Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Epc-Module 4 (A)
Epc-Module 4 (A)
Uploaded by
karanphutane2254Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Epc-Module 4 (A)
Epc-Module 4 (A)
Uploaded by
karanphutane2254Copyright:
Available Formats
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
M o dule 4(a) – Negative feedback
Negative Feedback: Four Types of Negative Feedback, VCVS Voltage gain, Other VCVS Equations, ICVS
Amplifier, VCIS Amplifier, ICIS Amplifier (No Mathematical Derivation).
Introduction
Feedback plays an important role in almost all electronic circuits and is invariably used in amplifiers to
improve its performance and to make it more ideal. A feedback amplifier is also called as a closed loop
amplifier, since feedback forms a closed loop between the input and the output. In the process of
feedback, a part of the output (which can be current or voltage) is sampled and fed back to the input of
the amplifier. Hence at the input, there are two signals: input signal and the part of the output which is
fed back to the input (feedback signal).Both these signals may be in phase or out of phase.
Hence there are two categories of feedback as – (i) Positive feedback (ii) Negative feedback
Negative Feedback:
When the input signal and feedback signal are out of phase (feedback signal is subtracted from input
signal), then the feedback is known as negative feedback.
Features of Negative Feedback (Properties of Negative Feedback)
i. Desensitize the gain – make gain less sensitive to variations
ii. Decreased gain
iii. Increased bandwidth
iv. Reduction in non-linear operation
v. Control the input and output resistances
vi. Improvement in noise immunity
vii. Make the amplifier system stable
General feedback Structure
Many practical amplifiers use negative feedback in order to precisely control the gain, reduce
distortion and improve bandwidth. Figure shows the block diagram of an amplifier stage with negative
feedback applied.
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 1
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
The open gain of the amplifier without feedback is A and can be expressed as
The overall gain of the amplifier with feedback is Af or AV(CL) can be expressed as
Hence, the overall gain with negative feedback applied will be less than the gain without feedback.
For A >>1: ➔ Af = (1 / β). The product term Aβ is known as Loop gain of a feedback
amplifier and term (1+ Aβ ) is called as Amount of feedback
Example : (a) An amplifier with negative feedback applied has an open-loop voltage gain
of 50, and (1/10) of its output is fed back to the input . Determine the overall voltage gain
with negative feedback applied. (b)If the amplifier’s open-loop voltage gain increases by
20%, determine the percentage increase in overall voltage gain.
Solution – Given A = 50; β = 0.1
(a) With negative feedback applied the overall voltage gain will be given by:
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 2
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
(b) The new value of open loop voltage gain A1 = A + 0.2A = 1.2A = 1.2(50) = 60
The overall voltage gain with negative feedback
The increase in overall voltage gain, expressed as percentage
The Four Basic Feedback Topologies and their Comparison
Based on the quantity to be amplified (voltage or current) and on the desired form of output (voltage or current)
feedback amplifiers can be classified into four categories –
(i) Voltage Controlled Voltage Source (VCVS) amplifier
(ii) Voltage Controlled Current Source (VCIS) Amplifiers
(iii) Current Controlled Current Source (ICIS) Amplifiers and
(iv) Current Controlled Voltage Source (ICVS) Amplifiers
Voltage Controlled Voltage Source (VCVS) Amplifier
A VCVS is an ideal Voltage amplifier because it has a stabilized voltage gain, infinite
input impedance, and zero output impedance
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 3
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
Current Controlled Current Source (ICIS) Amplifiers
A ICIS is an ideal Current amplifier because it has a stabilized current gain, zero input
impedance, and infinite output impedance.
Voltage Controlled Current Source (VCIS) Amplifier
A VCIS is an ideal Voltage to Current Converter because the input voltage controlling an output
current, has high input impedance, and high output impedance
The conversion factor of the VCIS is called Transconductance, symbolized gm and expressed in
Siemens (mhos).
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 4
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
Current Controlled Voltage Source (ICVS) Amplifiers
A ICVS is an ideal Current to Voltage Converter because the input current controlling an output
voltage, has low input impedance, and low output impedance
The conversion factor of the ICVS is called Transresistance, symbolized rm and expressed in Ohms.
1. Voltage Controlled Voltage Source (VCVS) Amplifier (Voltage Series Feedback Amplifier):
Figure shows the circuit diagram of a VCVS Non-inverting amplifier using voltage series
feedback with a part of the output voltage fed back in series with the input signal, resulting in
an overall gain reduction
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 5
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
Expression for Closed loop Gain :
The closed-loop gain of the amplifier AV(CL) is given by
In the absence of the feedback (Vf = 0),
the output voltage Vout = AVOL Vd = AVOL (V1 – V2)
For an ideal amplifier, AVOL >>1, hence (1+AVOL) = 1
Input Resistance with Feedback Rif :
Consider the Thevenin’s equivalent circuit of non-inverting amplifier. Input resistance with feedback
Zin(CL) is given by
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 6
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
Input resistance of the amplifier with feedback increases by a factor (1+ AVOL )
Output Resistance with Feedback Zout(CL) :
The closed loop output impedence is the overall output impedence looking back into the VCVS amplifier.The
exact equation for this closed-loop output impedence is:
Nonlinear distorsion:
When the input and output signals are not proportional to each other results in nonlinear distortion
which in-turn produces harmonics of the input signal in the output. For instance, if a sinusoidal voltage
signal has a frequency of 1 kHz, the distorted output current will contain sinusoidal signals with frequencies of
1, 2, 3 kHz, and so forth. The fundamental frequency is 1 kHz, and all others are harmonics.
The rms value of all the harmonics measured together indicates how much distortion has occurred and is
known as Harmonic distortion. Harmonic distortion is measured with an instrument called a Distortion
analyzer and can be expressed as
Negative feedback reduces the harmonic distortion and the equation for it is expressed as THDOL
Closed loop Harmonic distortion
where THDOL is open-loop harmonic distortion
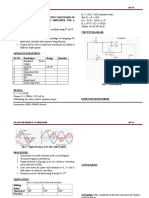
Calculate the feedback fraction, the ideal closed-loop voltage gain, the percent error, and the
exact closed-loop voltage gain Closed loop input and output impedance for the op-amp
circuit shown. Use a typical AVOL of 100,000, Rin =2Mohm, RCM = 200 Mohm and Rout =
75 ohm for the 741C. Suppose the amplifier has an open-loop total harmonic distortion of 7.5
percent. What is the closed-loop total harmonic distortion?
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 7
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
What is the closed loop total harmonic distortion?
2. Current Controlled Voltage Source Amplifier (Transresistance Amplifier)
It has an input current and an output voltage and is called Voltage Shunt Feedback
amplifier. The ICVS amplifier is an almost perfect current-to-voltage converter because it has
zero input impedance and zero output impedance.
The exact output voltage is given by
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 8
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
Where R is is the transresistance.
f
Note - Since the inv- input is a virtual ground to voltage not to current; all of the input current must
flow through the feedback resistor Rf . Since the left end of this resistor is grounded, the magnitude of
the output voltage is given by: Vout = – (iinRf)
The closed loop input and output impedances are given by
The Inverting Amplifier
The inverting amplifier is basically a current to voltage converter is shown below. The closed loop gain of the
amplifier is given
Because of the virtual ground on the inverting input, the input current equals
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 9
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
Problem: Determine the output voltage, Closed loop input and output impedance for the op-amp
circuit shown.
3. The Voltage Controlled Current Source (VCIS) Amplifier (Transconductance Amplifier)
With a VCIS amplifier, an input voltage controls an output current. Because of the heavy negative
feedback in this kind of amplifier, the input voltage is converted to a precise value of output current.
The circuit is basically a voltage-to-current converter. Figure shows a transconductance amplifier with
floating load RL which is acting as the load resistor as well as the feedback resistor. The active output is
not the voltage across (R1 + RL) rather, it is the current through RL. This output current is
stabilized; that is, a specific value of input voltage produces a precise value of output current.
The exact equation for output current is:
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 10
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
The closed loop input and output impedances are given by
Problem: In the given circuit, What is the load current ? The load power? What happens if
the load resistance changes to 4 ohms?
4. The Current Controlled Current Source (ICIS) Amplifier
An ICIS circuit amplifies the input current. Because of the heavy negative feedback, the ICIS amplifier
tends to act like a perfect current amplifier. It has a very low input impedance and a very high output
impedance. Figure shows an inverting current amplifier.
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 11
Electronic principles and circuits (BEC303) 2023-24
The closed-loop current gain is stabilized and given by:
Problem:In the given circuit, What is the load current ? The load power? If the load
resistance changes to 2ohms , what is the load current and power?
Suma C, Dept of ECE, AIT Page 12
You might also like
- Design of A Discrete BJT Operational AmplifierDocument6 pagesDesign of A Discrete BJT Operational Amplifierjonesy5000No ratings yet
- An Overview of Teaching Techniques in Basic Electronics and Communication Engineering.Document33 pagesAn Overview of Teaching Techniques in Basic Electronics and Communication Engineering.Hartbeet - SandalwoodNo ratings yet
- Lagos City Polytechnic: Lecture NoteDocument28 pagesLagos City Polytechnic: Lecture NoteOlatidoye EzekielNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifierDocument6 pagesFeedback AmplifierSaadnan TahsinNo ratings yet
- Feedback AmplifiersDocument36 pagesFeedback Amplifierssaravananvaratharajan4No ratings yet
- Feedback Amplifiers NoteDocument6 pagesFeedback Amplifiers NoteSaadnan TahsinNo ratings yet
- Topics To Be Discussed: Operational Amplifiers - Parameters - Characteristics - Configurations - CircuitsDocument17 pagesTopics To Be Discussed: Operational Amplifiers - Parameters - Characteristics - Configurations - CircuitsRajathos OsNo ratings yet
- Inverting AmplifierDocument9 pagesInverting AmplifierKenzie WalipiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4-Multistage AmplifierDocument29 pagesTopic 4-Multistage AmplifierSha Edd'sNo ratings yet
- AB 16 Wzmacniacz Ze Wspolnym Kolektorem 2Document21 pagesAB 16 Wzmacniacz Ze Wspolnym Kolektorem 2ReddyKishoreNo ratings yet
- MC Electronic Circuit AnalysisDocument7 pagesMC Electronic Circuit AnalysisMelvin Garcia QuirosNo ratings yet
- V Unit OscillatorsDocument91 pagesV Unit OscillatorsÑaýaň ŇăwğhårēNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Ii Unit 1Document53 pagesElectronic Circuits Ii Unit 1Md. Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lic Lab ManualDocument89 pagesLic Lab ManualKALAIMATHI100% (1)
- Analog CircuitsDocument92 pagesAnalog Circuitsmaganga magangaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Intro To Op AmpsDocument14 pagesLecture 1 - Intro To Op AmpsRap JaviniarNo ratings yet
- Elecs OsciDocument9 pagesElecs Oscihillary100% (1)
- BE Unit-IVDocument13 pagesBE Unit-IVjagadeesh KaruturiNo ratings yet
- ELEC 310 - Week 3: Amplifier SystemDocument8 pagesELEC 310 - Week 3: Amplifier System( L)paino(L)No ratings yet
- Op-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpDocument7 pagesOp-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpSteven Nelson100% (1)
- Feed Back SystemsDocument26 pagesFeed Back SystemsDhanushka MadushanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Feedback AmplifiersDocument42 pagesChapter One Feedback AmplifiersTemesgen MekonenNo ratings yet
- Ec8353-Electronics Devices and Circuits: Prepared by Mrs..G.KAVITHA, Ap/EceDocument21 pagesEc8353-Electronics Devices and Circuits: Prepared by Mrs..G.KAVITHA, Ap/EceSolangkilisaravananNo ratings yet
- Lab - 01 (BME-202)Document9 pagesLab - 01 (BME-202)Darakhshan MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Op-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpDocument11 pagesChapter 1: Op-Amps: I. Practical Op-Amprockrockyrocker123No ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Practice Lab: Experiment-6: Basic Operational AmplifiersDocument10 pagesAnalog Circuits Practice Lab: Experiment-6: Basic Operational AmplifiersDeepikaNo ratings yet
- EC - Unit 4 - Negative FeedbackDocument12 pagesEC - Unit 4 - Negative Feedbacknanobala15No ratings yet
- Ec2251 Electronic CircuitsDocument23 pagesEc2251 Electronic Circuitssatyanarayana12No ratings yet
- EC8452 2marks PDFDocument21 pagesEC8452 2marks PDFKaviyaNo ratings yet
- B.Sc.-Semester - VI: Physics (Paper - II)Document26 pagesB.Sc.-Semester - VI: Physics (Paper - II)Vivek ChardeNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics II, ECE-204: Chapter-1: Feedback ConceptsDocument31 pagesAnalog Electronics II, ECE-204: Chapter-1: Feedback ConceptstsegayNo ratings yet
- EC2 NotesDocument89 pagesEC2 NotesSalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- Feedback: Depending On The Relative PolarityDocument41 pagesFeedback: Depending On The Relative PolarityAbcdNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument6 pagesBJTengineerluvNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Module1 (B) 2023-24 AmplifiersDocument5 pagesBasic Electronics Module1 (B) 2023-24 AmplifierssathwikdbhatNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Unit-4Document81 pagesOp-Amp Unit-4ShaktiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document24 pagesChapter 2Bharat G HegdeNo ratings yet
- By: Gebremariam Fisseha Adigrat University, Ethiopia 2010E.CDocument21 pagesBy: Gebremariam Fisseha Adigrat University, Ethiopia 2010E.CmillionNo ratings yet
- 4.1. Feedback AmplifiersDocument22 pages4.1. Feedback AmplifiersRohit Kumar100% (2)
- Ec6401 Electronic Circuits II QBW (r2013)Document18 pagesEc6401 Electronic Circuits II QBW (r2013)Bharath PonNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier BasicsDocument8 pagesOperational Amplifier BasicsT BlackNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifiersDocument16 pagesOperational Amplifiersvishal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument16 pagesUnit Iiikannan305No ratings yet
- Experiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveDocument13 pagesExperiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveskmrajkumarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Part 2 Amplifiers Presentation PDFDocument24 pagesModule 1 Part 2 Amplifiers Presentation PDFayushsingh102005No ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument44 pagesChapter OneDaniel TeferiNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifiersDocument16 pagesOperational Amplifiershimangshu1234No ratings yet
- شرح الكترونيات 1 AmplifiersDocument43 pagesشرح الكترونيات 1 AmplifiersAboodA.KhraishiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document13 pagesChapter 03Tushar BhoiNo ratings yet
- Uit RGPV Project For BEDocument13 pagesUit RGPV Project For BEraviteja62No ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier BasicsDocument8 pagesOperational Amplifier BasicsEum MavNo ratings yet
- 90 1702009711439Document20 pages90 1702009711439Fairoz FairozNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9: Feedback AmplifierDocument55 pagesChapter-9: Feedback AmplifierKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Feedback AMplifiersDocument22 pagesUnit 3 Feedback AMplifiersvijay78rNo ratings yet
- Amplifiers 18 10 2010Document44 pagesAmplifiers 18 10 2010Madan R HonnalagereNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers Are Linear Devices That Have All The PropertiesDocument10 pagesOperational Amplifiers Are Linear Devices That Have All The PropertiesNagamani VNo ratings yet
- Basic Operational Amplifiers: 1 Objective/AIMDocument15 pagesBasic Operational Amplifiers: 1 Objective/AIMVinay Noel AtluriNo ratings yet
- Feedback in AmplifiersDocument2 pagesFeedback in AmplifiersDinesh VelNo ratings yet
- Module 4 18ELN14Document20 pagesModule 4 18ELN14RickyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- PG5 UsDocument2 pagesPG5 Usmuhammadmosab0No ratings yet
- AC BJT Analysis Lecture 2Document6 pagesAC BJT Analysis Lecture 2Xxx CccNo ratings yet
- Date: 08/02/2021 Aim:: Experiment-5Document6 pagesDate: 08/02/2021 Aim:: Experiment-5Vishal ManwaniNo ratings yet
- CMOS AmplifiersDocument39 pagesCMOS AmplifiersLaura MendozaNo ratings yet
- LIC LAB REPORT NewDocument27 pagesLIC LAB REPORT NewWINORLOSENo ratings yet
- The Transistor Astable Multi VibratorDocument6 pagesThe Transistor Astable Multi VibratorTavleen KaurNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Oscillator Sem II 2015 UPLOADDocument53 pagesCH 4 - Oscillator Sem II 2015 UPLOADdemonones100% (1)
- Record of Attendance and Assessment - A LabDocument19 pagesRecord of Attendance and Assessment - A Labaarthir88No ratings yet
- Mel ZG632Document10 pagesMel ZG632ANo ratings yet
- Assessment7 Globiogo CpE32Document3 pagesAssessment7 Globiogo CpE32Jastine GlobiogoNo ratings yet
- 25 Input Voltage: 50 Igbt ResultDocument3 pages25 Input Voltage: 50 Igbt ResultEdwin KevynNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument11 pagesWein Bridge OscillatorDimas RioNo ratings yet
- BEEE 2353 - 2354 - Lab 4 Wein-Bridge OscillatorDocument4 pagesBEEE 2353 - 2354 - Lab 4 Wein-Bridge Oscillatorafieq 1310No ratings yet
- JBOT - An Easy QRP Linear AmplifierDocument3 pagesJBOT - An Easy QRP Linear AmplifierJuan Manuel MartorellNo ratings yet
- AC CharsDocument43 pagesAC CharsDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. Multi - Stage Transistor Amplifers - For UploadingDocument114 pagesLecture 4. Multi - Stage Transistor Amplifers - For Uploading22029013 Khuất Nguyễn Diệu TrangNo ratings yet
- Conclusion Elec Exp2Document1 pageConclusion Elec Exp2Gena Lapuz100% (2)
- Wide Swing Cascode Current MirrorDocument4 pagesWide Swing Cascode Current MirrorSunil M. PaiNo ratings yet
- 3.RC Phase ShiftDocument3 pages3.RC Phase ShiftpoojaNo ratings yet
- Unitt 4Document7 pagesUnitt 4lalit24006No ratings yet
- SS Opamp V5i Datasheet V1.0Document2 pagesSS Opamp V5i Datasheet V1.0Alberto VazNo ratings yet
- ECA Mid-II Online BitsDocument22 pagesECA Mid-II Online Bitslucky jNo ratings yet
- Ac Circuit Simulation: i (t) =I sin (ωt) =I si n (2 π f t)Document4 pagesAc Circuit Simulation: i (t) =I sin (ωt) =I si n (2 π f t)M.USMAN BIN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Square Wave Generator Using Op-AMP: How To Make An Astable or Free Running Multi Vibrator Using 741 Op-Amp ?Document2 pagesSquare Wave Generator Using Op-AMP: How To Make An Astable or Free Running Multi Vibrator Using 741 Op-Amp ?Prathyusha YedlaNo ratings yet
- 1.CMOS VLSI DesignDocument2 pages1.CMOS VLSI DesignSYAMALA100% (1)
- Ade Q3Document1 pageAde Q3Nitish KumarNo ratings yet
- JMPGuitars 18W Xtra TMB LayoutDocument1 pageJMPGuitars 18W Xtra TMB LayoutRenan Franzon GoettenNo ratings yet
- Bitx3B Exiter Updated Sch.2MAY2014Document1 pageBitx3B Exiter Updated Sch.2MAY2014DARU WIRANTONo ratings yet
- BJT Written Report Group 8Document11 pagesBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemNo ratings yet