Professional Documents
Culture Documents
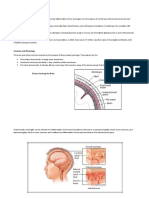
Brain Abscess
Brain Abscess
Uploaded by
Andrew JavierOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain Abscess
Brain Abscess
Uploaded by
Andrew JavierCopyright:
Available Formats
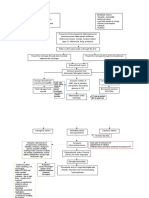
Pathogenesis and pathophysiology Laboratory Management
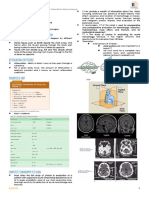
Bacterial invasion of brain parenchyma NEUROIMAGING STUDIES OPTIMAL THERAPY
Preexisting or concomitant areas of ischemia, Cerebritis High-dose parenteral antibiotics +
necrosis, or hypoxemia in brain tissue T1W MRI: area of low signal neurosurgical drainage
Intact brain parenchyma - relatively resistant intensity w/ irregular post-Gd
to infection enhancement MEDICAL THERAPY
Evolution of abscess influenced by:
Nature of infecting organism
T2W MRI: area of increased signal Indications:
intensity o Neurosurgically inaccessible
Immunocompetence of host
Stages: CT scan: often not visualized; area abscesses
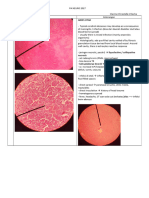
1. Early cerebritis stage (days 1-3) of hypodensity o Small (<2-3 cm) or non-
o Perivascular infiltration of encapsulated abscesses
Mature brain abscess (cerebritis)
inflammatory cells
o Condition is too tenuous to allow
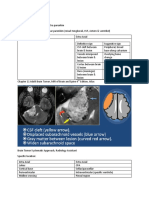
o Surrounds a central core of Contrast-enhanced CT scan: performance of a neurosurgical
coagulative necrosis o Center: (focal) procedure
o Marked edema surrounds hypodense
the lesion Duration:
o Ring: enhanced o Minimum of 6-8 wk (parenteral
2. Late cerebritis stage (days 4-9)
o Pus formation enlarges o Edema: hypodense antibiotic therapy)
necrotic center bordered by Contrast-enhanced T1W MRI: Condition:
inflammatory infiltrate of o Center: hypodense o Community-acquired brain
macrophages and o Ring: enhanced abscess, immunocompetent host
fibroblasts o Edema: hypodense 3rd or 4th-gen
o Thin capsule of fibroblasts Contrast-enhanced T2W MRI: cephalosporin (e.g.,
and reticular fibers develop o Center: hyperintense cefotaxime,
o Edema becomes more o Ring: hypodense ceftriaxone,
distinct o Edema: hyperintense cefepime; and
3. Early capsule formation (days 10-13) Metronidazole
o Capsule is better developed MICROBIOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS o Penetrating head trauma or
on the cortical (than on the Gram’s stain and culture recent neurosurgical procedure
ventricular) side of the Abscess material obtained via CT- Ceftazidime
lesion guided stereotactic needle (Pseudomonas spp.);
o Appearance of a ring- aspiration and
enhancing capsule on Vancomycin
neuroimaging studies INFLAMMATORY MARKERS (Staphylococci); or
4. Late capsule formation (day 14 and Peripheral leukocytosis (50%) Meropenem +
beyond) Elevated ESR (60%) vancomycin
o Well-formed necrotic center Elevated CRP (80%)
o Dense collagenous capsule ASPIRATION AND DRAINAGE
o Edema has regressed BLOOD CULTURES Under stereotactic guidance
o Marked gliosis w/ large no. Positive in 10% of cases overall
of reactive astrocytes Positive in >85% (Listeria) COMPLETE EXCISION
outside the capsule
Seizures as a DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Craniotomy or craniectomy
sequela Conditions that cause HA, FVR, o For multiloculated abscesses
focal neurologic signs, and seizure o If stereotactic aspiration is
activity: unsuccessful
o Brain abscess
o Subdural empyema PROPHYLAXIS
o Bacterial meningitis Anticonvulsant therapy
o Viral o d/t high risk (35%) of focal or
meningoencephalitis generalized seizures
o Superior sagittal sinus o Cont'd at least 3 mo after
thrombosis resolution
o Acute disseminated o Withdrawal based on EEG results
encephalomyelitis
CORTICOSTEROIDS
Not given routinely
IV dexamethasone 10 mg q6h
o For Px w/ substantial periabscess
edema, mass effect, inc. ICP
o Tapered as rapidly as possible
To allow for natural
encapsulation of
abscess
SERIAL MRI OR CT SCANS
Monthly or bimonthly
Weekly if Px receiving antibiotic therapy
alone
PROGNOSIS
Mortality rate <15%
Significant sequelae (>20% of survivors):
o Seizures
o Persisting weakness
o Aphasia
o Mental impairment
You might also like
- Path CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Document37 pagesPath CNS Robbins Outline: Owl Club Review Sheets 1Coy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Arthroscopy 2nd Edition PDFDocument378 pagesShoulder Arthroscopy 2nd Edition PDFLuís Alves100% (2)
- CVS MonitoringDocument33 pagesCVS MonitoringMicheal NorrisNo ratings yet
- Pathology BrainDocument4 pagesPathology BrainAshuNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Patho6 - Cns Infection 2015bDocument8 pages7.2 Patho6 - Cns Infection 2015bMiguel Cuevas Dolot100% (1)
- Chapter 6 CNS InfectionsDocument5 pagesChapter 6 CNS Infectionssybico.xray.abadclinicNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Raised Intracranial PressureDocument9 pagesLec 3 Raised Intracranial PressureEmily MurrayNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumor DDDocument9 pagesBrain Tumor DDSolo UpdateNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumor DDDocument9 pagesBrain Tumor DDbebbyNo ratings yet
- Tables NurologyDocument5 pagesTables NurologyRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument3 pagesMeningitisDiana Fadhilah SariNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Ii: Summary: Nationality (Will Tell You Incidence, For Example, AsiansDocument29 pagesNeuroscience Ii: Summary: Nationality (Will Tell You Incidence, For Example, AsiansAngelaTrinidad100% (2)
- Abses Cerebri (Ham)Document23 pagesAbses Cerebri (Ham)Yanti SoelistyawanNo ratings yet
- An Update On Cutaneous Tumours With Neural DifferentiationDocument24 pagesAn Update On Cutaneous Tumours With Neural DifferentiationAdriana Gabriela Ugarte MacíasNo ratings yet
- I. Reactive Lesions: Stacey MendozaDocument11 pagesI. Reactive Lesions: Stacey MendozaRianNo ratings yet
- Increased ICP: A) HeadacheDocument5 pagesIncreased ICP: A) Headachemohamed nagyNo ratings yet
- Insignis Surgery NeurosurgeryDocument15 pagesInsignis Surgery NeurosurgeryAla'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Brain ImagingDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Introduction To Brain Imagingsybico.xray.abadclinicNo ratings yet
- PATHOPISIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPISIOLOGYjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Bacterial and Parasitic Cns InfxnsDocument35 pagesBacterial and Parasitic Cns InfxnsLajja Parikh PatelNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes in Pedia Neuro2Document4 pagesAdditional Notes in Pedia Neuro2Geraldine Marie SalvoNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Pharmacotherapy: Lesson 5 Central Nervous System InfectionDocument63 pagesInfectious Diseases Pharmacotherapy: Lesson 5 Central Nervous System Infectionbest batiNo ratings yet
- Micky Infectious NotesDocument10 pagesMicky Infectious NotesNoelani-Mei AscioNo ratings yet
- Enumerate The Aetiological Agents of Meningeal Involvement in ChildrenDocument21 pagesEnumerate The Aetiological Agents of Meningeal Involvement in ChildrenAbhirup BoseNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Brain Function (Neurological) 3Document12 pagesDisorders of Brain Function (Neurological) 3Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine 2 - Nasir VersionDocument55 pagesInternal Medicine 2 - Nasir VersionAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Macroscopic Diagnostic For Pathoanathomy and Cytopathology ExamDocument21 pagesMacroscopic Diagnostic For Pathoanathomy and Cytopathology Examkapil pancholiNo ratings yet
- Radiological Semiotics of Diseases of Central Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesRadiological Semiotics of Diseases of Central Nervous Systemnikhil gendreNo ratings yet
- Ophtha ReviewerDocument3 pagesOphtha ReviewerToni Sy EncinaresNo ratings yet
- How COVID-19 Affects The Brain: Neuroscience and PsychiatryDocument2 pagesHow COVID-19 Affects The Brain: Neuroscience and PsychiatryEnderson CorreaNo ratings yet
- Supratentorial: Common Neuro Surgeries Common Drugs Administered PreopDocument4 pagesSupratentorial: Common Neuro Surgeries Common Drugs Administered PreopMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- CSF and CNS InfectionsDocument9 pagesCSF and CNS InfectionsJorelyn Frias100% (1)
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Microorganism Invades CNS (Bloodstream) : Lymphocytes & MacrophageDocument1 pageMicroorganism Invades CNS (Bloodstream) : Lymphocytes & MacrophageGiann PersonaNo ratings yet
- PyomeningitisDocument54 pagesPyomeningitisRiya BagdiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis I.: IV. Basic Medical SciencesDocument11 pagesMultiple Sclerosis I.: IV. Basic Medical SciencesMarielle RamesoNo ratings yet
- 5-Bronchogenic Carcinoma & ParamalignantDocument20 pages5-Bronchogenic Carcinoma & ParamalignantMayar JaradNo ratings yet
- ISMT12 - Day 457 - Vito - Cerebellar DisorderDocument17 pagesISMT12 - Day 457 - Vito - Cerebellar DisorderVito MasagusNo ratings yet
- 8-Complications of Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument2 pages8-Complications of Suppurative Otitis MediaAnmarNo ratings yet
- The Management of Intracranial AbscessesDocument3 pagesThe Management of Intracranial AbscessesDio AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumor - IntraExtra AxialDocument6 pagesBrain Tumor - IntraExtra AxialregarskidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 CSFDocument4 pagesChapter 9 CSFJhunrick Corpuz TumpalanNo ratings yet
- Description of The Disease MeningitisDocument3 pagesDescription of The Disease MeningitisLance SilvaNo ratings yet
- Requirement in PathophysiologyDocument38 pagesRequirement in PathophysiologyckathreenahNo ratings yet
- Pathology-CNS Fast TrackDocument18 pagesPathology-CNS Fast Tracklmc xiiNo ratings yet
- L3 Infectious MED NL2Document199 pagesL3 Infectious MED NL26210310123No ratings yet
- Meningitis: Neonates (65)Document5 pagesMeningitis: Neonates (65)Eugina Naiborhu08No ratings yet
- Adenoma Pleiomorfik Tampak Massa Di Superior, Berkapsul, Tidak Tampak Kalsifikasi Dan Destruksi TulangDocument5 pagesAdenoma Pleiomorfik Tampak Massa Di Superior, Berkapsul, Tidak Tampak Kalsifikasi Dan Destruksi TulangristaniatauhidNo ratings yet
- Nervous System, Jan 2011Document53 pagesNervous System, Jan 2011Shamalah KandayahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 CNS (2nd Edition)Document21 pagesChapter 24 CNS (2nd Edition)vs7ksgrj8pNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman TumorDocument31 pagesRangkuman TumorraishapiNo ratings yet
- BKO BOOK CHAPTER CH 33 Approach To A Patient With HemiparesisDocument8 pagesBKO BOOK CHAPTER CH 33 Approach To A Patient With HemiparesisBal Krishna OjhaNo ratings yet
- Intracranial SepsisDocument60 pagesIntracranial SepsisHarun MohamedNo ratings yet
- CNS Micro ImpulseDocument44 pagesCNS Micro Impulsedineshvd75No ratings yet
- Pa NeuroDocument10 pagesPa Neurowilliam atmadjiNo ratings yet
- Pituitaria SEMINARSDocument12 pagesPituitaria SEMINARSNathaly CantorNo ratings yet
- Intradural Extramedullary TumorsDocument10 pagesIntradural Extramedullary TumorsFaizyab Ahmed100% (1)
- Case Chest Pain and DyspneaDocument1 pageCase Chest Pain and DyspneaVineeNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument2 pagesMeningitisedrian02No ratings yet
- Seizure: Café Au Lait SpotsDocument2 pagesSeizure: Café Au Lait SpotsAnas AbuseifNo ratings yet
- Pathology Revision Practicals: Presented by Roll No. 061-090Document60 pagesPathology Revision Practicals: Presented by Roll No. 061-090PeaceNo ratings yet
- BHPS FinalPaper JavierDocument3 pagesBHPS FinalPaper JavierAndrew JavierNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ClassificationDocument2 pagesBacterial ClassificationAndrew JavierNo ratings yet
- ASOCENADocument5 pagesASOCENAAndrew JavierNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Classification of Animals PDFDocument5 pagesActivity 3 Classification of Animals PDFAndrew JavierNo ratings yet
- PURCOM E - Inquiry LetterDocument1 pagePURCOM E - Inquiry LetterAndrew JavierNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 Requires Respondus LockDown Browser Webcam PDFDocument40 pagesQUIZ 1 Requires Respondus LockDown Browser Webcam PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Case 4 - 2023Document11 pagesCase 4 - 2023Katherine VadilloNo ratings yet
- RevealDocument15 pagesRevealdrsajusvNo ratings yet
- The Medical City ClarkDocument16 pagesThe Medical City ClarkPaopao Bacaling0% (1)
- CCT in Anaesthetics - Assessment Blueprint Aug 2010 V1.3Document14 pagesCCT in Anaesthetics - Assessment Blueprint Aug 2010 V1.3sherif11110% (1)
- Curiculum Vitae Iyere Faith-1Document4 pagesCuriculum Vitae Iyere Faith-1Halleluyah HalleluyahNo ratings yet
- Hydrocelectomy Post-Operative InstructionsDocument1 pageHydrocelectomy Post-Operative InstructionsShimbi Lugamba LugomaNo ratings yet
- The Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelyDocument11 pagesThe Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelypriyankaNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan CT ScanDocument2 pagesPengenalan CT ScanAhmad HaririNo ratings yet
- Drains in SurgeryDocument66 pagesDrains in SurgeryBalaji MallaNo ratings yet
- Sono V10: Diagnos C Needs!Document12 pagesSono V10: Diagnos C Needs!Daddy MishraNo ratings yet
- AOI APState August10Document141 pagesAOI APState August10Anoop BabuNo ratings yet
- Campbells Operative Orthopaedics 4 Volume Set 14Th Edition Frederick M Azar Full ChapterDocument67 pagesCampbells Operative Orthopaedics 4 Volume Set 14Th Edition Frederick M Azar Full Chapteredith.beltran702100% (4)
- Clinical Presentation of Abdominal TuberculosisDocument4 pagesClinical Presentation of Abdominal TuberculosisRizky AmaliahNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1Void LessNo ratings yet
- Produk e Katalog 2023Document12 pagesProduk e Katalog 2023Bedo Sari AntonNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS)Document27 pagesAdvanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS)Sara Ali100% (4)
- CataractDocument52 pagesCataracttammycristobalmd100% (4)
- Kanker Payudara PDFDocument20 pagesKanker Payudara PDFbabehNo ratings yet
- Labia Majora Augmentation: A Systematic Review of The LiteratureDocument8 pagesLabia Majora Augmentation: A Systematic Review of The LiteratureAleja MoraNo ratings yet
- Disease of Extenal Nose and VestibuleDocument5 pagesDisease of Extenal Nose and VestibuleNaseem SaeedNo ratings yet
- Otvori Pediatric Surgical Diseases A Radiologic Surgical Case Study ApproachDocument551 pagesOtvori Pediatric Surgical Diseases A Radiologic Surgical Case Study ApproachslatkaNo ratings yet
- Views Catheters and Wires PDFDocument47 pagesViews Catheters and Wires PDFRedhwan Abdullah qaid AlshubiNo ratings yet
- CGHS RateListDocument45 pagesCGHS RateListSandip SharmaNo ratings yet
- UroLap 2.0 - BrochureDocument3 pagesUroLap 2.0 - Brochurehindi channelNo ratings yet
- LMS: View Results: No Question Type Weightage Questions Associate Answers Score StatusDocument5 pagesLMS: View Results: No Question Type Weightage Questions Associate Answers Score StatusRaja SolaimalaiNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Study Comparing The Static Navigation Technique and Free Hand Bur Useage To Remove PostDocument14 pagesA Laboratory Study Comparing The Static Navigation Technique and Free Hand Bur Useage To Remove PostMegha GhoshNo ratings yet
- Development of Heart & Vasculature - Part 1 - F2023 - DR D CostaDocument25 pagesDevelopment of Heart & Vasculature - Part 1 - F2023 - DR D CostaJose PerezNo ratings yet