Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Based Discussion For Palliative Care
Case Based Discussion For Palliative Care
Uploaded by
nathanaellee920 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThis document discusses three palliative care scenarios and provides relevant clinical details for each case.
Scenario 1 involves a 41-year-old man with metastatic colon cancer who started opioids 5 days ago and is now experiencing nausea, abdominal discomfort, and dehydration.
Scenario 2 is a 74-year-old man with prostate cancer and bone metastases causing lower back pain. He is taking oral opioids and NSAIDs with intermittent relief of severe pain.
Scenario 3 is a 68-year-old man with COPD who is increasingly short of breath and now immobile. He has been hospitalized several times recently for exacerbations and is anxious about his future health status.
Original Description:
Global Health
Original Title
Case based discussion for palliative care
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses three palliative care scenarios and provides relevant clinical details for each case.
Scenario 1 involves a 41-year-old man with metastatic colon cancer who started opioids 5 days ago and is now experiencing nausea, abdominal discomfort, and dehydration.
Scenario 2 is a 74-year-old man with prostate cancer and bone metastases causing lower back pain. He is taking oral opioids and NSAIDs with intermittent relief of severe pain.
Scenario 3 is a 68-year-old man with COPD who is increasingly short of breath and now immobile. He has been hospitalized several times recently for exacerbations and is anxious about his future health status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCase Based Discussion For Palliative Care
Case Based Discussion For Palliative Care
Uploaded by
nathanaellee92This document discusses three palliative care scenarios and provides relevant clinical details for each case.
Scenario 1 involves a 41-year-old man with metastatic colon cancer who started opioids 5 days ago and is now experiencing nausea, abdominal discomfort, and dehydration.
Scenario 2 is a 74-year-old man with prostate cancer and bone metastases causing lower back pain. He is taking oral opioids and NSAIDs with intermittent relief of severe pain.
Scenario 3 is a 68-year-old man with COPD who is increasingly short of breath and now immobile. He has been hospitalized several times recently for exacerbations and is anxious about his future health status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
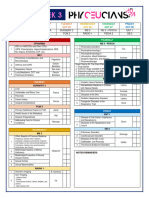
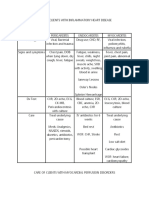
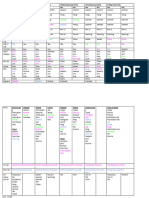
Case-based discussion for palliative care
Scenario 1 Scenario 2 Scenario 3
Case 41 man with metastatic colon ca. started 74 male with prostate ca and bone mets; 68 male at respiratory clinic; dx with
OPIOIDS 5 days ago, now c/o nausea, has lower back pain (lumbar spine bone COPD in 2010 – reduced QOL; SOB at
abdominal discomfort, he is pale, mets); pain onset is intermittent and suddenrest, worsening in the past 4 weeks, now
dehydrated. (lasts HOURS). Regular oral IBUPROFEN 400 immobile due to SOB; 3 admissions in
1. Dehydrated mg TDS and oral immediate release past 5 months due to AECOPD; now
2. Nauseated morphine PRN 10mg BD reluctant to go to ED for future
3. Discomfort 1. Lower back pain episodes. Anxious about his future.
4. Pale 2. Prostatism 1. DVT/PE
5. Anorexia 3. UTI symptoms 2. SOB
4. SOB due to severe pain 3. Pressure sores
5. Immobility (loss of function) 4. Depression
6. LGIB/UGIB 5. Side effect of steroids
3 further 1. Passing flatus, intestinal 1. Features of hypercalcemia 1. Medication history
details in obstruction, constipation symptoms 2. Social background
history 2. Urine and bowel output 2. Prostatism and UTI sx 3. Advanced directive because
3. Opioid type + dose + usage of 3. Incontinence due to spinal cord worried about future options
breakthrough pain involvement esp if new symptoms of 4. Features of cor pulmonale
4. Poor oral intake back pain (saddle anesthesia, new 5. Features of DVT
5. Hypercalcemia symptoms urinary retention) 6. Risk factors for DVT
6. Any recent UGIB/LGIB – taking any 4. CES symptoms like saddle 7. Family history of clotting
NSAIDS for painkiller anesthesia disorders
8. Any recent lung infections –TB
(MM – URINARY OVERFLOW symptoms, LRTI
FOLLOWED BY URINARY RETENTION 9. Vaccination history
DEPENDING ON LEVEL OF CORD 10. Home conditions – for
AFFECTED) domiciliary LTOT
DDX 1. Colon ca 1. Pathological fractures due to bone 1. AECOPD
2. Opioid side effect mets 2. Corpulmonale decompensating
3. Liver mets 2. Inadequate analgesia 3. PE microinfarcts
3. MM/TB SPINE 4. Anxiety
Investigations CECT Spine XR followed by Spine CT lateral i/v/o FEV as palliative care indictor and
AXR cord involvement prognosticator
PR CXR
Blood and sputum C/S
3 main steps 1. Fluid for dehydration 1. Analgesia – morphine 10MG QID 1. Titrated oxygen +chest physio +
of 2. If constipation – stool softener 2. Bisphosphonates to stabilize DVT prx
management 3. Nausea – fractures 2. Counsel for LTOT after
in each case 4. Dexamethasone to reduce 3. Add 2.5mg to established dose and discussing prognosis
gastrointestinal edema reassess after 24 hours , then 3. Discuss prognosis with patient
5. Surgical – stenting OR palliative recalculate rescue dose 4. Family conference to discuss his
laparoscopic ileostomy 4. Palliative RTX to reduce pain due to health before counselling for
compression of bone/nerves by LTOT
mass/ improve lung obstruction 5. Advanced care planning
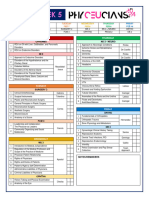
5 common medications in palliative care with side effects
1 NSAIDS GIB, renal toxicity
2 ANTIEMETICS Seizure threshold reduced, constipation
3 OPIOIDS Constipation, nausea, respiratory depression
4 STEROIDS Cushingoid
5 LAXATIVES Bloating, cramping, diarrhea
5 conditions excluding malignancy and outline one symptom relevant to each condition which needs palliation
1 HIV Pruritus, persistent cough, diarrhea, fatigue
2 CCF NHYA ¾ SOB
3 COPD GOLD D (<30% SOB
FEV1)
4 ADVANCED DEMENTIA Dysphagia
5 Motor neurone disease Dysphagia, respiratory failure
You might also like
- DR - Mo Sobhy: Simman Examination & Combined & Teaching ProceduresDocument1 pageDR - Mo Sobhy: Simman Examination & Combined & Teaching ProcedurespeterNo ratings yet
- Disease Signs and Symptoms Lab Findings Pathophysiology Nursing Interventions Drug Study/ NRSG ResponsibilitiesDocument37 pagesDisease Signs and Symptoms Lab Findings Pathophysiology Nursing Interventions Drug Study/ NRSG ResponsibilitiesEmmanuel Valmonte100% (11)
- The Use of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine in The Treatment of 5 Cases of Neoplastic Bone DiseaseDocument12 pagesThe Use of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine in The Treatment of 5 Cases of Neoplastic Bone DiseaseDonnaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Status Epilepticus)Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (Status Epilepticus)Marvin John Labiano33% (3)
- History TakingDocument130 pagesHistory Takingvwpwh86gfhNo ratings yet
- Wilm's Tumor EtcDocument5 pagesWilm's Tumor EtcDanica BonNo ratings yet
- Symptom Flow Chart (Difficulty Breathing)Document2 pagesSymptom Flow Chart (Difficulty Breathing)Jeff ZhouNo ratings yet
- Mapping Aqsa 2, Sabtu 06 November 2021Document10 pagesMapping Aqsa 2, Sabtu 06 November 2021Febbby Mutia SafiraNo ratings yet
- Addison Dse & Cushing SyndromeDocument2 pagesAddison Dse & Cushing SyndromeLot RositNo ratings yet
- BCR 2017 221405.fullDocument6 pagesBCR 2017 221405.fullAlinDorneanuNo ratings yet
- IBD - Role PlayDocument2 pagesIBD - Role Playnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Lecture ListDocument2 pagesLecture ListYavani KulasinghamNo ratings yet
- Guide To Case Presentation-1Document36 pagesGuide To Case Presentation-1Amanda Rodriguez TejedaNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument45 pagesPharmacologySaurabh PaudyalNo ratings yet
- Case Based Discussion For NeurologyDocument2 pagesCase Based Discussion For Neurologynathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Viva 1 Group C FammedDocument6 pagesViva 1 Group C FammedSheera EiyraaNo ratings yet
- Sweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesDocument7 pagesSweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesAnonymous GfqHQ5SNwNo ratings yet
- MR 22-11-22Document30 pagesMR 22-11-22abeeNo ratings yet
- Lung AuscultogramDocument35 pagesLung AuscultogramRocio SandersNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug Study FormKuro Mufu100% (2)
- Spinal AnaesthesiaDocument2 pagesSpinal AnaesthesiaMusfique RashidNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Activity 2 Drug Study Ciprofloxacin PaxilDocument6 pagesModule 3 Activity 2 Drug Study Ciprofloxacin PaxilEugene MananganNo ratings yet
- Abdomen OSCE (Keys)Document13 pagesAbdomen OSCE (Keys)Saran KumarNo ratings yet
- First Aid & Management of Snake BitesDocument38 pagesFirst Aid & Management of Snake BitesDeepak BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Ms NotesDocument49 pagesCompilation of Ms Noteschoyaks100% (1)
- Aiims NOV 2010: SolutionsDocument25 pagesAiims NOV 2010: SolutionsPranav DevaniNo ratings yet
- Module 17 Part 2 Ratio 19 22 EndoDocument102 pagesModule 17 Part 2 Ratio 19 22 EndoLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Whole Case1 DoneDocument5 pagesWhole Case1 Donejovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Git SystemDocument16 pagesGit SystemedithlucnasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyEden Astred ObilloNo ratings yet
- Haad RN QuestionDocument7 pagesHaad RN Questionsabu0099No ratings yet
- RTM 5Document7 pagesRTM 5Christine Danica BiteraNo ratings yet
- Adibah Binti Aminuddin - 2020611856Document7 pagesAdibah Binti Aminuddin - 2020611856MOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- Gastric Cancer: Surgical ManagementDocument3 pagesGastric Cancer: Surgical ManagementMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument6 pagesName of DrugGail Leslie HernandezNo ratings yet
- Os Ce Stem Session 1Document6 pagesOs Ce Stem Session 1Isaac OngNo ratings yet
- Lupus: Therapy T.Document10 pagesLupus: Therapy T.Sharifah ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cue and Clue Problem List and Initial Diagnosis PlanningDocument2 pagesCue and Clue Problem List and Initial Diagnosis PlanningWilujeng AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Functional Gi DisordersDocument29 pagesFunctional Gi DisordersSyafril LubisNo ratings yet
- Advisor Dikara W.S. Maulidy:: DR., SP - PDDocument12 pagesAdvisor Dikara W.S. Maulidy:: DR., SP - PDKikiNo ratings yet
- Exam Week 3 v2Document1 pageExam Week 3 v2Paolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Exam Week 5 V2Document1 pageExam Week 5 V2Paolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Pathophysiologic Effects of Cancer and Treatment ModalitiesDocument2 pagesMod 1 Pathophysiologic Effects of Cancer and Treatment ModalitiesJorese Hannah VictorinoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Devang Rana-Prescription and CriticismDocument60 pagesDr. Devang Rana-Prescription and CriticismSaumil DarjiNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Document7 pagesMed Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Maxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Cue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX P.Mo Pharmacology P.MoDocument4 pagesCue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX P.Mo Pharmacology P.MoNaura AnindyaNo ratings yet
- Contora, Isah TblrenalDocument7 pagesContora, Isah TblrenalisahNo ratings yet
- Serum Plasma Minus Fibrinogen Albumin Provides Osmotic PressureDocument13 pagesSerum Plasma Minus Fibrinogen Albumin Provides Osmotic PressureFreeNursingNotesNo ratings yet
- Chirurgia Geriatrica ADDOME ACUTODocument53 pagesChirurgia Geriatrica ADDOME ACUTOzemby87No ratings yet
- TOACSDocument18 pagesTOACSarjumandNo ratings yet
- OSPE Peads Medicine PDFDocument54 pagesOSPE Peads Medicine PDFKamran MallickNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Document4 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)annie kolandjianNo ratings yet
- Medurg MidtermDocument4 pagesMedurg Midtermmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Panduan Praktik Klinis (PPK) : Bedah (ICD 10: C73) 1. Pengertian 2. Anamnesis 3. Pemeriksaan FisikDocument2 pagesPanduan Praktik Klinis (PPK) : Bedah (ICD 10: C73) 1. Pengertian 2. Anamnesis 3. Pemeriksaan Fisiksoedjono indraNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post OperationDocument5 pagesPre and Post Operationhacker ammerNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY HXDocument13 pagesRESPIRATORY HXOnly MrcpNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Cardiovascular Research and Therapeutics: Molecular and Nutraceutical PerspectivesFrom EverandAdvancements in Cardiovascular Research and Therapeutics: Molecular and Nutraceutical PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandUlcerative Colitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- GERD: A New Understanding of Pathology, Pathophysiology, and TreatmentFrom EverandGERD: A New Understanding of Pathology, Pathophysiology, and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of the Enteric Nervous System: A Basis for Understanding Functional DiseasesFrom EverandPathophysiology of the Enteric Nervous System: A Basis for Understanding Functional DiseasesRobin SpillerNo ratings yet
- Cestode InfectionsDocument11 pagesCestode Infectionsnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- West Nile VirusDocument42 pagesWest Nile Virusnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0166354222002868 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0166354222002868 Mainnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- PNTD 0006062Document27 pagesPNTD 0006062nathanaellee92No ratings yet
- AmoebiasisDocument56 pagesAmoebiasisnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- SRF 2304073085 231121152844Document1 pageSRF 2304073085 231121152844nathanaellee92No ratings yet
- COPD-ASTHMA Patient HistoryDocument3 pagesCOPD-ASTHMA Patient Historynathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis Management PDF 66141712632517Document31 pagesUlcerative Colitis Management PDF 66141712632517nathanaellee92No ratings yet
- 1 ClubbingDocument10 pages1 Clubbingnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- AWARE PrintDocument8 pagesAWARE Printnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- COUGHDocument3 pagesCOUGHnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Introduction To Humanitarian Health Programming by David Wightwick (UK-MED) Audio TranscriptionDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Humanitarian Health Programming by David Wightwick (UK-MED) Audio Transcriptionnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Bmjopen 2022 April 12 4 Inline Supplementary Material 2Document4 pagesBmjopen 2022 April 12 4 Inline Supplementary Material 2nathanaellee92No ratings yet
- JAUNDICE - Role PlayDocument2 pagesJAUNDICE - Role Playnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- DIET 1 Communications Upto 18 2 25Document6 pagesDIET 1 Communications Upto 18 2 25nathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Case Based Discussion For NeurologyDocument2 pagesCase Based Discussion For Neurologynathanaellee92No ratings yet
- 3rd Week March 2024Document3 pages3rd Week March 2024nathanaellee92No ratings yet
- FireShot Pro Webpage Capture 278 - 'Section - Microscopy - Practice I 2023-24 DTMH - Course Hub I Moodle2' - Moodle - Gla.ac - UkDocument4 pagesFireShot Pro Webpage Capture 278 - 'Section - Microscopy - Practice I 2023-24 DTMH - Course Hub I Moodle2' - Moodle - Gla.ac - Uknathanaellee92No ratings yet
- DIET 1 2024 Communications Collections ThuDocument5 pagesDIET 1 2024 Communications Collections Thunathanaellee92No ratings yet
- FireShot Pro Webpage Capture 280 - 'Section - Revision Quizzes I 2023-24 DTMH - Course Hub I Moodle2' - Moodle - Gla.ac - UkDocument2 pagesFireShot Pro Webpage Capture 280 - 'Section - Revision Quizzes I 2023-24 DTMH - Course Hub I Moodle2' - Moodle - Gla.ac - Uknathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Migration and Refugee Health by Teresa Afonso (UK-MED) Audio TranscriptionDocument27 pagesMigration and Refugee Health by Teresa Afonso (UK-MED) Audio Transcriptionnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Risk Communication & Community Engagement by Diana Maddah (UK-MED) Audio TranscriptionDocument28 pagesRisk Communication & Community Engagement by Diana Maddah (UK-MED) Audio Transcriptionnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Sustainability Capacity Building by Michelle Hanegård (UK-MED) Audio TranscriptionDocument23 pagesSustainability Capacity Building by Michelle Hanegård (UK-MED) Audio Transcriptionnathanaellee92No ratings yet
- Dental Accreditation StandardsDocument66 pagesDental Accreditation Standardsdhir.ankurNo ratings yet
- Evans Et Al-2014-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDocument48 pagesEvans Et Al-2014-Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsIndah KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- RKNLKNKL 255Document2 pagesRKNLKNKL 255Adam AdamakoNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument80 pagesStress ManagementJitendra Bhatia100% (1)
- DR - Kavita Priya Iicm 1Document68 pagesDR - Kavita Priya Iicm 1Kavita PriyaNo ratings yet
- MalaysiakuDocument50 pagesMalaysiakuImam SyafaatNo ratings yet
- Prosiding-ASF 2017 OK - Compressed Compressed-1 PDFDocument430 pagesProsiding-ASF 2017 OK - Compressed Compressed-1 PDFLisda MariaNo ratings yet
- Singlife Philippines Medical Insurance PolicyDocument131 pagesSinglife Philippines Medical Insurance PolicyayakentNo ratings yet
- Medical AbbreviationsDocument54 pagesMedical AbbreviationsHardeep Singh BaliNo ratings yet
- Telephone Directory - 2021Document34 pagesTelephone Directory - 2021margarita BelleNo ratings yet
- Right Ventricular Function and Failure: Special ReportDocument10 pagesRight Ventricular Function and Failure: Special ReportAny CórdovaNo ratings yet
- EpidemiologyDocument23 pagesEpidemiologyBabita DhruwNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Manifestations of Down Syndrome: ReviewDocument6 pagesEndocrine Manifestations of Down Syndrome: ReviewDaimon MichikoNo ratings yet
- Post Abortion CareDocument35 pagesPost Abortion CareNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Hunter2019 PDFDocument15 pagesHunter2019 PDFCarlos Andrés BernalNo ratings yet
- The Work of The National Patient Safety Agency: Joan Russell Safer Practice Lead-Emergency CareDocument43 pagesThe Work of The National Patient Safety Agency: Joan Russell Safer Practice Lead-Emergency CareMohammed HammedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Patient SafetyDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Patient SafetySarah AjodhaNo ratings yet
- Glycemic Control (3) - 1Document17 pagesGlycemic Control (3) - 1robert mbwamboNo ratings yet
- NMC Resit Registration RGNDocument7 pagesNMC Resit Registration RGNIgnatius Appiah AcheampongNo ratings yet
- Holistic Handbook: Andrew Williams, JRDocument32 pagesHolistic Handbook: Andrew Williams, JRAndrew Williams JrNo ratings yet
- CCS Content Outline Update 090718Document2 pagesCCS Content Outline Update 090718Sundarajan ManiNo ratings yet
- Malignant HyperthermiaDocument7 pagesMalignant HyperthermiaarbntmareNo ratings yet
- The Homoeopathic Physician Vol 1 Issue 1Document42 pagesThe Homoeopathic Physician Vol 1 Issue 1Victoria GomezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Fungal EndocarditisDocument9 pagesPediatric Fungal EndocarditisGuntur Marganing Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Quarantine and Isolation - CDCDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 Quarantine and Isolation - CDCFraulein LiNo ratings yet
- 52389924-IV-therapy NotesDocument57 pages52389924-IV-therapy Notesrye08No ratings yet
- 10 Personality DisorderDocument3 pages10 Personality DisorderaninNo ratings yet
- AMC Recall Questions July 20101Document4 pagesAMC Recall Questions July 20101elboss18No ratings yet
- Abvd Chemotherapy RegimenDocument5 pagesAbvd Chemotherapy Regimenmarik0No ratings yet