Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orgo Notes
Orgo Notes
Uploaded by
jadesimmons71Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orgo Notes
Orgo Notes
Uploaded by
jadesimmons71Copyright:
Available Formats
Kinetics Class NotesheetI. Introduction to Chemical KineticsA.
Definition* Chemical
kinetics is the study of reaction rates and the factors influencing them.B.
Importance* Understanding reaction rates is crucial for designing and optimizing
chemical processes.II. Rate LawsA. Definition* Rate law describes the relationship
between the rate of a reaction and the concentrations of reactants.B. General Form*
For a general reaction: ��+��?��+��aA+bB?cC+dD* The rate law:
Rate=�[�]�[�]�Rate=k[A]m[B]nC. Reaction Order* The sum of the exponents (m + n)
gives the overall reaction order.* Individual exponents (m and n) represent the
order with respect to each reactant.III. Integrated Rate LawsA. Zero-Order
Reactions* [�]�=?��+[�]0[A]t?=?kt+[A]0?B. First-Order Reactions* ln?[�]�=?��+ln?
[�]0ln[A]t?=?kt+ln[A]0?C. Second-Order Reactions* 1[�]�=��+1[�]0[A]t?1?=kt+[A]0?1?
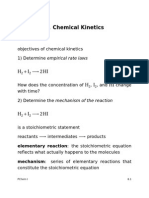
IV. Reaction MechanismsA. Elementary Steps* Reactions occur in elementary steps,
each with a specific rate law.B. Rate-Determining Step* The slowest step in a
reaction mechanism determines the overall rate.V. Activation EnergyA. Definition*
Activation energy (��Ea?) is the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.B.
Arrhenius Equation* �=��?����k=Ae?RTEa??VI. CatalysisA. Catalysts* Substances that
increase reaction rates by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower
activation energy.B. Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous CatalysisVII. Temperature
DependenceA. Effect on Reaction Rate* Generally, reaction rates increase with
temperature due to more energetic collisions.B. Temperature Dependence in Arrhenius
EquationVIII. Reaction Rate ConstantsA. Units* The units of �k depend on the
overall reaction order.B. Determining �k* Experimental methods and data analysis.
You might also like
- KINETICS Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument9 pagesKINETICS Practice Problems and SolutionsnairdanipsoNo ratings yet
- Chap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRADocument129 pagesChap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRA黄麒安No ratings yet
- AP Chem Ch12 Practice QuizDocument8 pagesAP Chem Ch12 Practice QuizlhijeanNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Chemical Kinetics NotesDocument6 pagesZumdahl Chemical Kinetics NotesMalletNjonkemNo ratings yet
- 11 Reaction KineticsDocument95 pages11 Reaction KineticsSyamil Adzman100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics - Reaction RatesDocument35 pagesChemical Kinetics - Reaction RatesRichie SuyaoNo ratings yet
- 13 KineticsDocument43 pages13 KineticsharriolaNo ratings yet
- Imp Qns Chemical KineticsDocument5 pagesImp Qns Chemical Kineticsabuthahir1.mcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Chemical KineticsDocument92 pagesChapter 2 - Chemical KineticssabNo ratings yet
- 65G12 Week 2 T2 47158Document24 pages65G12 Week 2 T2 47158mariam.moh.nassefNo ratings yet
- 102 MSJC 13Document11 pages102 MSJC 13noelNo ratings yet
- Kinetic For A2Document23 pagesKinetic For A2alvin2282No ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Chemical KineticsDocument49 pagesChapter 13: Chemical KineticsUddinTauhidNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction Quiz (2)Document10 pagesRate of Reaction Quiz (2)mmesomaezenwuneNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument32 pagesChemical KineticsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Module 5 KineticsDocument12 pagesLecture Notes Module 5 KineticsFaith SmithNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetic Note 03Document28 pagesChemical Kinetic Note 03Nurul Izzanie AdnanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics2Document29 pagesChemical Kinetics2XKnightNo ratings yet
- (EN) 13 (Ch. 7 - Kinetika Kimia) Part 1 PDFDocument4 pages(EN) 13 (Ch. 7 - Kinetika Kimia) Part 1 PDFDila RahmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Document10 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Gaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument56 pagesChemical KineticsMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Fundamental DefinitionsDocument44 pagesChapter 1. Fundamental DefinitionsTrucNo ratings yet
- Modified Release Dosage FormsDocument26 pagesModified Release Dosage FormshassenkadegaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics/Rate of Chemical ReactionDocument13 pagesChemical Kinetics/Rate of Chemical ReactionHiNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 6 - Chemical KineticsDocument45 pagesChapter No 6 - Chemical KineticsTanish SalviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Lecture NotesDocument59 pagesChapter 14 Lecture NotesDavis LundNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 (Kinetics)Document9 pagesChapter 16 (Kinetics)Richard KimNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument73 pagesChemical Kineticsssatechies62No ratings yet
- 7 Reaction KineticsDocument38 pages7 Reaction KineticsArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Chem Kinetics - Modified GutoDocument40 pagesLecture 4 - Chem Kinetics - Modified GutoSamwel MwetichNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document116 pagesLec 3Cheng Chao HanNo ratings yet
- Second-Order Rate Laws: Self-Study AssignmentDocument0 pagesSecond-Order Rate Laws: Self-Study AssignmentDoris GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument43 pagesChemical KineticsJohn SlyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-3Document17 pagesChemical Kinetics-3Ashutosh KunwarNo ratings yet
- 15 Chem KinetDocument51 pages15 Chem KinetRoua Ali100% (2)
- Module in 2: General ChemistryDocument5 pagesModule in 2: General Chemistryriza amoresNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Enzyme Kinetics Lecture 2Document47 pagesChemical and Enzyme Kinetics Lecture 2downdstairs45No ratings yet
- Basic Physical Chem Notes FullDocument145 pagesBasic Physical Chem Notes FullAkil Ladzinrank100% (1)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2Document18 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2ridwan100% (2)
- Chemical Kinetics: H + I 2 HI H I HIDocument49 pagesChemical Kinetics: H + I 2 HI H I HIputriprastyarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics FTDocument13 pagesChemical Kinetics FTarshbirksidhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 - Reaction KineticsDocument11 pagesChapter 23 - Reaction KineticsnuofanxiaNo ratings yet
- Main Factors Which Influence Reaction Rate:: Concentrations of Reactants Reaction Temperature Presence of A CatalystDocument32 pagesMain Factors Which Influence Reaction Rate:: Concentrations of Reactants Reaction Temperature Presence of A CatalystsareddyNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument51 pagesChemical KineticsdkaurNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Lec-1 NEET ChalisaDocument35 pagesKinetics Lec-1 NEET Chalisaashustarguy005No ratings yet
- Tro 13 KineticsDocument13 pagesTro 13 KineticsNikoletta StrandbergNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Rate of Reaction MechanismDocument60 pagesChemical Kinetics: Rate of Reaction MechanismAneudis Javier BritoNo ratings yet
- (2090) Lecture Notes Chemical Kinetics Radioactivity eDocument42 pages(2090) Lecture Notes Chemical Kinetics Radioactivity eRamJiPandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12chemical KineticsDocument5 pagesChapter 12chemical KineticsKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument29 pagesChemistry ProjectMuhannad RabeeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Modeling of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication ProblemsFrom EverandFinite Element Modeling of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Matrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersFrom EverandMatrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersNo ratings yet
- TemDocument1 pageTemjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- DSCDocument1 pageDSCjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- TgaDocument1 pageTgajadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Chem Eng NotesDocument1 pageChem Eng Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- XRDDocument1 pageXRDjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Art NotesDocument1 pageArt Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Mat Prop NotesDocument1 pageMat Prop Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Mates Selection NotesDocument1 pageMates Selection Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Acoustics NotesDocument1 pageAcoustics Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Band Theory and Electronic Properties Equation SheetDocument1 pageBand Theory and Electronic Properties Equation Sheetjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Thermo Post NotesDocument1 pageThermo Post Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Calc NotesDocument1 pageCalc Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Ecology NotesDocument1 pageEcology Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Thermo PDocument1 pageThermo Pjadesimmons71No ratings yet