Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsXRD
XRD
Uploaded by
jadesimmons71X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis involves exposing a sample to X-rays to produce a diffraction pattern from which information about the crystal structure can be extracted. The main steps are: (1) collecting and preprocessing the raw XRD data, (2) identifying peaks in the pattern corresponding to crystal planes, and (3) indexing peaks to determine lattice parameters and crystal system. More advanced techniques allow determining atomic positions, identifying phases by comparing to databases, and quantifying amorphous content. Software aids in peak fitting, indexing, and Rietveld refinement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Aircraft Maintenance Engineering: Nanyang Technological UniversityDocument31 pagesAircraft Maintenance Engineering: Nanyang Technological UniversitySaitama FishNo ratings yet
- NSC46 Workshop PDFDocument73 pagesNSC46 Workshop PDFlinni123No ratings yet
- Research Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-DefinitionDocument5 pagesResearch Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-Definitionsarah sindoroNo ratings yet
- Wi-Expd-01 Rev.00 Work Instruction - Expediting Report Contents GuidelinesDocument19 pagesWi-Expd-01 Rev.00 Work Instruction - Expediting Report Contents GuidelinesRakesh MishraNo ratings yet
- 01 XRD IntroDocument22 pages01 XRD IntroSherlyn EnovejasNo ratings yet
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD) : = 2dsinθDocument3 pagesX-ray Diffraction (XRD) : = 2dsinθmmak946.lkiNo ratings yet
- TemDocument1 pageTemjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Research Paper On XRDDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On XRDupvipbqlg100% (1)
- Nanomaterials Technical BulletinDocument16 pagesNanomaterials Technical BulletinIsmael SantosNo ratings yet
- CS3362 DSDocument2 pagesCS3362 DSgunaNo ratings yet
- Materiall PresentationDocument33 pagesMateriall Presentationyilma wendayehuNo ratings yet
- Studying Root Report by ZafarDocument5 pagesStudying Root Report by Zafarzafarsahito185No ratings yet
- Laboratory Lab Report On X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Document11 pagesLaboratory Lab Report On X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Ira Maya Pitri SibaraniNo ratings yet
- XRD AnalysisDocument5 pagesXRD Analysisbudhlada100% (2)
- X-Pert High Score Plus (ICC Database) : Such As A Piece of Mounting Clay or Any Crystalline Material That You WantDocument1 pageX-Pert High Score Plus (ICC Database) : Such As A Piece of Mounting Clay or Any Crystalline Material That You WantKamranAslamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Sciences Term Project by Ayesha AbbasDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Data Sciences Term Project by Ayesha AbbasAyesha SajniNo ratings yet
- Nist DataDocument12 pagesNist DataArturo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- X-Ray DiffractionDocument26 pagesX-Ray DiffractionZain Ali KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Combined XRD and XRF: For Comprehensive Materials AnalysisDocument5 pagesCombined XRD and XRF: For Comprehensive Materials AnalysisRodolfo Real CorralesNo ratings yet
- Research Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-DefinitionDocument5 pagesResearch Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-DefinitionnaningNo ratings yet
- Data PDFDocument5 pagesData PDFCatherine JumadiaoNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument44 pagesDocumenthardikcockingNo ratings yet
- Lec 08 - XRD AnalysisDocument22 pagesLec 08 - XRD AnalysisAbro HasanNo ratings yet
- 2021 MM 05Document8 pages2021 MM 05Ayyan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Classification of Objects by Shape Applied To AmbeDocument14 pagesClassification of Objects by Shape Applied To AmbeKashyap MauryaNo ratings yet
- Predicting Earthquakes Through Data MiningDocument12 pagesPredicting Earthquakes Through Data MiningPrathyusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Unit-IvDocument34 pagesData Mining Unit-Ivlokeshappalaneni9No ratings yet
- 01-XRD IntroDocument22 pages01-XRD IntroMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Qualities of Clusters by Eliminating Outlier For Data Mining Application in EducationDocument27 pagesEnhancement of Qualities of Clusters by Eliminating Outlier For Data Mining Application in Educationdiptipatil20No ratings yet
- Danish Rafaqat XRDDocument5 pagesDanish Rafaqat XRDdanish rafaqatNo ratings yet
- Data Science New ReportDocument39 pagesData Science New Reportpriyachinni1205No ratings yet
- Importing Rayfiles and Ray-Measurement Files of LEDsDocument8 pagesImporting Rayfiles and Ray-Measurement Files of LEDsGines RoaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah-10 XRD-2024Document53 pagesKuliah-10 XRD-2024pendidikankeilmuanbemuiNo ratings yet
- DWDM R13 Unit 1 PDFDocument10 pagesDWDM R13 Unit 1 PDFindiraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Mining: Dr. Dipti Chauhan Assistant Professor SCSIT, SUAS IndoreDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Data Mining: Dr. Dipti Chauhan Assistant Professor SCSIT, SUAS IndoreroochinNo ratings yet
- ALL PH.D - CourseSyllabusDocument27 pagesALL PH.D - CourseSyllabusVIPIN KUMAR MAURYANo ratings yet
- Dav Exps - Merged - MergedDocument99 pagesDav Exps - Merged - MergedSahil SurveNo ratings yet
- What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawDocument8 pagesWhat Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawsafiNo ratings yet
- Detection of Unknown Specimen PPT Using XRDDocument10 pagesDetection of Unknown Specimen PPT Using XRDNitesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning For Astronomy: Rob FergusDocument80 pagesMachine Learning For Astronomy: Rob FergusMastering Zinc OxideNo ratings yet
- It5003 - Data Warehousing and Data Mining-1Document5 pagesIt5003 - Data Warehousing and Data Mining-1yototi8935No ratings yet
- Chatgpt AdvicesDocument15 pagesChatgpt Advicesfotini81729No ratings yet
- Data Mining Moodle Notes U1Document11 pagesData Mining Moodle Notes U1Sahu Sahu SubhamNo ratings yet
- Richards 2005Document11 pagesRichards 2005Christopher PáduaNo ratings yet
- Cs1004: Data Warehousing and Mining Two Marks Questions and Answers Unit IDocument31 pagesCs1004: Data Warehousing and Mining Two Marks Questions and Answers Unit IJasim KhanNo ratings yet
- Electron Diffraction: Applications Using The PDF 4+ Relational DatabaseDocument18 pagesElectron Diffraction: Applications Using The PDF 4+ Relational DatabaseKalinga BalNo ratings yet
- 1.BIT 02105 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Course OutlineDocument3 pages1.BIT 02105 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Course Outlinestaticbreeze100No ratings yet
- XRD - 07 09 2022Document23 pagesXRD - 07 09 2022KINGSHUK MUKHERJEENo ratings yet
- A Parallel Study On Clustering Algorithms in Data MiningDocument7 pagesA Parallel Study On Clustering Algorithms in Data MiningAnu IshwaryaNo ratings yet
- Astroebsd: Exploring New Space in Pattern Indexing With Methods Launched From An Astronomical ApproachDocument10 pagesAstroebsd: Exploring New Space in Pattern Indexing With Methods Launched From An Astronomical ApproachLívia RodriguesNo ratings yet
- CS2032 2 Marks & 16 Marks With AnswersDocument30 pagesCS2032 2 Marks & 16 Marks With AnswersThiyagarajan Ganesan100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Data Science StudentsDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Data Science Students123sanjaypurohitNo ratings yet
- Exp 10 Analysis of XRD Pattern PDFDocument4 pagesExp 10 Analysis of XRD Pattern PDFHamza HassanNo ratings yet
- What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Document7 pagesWhat Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Ahmad NawazNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 RSDocument12 pagesLab Report 1 RSMuhammad Hatim Hakimi Bin Rusli E22A0096No ratings yet
- 01-Introduction To DS With PythonDocument32 pages01-Introduction To DS With PythonSabrina SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Statistical Data Analysis Explained: Applied Environmental Statistics with RFrom EverandStatistical Data Analysis Explained: Applied Environmental Statistics with RNo ratings yet
- Quadtree: Exploring Hierarchical Data Structures for Image AnalysisFrom EverandQuadtree: Exploring Hierarchical Data Structures for Image AnalysisNo ratings yet
- TemDocument1 pageTemjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- DSCDocument1 pageDSCjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- TgaDocument1 pageTgajadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Orgo NotesDocument1 pageOrgo Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Chem Eng NotesDocument1 pageChem Eng Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Art NotesDocument1 pageArt Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Mat Prop NotesDocument1 pageMat Prop Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Mates Selection NotesDocument1 pageMates Selection Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Acoustics NotesDocument1 pageAcoustics Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Band Theory and Electronic Properties Equation SheetDocument1 pageBand Theory and Electronic Properties Equation Sheetjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Thermo Post NotesDocument1 pageThermo Post Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Calc NotesDocument1 pageCalc Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Ecology NotesDocument1 pageEcology Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Thermo PDocument1 pageThermo Pjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Facts Versus OpinionDocument20 pagesFacts Versus OpinionIrish Ga-aNo ratings yet
- Initial Message and TasksDocument6 pagesInitial Message and TasksAman GargNo ratings yet
- Morphological Research in Planning Urban Design and Architecture 2021Document261 pagesMorphological Research in Planning Urban Design and Architecture 2021chichaNo ratings yet
- Geospatial Application of Storm Surge VulnerabilityDocument36 pagesGeospatial Application of Storm Surge VulnerabilityDiego Acevedo FernandezNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Energy Levels of A Free Electron Under The Optical Pumping of RubidiumDocument9 pagesAn Investigation Into The Energy Levels of A Free Electron Under The Optical Pumping of RubidiumJack RankinNo ratings yet
- Change Your Mind 57 Ways To Unlock Your Creative SelfDocument194 pagesChange Your Mind 57 Ways To Unlock Your Creative Selfhquecan9634No ratings yet
- Marian Boy'S and Marian Girls' High Schools Pre-Form Five Holiday Package - 2020 Advanced MathematicsDocument22 pagesMarian Boy'S and Marian Girls' High Schools Pre-Form Five Holiday Package - 2020 Advanced MathematicsYøüñg Bøë100% (1)
- The Design of Electric Reduction Furnaces For Ferro-Alloy ProductionDocument21 pagesThe Design of Electric Reduction Furnaces For Ferro-Alloy Productionhassan materialsNo ratings yet
- Kolkata Sahodaya Question Bank Google Drive LinksDocument3 pagesKolkata Sahodaya Question Bank Google Drive LinksMalhar DaveNo ratings yet
- Joy and Heron in The Application of The Relationship TheoryDocument6 pagesJoy and Heron in The Application of The Relationship TheoryMacky Cordero100% (1)
- Timeline 12 WeeksDocument311 pagesTimeline 12 Weekstusharbanga2405No ratings yet
- Aeron Systems: Inertial Sensors and Navigation SystemsDocument7 pagesAeron Systems: Inertial Sensors and Navigation SystemsBhagavad GitaNo ratings yet
- PDocument25 pagesPnuuktuugNo ratings yet
- Mitro VicDocument25 pagesMitro VicMiguel Suárez AraméndizNo ratings yet
- Directions (11-15) : Answer Question 11 To 15 Based On The Following SequenceDocument41 pagesDirections (11-15) : Answer Question 11 To 15 Based On The Following SequencePradeep B AppiNo ratings yet
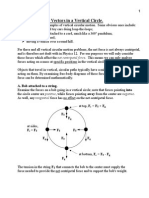
- Forces in A Vertical Circle NotesDocument4 pagesForces in A Vertical Circle NotesAuLia Az Zahra NieSa100% (1)
- Note Taking: Unit Pendidikan Kedokteran FK Umsu 2016Document21 pagesNote Taking: Unit Pendidikan Kedokteran FK Umsu 2016Khemal MubaraqNo ratings yet
- Is The Customer Always Right..........Document37 pagesIs The Customer Always Right..........bhavnaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Fragility of Transportation Lifeline Piers in The Philippines, Under Confinement and Shear Failure.Document20 pagesSeismic Fragility of Transportation Lifeline Piers in The Philippines, Under Confinement and Shear Failure.Michael Bautista BaylonNo ratings yet
- Composite ChartDocument6 pagesComposite ChartItamar ItzNo ratings yet
- Economics - Definition and Nature & Scope of Economics - Divisions of EconomicsDocument8 pagesEconomics - Definition and Nature & Scope of Economics - Divisions of EconomicsNikita 07No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 6Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 6Mary Joy RobisNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Painting Works (1Document7 pagesRisk Assessment - Painting Works (1Bashir Khan100% (2)
- hjfb5m8w) 25 D HNDocument27 pageshjfb5m8w) 25 D HNSav OliNo ratings yet
- Star Wars Saga Edition - Core Rulebook ErrataDocument6 pagesStar Wars Saga Edition - Core Rulebook ErrataClayton RyderNo ratings yet
- How To Perform Surgical Hand ScrubsDocument4 pagesHow To Perform Surgical Hand ScrubsInna XiiNo ratings yet
- Ducted System Handing Over Report: Form SH-1Document4 pagesDucted System Handing Over Report: Form SH-1akashNo ratings yet
- Long Eddy - Administrative Capacity Assumptions in Federal GrantsDocument24 pagesLong Eddy - Administrative Capacity Assumptions in Federal GrantsWilliam P. KittredgeNo ratings yet
XRD
XRD
Uploaded by
jadesimmons710 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageX-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis involves exposing a sample to X-rays to produce a diffraction pattern from which information about the crystal structure can be extracted. The main steps are: (1) collecting and preprocessing the raw XRD data, (2) identifying peaks in the pattern corresponding to crystal planes, and (3) indexing peaks to determine lattice parameters and crystal system. More advanced techniques allow determining atomic positions, identifying phases by comparing to databases, and quantifying amorphous content. Software aids in peak fitting, indexing, and Rietveld refinement.
Original Description:
Original Title
xrd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentX-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis involves exposing a sample to X-rays to produce a diffraction pattern from which information about the crystal structure can be extracted. The main steps are: (1) collecting and preprocessing the raw XRD data, (2) identifying peaks in the pattern corresponding to crystal planes, and (3) indexing peaks to determine lattice parameters and crystal system. More advanced techniques allow determining atomic positions, identifying phases by comparing to databases, and quantifying amorphous content. Software aids in peak fitting, indexing, and Rietveld refinement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageXRD
XRD
Uploaded by
jadesimmons71X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis involves exposing a sample to X-rays to produce a diffraction pattern from which information about the crystal structure can be extracted. The main steps are: (1) collecting and preprocessing the raw XRD data, (2) identifying peaks in the pattern corresponding to crystal planes, and (3) indexing peaks to determine lattice parameters and crystal system. More advanced techniques allow determining atomic positions, identifying phases by comparing to databases, and quantifying amorphous content. Software aids in peak fitting, indexing, and Rietveld refinement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Analyzing X-ray Diffraction (XRD) data involves extracting information about the
crystal structure of a material based on the diffraction pattern produced when X-
rays interact with the crystal lattice. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to
analyze XRD data:Data Acquisition:1. Data Collection:* Collect XRD data by exposing
the sample to X-rays and recording the resulting diffraction pattern.* Use a
suitable X-ray source (commonly Cu K? radiation), a sample holder, and a detector.
Data Processing:2. Data Reduction:* Pre-process the raw data by correcting for
background, removing noise, and scaling the intensity.3. Peak Identification:*
Identify the peaks in the XRD pattern. Each peak corresponds to a specific set of
crystal planes.Crystallographic Analysis:4. Indexing:* Determine the crystal
lattice parameters (a, b, c, ?, ?, ?) by indexing the peaks in the pattern. This
step establishes the crystal system and unit cell.5. Peak Profile Analysis:*
Analyze the shape and width of diffraction peaks to obtain information about
crystallite size, strain, and preferred orientation.6. Rietveld Refinement:*
Perform Rietveld refinement to refine crystal structure parameters, such as atomic
positions, thermal vibrations, and occupancy factors. This is a more advanced
technique and requires structural models.Phase Identification:7. Database Search:*
Identify phases present in the sample by comparing the observed diffraction pattern
with entries in crystallographic databases (e.g., ICSD, PDF).8. Pattern Matching
Software:* Utilize pattern matching software (e.g., Match!, ICDD PDF-4+) to compare
and identify phases in the sample.Additional Considerations:9. Amorphous Content:*
If an amorphous phase is present, quantify its content by subtracting the amorphous
contribution from the total pattern.10. Texture Analysis:* Analyze texture or
preferred orientation in polycrystalline samples. Texture information is often
obtained from pole figure data.11. Advanced Techniques:* Consider advanced
techniques such as quantitative phase analysis, pair distribution function (PDF)
analysis, or ab initio structure determination for more detailed investigations.
Resources and Tools:12. Software:* Use XRD analysis software such as FullProf,
GSAS, TOPAS, or others for peak fitting, indexing, and Rietveld refinement.13.
Databases:* Refer to crystallographic databases like ICSD, PDF, or other
specialized databases for phase identification.14. Literature and Tutorials:*
Explore literature, textbooks, and online tutorials on XRD analysis for in-depth
learning.Collaboration with experts, attending workshops, and hands-on experience
with XRD instruments and software will enhance your proficiency in interpreting XRD
data.
You might also like
- Aircraft Maintenance Engineering: Nanyang Technological UniversityDocument31 pagesAircraft Maintenance Engineering: Nanyang Technological UniversitySaitama FishNo ratings yet
- NSC46 Workshop PDFDocument73 pagesNSC46 Workshop PDFlinni123No ratings yet
- Research Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-DefinitionDocument5 pagesResearch Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-Definitionsarah sindoroNo ratings yet
- Wi-Expd-01 Rev.00 Work Instruction - Expediting Report Contents GuidelinesDocument19 pagesWi-Expd-01 Rev.00 Work Instruction - Expediting Report Contents GuidelinesRakesh MishraNo ratings yet
- 01 XRD IntroDocument22 pages01 XRD IntroSherlyn EnovejasNo ratings yet
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD) : = 2dsinθDocument3 pagesX-ray Diffraction (XRD) : = 2dsinθmmak946.lkiNo ratings yet
- TemDocument1 pageTemjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Research Paper On XRDDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On XRDupvipbqlg100% (1)
- Nanomaterials Technical BulletinDocument16 pagesNanomaterials Technical BulletinIsmael SantosNo ratings yet
- CS3362 DSDocument2 pagesCS3362 DSgunaNo ratings yet
- Materiall PresentationDocument33 pagesMateriall Presentationyilma wendayehuNo ratings yet
- Studying Root Report by ZafarDocument5 pagesStudying Root Report by Zafarzafarsahito185No ratings yet
- Laboratory Lab Report On X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Document11 pagesLaboratory Lab Report On X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Ira Maya Pitri SibaraniNo ratings yet
- XRD AnalysisDocument5 pagesXRD Analysisbudhlada100% (2)
- X-Pert High Score Plus (ICC Database) : Such As A Piece of Mounting Clay or Any Crystalline Material That You WantDocument1 pageX-Pert High Score Plus (ICC Database) : Such As A Piece of Mounting Clay or Any Crystalline Material That You WantKamranAslamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Sciences Term Project by Ayesha AbbasDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Data Sciences Term Project by Ayesha AbbasAyesha SajniNo ratings yet
- Nist DataDocument12 pagesNist DataArturo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- X-Ray DiffractionDocument26 pagesX-Ray DiffractionZain Ali KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Combined XRD and XRF: For Comprehensive Materials AnalysisDocument5 pagesCombined XRD and XRF: For Comprehensive Materials AnalysisRodolfo Real CorralesNo ratings yet
- Research Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-DefinitionDocument5 pagesResearch Data - Definitions: Support/data-Library/research-Data-Mgmt/data-Mgmt/research-Data-DefinitionnaningNo ratings yet
- Data PDFDocument5 pagesData PDFCatherine JumadiaoNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument44 pagesDocumenthardikcockingNo ratings yet
- Lec 08 - XRD AnalysisDocument22 pagesLec 08 - XRD AnalysisAbro HasanNo ratings yet
- 2021 MM 05Document8 pages2021 MM 05Ayyan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Classification of Objects by Shape Applied To AmbeDocument14 pagesClassification of Objects by Shape Applied To AmbeKashyap MauryaNo ratings yet
- Predicting Earthquakes Through Data MiningDocument12 pagesPredicting Earthquakes Through Data MiningPrathyusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Unit-IvDocument34 pagesData Mining Unit-Ivlokeshappalaneni9No ratings yet
- 01-XRD IntroDocument22 pages01-XRD IntroMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Qualities of Clusters by Eliminating Outlier For Data Mining Application in EducationDocument27 pagesEnhancement of Qualities of Clusters by Eliminating Outlier For Data Mining Application in Educationdiptipatil20No ratings yet
- Danish Rafaqat XRDDocument5 pagesDanish Rafaqat XRDdanish rafaqatNo ratings yet
- Data Science New ReportDocument39 pagesData Science New Reportpriyachinni1205No ratings yet
- Importing Rayfiles and Ray-Measurement Files of LEDsDocument8 pagesImporting Rayfiles and Ray-Measurement Files of LEDsGines RoaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah-10 XRD-2024Document53 pagesKuliah-10 XRD-2024pendidikankeilmuanbemuiNo ratings yet
- DWDM R13 Unit 1 PDFDocument10 pagesDWDM R13 Unit 1 PDFindiraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Mining: Dr. Dipti Chauhan Assistant Professor SCSIT, SUAS IndoreDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Data Mining: Dr. Dipti Chauhan Assistant Professor SCSIT, SUAS IndoreroochinNo ratings yet
- ALL PH.D - CourseSyllabusDocument27 pagesALL PH.D - CourseSyllabusVIPIN KUMAR MAURYANo ratings yet
- Dav Exps - Merged - MergedDocument99 pagesDav Exps - Merged - MergedSahil SurveNo ratings yet
- What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawDocument8 pagesWhat Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawsafiNo ratings yet
- Detection of Unknown Specimen PPT Using XRDDocument10 pagesDetection of Unknown Specimen PPT Using XRDNitesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning For Astronomy: Rob FergusDocument80 pagesMachine Learning For Astronomy: Rob FergusMastering Zinc OxideNo ratings yet
- It5003 - Data Warehousing and Data Mining-1Document5 pagesIt5003 - Data Warehousing and Data Mining-1yototi8935No ratings yet
- Chatgpt AdvicesDocument15 pagesChatgpt Advicesfotini81729No ratings yet
- Data Mining Moodle Notes U1Document11 pagesData Mining Moodle Notes U1Sahu Sahu SubhamNo ratings yet
- Richards 2005Document11 pagesRichards 2005Christopher PáduaNo ratings yet
- Cs1004: Data Warehousing and Mining Two Marks Questions and Answers Unit IDocument31 pagesCs1004: Data Warehousing and Mining Two Marks Questions and Answers Unit IJasim KhanNo ratings yet
- Electron Diffraction: Applications Using The PDF 4+ Relational DatabaseDocument18 pagesElectron Diffraction: Applications Using The PDF 4+ Relational DatabaseKalinga BalNo ratings yet
- 1.BIT 02105 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Course OutlineDocument3 pages1.BIT 02105 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Course Outlinestaticbreeze100No ratings yet
- XRD - 07 09 2022Document23 pagesXRD - 07 09 2022KINGSHUK MUKHERJEENo ratings yet
- A Parallel Study On Clustering Algorithms in Data MiningDocument7 pagesA Parallel Study On Clustering Algorithms in Data MiningAnu IshwaryaNo ratings yet
- Astroebsd: Exploring New Space in Pattern Indexing With Methods Launched From An Astronomical ApproachDocument10 pagesAstroebsd: Exploring New Space in Pattern Indexing With Methods Launched From An Astronomical ApproachLívia RodriguesNo ratings yet
- CS2032 2 Marks & 16 Marks With AnswersDocument30 pagesCS2032 2 Marks & 16 Marks With AnswersThiyagarajan Ganesan100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Data Science StudentsDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Data Science Students123sanjaypurohitNo ratings yet
- Exp 10 Analysis of XRD Pattern PDFDocument4 pagesExp 10 Analysis of XRD Pattern PDFHamza HassanNo ratings yet
- What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Document7 pagesWhat Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Ahmad NawazNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 RSDocument12 pagesLab Report 1 RSMuhammad Hatim Hakimi Bin Rusli E22A0096No ratings yet
- 01-Introduction To DS With PythonDocument32 pages01-Introduction To DS With PythonSabrina SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Statistical Data Analysis Explained: Applied Environmental Statistics with RFrom EverandStatistical Data Analysis Explained: Applied Environmental Statistics with RNo ratings yet
- Quadtree: Exploring Hierarchical Data Structures for Image AnalysisFrom EverandQuadtree: Exploring Hierarchical Data Structures for Image AnalysisNo ratings yet
- TemDocument1 pageTemjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- DSCDocument1 pageDSCjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- TgaDocument1 pageTgajadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Orgo NotesDocument1 pageOrgo Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Chem Eng NotesDocument1 pageChem Eng Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Art NotesDocument1 pageArt Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Mat Prop NotesDocument1 pageMat Prop Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Mates Selection NotesDocument1 pageMates Selection Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Acoustics NotesDocument1 pageAcoustics Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Band Theory and Electronic Properties Equation SheetDocument1 pageBand Theory and Electronic Properties Equation Sheetjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Thermo Post NotesDocument1 pageThermo Post Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Calc NotesDocument1 pageCalc Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Ecology NotesDocument1 pageEcology Notesjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Thermo PDocument1 pageThermo Pjadesimmons71No ratings yet
- Facts Versus OpinionDocument20 pagesFacts Versus OpinionIrish Ga-aNo ratings yet
- Initial Message and TasksDocument6 pagesInitial Message and TasksAman GargNo ratings yet
- Morphological Research in Planning Urban Design and Architecture 2021Document261 pagesMorphological Research in Planning Urban Design and Architecture 2021chichaNo ratings yet
- Geospatial Application of Storm Surge VulnerabilityDocument36 pagesGeospatial Application of Storm Surge VulnerabilityDiego Acevedo FernandezNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Energy Levels of A Free Electron Under The Optical Pumping of RubidiumDocument9 pagesAn Investigation Into The Energy Levels of A Free Electron Under The Optical Pumping of RubidiumJack RankinNo ratings yet
- Change Your Mind 57 Ways To Unlock Your Creative SelfDocument194 pagesChange Your Mind 57 Ways To Unlock Your Creative Selfhquecan9634No ratings yet
- Marian Boy'S and Marian Girls' High Schools Pre-Form Five Holiday Package - 2020 Advanced MathematicsDocument22 pagesMarian Boy'S and Marian Girls' High Schools Pre-Form Five Holiday Package - 2020 Advanced MathematicsYøüñg Bøë100% (1)
- The Design of Electric Reduction Furnaces For Ferro-Alloy ProductionDocument21 pagesThe Design of Electric Reduction Furnaces For Ferro-Alloy Productionhassan materialsNo ratings yet
- Kolkata Sahodaya Question Bank Google Drive LinksDocument3 pagesKolkata Sahodaya Question Bank Google Drive LinksMalhar DaveNo ratings yet
- Joy and Heron in The Application of The Relationship TheoryDocument6 pagesJoy and Heron in The Application of The Relationship TheoryMacky Cordero100% (1)
- Timeline 12 WeeksDocument311 pagesTimeline 12 Weekstusharbanga2405No ratings yet
- Aeron Systems: Inertial Sensors and Navigation SystemsDocument7 pagesAeron Systems: Inertial Sensors and Navigation SystemsBhagavad GitaNo ratings yet
- PDocument25 pagesPnuuktuugNo ratings yet
- Mitro VicDocument25 pagesMitro VicMiguel Suárez AraméndizNo ratings yet
- Directions (11-15) : Answer Question 11 To 15 Based On The Following SequenceDocument41 pagesDirections (11-15) : Answer Question 11 To 15 Based On The Following SequencePradeep B AppiNo ratings yet
- Forces in A Vertical Circle NotesDocument4 pagesForces in A Vertical Circle NotesAuLia Az Zahra NieSa100% (1)
- Note Taking: Unit Pendidikan Kedokteran FK Umsu 2016Document21 pagesNote Taking: Unit Pendidikan Kedokteran FK Umsu 2016Khemal MubaraqNo ratings yet
- Is The Customer Always Right..........Document37 pagesIs The Customer Always Right..........bhavnaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Fragility of Transportation Lifeline Piers in The Philippines, Under Confinement and Shear Failure.Document20 pagesSeismic Fragility of Transportation Lifeline Piers in The Philippines, Under Confinement and Shear Failure.Michael Bautista BaylonNo ratings yet
- Composite ChartDocument6 pagesComposite ChartItamar ItzNo ratings yet
- Economics - Definition and Nature & Scope of Economics - Divisions of EconomicsDocument8 pagesEconomics - Definition and Nature & Scope of Economics - Divisions of EconomicsNikita 07No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 6Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Grade 6Mary Joy RobisNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Painting Works (1Document7 pagesRisk Assessment - Painting Works (1Bashir Khan100% (2)
- hjfb5m8w) 25 D HNDocument27 pageshjfb5m8w) 25 D HNSav OliNo ratings yet
- Star Wars Saga Edition - Core Rulebook ErrataDocument6 pagesStar Wars Saga Edition - Core Rulebook ErrataClayton RyderNo ratings yet
- How To Perform Surgical Hand ScrubsDocument4 pagesHow To Perform Surgical Hand ScrubsInna XiiNo ratings yet
- Ducted System Handing Over Report: Form SH-1Document4 pagesDucted System Handing Over Report: Form SH-1akashNo ratings yet
- Long Eddy - Administrative Capacity Assumptions in Federal GrantsDocument24 pagesLong Eddy - Administrative Capacity Assumptions in Federal GrantsWilliam P. KittredgeNo ratings yet