Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SQL
SQL
Uploaded by
Yitages kefelew0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesThe document discusses statistical quality control procedures used by companies to minimize costs and risks when testing product samples. It provides three examples where companies test samples of light bulbs, cups, and plates to determine whether entire batches should be accepted or rejected based on the sample results. The document notes that sampling involves costs and risks of wrongly accepting or rejecting products. It states that the aim of statistical quality control is to develop procedures that have low costs, low producer risks, and low buyer risks. Finally, it outlines that statistical quality control has two main areas - statistical process control which monitors manufacturing quality, and acceptance sampling which investigates final products to determine batch acceptance.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses statistical quality control procedures used by companies to minimize costs and risks when testing product samples. It provides three examples where companies test samples of light bulbs, cups, and plates to determine whether entire batches should be accepted or rejected based on the sample results. The document notes that sampling involves costs and risks of wrongly accepting or rejecting products. It states that the aim of statistical quality control is to develop procedures that have low costs, low producer risks, and low buyer risks. Finally, it outlines that statistical quality control has two main areas - statistical process control which monitors manufacturing quality, and acceptance sampling which investigates final products to determine batch acceptance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesSQL
SQL
Uploaded by
Yitages kefelewThe document discusses statistical quality control procedures used by companies to minimize costs and risks when testing product samples. It provides three examples where companies test samples of light bulbs, cups, and plates to determine whether entire batches should be accepted or rejected based on the sample results. The document notes that sampling involves costs and risks of wrongly accepting or rejecting products. It states that the aim of statistical quality control is to develop procedures that have low costs, low producer risks, and low buyer risks. Finally, it outlines that statistical quality control has two main areas - statistical process control which monitors manufacturing quality, and acceptance sampling which investigates final products to determine batch acceptance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Example 2.
An electrical company makes light
bulbs that are supposed to have an average life time
of 1000 hours. A buyer intends to buy a batch of
10,000 bulbs. The buyer first test a sample of 100
light bulbs. If they have a mean life time of 1000
hours he accepts the batch, otherwise the batch is
rejected.
Example 3. A company makes cups and plates. Some
of cups might be chipped or cracked. A sample will be
taken to cheek the proportion of cracked cups. If this is
above a certain value the process must be adjusted.
In all above three examples
There is a cost involving in sampling.
There is a decision to be made that can result in an
error.
Wrongly rejects a good product - supplier or
producer risk.
Wrongly accept a bad product - or
risk.
The aim is to develop statistical procedures that have
Low cost i.e. the ability to minimize cost.
Low producer risk.
Low buyers risk.
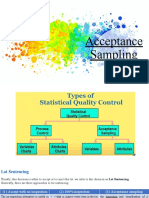
Statistical quality control can be divided into two main
areas.
1. Statistical process control
This involves investigating the procedures used
during the manufacturing process.
Monitor the quality of manufacturing process.
2. Acceptance sampling
This includes investigating a final product and deciding
whether or not the final product is of acceptable
quality.
The objective is only to pass a judgment on lots
(batch) of products.
You might also like
- Acceptance Sampling Plans: SupplementDocument15 pagesAcceptance Sampling Plans: SupplementAntonio Palomares DiazNo ratings yet
- Sampling Plan PDFDocument13 pagesSampling Plan PDFYuliyanto NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Acceptance SamplingDocument10 pagesSeminar On Acceptance SamplingTaran bolaNo ratings yet
- How Many Samples To InspectDocument9 pagesHow Many Samples To InspectRudi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- The Course Is Designed To Provide Quality PractitionersDocument5 pagesThe Course Is Designed To Provide Quality PractitionersRabia ZulqarnainNo ratings yet
- Unified HomeworkDocument10 pagesUnified HomeworkVinicio CastroNo ratings yet
- Supplement To Chapter 9Document2 pagesSupplement To Chapter 9hello_khayNo ratings yet
- Lecture On A - SamplingDocument10 pagesLecture On A - SamplingJasim UddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Acceptance SamplingDocument97 pagesChapter 9 Acceptance Samplingk.ghanemNo ratings yet
- Acceptance SamplingDocument22 pagesAcceptance SamplingAby MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Chapter Six Acceptable SamplingDocument27 pagesChapter Six Chapter Six Acceptable Samplingzewdu mekonnenNo ratings yet
- SQC Chapter 4Document74 pagesSQC Chapter 4joy fulNo ratings yet
- Acceptance SamplingDocument9 pagesAcceptance SamplingTJ 17 ChannelNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Quality and Quality Control: Quality, Sample Acceptance, Sampling PlanDocument44 pagesUnit 3 Quality and Quality Control: Quality, Sample Acceptance, Sampling Planjawaharkumar MBANo ratings yet
- IMChap 010Document46 pagesIMChap 010Jatinder KumarNo ratings yet
- IQC CH 5Document10 pagesIQC CH 5AKSHIT 12No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Acceptance Sampling Plans: StructureDocument18 pagesUnit 5 Acceptance Sampling Plans: Structurevinay100% (2)
- Module 4 - Sampling InspectionDocument16 pagesModule 4 - Sampling InspectionAmogh Bhaskar100% (1)
- Mohamed Ahmed Hassan (P8) : Eng: Alaa HamadaDocument12 pagesMohamed Ahmed Hassan (P8) : Eng: Alaa HamadaMedo ElzaeemNo ratings yet
- SQC (Chapter 1)Document47 pagesSQC (Chapter 1)Yitages kefelewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Specifying Quality For Tourism and Hospitality ServicesDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Specifying Quality For Tourism and Hospitality ServicesMaureen AlmazarNo ratings yet
- SQL IntroductionDocument46 pagesSQL IntroductionYitages kefelewNo ratings yet
- Sampling For Oil and Gas AnalysisDocument7 pagesSampling For Oil and Gas AnalysisBenito CameñaNo ratings yet
- 3 Acceptancesampling 130413113554 Phpapp02Document16 pages3 Acceptancesampling 130413113554 Phpapp02Sandeep ShardaNo ratings yet
- AQL GoodoneDocument4 pagesAQL GoodonemehrasunilNo ratings yet
- 2011 Enciclopedia-Mine ASG PDFDocument5 pages2011 Enciclopedia-Mine ASG PDFAhmed OmarNo ratings yet
- Facultad de Ingenieria de Industrias AlimentariasDocument4 pagesFacultad de Ingenieria de Industrias AlimentariasHasler Machaca ParedesNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document34 pagesCH 2tolossa assefaNo ratings yet
- SPC 7Document70 pagesSPC 7bakr hagagNo ratings yet
- Optimization of End-of-Life SystemDocument40 pagesOptimization of End-of-Life SystemLizard WhiteNo ratings yet
- Production Management: SamplingDocument4 pagesProduction Management: SamplingAbhisek Sarkar0% (1)
- Product InspectionDocument16 pagesProduct InspectionZaman ParvezNo ratings yet
- Statistical Quality ControlDocument18 pagesStatistical Quality ControlRahul Itankar100% (1)
- QC & SQCDocument11 pagesQC & SQCShahenaNo ratings yet
- Aql N QualityDocument23 pagesAql N QualityAnkur MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Che Elective 2 - Design EngineeringDocument10 pagesChe Elective 2 - Design EngineeringmichsantosNo ratings yet
- Woven Project by Peer 3Document13 pagesWoven Project by Peer 3abrham belaynehNo ratings yet
- Acceptence SamplingDocument24 pagesAcceptence SamplingFaysal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sampling Plan: TQM Department SampleDocument5 pagesSampling Plan: TQM Department SampleQuality SecretNo ratings yet
- Inspection & Quality Control 1.0 DefinitionDocument12 pagesInspection & Quality Control 1.0 DefinitionanishvanchaNo ratings yet
- Week 06 - Acceptance SamplingDocument11 pagesWeek 06 - Acceptance SamplingAli shayanNo ratings yet
- MEP-03 Acceptance Sampling ProcedureDocument31 pagesMEP-03 Acceptance Sampling ProcedureRik PtlNo ratings yet
- BME OM Finals 4Document9 pagesBME OM Finals 4Lorraine Noquilla TabaldoNo ratings yet
- Aql 1Document15 pagesAql 1bahrim adrianNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Sampling: Dr. Syed Amir IqbalDocument30 pagesAcceptance Sampling: Dr. Syed Amir IqbalSyedAneelMussawerNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Reasons For Textile TestingDocument25 pages1.1 Reasons For Textile TestingRamesh KannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 DJF51082Document20 pagesChapter4 DJF51082Fiq IFTNo ratings yet
- Chi-Kong NG, ENGG2780B, Dept. of SEEM, CUHK 1:1Document16 pagesChi-Kong NG, ENGG2780B, Dept. of SEEM, CUHK 1:1BaoYu MoZhiNo ratings yet
- Activity # 4Document7 pagesActivity # 4Diendo Boquiren MahlyNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Inventory ManagementDocument11 pagesA Case Study On Inventory ManagementNelLopez100% (1)
- S2 2014 327462 Chapter1Document8 pagesS2 2014 327462 Chapter1Bilzam Maisa SondaqNo ratings yet
- Garment InspectionDocument16 pagesGarment InspectionJason MurphyNo ratings yet
- Durability (How Does The Product Last)Document1 pageDurability (How Does The Product Last)Karen Joy Jacinto ElloNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Sampling2Document25 pagesAcceptance Sampling2Arun ChhikaraNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Production ControlDocument55 pagesModule 3 - Production ControlRahul LoharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document9 pagesChapter 9ellechernuebNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Sampling PlansDocument31 pagesAcceptance Sampling PlansMalaika QaiserNo ratings yet
- The Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1From EverandThe Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- SQC (Chapter 4)Document72 pagesSQC (Chapter 4)Yitages kefelewNo ratings yet
- SQC (Chapter 3)Document34 pagesSQC (Chapter 3)Yitages kefelewNo ratings yet
- SQC (Chapter 2)Document59 pagesSQC (Chapter 2)Yitages kefelewNo ratings yet
- SQL IntroductionDocument46 pagesSQL IntroductionYitages kefelewNo ratings yet