 2 SolutionDocument11 pagesMath Paper 2 SolutionAka NainNo ratings yet
- S3 Math - Difference of Two Squares - by GHSDocument2 pagesS3 Math - Difference of Two Squares - by GHSNathan PrayerNo ratings yet
- Final Differential and Integral CalculusDocument3 pagesFinal Differential and Integral CalculusRook LiftNo ratings yet
- Aula 2 Equações Do 1º E 2º Grau.: Licenciatura em QuimicaDocument2 pagesAula 2 Equações Do 1º E 2º Grau.: Licenciatura em QuimicaWellington Victor NevesNo ratings yet
- O Level A Maths 2016 Paper 1Document10 pagesO Level A Maths 2016 Paper 1Lawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- Math AssignmentDocument3 pagesMath Assignmentnihhaal bharathNo ratings yet
- 2011 Cambridge H2Maths Paper1 SolutionsDocument14 pages2011 Cambridge H2Maths Paper1 SolutionsLinda aiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Alternative A AnswersDocument5 pagesMathematics Alternative A Answersmoggadavid480No ratings yet
- Guía Ejerc-Exam 1er Inter-P55Document2 pagesGuía Ejerc-Exam 1er Inter-P55Jaime Andres GarzónNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Additional Mathematics Additional Mathematics Basic SkillsDocument1 pageForm 4: Additional Mathematics Additional Mathematics Basic SkillsSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- MTH 211 CivilDocument1 pageMTH 211 CivilZaid HabibuNo ratings yet
- Calculus Midterm Exam Review JensenDocument6 pagesCalculus Midterm Exam Review JensenJivan KaprielianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet For MA210 Engineering Maths 2021 COVID YearDocument4 pagesTutorial Sheet For MA210 Engineering Maths 2021 COVID YearPrinceNo ratings yet
- Actividad 3Document3 pagesActividad 3LeoNo ratings yet
- Ficha de DerivadasDocument1 pageFicha de DerivadasSilvia Pañeda GonzálezNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths Guess Paper For Annual Exam Session 23-23 by Prof. M Saqib Nauman (1) - 1Document8 pagesXI - Maths Guess Paper For Annual Exam Session 23-23 by Prof. M Saqib Nauman (1) - 1bloodygaming7879No ratings yet
- AQA A Level Further Maths Module 1 Assignment AnswersDocument4 pagesAQA A Level Further Maths Module 1 Assignment Answersjlawler69420No ratings yet
- DPP 1 PolynomialsDocument3 pagesDPP 1 Polynomialsmrmath8889No ratings yet
- FunctionDocument1 pageFunctionpravin.mepg14No ratings yet
- Homework (1) Calculus 1 First Semester 2022 2023Document2 pagesHomework (1) Calculus 1 First Semester 2022 2023Wael DemeriNo ratings yet
- Ms H.W AlgebraDocument44 pagesMs H.W Algebravqwssvd2h9No ratings yet
- CH2 Revision DerivativesDocument10 pagesCH2 Revision DerivativesH A M ONo ratings yet
- Test-IV - Class XIIDocument2 pagesTest-IV - Class XIIHarsh MandhianNo ratings yet
- M-1 (UNIT-3) (MCQS)Document19 pagesM-1 (UNIT-3) (MCQS)Aniket RupnawarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnswersDocument9 pagesChapter 7 AnswersabhijeetNo ratings yet
- Apostila MB 2013 2Document5 pagesApostila MB 2013 2jbg2005No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module Tests AnswersDocument28 pagesUnit 2 Module Tests AnswersashtigosineNo ratings yet
- Alevelh 2 Maths 2012 Paper 2Document11 pagesAlevelh 2 Maths 2012 Paper 2Ethan RiceNo ratings yet
- Material Aula 7Document3 pagesMaterial Aula 7Vitoria MirandaNo ratings yet
- QB BMS-311302 - Sem-I Ut-2 111223Document3 pagesQB BMS-311302 - Sem-I Ut-2 111223pagareaaryan.2007No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations NotesDocument36 pagesQuadratic Equations Notesfazluddinshaik96No ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesCheat SheetAkhiJarodiaNo ratings yet
- LN4 DiagonalizationDocument3 pagesLN4 DiagonalizationNikhilesh PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- LA QuestionbankDocument22 pagesLA QuestionbankK S Sadiya 1SI19CH014No ratings yet
- Calculus and Matrix AlgebraDocument64 pagesCalculus and Matrix AlgebraJEYADURGANo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra For Test and Analysis: Imac - XixDocument74 pagesLinear Algebra For Test and Analysis: Imac - XixVitor PereiraNo ratings yet
- MAN-102, Tutorial Sheet-1: Linear Algebra: (Vector SpringDocument2 pagesMAN-102, Tutorial Sheet-1: Linear Algebra: (Vector SpringSHIVAM MAANNo ratings yet
- Matrix Module 12Document54 pagesMatrix Module 12FITSUM SEID100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1lallamayandNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1Document32 pagesLecture Note 1Workineh Asmare KassieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document29 pagesUnit 4asdfgNo ratings yet
- Rajendra Higher Secondary School, Balangir Academic Session 2020-21Document19 pagesRajendra Higher Secondary School, Balangir Academic Session 2020-21aaaa100% (1)
- Matrix MCQDocument32 pagesMatrix MCQAbu Talha RongonNo ratings yet
- Matrices: 2.1 Operations With Matrices 2.2 Properties of Matrix OperationsDocument29 pagesMatrices: 2.1 Operations With Matrices 2.2 Properties of Matrix OperationscharlynNo ratings yet
- Assignment Linear Algebra 2021Document2 pagesAssignment Linear Algebra 2021Muhammad Ali100% (1)
- Determinants and Matrices - SummaryDocument11 pagesDeterminants and Matrices - Summaryaryanraj24001728No ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document15 pagesLecture 01raja hahaNo ratings yet
- The Kernels of The Hankel and Toeplitz OperatorDocument43 pagesThe Kernels of The Hankel and Toeplitz OperatorJim-Felix LobsienNo ratings yet
- Level-Up Linear Algebra 2Document89 pagesLevel-Up Linear Algebra 2hafemik287No ratings yet
- Cis515 13 sl1 C PDFDocument68 pagesCis515 13 sl1 C PDFMathSpaceNo ratings yet
- MTH641 Quiz#2 - Data 1Document2 pagesMTH641 Quiz#2 - Data 1shining star100% (2)
- Adjoint and Inverse Matrices Linear EquationsDocument9 pagesAdjoint and Inverse Matrices Linear EquationsGeraldine TimpocNo ratings yet
- CH 4 MCQDocument19 pagesCH 4 MCQANIKET ROYNo ratings yet
- Cayley Hamilton Theorem Example PDFDocument7 pagesCayley Hamilton Theorem Example PDFNaman GaurNo ratings yet
- Applied and Computational Linear AlgebraDocument504 pagesApplied and Computational Linear AlgebraSelf-Developer100% (1)
- Integral PDFDocument1 pageIntegral PDFIsaac Farfan CondorNo ratings yet
- Fast Transforms: Banded Matrices With Banded InversesDocument4 pagesFast Transforms: Banded Matrices With Banded InversesHaris KhawarNo ratings yet
- Ma8352 IqDocument17 pagesMa8352 IqBkNo ratings yet
- Sturm-Liouville TheoryDocument12 pagesSturm-Liouville TheorywaveletNo ratings yet
- Matrices That Commute With Their Conjugate and Transpose: Geoffrey GoodsonDocument4 pagesMatrices That Commute With Their Conjugate and Transpose: Geoffrey GoodsonJade Bong NatuilNo ratings yet