Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Creative Nonfiction Reviewer
Creative Nonfiction Reviewer
Uploaded by
azaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo ChurchDocument28 pagesEthiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Churchmtebeje0% (1)
- Bhattacharya - 2020 - More Studies On The Cārvāka - LokāyataDocument292 pagesBhattacharya - 2020 - More Studies On The Cārvāka - LokāyataminoozolaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century 3DAYS ACTDocument9 pages21st Century 3DAYS ACTRowelyn BakekeNo ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesCNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterKYZEIR JOVER JAVIERNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Compare and Contrast Various 21ST Century Genres From Earlier Genres-PeriodDocument20 pagesLesson 3 - Compare and Contrast Various 21ST Century Genres From Earlier Genres-PeriodAndrea Ibañez80% (5)
- English Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THDocument6 pagesEnglish Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THMelissa PasoquinNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument15 pagesNotesHazel Loraenne ConarcoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Module 2Document21 pages21st Century Literature Module 2Raymart DiaperaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument2 pages21st Century LiteratureMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Local Media7165870540832856673Document4 pagesLocal Media7165870540832856673HammadiNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature q1 Module 2Document27 pages21st Century Literature q1 Module 2Raymart DiaperaNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices: Literary Elements & Literary TechniquesDocument10 pagesLiterary Devices: Literary Elements & Literary TechniquesAnie Grace Garcia100% (1)
- Phil Lit - Introduction IIDocument3 pagesPhil Lit - Introduction IIJessica AbuqueNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument30 pages21st Century LiteratureJovelle TugadeNo ratings yet
- ATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Document8 pagesATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Andrea M. IbañezNo ratings yet
- Year 10 English Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet Knowledge Book For Assessments 2017-2018Document25 pagesYear 10 English Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet Knowledge Book For Assessments 2017-2018agamNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Lit Midterms ReviewerDocument7 pages21st Century Lit Midterms Reviewerronanmorales93No ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer W1 2Document4 pagesCNF Reviewer W1 2ZairaNo ratings yet
- LITR 102 Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesLITR 102 Midterm ReviewerMae MartinezNo ratings yet
- Literary Report Art AppreciationDocument45 pagesLiterary Report Art AppreciationJemma Rose TegioNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaDocument8 pages21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaJenrich MarceloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LiteratureDocument3 pagesIntroduction To LiteraturealaamohbenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Authors Craft Teaching Plan 2019-20Document2 pagesUnit 1 Authors Craft Teaching Plan 2019-20api-479558866No ratings yet
- Reviewer-Literature LESSON 1Document4 pagesReviewer-Literature LESSON 1Charisse Deirdre TulioNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Summary of DiscussionsDocument6 pagesCreative Writing Summary of DiscussionsKEN ZEUS GOLLOYNo ratings yet
- Lit ReviewerDocument6 pagesLit ReviewerSheryl NunialNo ratings yet
- 9 Grade Literature - Novels, Short Stories, Non-Fiction, Poetry, DramaDocument15 pages9 Grade Literature - Novels, Short Stories, Non-Fiction, Poetry, DramaAizel Nova Fermilan ArañezNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices and Literary TermsDocument1 pageLiterary Devices and Literary TermsAna-Alicia Burrows-BlairNo ratings yet
- Literary Elementsworksheet 1Document1 pageLiterary Elementsworksheet 1Amr SaadNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature GenresDocument20 pagesPhilippine Literature GenresRyce SumayloNo ratings yet
- CNF Module 1Document6 pagesCNF Module 1Robert AquinoNo ratings yet
- What Is Poetry?Document41 pagesWhat Is Poetry?Jeah Asilum DalogdogNo ratings yet
- ATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Document8 pagesATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Andrea M. IbañezNo ratings yet
- English Reviewer 9.1Document6 pagesEnglish Reviewer 9.1Lexine Cyra PinauinNo ratings yet
- World LitDocument30 pagesWorld LitPearl AlanoNo ratings yet
- Genres of Literature Fiction: "It", "They", Etc. It Is LikeDocument5 pagesGenres of Literature Fiction: "It", "They", Etc. It Is LikeAleli Isabel DemecilloNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms Worksheet: Definitions: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesLiterary Terms Worksheet: Definitions: Name: - DateRaja SaadNo ratings yet
- Theme, Character & Language StyleDocument15 pagesTheme, Character & Language StyleNanacyNo ratings yet
- 21 Lit Nat ReviewerDocument5 pages21 Lit Nat ReviewerApricus BenciNo ratings yet
- 21STDocument82 pages21STitzoceanmarkNo ratings yet
- Objecti Ves-Facts Subjecti Ve - Opinion S: Sensory DetailsDocument2 pagesObjecti Ves-Facts Subjecti Ve - Opinion S: Sensory DetailsDebil DimunyuNo ratings yet
- Literary CriticismDocument33 pagesLiterary CriticismJoanne RanarioNo ratings yet
- схема анализаDocument2 pagesсхема анализаValeriia ChoiNo ratings yet
- 1 Whats LitDocument10 pages1 Whats LitHisyam SurachmanNo ratings yet
- Asean ReviewerDocument7 pagesAsean ReviewerMarynissa CatibogNo ratings yet
- 21clpw ReviewerDocument8 pages21clpw ReviewerpatNo ratings yet
- NON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyDocument4 pagesNON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyJomir Kimberly DomingoNo ratings yet
- Expo 2 - L' IVDocument6 pagesExpo 2 - L' IVCarolina Flores BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (B) - 21st Century Philippine Literature (Week 2)Document10 pagesModule 1 (B) - 21st Century Philippine Literature (Week 2)Kaycee Lyn LugtuNo ratings yet
- 21st Century NotesDocument8 pages21st Century NotesFritzer Kayle Padilla YocampoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Literature TestDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Literature TestKla UdiaNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism: According To UsageDocument20 pagesLiterary Criticism: According To UsageNhor Halil QuibelNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewerDocument7 pagesLiterature ReviewerLovelle Pirante OyzonNo ratings yet
- Literature DefinitionsDocument11 pagesLiterature DefinitionsTishaSuperableNo ratings yet
- Distinctive Features of PoetryDocument1 pageDistinctive Features of PoetryDung ThanhNo ratings yet
- 21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDocument7 pages21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDenise Nicole T. LopezNo ratings yet
- Elements and DevicesDocument48 pagesElements and DevicesLorenz RotomoNo ratings yet
- Lit of PH - Reviewer - Short StoryDocument5 pagesLit of PH - Reviewer - Short StoryAndrei AmoraNo ratings yet
- 12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Document5 pages12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Blessy Myl MagrataNo ratings yet
- Esquema Tema 33Document3 pagesEsquema Tema 33Ana Giráldez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- CNF11 - 12 - Q1 - 0103M - SG - Conventions Elements and Techniques of PoetryDocument20 pagesCNF11 - 12 - Q1 - 0103M - SG - Conventions Elements and Techniques of PoetryMischlaine Kelly MobidoNo ratings yet
- The Hunchback of Notre Dame Musical ScriptDocument30 pagesThe Hunchback of Notre Dame Musical ScriptazaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing - Psychoanalysis, Rational Choice and InstitutionalismDocument31 pagesAnalyzing - Psychoanalysis, Rational Choice and InstitutionalismazaNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic VS SympatheticDocument6 pagesParasympathetic VS SympatheticazaNo ratings yet
- Concept of LifeDocument78 pagesConcept of LifeazaNo ratings yet
- Integrative Art As Applied To Contemporary ArtDocument14 pagesIntegrative Art As Applied To Contemporary ArtazaNo ratings yet
- The Language of Art: Elements and PrinciplesDocument31 pagesThe Language of Art: Elements and PrinciplesazaNo ratings yet
- Literary History Region:: Title: YearDocument1 pageLiterary History Region:: Title: YearazaNo ratings yet
- Dasiy Al Amir The Next StepDocument3 pagesDasiy Al Amir The Next Stepamaniyasin01No ratings yet
- Gamme Mifare 101 en enDocument2 pagesGamme Mifare 101 en enHidalgo HerbertNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Advanced English SpeakingDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - Advanced English SpeakingJulia Sánchez GrañaNo ratings yet
- CST JSS 3 Examination QuestionDocument7 pagesCST JSS 3 Examination QuestionDauda KehindeNo ratings yet
- C++ Project On Video Library ManagementDocument40 pagesC++ Project On Video Library ManagementSuman Karar0% (2)
- May 2021 - Plane Trigonometry 1Document2 pagesMay 2021 - Plane Trigonometry 1paul macasaetNo ratings yet
- NWAdmin Operations 2013Document56 pagesNWAdmin Operations 2013Anonymous ADZ6Pr5UFNo ratings yet
- English Within 20 Minutes SPMDocument43 pagesEnglish Within 20 Minutes SPMsakinah0% (1)
- The Bible Is The Sacred Book of Christians. It Express God's Character and Deliver Us God's Revelation of Himself To His PeopleDocument2 pagesThe Bible Is The Sacred Book of Christians. It Express God's Character and Deliver Us God's Revelation of Himself To His PeopleMish Lei FranxhNo ratings yet
- Tasl 2 - Maureen JimenezDocument8 pagesTasl 2 - Maureen JimenezMaureen JimenezNo ratings yet
- Communicative English (Code No. 101) 2023-24Document18 pagesCommunicative English (Code No. 101) 2023-24Sunita SahuwalaNo ratings yet
- Dogon Study NotesDocument4 pagesDogon Study NotesMxolisi Bob Thabethe100% (1)
- May and Might English Grammar WorksheetDocument2 pagesMay and Might English Grammar WorksheetVeronica Vise MenéndezNo ratings yet
- Simatic Net Industrial Communication Commissioning PC Stations - Manual and Quick StartDocument436 pagesSimatic Net Industrial Communication Commissioning PC Stations - Manual and Quick StartandrecwtNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 10th Social Science Volume 2 Paragraph Study Material em 216415 PDFDocument6 pagesNamma Kalvi 10th Social Science Volume 2 Paragraph Study Material em 216415 PDFHARISH RAJASEKARNo ratings yet
- Oel CCN PDFDocument9 pagesOel CCN PDFAbdul ShakoorNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE. Lexical and Syntactic Analysis 1Document11 pagesSAMPLE. Lexical and Syntactic Analysis 1KEIZE LOUISE ESPAÑOLANo ratings yet
- SYBSc Paper I, Unit-III, AlcoholDocument74 pagesSYBSc Paper I, Unit-III, Alcoholmyebooks.pramodNo ratings yet
- Lista Completa de Verbos Irregulares em EnglishDocument3 pagesLista Completa de Verbos Irregulares em EnglishedtonssNo ratings yet
- Umbrello Handbook XDocument41 pagesUmbrello Handbook Xdeive2194No ratings yet
- Muhammad Kashif Manzoor - CVDocument4 pagesMuhammad Kashif Manzoor - CVaheerpk77No ratings yet
- Copia de ECCE (Simple Past-Past Perfect)Document2 pagesCopia de ECCE (Simple Past-Past Perfect)Javier ReyesNo ratings yet
- IDL Smart Printing Resource Kit Developer Guide PDFDocument28 pagesIDL Smart Printing Resource Kit Developer Guide PDFMarwan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Math4 Exercises: 1.1 Double IntegralsDocument14 pagesMath4 Exercises: 1.1 Double IntegralsTrần Trọng KỳNo ratings yet
- Whaling Back ThenDocument9 pagesWhaling Back ThenMagdalena Quiñones MorenoNo ratings yet
- Verbal NegationDocument10 pagesVerbal NegationBaek Na-kyumNo ratings yet
- Devoir de Synthèse N°3 - Anglais - 1ère AS (2012-2013) Mme Besma DZIRIDocument4 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°3 - Anglais - 1ère AS (2012-2013) Mme Besma DZIRIMayssem Ben AmeurNo ratings yet
- Marketing LandscapeDocument10 pagesMarketing LandscapePrata BestoNo ratings yet
Creative Nonfiction Reviewer
Creative Nonfiction Reviewer
Uploaded by
azaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Creative Nonfiction Reviewer
Creative Nonfiction Reviewer
Uploaded by
azaCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 1 4.
Meter (Rhythm being established by
Introduction of Literary Genres a poem)
5. Rhyme (Words with same ending)
6. Figurative Language
Literature
- Simile
- Comes from the Latin word
- Metaphor
Literatura (learned, literate, learning
- Hyperbole
from literatus).
- Idiom
- Both oral and written
- Personification
Characteristics
7. Connotation (Word association)
- Expressive, Imaginative
8. Denotation (Dictionary Meaning)
- Nobility of thoughts
9. Repetition (Author repeats a word,
- Universality
line or phrase)
- Timelessness
10. Alliteration (Words with same
beginning sound)
Four Major Literary Genres
11. Imagery (Sight, Touch, Smell,
Sound, Taste)
1. Poetry
12. Irony (Difference between the way
- Narrative
something appears and what is
- Lyric
actually true)
- Dramatic
13. Voice of P.O.V
14. Assonance (Words with same
2. Fiction
middle sound)
- Short Story
15. Form (Ballad, Free Verse, Sonnet)
- Novel
16. Stanza (Division of lines into groups)
- Novelette
17. Word Order (Author varieties word
order for meaning and effect)
3. Drama
18. Onomatopoeia (words formed by
- Plays
imitating the sound they make)
- Tragedy
- Dramatic HIstory
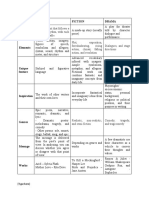
Elements of Fiction
● Setting, Theme, Character, Conflict,
4. Non-Fiction
Plot, Point of View
- Essays
- Biographies, Autobiographies
Elements of Drama
- Travelogue
● Drama, Actors, Script, Acts, Scenes,
- Testimonio
Dialogue, Monologue, Theater,
- Reportage
Props
Elements of Poetry
Elements of Nonfiction
● Facts, Author Point of View, Mood,
1. Mood (Reader’s Feelings)
Author’s Style
2. Tone (Author’s Feelings)
3. Symbolism (Representation)
Features of Nonfiction Common Literary Techniques
1. Title 1. Imagery
2. Title Page 2. Simile and Metaphor
3. Table of Contents 3. Hyperbole
4. Index 4. Personification
5. Glossary 5. Alliteration
6. Heading 6. Allegory (When abstract ideas are
7. Photograph given a form of characters, actions,
8. Illustration or events.)
9. Caption 7. Irony
10. Labels
11. Graph Function of Literary Devices
12. Table 1. Compare the work of one writer to
another.
LESSON 2 2. Beautify the piece to give deeper
meaning.
Literary devices Vs. Literary
3. Testing readers.
Techniques 4. Motivating readers.
Difference of Literary Elements, Devices,
and Techniques
Lesson 3
Literary Devices (Elements and
1. Literary Devices/Techniques Techniques of Fiction)
(Typical structures used to convey
author’s message) Literary Devices of Fiction
2. Literary Elements (used by the - Setting, Plot, Character, Conflict,
reader to analyze and understand Point of View, Theme, Mood,
any work of literature) Dialogue
- Rhetorical Devices, Flashback,
Two Kinds of Literary Devices Foreshadowing, Figurative
● Literary elements, Literary Language, Sensory Details, Allusion
Techniques
Types of Characters (Element)
Common Literary Elements 1. Dynamic Character - A character
1. Plot that changes.
2. Setting 2. Static Character - A character who
3. Protagonist remains the same.
4. Antagonist 3. Round Character - Well developed
5. Narrator character who demonstrates varied
6. Narrative Method and sometimes contradictory traits.
7. Dialogue 4. Flat Character - Relatively
8. Conflict uncomplicated character
9. Mood Stock Character - Flat character who
10. Theme is instantly recognizable
(Stereotypical).
- Unreliable Narrator - The reader
questions or seeks to qualify the
statements of fact and judgment.
5. Protagonist - Main character
6. Antagonist - Opposition of the
protagonist.
7. Character Foil - Secondary
character who highlights the
protagonist’s personality.
Types of Conflict
1. Character Vs. Character
2. Character Vs. Nature
3. Character Vs. Society
4. Character Vs. Self
Characterization
- Representation by the author of the
character through direct description.
(External Characterization)
- Representation from within a
character, without comment by the
author. (Internal Characterization)
Character Development
Internal Character External Character
Development Development
- Feelings - Actions
- Thoughts - Relationship
- Emotions s
- Dialogues
Character Motivation
- Reasons, justifications, and
explanations for the action of a
character.
Point of View - Narrator
- Reliable Narrator - The reader
accepts the statements of fact and
judgment without question.
You might also like
- Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo ChurchDocument28 pagesEthiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Churchmtebeje0% (1)
- Bhattacharya - 2020 - More Studies On The Cārvāka - LokāyataDocument292 pagesBhattacharya - 2020 - More Studies On The Cārvāka - LokāyataminoozolaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century 3DAYS ACTDocument9 pages21st Century 3DAYS ACTRowelyn BakekeNo ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesCNF Reviewer: 3rd QuarterKYZEIR JOVER JAVIERNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Compare and Contrast Various 21ST Century Genres From Earlier Genres-PeriodDocument20 pagesLesson 3 - Compare and Contrast Various 21ST Century Genres From Earlier Genres-PeriodAndrea Ibañez80% (5)
- English Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THDocument6 pagesEnglish Reviewer: ST ND TH RD THMelissa PasoquinNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument15 pagesNotesHazel Loraenne ConarcoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Module 2Document21 pages21st Century Literature Module 2Raymart DiaperaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument2 pages21st Century LiteratureMark PalomarNo ratings yet
- Local Media7165870540832856673Document4 pagesLocal Media7165870540832856673HammadiNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature q1 Module 2Document27 pages21st Century Literature q1 Module 2Raymart DiaperaNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices: Literary Elements & Literary TechniquesDocument10 pagesLiterary Devices: Literary Elements & Literary TechniquesAnie Grace Garcia100% (1)
- Phil Lit - Introduction IIDocument3 pagesPhil Lit - Introduction IIJessica AbuqueNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument30 pages21st Century LiteratureJovelle TugadeNo ratings yet
- ATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Document8 pagesATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Andrea M. IbañezNo ratings yet
- Year 10 English Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet Knowledge Book For Assessments 2017-2018Document25 pagesYear 10 English Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet Knowledge Book For Assessments 2017-2018agamNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Lit Midterms ReviewerDocument7 pages21st Century Lit Midterms Reviewerronanmorales93No ratings yet
- CNF Reviewer W1 2Document4 pagesCNF Reviewer W1 2ZairaNo ratings yet
- LITR 102 Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesLITR 102 Midterm ReviewerMae MartinezNo ratings yet
- Literary Report Art AppreciationDocument45 pagesLiterary Report Art AppreciationJemma Rose TegioNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaDocument8 pages21st Century Literature 3rd Q NayyesaJenrich MarceloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LiteratureDocument3 pagesIntroduction To LiteraturealaamohbenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Authors Craft Teaching Plan 2019-20Document2 pagesUnit 1 Authors Craft Teaching Plan 2019-20api-479558866No ratings yet
- Reviewer-Literature LESSON 1Document4 pagesReviewer-Literature LESSON 1Charisse Deirdre TulioNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Summary of DiscussionsDocument6 pagesCreative Writing Summary of DiscussionsKEN ZEUS GOLLOYNo ratings yet
- Lit ReviewerDocument6 pagesLit ReviewerSheryl NunialNo ratings yet
- 9 Grade Literature - Novels, Short Stories, Non-Fiction, Poetry, DramaDocument15 pages9 Grade Literature - Novels, Short Stories, Non-Fiction, Poetry, DramaAizel Nova Fermilan ArañezNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices and Literary TermsDocument1 pageLiterary Devices and Literary TermsAna-Alicia Burrows-BlairNo ratings yet
- Literary Elementsworksheet 1Document1 pageLiterary Elementsworksheet 1Amr SaadNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature GenresDocument20 pagesPhilippine Literature GenresRyce SumayloNo ratings yet
- CNF Module 1Document6 pagesCNF Module 1Robert AquinoNo ratings yet
- What Is Poetry?Document41 pagesWhat Is Poetry?Jeah Asilum DalogdogNo ratings yet
- ATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Document8 pagesATG - Ibanez, Andrea M.Andrea M. IbañezNo ratings yet
- English Reviewer 9.1Document6 pagesEnglish Reviewer 9.1Lexine Cyra PinauinNo ratings yet
- World LitDocument30 pagesWorld LitPearl AlanoNo ratings yet
- Genres of Literature Fiction: "It", "They", Etc. It Is LikeDocument5 pagesGenres of Literature Fiction: "It", "They", Etc. It Is LikeAleli Isabel DemecilloNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms Worksheet: Definitions: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesLiterary Terms Worksheet: Definitions: Name: - DateRaja SaadNo ratings yet
- Theme, Character & Language StyleDocument15 pagesTheme, Character & Language StyleNanacyNo ratings yet
- 21 Lit Nat ReviewerDocument5 pages21 Lit Nat ReviewerApricus BenciNo ratings yet
- 21STDocument82 pages21STitzoceanmarkNo ratings yet
- Objecti Ves-Facts Subjecti Ve - Opinion S: Sensory DetailsDocument2 pagesObjecti Ves-Facts Subjecti Ve - Opinion S: Sensory DetailsDebil DimunyuNo ratings yet
- Literary CriticismDocument33 pagesLiterary CriticismJoanne RanarioNo ratings yet
- схема анализаDocument2 pagesсхема анализаValeriia ChoiNo ratings yet
- 1 Whats LitDocument10 pages1 Whats LitHisyam SurachmanNo ratings yet
- Asean ReviewerDocument7 pagesAsean ReviewerMarynissa CatibogNo ratings yet
- 21clpw ReviewerDocument8 pages21clpw ReviewerpatNo ratings yet
- NON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyDocument4 pagesNON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyJomir Kimberly DomingoNo ratings yet
- Expo 2 - L' IVDocument6 pagesExpo 2 - L' IVCarolina Flores BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (B) - 21st Century Philippine Literature (Week 2)Document10 pagesModule 1 (B) - 21st Century Philippine Literature (Week 2)Kaycee Lyn LugtuNo ratings yet
- 21st Century NotesDocument8 pages21st Century NotesFritzer Kayle Padilla YocampoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Literature TestDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Literature TestKla UdiaNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism: According To UsageDocument20 pagesLiterary Criticism: According To UsageNhor Halil QuibelNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewerDocument7 pagesLiterature ReviewerLovelle Pirante OyzonNo ratings yet
- Literature DefinitionsDocument11 pagesLiterature DefinitionsTishaSuperableNo ratings yet
- Distinctive Features of PoetryDocument1 pageDistinctive Features of PoetryDung ThanhNo ratings yet
- 21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDocument7 pages21ST First Quarter Lesson CompilationDenise Nicole T. LopezNo ratings yet
- Elements and DevicesDocument48 pagesElements and DevicesLorenz RotomoNo ratings yet
- Lit of PH - Reviewer - Short StoryDocument5 pagesLit of PH - Reviewer - Short StoryAndrei AmoraNo ratings yet
- 12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Document5 pages12 - 21ST Century Literature (1-5)Blessy Myl MagrataNo ratings yet
- Esquema Tema 33Document3 pagesEsquema Tema 33Ana Giráldez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- CNF11 - 12 - Q1 - 0103M - SG - Conventions Elements and Techniques of PoetryDocument20 pagesCNF11 - 12 - Q1 - 0103M - SG - Conventions Elements and Techniques of PoetryMischlaine Kelly MobidoNo ratings yet
- The Hunchback of Notre Dame Musical ScriptDocument30 pagesThe Hunchback of Notre Dame Musical ScriptazaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing - Psychoanalysis, Rational Choice and InstitutionalismDocument31 pagesAnalyzing - Psychoanalysis, Rational Choice and InstitutionalismazaNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic VS SympatheticDocument6 pagesParasympathetic VS SympatheticazaNo ratings yet
- Concept of LifeDocument78 pagesConcept of LifeazaNo ratings yet
- Integrative Art As Applied To Contemporary ArtDocument14 pagesIntegrative Art As Applied To Contemporary ArtazaNo ratings yet
- The Language of Art: Elements and PrinciplesDocument31 pagesThe Language of Art: Elements and PrinciplesazaNo ratings yet
- Literary History Region:: Title: YearDocument1 pageLiterary History Region:: Title: YearazaNo ratings yet
- Dasiy Al Amir The Next StepDocument3 pagesDasiy Al Amir The Next Stepamaniyasin01No ratings yet
- Gamme Mifare 101 en enDocument2 pagesGamme Mifare 101 en enHidalgo HerbertNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Advanced English SpeakingDocument8 pagesLesson 1 - Advanced English SpeakingJulia Sánchez GrañaNo ratings yet
- CST JSS 3 Examination QuestionDocument7 pagesCST JSS 3 Examination QuestionDauda KehindeNo ratings yet
- C++ Project On Video Library ManagementDocument40 pagesC++ Project On Video Library ManagementSuman Karar0% (2)
- May 2021 - Plane Trigonometry 1Document2 pagesMay 2021 - Plane Trigonometry 1paul macasaetNo ratings yet
- NWAdmin Operations 2013Document56 pagesNWAdmin Operations 2013Anonymous ADZ6Pr5UFNo ratings yet
- English Within 20 Minutes SPMDocument43 pagesEnglish Within 20 Minutes SPMsakinah0% (1)
- The Bible Is The Sacred Book of Christians. It Express God's Character and Deliver Us God's Revelation of Himself To His PeopleDocument2 pagesThe Bible Is The Sacred Book of Christians. It Express God's Character and Deliver Us God's Revelation of Himself To His PeopleMish Lei FranxhNo ratings yet
- Tasl 2 - Maureen JimenezDocument8 pagesTasl 2 - Maureen JimenezMaureen JimenezNo ratings yet
- Communicative English (Code No. 101) 2023-24Document18 pagesCommunicative English (Code No. 101) 2023-24Sunita SahuwalaNo ratings yet
- Dogon Study NotesDocument4 pagesDogon Study NotesMxolisi Bob Thabethe100% (1)
- May and Might English Grammar WorksheetDocument2 pagesMay and Might English Grammar WorksheetVeronica Vise MenéndezNo ratings yet
- Simatic Net Industrial Communication Commissioning PC Stations - Manual and Quick StartDocument436 pagesSimatic Net Industrial Communication Commissioning PC Stations - Manual and Quick StartandrecwtNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 10th Social Science Volume 2 Paragraph Study Material em 216415 PDFDocument6 pagesNamma Kalvi 10th Social Science Volume 2 Paragraph Study Material em 216415 PDFHARISH RAJASEKARNo ratings yet
- Oel CCN PDFDocument9 pagesOel CCN PDFAbdul ShakoorNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE. Lexical and Syntactic Analysis 1Document11 pagesSAMPLE. Lexical and Syntactic Analysis 1KEIZE LOUISE ESPAÑOLANo ratings yet
- SYBSc Paper I, Unit-III, AlcoholDocument74 pagesSYBSc Paper I, Unit-III, Alcoholmyebooks.pramodNo ratings yet
- Lista Completa de Verbos Irregulares em EnglishDocument3 pagesLista Completa de Verbos Irregulares em EnglishedtonssNo ratings yet
- Umbrello Handbook XDocument41 pagesUmbrello Handbook Xdeive2194No ratings yet
- Muhammad Kashif Manzoor - CVDocument4 pagesMuhammad Kashif Manzoor - CVaheerpk77No ratings yet
- Copia de ECCE (Simple Past-Past Perfect)Document2 pagesCopia de ECCE (Simple Past-Past Perfect)Javier ReyesNo ratings yet
- IDL Smart Printing Resource Kit Developer Guide PDFDocument28 pagesIDL Smart Printing Resource Kit Developer Guide PDFMarwan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Math4 Exercises: 1.1 Double IntegralsDocument14 pagesMath4 Exercises: 1.1 Double IntegralsTrần Trọng KỳNo ratings yet
- Whaling Back ThenDocument9 pagesWhaling Back ThenMagdalena Quiñones MorenoNo ratings yet
- Verbal NegationDocument10 pagesVerbal NegationBaek Na-kyumNo ratings yet
- Devoir de Synthèse N°3 - Anglais - 1ère AS (2012-2013) Mme Besma DZIRIDocument4 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°3 - Anglais - 1ère AS (2012-2013) Mme Besma DZIRIMayssem Ben AmeurNo ratings yet
- Marketing LandscapeDocument10 pagesMarketing LandscapePrata BestoNo ratings yet