Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsBoilogy 2
Boilogy 2
Uploaded by
Merced CodillaThis document provides information about the key characteristics of living things:
- Organization - Living things have a hierarchical structure that functions seamlessly.
- Metabolism - The ability to acquire and use energy to sustain life processes.
- Response to stimuli - Living things adapt to changes in their environment to ensure survival.
- Reproduction - The ability to produce offspring and ensure continuation of the species.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Manual Reparacion Motor K25 PDFDocument135 pagesManual Reparacion Motor K25 PDFRojasDura.83% (41)
- Mcq. SurgeryDocument132 pagesMcq. Surgeryمنتظر اللاميNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Practical Biology: For Senior Secondary Schools and CollegesFrom EverandFundamentals of Practical Biology: For Senior Secondary Schools and CollegesNo ratings yet
- Management Information System of EDCLDocument47 pagesManagement Information System of EDCLAbir MohammadNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy Poster 2Document1 pageGeothermal Energy Poster 2api-298575301100% (2)
- Genbio 2Document3 pagesGenbio 2kaba.contaoi.upNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Reproduction in AnimalsDocument43 pagesChapter 9 - Reproduction in AnimalsNURUL AINUN MUHAMMAD NORNo ratings yet
- Bio 5 PhotoMasterICDocument28 pagesBio 5 PhotoMasterICJavier NourryNo ratings yet
- GenBio 2NDQDocument12 pagesGenBio 2NDQKisses MacapugasNo ratings yet
- RecapDocument2 pagesRecapMAHMUD, ZAINAB SARAJANNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Concept-map-about-Biochemistry - BorbonDocument1 pageActivity 1Concept-map-about-Biochemistry - BorbonAbigail BorbonNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument7 pagesReproductionhernandezlovenson65No ratings yet
- Bio BYJU'S 1 Living OrganismsDocument9 pagesBio BYJU'S 1 Living OrganismsReview ZodiacNo ratings yet
- Class Note 1Document14 pagesClass Note 1sushillai deviNo ratings yet
- Living WorldDocument33 pagesLiving WorldShuryans MishraNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 19 Mar 2022Document7 pagesAdobe Scan 19 Mar 2022Abirami SathishNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument12 pagesHeredity and EvolutionDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- DEVPSYCH 3 - Forming A New LifeDocument4 pagesDEVPSYCH 3 - Forming A New LifeRedgie G. GabaneNo ratings yet
- Population GeneticsDocument16 pagesPopulation Geneticsnandithas175No ratings yet
- My CologyDocument21 pagesMy CologyCarl PinedaNo ratings yet
- Completed Evolution Packet 2017-2018Document42 pagesCompleted Evolution Packet 2017-2018Talijah JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 2Document5 pagesLesson 1 - 2FLORENE BHON GUMAPACNo ratings yet
- Measuring Genetic Biodiversity Classification Adaptation To NicheDocument2 pagesMeasuring Genetic Biodiversity Classification Adaptation To NicheSarah LolyNo ratings yet
- Biochem - Lesson 1&2Document3 pagesBiochem - Lesson 1&2Lester John RagudoNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 7 To 10 Botany LecDocument2 pagesNotes Lesson 7 To 10 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution by Natural SelectionDocument27 pagesTheory of Evolution by Natural Selectionelaine loveluckNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument1 pageAnswer KeyYour boy jj WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument1 pageAnswer KeySamuel SiyumNo ratings yet
- Answer - Key 2 PDFDocument1 pageAnswer - Key 2 PDFTekeria PresleyNo ratings yet
- C8.1 - Intro. To Animal & Plant ReproductionDocument13 pagesC8.1 - Intro. To Animal & Plant ReproductionNURULAIN MOHD ASRINo ratings yet
- Genetics, Evolution, Development, and PlasticityDocument8 pagesGenetics, Evolution, Development, and PlasticityMerryNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: ACTIVITY 1: Plant and Animal Sexual ReproductionDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: ACTIVITY 1: Plant and Animal Sexual ReproductionEunice PaulNo ratings yet
- Population GeneticsDocument22 pagesPopulation GeneticsJ15No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science (Week 4) - q2Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science (Week 4) - q2Rica ParillaNo ratings yet
- Caracteristicas de Los Seres VivosDocument1 pageCaracteristicas de Los Seres Vivosfloresyack11181No ratings yet
- Scan 08 Oct 2022Document20 pagesScan 08 Oct 2022sahil143psNo ratings yet
- Decline of Induction Capability by Outer Membrane V - 2024 - International BiodeDocument9 pagesDecline of Induction Capability by Outer Membrane V - 2024 - International BiodeLuis GómezNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce VerifiedDocument10 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Verifiedlavi krishnaniNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class NotesDocument19 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Class NotesTripura NeelimaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GENETICSDocument31 pagesLesson 1 GENETICSPewpew IsheeeNo ratings yet
- Living BeingsDocument1 pageLiving Beingsfloresyack11181No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Chapter 1 To 5 Loyola Ec Guide em PDFDocument126 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Chapter 1 To 5 Loyola Ec Guide em PDFjoel john100% (4)
- Ass 2012Document4 pagesAss 2012Ishaan “Toxx” KatariaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 22, 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan Nov 22, 2022ArpithaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument11 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesSexual Reproductionghechchoutang123No ratings yet
- Notes CompanaDocument10 pagesNotes CompanaKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Animal Characteristics 2022Document29 pagesAnimal Characteristics 2022Anisah Nur FatimahNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Organisms.Document3 pagesReproduction in Organisms.hbhaiya643No ratings yet
- Evolution & Speciation: Biological Species ConceptDocument34 pagesEvolution & Speciation: Biological Species ConceptMilka RahmanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledGenesis De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Unique Features of The Plant Life Cycle and Their ConsequencesDocument12 pagesUnique Features of The Plant Life Cycle and Their ConsequencesSushree JnanadaNo ratings yet
- 12th Zoology Chapter 1 To 4 Sura Guide em 214857Document81 pages12th Zoology Chapter 1 To 4 Sura Guide em 214857jeevajeevam2021No ratings yet
- Earth and Life - 2nd Q - Topic1Document5 pagesEarth and Life - 2nd Q - Topic1figuerassandrajuliasaaNo ratings yet
- FBT Lecture 2-1Document32 pagesFBT Lecture 2-1Ananta AnweshaNo ratings yet
- 24 Lecture Presentation 0Document39 pages24 Lecture Presentation 0stri47958No ratings yet
- The Marriage Between Molecular Biology and NutritionDocument37 pagesThe Marriage Between Molecular Biology and NutritionOng Chen MeiNo ratings yet
- FragmentationDocument3 pagesFragmentationTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- EnzimDocument29 pagesEnzimyasmine aurelliaNo ratings yet
- Life Process 8Document38 pagesLife Process 8Hridayangam KashyapNo ratings yet
- Supporting Details About Morphological and Physiological... - Google ScholarDocument1 pageSupporting Details About Morphological and Physiological... - Google ScholarcfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- Biology REVISION - SCIENCE (YT)Document47 pagesBiology REVISION - SCIENCE (YT)jyotiNo ratings yet
- MammaliaDocument8 pagesMammaliaGabrielle ForgetNo ratings yet
- Clinical Research HypertensionDocument4 pagesClinical Research HypertensionJay Linus Rante SanchezNo ratings yet
- NRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDocument5 pagesNRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDiego VilaNo ratings yet
- Manual PDFDocument4 pagesManual PDFrpichoNo ratings yet
- English For Business l1 Past Paper Series 2 2012Document9 pagesEnglish For Business l1 Past Paper Series 2 2012GuitargirlMimi0% (1)
- Shamanic HealingDocument41 pagesShamanic HealingMeraki Mary50% (2)
- Bombas SumergiblesDocument79 pagesBombas SumergiblesInstinct_brNo ratings yet
- Divergent Plate BoundaryDocument4 pagesDivergent Plate BoundaryGreg ManNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionDocument5 pagesTop 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionGabaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Revision SheetDocument2 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Revision Sheetyashvibhatia5No ratings yet
- RA For Assessment For Lifting OperationsDocument19 pagesRA For Assessment For Lifting OperationsMohamedSaidNo ratings yet
- Fossils Flashcards 3rd GradeDocument3 pagesFossils Flashcards 3rd Gradeapi-345686634100% (1)
- Modul Science Form 1Document31 pagesModul Science Form 1Norafiza HashimNo ratings yet
- 3att 1435070407870 Katura ResumeDocument2 pages3att 1435070407870 Katura Resumeapi-362299218No ratings yet
- Employment Document Folder ListsDocument90 pagesEmployment Document Folder ListsIsna FauziahNo ratings yet
- Case Study Structure - Sarda Sahayak Pariyojana - Feb 2010Document25 pagesCase Study Structure - Sarda Sahayak Pariyojana - Feb 2010Bhushan Kankal100% (3)
- P4 - Rolled TrufflesDocument4 pagesP4 - Rolled TrufflesWendy JacksonNo ratings yet
- EpitheliumDocument48 pagesEpitheliumdrpankaj28100% (1)
- PRISMA 2020 Flow Diagram For Updated Systematic Reviews Which Included Searches of Databases, Registers and Other SourcesDocument1 pagePRISMA 2020 Flow Diagram For Updated Systematic Reviews Which Included Searches of Databases, Registers and Other SourcesSurya WijayaNo ratings yet
- Social and Self Control TheoryDocument2 pagesSocial and Self Control TheoryKarl Amiel EspirituNo ratings yet
- Thrive The Vegan Nutrition Guide Brendan Brazier.15709 - 1contents - and - IntroductionDocument8 pagesThrive The Vegan Nutrition Guide Brendan Brazier.15709 - 1contents - and - IntroductionCristhian ChávezNo ratings yet
- Father's of Various FieldsDocument5 pagesFather's of Various FieldsAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Industrial HygineDocument33 pagesIndustrial HygineNiraj RanjanNo ratings yet
- HPV and Related Diseases Report HPV Informacion CentreDocument303 pagesHPV and Related Diseases Report HPV Informacion CentreRenée Elizade Martinez-PeñuelaNo ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideDocument11 pagesGas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideSandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Demonizing Drugmakers: The Political Assault On The Pharmaceutical Industry, Cato Policy Analysis No. 475Document56 pagesDemonizing Drugmakers: The Political Assault On The Pharmaceutical Industry, Cato Policy Analysis No. 475Cato InstituteNo ratings yet
Boilogy 2
Boilogy 2
Uploaded by
Merced Codilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesThis document provides information about the key characteristics of living things:
- Organization - Living things have a hierarchical structure that functions seamlessly.
- Metabolism - The ability to acquire and use energy to sustain life processes.
- Response to stimuli - Living things adapt to changes in their environment to ensure survival.
- Reproduction - The ability to produce offspring and ensure continuation of the species.
Original Description:
gen bio notes
Original Title
BOILOGY 2 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about the key characteristics of living things:
- Organization - Living things have a hierarchical structure that functions seamlessly.
- Metabolism - The ability to acquire and use energy to sustain life processes.
- Response to stimuli - Living things adapt to changes in their environment to ensure survival.
- Reproduction - The ability to produce offspring and ensure continuation of the species.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesBoilogy 2
Boilogy 2
Uploaded by
Merced CodillaThis document provides information about the key characteristics of living things:
- Organization - Living things have a hierarchical structure that functions seamlessly.
- Metabolism - The ability to acquire and use energy to sustain life processes.
- Response to stimuli - Living things adapt to changes in their environment to ensure survival.
- Reproduction - The ability to produce offspring and ensure continuation of the species.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
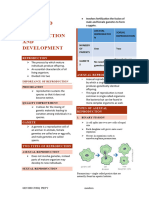
Lesson Title: Describing the Characteristics of maintain stability while adjusting sperm and egg for a partner
fertilization leads to o Offers advantages
Living Things (SAS 1) to conditions that are optimal for genetic diversity and in rapid
survival. adaptation. production growth
o Bi parental and adaptation in
o Germ cells are stable
DYNAMIC EQUILIBIUM involved environments.
ORGANIZATION o Offspring are not o Reproduction is
o Continuous change occurs yet genetically identical FAST
o Life originated on a hierarchical structure relatively uniform conditions to parents o No Variation
o Reproduction is
that functions together seamlessly. prevail. SLOWER
o Genetic Variation
HERIDITY
METABOLISM
o Refers to the genetic heritage
Plant Animal
o The ability to acquire and utilize energy to passed down by our biological Reproduction Reproduction
sustain life process parents.
Life Cycle Alteration of No Alteration of
MOVEMENT Generations Generations
RESPONSE TO STIMULI Gametes Haploid Gametes Haploid Gametes
o Living things need to move to find
o Living things respond to changes in their nutrition, to breed, to excrete waste Spores Haploid Spores No spores
environment; this adaptability ensures products, to respire, to get a sense
survival. of the world, and to grow. Gametes Haploid Diploid Organism, by
Made by gametophyte, by Meiosis
Mitosis
REPRODUCTION ADAPTATION Spores made Diploid sporophyte, No spores
by by Meiosis
o The ability to produce offspring; and o The ability to change over time in
ensure the continuation of their species. response to the environment.
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Lesson Title: PLANT AND ANIMAL
REPRODUCTION, NUTRITION AND GAS
o Increase in size, shape, and changes in EXHANGE (SAS 2)
features NUTRITION
ADAPTABILITY Refers to the activities by which
living things obtain raw materials
o Evolve and adapt over time; species change from the environment and
and develop traits better suited for their transport them into their cells.
REPRODUCTION
environment.
o The process by which plants and animals
produce offspring. There are two main
HOMEOSTASIS forms: sexual and asexual reproduction.
o Self–regulating process by which SEXUAL ASEXUAL
biological systems tend to o Involves courtships o Reproducing
and the union of without the need
Is a migratory response that is elicited by PLANTS ANIMALS
chemicals. Hydrophytes - a plant that Living together
grows either partly or
THERMOTROPISM totally submerged in water.
Is a movement or growth in response to also : a plant growing in
heat or temperature. waterlogged soil.
hydrophytic.
PHOTOTAXIS Hygrophytes - a plant living Migration - used by a variety
Is an animal's response toward/away from above ground that is adapted of different species. The most
to the conditions of abundant common reasons for
light stimulus. moisture pads of surrounding migration are finding food
HYDROTROPISM air. and a good place to mate.
Is a plant's movement or growth in Halophytes - plants that Hibernation - a state of
response to water. naturally inhabit saline reduced metabolic activity in
HERBIVORES environments and benefit animals that allows them to
PHOTOTROPISM from having substantial
Animals that eat only plants. amounts of salt in the growth
conserve energy and survive
The plant's movement in response to light. during periods of extreme
CARNIVORES media. cold or reduced food
CHEMOTROPISM
Animals that eat only meat availability
is the movement or growth in response to
OMNIVORES chemicals. Xerophytes - plants that are Artificial Bigness - Some
Animals that eat plants and animals adapted to very dry animals can puff up or
conditions with a lot of sun expand their body to look
exposure, like cacti and much bigger than they are
ADAPTABILITY succulents. and scare predators.
PARASITE Mesophytes - terrestrial Camouflage - a defense or
Process of change by which organism or
plants that are neither adapted tactic that organisms use to
Organisms that get their nutrition species becomes better suited to its to particularly dry nor disguise their appearance,
through attaching themselves on thriving environment. particularly wet environments usually to blend in with their
inside a host. Often develop in response to a change in the surroundings.
Mimicry - when one species
organism habitat. of animal (the mimic)
REMINDER! resembles another species
that has easily recognizable
characteristics (the model)
and as a result deceives a
Photosynthesis is a process where plants use potential predator (the dupe)
light from the sun to convert carbon dioxide TYPES OF ADAPTABILITY that might otherwise capture
from the air and water from the soil into and eat it.
energy to feed the plant and oxygen is given PHYSICAL
out in the air. - Special body parts, shapes, skin,
IRRITABILITY
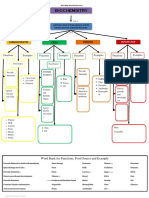
Lesson Title: Exploring Plant and Animal color- that helps organism survive
Irritability and Adaptability (SAS 3) in natural habitat.
PLANTS PHYSIOLOGICAL ANIMALS
THIGMOTROPHISM - Metabolic changes in an animal
Is a movement or growth in response to that helps them to survive.
STIMULI
touch or Anything
contact.that BHEAVIORAL
- When an animal changes
GEOTROPISM will cause an
organism to react behavior to survive the
A movement or growth in plants in
environment.
response to gravity.
CHEMOTAXIS
ADAPTABILITY
TROPISM The TAXIS is a response in
growth movement and which the organism moves
its direction. forward from the stimulus
(negative) a light source, is
widespread among marine larvae. Each inherited trait is defined by a gene
GEOTAXIS pair. Parental genes are randomly
-
a response to gravity, where separated to the sex cells so that sex cells
LAW OF DOMINANCE positive geotaxis means that the contain only one gene of the pair. Offspring
Thermotrophism organism moves with gravity. therefore inherit one genetic allele from
Aerotaxis
THIGMOTAXIS each parent when sex cells unite in
Phototropism Phototaxis - refers to a specific behavior of fertilization.
Geotropism animals (i.e., to stay close to walls Will be separated
Geotaxis
when exploring an open space) Gametes will be chromosome
Thigmotropism Thigmotaxis CHEMOTAXIS
Hydrotropism
- an animal must recognize a
Chemotaxis chemical, orient itself in the
gradient, and move in a coordinated
fashion to the peak concentration of
attractant.
REMINDER!!!
- The suffix – tropism is applicable
LAW OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT
to the plants while – Taxis/es is for
animals. Irritability on animals is Genes for
almost the same with that of plants. different
- The suffix – phytes refers to a traits are
taxonomic group of plants or algae. sorted
- Positive phototropism – growth of separately
plant towards a light resources. from one
AEROTAXIS - Negative Phototropism – growth another so
- Oxygen - dependent migration is away from light. that the
well-characterized in bacteria. inheritance
PHOTOAXIS Lesson Title: The Introduction to Genetics of one trait
- Directi (SAS 7) is not
onal dependent
on the
GREGOR MENDEL inheritance
discovered the fundamental laws of of another.
inheritance. Ensure genetic variations
tracked the segregation of parental genes
and their appearance in the offspring as
dominant or recessive traits.
Father of genetics An organism with alternate forms of a gene
Pisium sativum will express the form that is dominant.
movement along a light vector Was an Austrian Monk
towards (positive) or away from
LAW OF SEGREGATION
Lesson Title: Feedback Mechanism and convert biochemical energy from nutrients
Tracing the Process of Plant and Animal into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then
Excretion (SAS 4) release waste products.
FEEDBACK MECHANISM
PLANTS ANIMALS
Positive Feedback Negative Feedback
- occurs when a - occurs when a stimulus
stimulus creates a chain happens and triggers the
reaction that amplifies organism counteract the
as it goesCHEMICAL REACTION
on. It stimulus. To It completes the
reinforces the stimulus, opposite act, causing the
takes place in the cells of living organism and results in a much resulting effect to be
which is essential in carrying out the larger and much more lessened.
different life processes. The sum of all these significant response.
reactions is called METABOLISM.
EXCRETION
The removal of metabolic waste product HOMEOSTASIS
from the body of an organism due to
metabolism. the tendency of an organism and maintain
equilibrium, usually through a system of
REMINDER! stabilized health and functioning or cell to
Plants can remove their waste in 3 processes: these regulate its internal environment feedback
are photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration. controls (positive and negative), to stabilize
The waste/product that is produced during health and functioning.
Purpose of feedback mechanism:
photosynthesis is oxygen, meanwhile, in respiration, 1. If metabolic waste is not removed from the body, it
carbon dioxide is considered a by-product. Lastly, may become poisonous and kill living cells.
the waste that was removed during transpiration in 2. It maintains salt balance in the blood.
3. Keeps you from becoming a fecal grenade.
plants is water. This is excreted through the stomata
of the leaves.
VARIATION
the tendency of offspring to differ
from parents.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
a set of metabolic reactions and processes
that take place in the cells of organisms to
You might also like
- Manual Reparacion Motor K25 PDFDocument135 pagesManual Reparacion Motor K25 PDFRojasDura.83% (41)
- Mcq. SurgeryDocument132 pagesMcq. Surgeryمنتظر اللاميNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Practical Biology: For Senior Secondary Schools and CollegesFrom EverandFundamentals of Practical Biology: For Senior Secondary Schools and CollegesNo ratings yet
- Management Information System of EDCLDocument47 pagesManagement Information System of EDCLAbir MohammadNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy Poster 2Document1 pageGeothermal Energy Poster 2api-298575301100% (2)
- Genbio 2Document3 pagesGenbio 2kaba.contaoi.upNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Reproduction in AnimalsDocument43 pagesChapter 9 - Reproduction in AnimalsNURUL AINUN MUHAMMAD NORNo ratings yet
- Bio 5 PhotoMasterICDocument28 pagesBio 5 PhotoMasterICJavier NourryNo ratings yet
- GenBio 2NDQDocument12 pagesGenBio 2NDQKisses MacapugasNo ratings yet
- RecapDocument2 pagesRecapMAHMUD, ZAINAB SARAJANNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Concept-map-about-Biochemistry - BorbonDocument1 pageActivity 1Concept-map-about-Biochemistry - BorbonAbigail BorbonNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument7 pagesReproductionhernandezlovenson65No ratings yet
- Bio BYJU'S 1 Living OrganismsDocument9 pagesBio BYJU'S 1 Living OrganismsReview ZodiacNo ratings yet
- Class Note 1Document14 pagesClass Note 1sushillai deviNo ratings yet
- Living WorldDocument33 pagesLiving WorldShuryans MishraNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 19 Mar 2022Document7 pagesAdobe Scan 19 Mar 2022Abirami SathishNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument12 pagesHeredity and EvolutionDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- DEVPSYCH 3 - Forming A New LifeDocument4 pagesDEVPSYCH 3 - Forming A New LifeRedgie G. GabaneNo ratings yet
- Population GeneticsDocument16 pagesPopulation Geneticsnandithas175No ratings yet
- My CologyDocument21 pagesMy CologyCarl PinedaNo ratings yet
- Completed Evolution Packet 2017-2018Document42 pagesCompleted Evolution Packet 2017-2018Talijah JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 2Document5 pagesLesson 1 - 2FLORENE BHON GUMAPACNo ratings yet
- Measuring Genetic Biodiversity Classification Adaptation To NicheDocument2 pagesMeasuring Genetic Biodiversity Classification Adaptation To NicheSarah LolyNo ratings yet
- Biochem - Lesson 1&2Document3 pagesBiochem - Lesson 1&2Lester John RagudoNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 7 To 10 Botany LecDocument2 pagesNotes Lesson 7 To 10 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution by Natural SelectionDocument27 pagesTheory of Evolution by Natural Selectionelaine loveluckNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument1 pageAnswer KeyYour boy jj WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument1 pageAnswer KeySamuel SiyumNo ratings yet
- Answer - Key 2 PDFDocument1 pageAnswer - Key 2 PDFTekeria PresleyNo ratings yet
- C8.1 - Intro. To Animal & Plant ReproductionDocument13 pagesC8.1 - Intro. To Animal & Plant ReproductionNURULAIN MOHD ASRINo ratings yet
- Genetics, Evolution, Development, and PlasticityDocument8 pagesGenetics, Evolution, Development, and PlasticityMerryNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: ACTIVITY 1: Plant and Animal Sexual ReproductionDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: ACTIVITY 1: Plant and Animal Sexual ReproductionEunice PaulNo ratings yet
- Population GeneticsDocument22 pagesPopulation GeneticsJ15No ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science (Week 4) - q2Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science (Week 4) - q2Rica ParillaNo ratings yet
- Caracteristicas de Los Seres VivosDocument1 pageCaracteristicas de Los Seres Vivosfloresyack11181No ratings yet
- Scan 08 Oct 2022Document20 pagesScan 08 Oct 2022sahil143psNo ratings yet
- Decline of Induction Capability by Outer Membrane V - 2024 - International BiodeDocument9 pagesDecline of Induction Capability by Outer Membrane V - 2024 - International BiodeLuis GómezNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce VerifiedDocument10 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Verifiedlavi krishnaniNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class NotesDocument19 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Class NotesTripura NeelimaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GENETICSDocument31 pagesLesson 1 GENETICSPewpew IsheeeNo ratings yet
- Living BeingsDocument1 pageLiving Beingsfloresyack11181No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Chapter 1 To 5 Loyola Ec Guide em PDFDocument126 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Chapter 1 To 5 Loyola Ec Guide em PDFjoel john100% (4)
- Ass 2012Document4 pagesAss 2012Ishaan “Toxx” KatariaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 22, 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan Nov 22, 2022ArpithaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument11 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesSexual Reproductionghechchoutang123No ratings yet
- Notes CompanaDocument10 pagesNotes CompanaKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Animal Characteristics 2022Document29 pagesAnimal Characteristics 2022Anisah Nur FatimahNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Organisms.Document3 pagesReproduction in Organisms.hbhaiya643No ratings yet
- Evolution & Speciation: Biological Species ConceptDocument34 pagesEvolution & Speciation: Biological Species ConceptMilka RahmanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledGenesis De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Unique Features of The Plant Life Cycle and Their ConsequencesDocument12 pagesUnique Features of The Plant Life Cycle and Their ConsequencesSushree JnanadaNo ratings yet
- 12th Zoology Chapter 1 To 4 Sura Guide em 214857Document81 pages12th Zoology Chapter 1 To 4 Sura Guide em 214857jeevajeevam2021No ratings yet
- Earth and Life - 2nd Q - Topic1Document5 pagesEarth and Life - 2nd Q - Topic1figuerassandrajuliasaaNo ratings yet
- FBT Lecture 2-1Document32 pagesFBT Lecture 2-1Ananta AnweshaNo ratings yet
- 24 Lecture Presentation 0Document39 pages24 Lecture Presentation 0stri47958No ratings yet
- The Marriage Between Molecular Biology and NutritionDocument37 pagesThe Marriage Between Molecular Biology and NutritionOng Chen MeiNo ratings yet
- FragmentationDocument3 pagesFragmentationTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- EnzimDocument29 pagesEnzimyasmine aurelliaNo ratings yet
- Life Process 8Document38 pagesLife Process 8Hridayangam KashyapNo ratings yet
- Supporting Details About Morphological and Physiological... - Google ScholarDocument1 pageSupporting Details About Morphological and Physiological... - Google ScholarcfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- Biology REVISION - SCIENCE (YT)Document47 pagesBiology REVISION - SCIENCE (YT)jyotiNo ratings yet
- MammaliaDocument8 pagesMammaliaGabrielle ForgetNo ratings yet
- Clinical Research HypertensionDocument4 pagesClinical Research HypertensionJay Linus Rante SanchezNo ratings yet
- NRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDocument5 pagesNRCan's Explosives Eservices - Authorized Products SearchDiego VilaNo ratings yet
- Manual PDFDocument4 pagesManual PDFrpichoNo ratings yet
- English For Business l1 Past Paper Series 2 2012Document9 pagesEnglish For Business l1 Past Paper Series 2 2012GuitargirlMimi0% (1)
- Shamanic HealingDocument41 pagesShamanic HealingMeraki Mary50% (2)
- Bombas SumergiblesDocument79 pagesBombas SumergiblesInstinct_brNo ratings yet
- Divergent Plate BoundaryDocument4 pagesDivergent Plate BoundaryGreg ManNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionDocument5 pagesTop 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionGabaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Revision SheetDocument2 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Revision Sheetyashvibhatia5No ratings yet
- RA For Assessment For Lifting OperationsDocument19 pagesRA For Assessment For Lifting OperationsMohamedSaidNo ratings yet
- Fossils Flashcards 3rd GradeDocument3 pagesFossils Flashcards 3rd Gradeapi-345686634100% (1)
- Modul Science Form 1Document31 pagesModul Science Form 1Norafiza HashimNo ratings yet
- 3att 1435070407870 Katura ResumeDocument2 pages3att 1435070407870 Katura Resumeapi-362299218No ratings yet
- Employment Document Folder ListsDocument90 pagesEmployment Document Folder ListsIsna FauziahNo ratings yet
- Case Study Structure - Sarda Sahayak Pariyojana - Feb 2010Document25 pagesCase Study Structure - Sarda Sahayak Pariyojana - Feb 2010Bhushan Kankal100% (3)
- P4 - Rolled TrufflesDocument4 pagesP4 - Rolled TrufflesWendy JacksonNo ratings yet
- EpitheliumDocument48 pagesEpitheliumdrpankaj28100% (1)
- PRISMA 2020 Flow Diagram For Updated Systematic Reviews Which Included Searches of Databases, Registers and Other SourcesDocument1 pagePRISMA 2020 Flow Diagram For Updated Systematic Reviews Which Included Searches of Databases, Registers and Other SourcesSurya WijayaNo ratings yet
- Social and Self Control TheoryDocument2 pagesSocial and Self Control TheoryKarl Amiel EspirituNo ratings yet
- Thrive The Vegan Nutrition Guide Brendan Brazier.15709 - 1contents - and - IntroductionDocument8 pagesThrive The Vegan Nutrition Guide Brendan Brazier.15709 - 1contents - and - IntroductionCristhian ChávezNo ratings yet
- Father's of Various FieldsDocument5 pagesFather's of Various FieldsAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Industrial HygineDocument33 pagesIndustrial HygineNiraj RanjanNo ratings yet
- HPV and Related Diseases Report HPV Informacion CentreDocument303 pagesHPV and Related Diseases Report HPV Informacion CentreRenée Elizade Martinez-PeñuelaNo ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideDocument11 pagesGas Pressure Regulator Series 240Pl: Serving The Gas Industry WorldwideSandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Demonizing Drugmakers: The Political Assault On The Pharmaceutical Industry, Cato Policy Analysis No. 475Document56 pagesDemonizing Drugmakers: The Political Assault On The Pharmaceutical Industry, Cato Policy Analysis No. 475Cato InstituteNo ratings yet