Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry PDF
Organic Chemistry PDF
Uploaded by
Zeyad OsamaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Business English Leaving A MessageDocument2 pagesBusiness English Leaving A MessageZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- CRODA Surfactants and Alkoxylated Polyols Overview FEB 2013Document8 pagesCRODA Surfactants and Alkoxylated Polyols Overview FEB 2013Maria Eugenia CiveiraNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals Flowchart (ICIS)Document1 pagePetrochemicals Flowchart (ICIS)Guido BerdinaNo ratings yet
- ICIS-Petrochemicals Poster Online v7Document2 pagesICIS-Petrochemicals Poster Online v7remedali100% (1)
- Refinery ConfigurationDocument1 pageRefinery Configurationriverlife88100% (1)
- SSPC-SP 1 Solvent Cleaning PDFDocument2 pagesSSPC-SP 1 Solvent Cleaning PDFbhadresh_prajapati_188% (8)
- Cellular Transport Lab. Rep. (Bio. 100)Document16 pagesCellular Transport Lab. Rep. (Bio. 100)Jericho CarenaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry G Homologous & Denaturing To: CarbonylDocument7 pagesChemistry G Homologous & Denaturing To: CarbonyljfdhkskfNo ratings yet
- ICIS - Petchems FlowchartDocument2 pagesICIS - Petchems Flowchartxibs2009No ratings yet
- Crude Oil QPDocument12 pagesCrude Oil QPBethNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil QPDocument10 pagesCrude Oil QPSreeja Sen Year 10No ratings yet
- Equation (G) Nitrogen: HydrogenDocument1 pageEquation (G) Nitrogen: HydrogenMUHAMMAD LUQMAN HAKIMI MOHD ZAMRINo ratings yet
- ET Complete Chemistry GuideDocument18 pagesET Complete Chemistry GuideCesar BarretoNo ratings yet
- 02 Feedstocks & ProductsDocument135 pages02 Feedstocks & ProductsciclointermedioNo ratings yet
- Carpenter Carpol BrochureDocument3 pagesCarpenter Carpol Brochureimran_espana4968No ratings yet
- Chemical Compatability Complex PDFDocument4 pagesChemical Compatability Complex PDFArvind MohanramNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemAnnu AkNo ratings yet
- Main 6Document1 pageMain 6susCitiesNo ratings yet
- Hydroprocessing: Hydrocracking & HydrotreatingDocument45 pagesHydroprocessing: Hydrocracking & HydrotreatingRobin ZwartNo ratings yet
- CBEN409 07 Catalytic CrackingDocument37 pagesCBEN409 07 Catalytic Crackingrameshkarthik810No ratings yet
- 07 Catalytic Cracking PDFDocument37 pages07 Catalytic Cracking PDFjeedanNo ratings yet
- 239 Albert Replacement Cladding PanelsDocument4 pages239 Albert Replacement Cladding PanelsmeghadurganNo ratings yet
- Blending OptimizationDocument37 pagesBlending OptimizationAle Sanz100% (1)
- Periodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemClick LinkNo ratings yet
- Mon Nov 26 13:05:35 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Document1 pageMon Nov 26 13:05:35 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Hardika BayuNo ratings yet
- Data Ganryo 05Document3 pagesData Ganryo 05Ashesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Default FolderDocument6 pagesDefault FolderAtharva SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 13 - fcc1Document28 pages13 - fcc1ananth2012No ratings yet
- C8 Pre StudyDocument2 pagesC8 Pre Studyxnqt5n8q89No ratings yet
- 02 Feedstocks & Products PDFDocument124 pages02 Feedstocks & Products PDFdimasNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument2 pagesLipid MetabolismsnxuNo ratings yet
- טבלה מחזוריתDocument2 pagesטבלה מחזוריתorosipovNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster 2007Document1 pageFrac Moa Poster 2007David PanézNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets - UpdatedDocument267 pagesData Sheets - Updateddurgesh82338114100% (1)
- Comparison - Modeling1Document5 pagesComparison - Modeling1davidNo ratings yet
- Scan 29 Apr 2024Document1 pageScan 29 Apr 2024pwishnutama11No ratings yet
- 05 Delayed CokingDocument52 pages05 Delayed CokingRobin ZwartNo ratings yet
- Respiration SummaryDocument1 pageRespiration SummaryXyrex XNo ratings yet
- Mon Nov 26 13:09:22 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Document1 pageMon Nov 26 13:09:22 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Hardika BayuNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-05-04 at 22.38.50Document1 pageScreenshot 2024-05-04 at 22.38.50frazervibezNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document14 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2Tiên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Refinery Fundamentals-60-60Document1 pageRefinery Fundamentals-60-60Prem Preetham DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Zero Gasolene Refinery Configuration With SDA (Solvent Deashphaltene)Document9 pagesZero Gasolene Refinery Configuration With SDA (Solvent Deashphaltene)s k kumarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatHồng Ngọc VõNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble PolymersDocument9 pagesWater Soluble Polymers顾云飞No ratings yet
- Cargo Chart Sample PDFDocument1 pageCargo Chart Sample PDFRGCNo ratings yet
- Cargo Compatibility Chart: Reactive GroupsDocument1 pageCargo Compatibility Chart: Reactive GroupsRGCNo ratings yet
- 06 Delayed Coking PDFDocument34 pages06 Delayed Coking PDFsureshmechanical86No ratings yet
- 03 - Crude - Destillation Units PDFDocument35 pages03 - Crude - Destillation Units PDFRodrigo Goyzueta FloresNo ratings yet
- DQ of Biomolecules by Bharat Panchal SirDocument3 pagesDQ of Biomolecules by Bharat Panchal SirsashankkotaNo ratings yet
- Se Que Te Arrepentiras 2do TrombonDocument1 pageSe Que Te Arrepentiras 2do TrombonTutoriales De PercusionNo ratings yet
- Additives For Lubricants Product OverviewDocument5 pagesAdditives For Lubricants Product Overviewgaurav chauhanNo ratings yet
- CARMEN FANTASIA Per Flauto 1Document3 pagesCARMEN FANTASIA Per Flauto 1Giuseppe Di BenedettoNo ratings yet
- 06 Delayed CokingDocument36 pages06 Delayed CokingMilan TrengovskiNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 2, Core Pure Year 2 PDFDocument1 pageEverything You Need To Memorise - Part 2, Core Pure Year 2 PDFhanasilver96No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 14, 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan Jul 14, 2023horikyosuke24No ratings yet
- Denah Site Plan GFDocument1 pageDenah Site Plan GFRafiqi Faris SNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 10Th Edition Spencer L Seager Full ChapterDocument51 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 10Th Edition Spencer L Seager Full Chapterevelyn.whatley794100% (17)
- Everything SummarisedDocument2 pagesEverything SummarisedAryan GovenderNo ratings yet
- IMSLP772451-PMLP558152-02 - C. Ph. E. Bach - Flute Concerto in D Minor - FluteDocument11 pagesIMSLP772451-PMLP558152-02 - C. Ph. E. Bach - Flute Concerto in D Minor - Fluteluis lopezNo ratings yet
- Pieghevole Icap Sira Woodcoating Settembre 2022Document2 pagesPieghevole Icap Sira Woodcoating Settembre 2022kingkb58No ratings yet
- Esquema Elétrico NGD 9.3 PDFDocument2 pagesEsquema Elétrico NGD 9.3 PDFluiskovalchukNo ratings yet
- LKLKLDocument1 pageLKLKLZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Exercises MSDocument9 pagesQuadratic Equations Exercises MSZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Novel 1Document13 pagesNovel 1Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Main Words: Tags CreatedDocument12 pagesMain Words: Tags CreatedZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Book Review2Document4 pagesBook Review2Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- HackingDocument5 pagesHackingZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Document4 pagesSorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Bryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Adsorption in Packed Bed: Experiment No-3Document7 pagesAdsorption in Packed Bed: Experiment No-3Harsh DuttaNo ratings yet
- Cables and Wires CatalogueDocument16 pagesCables and Wires CatalogueVENITHA KNo ratings yet
- Using Chitosan To Extend Shelf Life Research Proposal MantillasDocument7 pagesUsing Chitosan To Extend Shelf Life Research Proposal MantillasTristan Jay AranasNo ratings yet
- Infor LN 10.5 Live CompanyDocument13 pagesInfor LN 10.5 Live CompanyMohamed SameerNo ratings yet
- Wbi11 01 Rms 20240307Document25 pagesWbi11 01 Rms 20240307ashfairfan30No ratings yet
- UY, BENITO PortfolioBio 4thQrtrDocument16 pagesUY, BENITO PortfolioBio 4thQrtrArlen Mae RayosNo ratings yet
- Adhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsDocument50 pagesAdhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsFatema86100% (2)
- Final ExamDocument11 pagesFinal Exammalak hilalNo ratings yet
- MSDS Novec 3MDocument9 pagesMSDS Novec 3MJun AntonioNo ratings yet
- 2016 IOGPGas Oil Industry NORMreport 412Document69 pages2016 IOGPGas Oil Industry NORMreport 412WrodolfoEPNNo ratings yet
- X Ray Films and Its TypesDocument41 pagesX Ray Films and Its TypespradeepNo ratings yet
- Product Presentation - Sony Energy Storage Station PDFDocument15 pagesProduct Presentation - Sony Energy Storage Station PDFCARLOS ANDRES SARMIENTO CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Ship Hull Coatings PDFDocument36 pagesShip Hull Coatings PDFBranko BrezecNo ratings yet
- Controlled Release Pellets: An Effective Tool in Chronic TherapyDocument26 pagesControlled Release Pellets: An Effective Tool in Chronic TherapyfakhriNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument6 pagesAromatic CompoundsSANIA FAJAR KHANNo ratings yet
- Palatihan ISCC 2023Document15 pagesPalatihan ISCC 2023imran.teknikkimiaNo ratings yet
- Roto Foodgrade Certificat NSF 2021Document1 pageRoto Foodgrade Certificat NSF 2021Erwan Le GuenNo ratings yet
- Ek-4-C Yurt Dişi İlaç Fi̇yat Li̇stesi̇Document3 pagesEk-4-C Yurt Dişi İlaç Fi̇yat Li̇stesi̇Ebru MeltemNo ratings yet
- Iwcf Exercise STC 1Document149 pagesIwcf Exercise STC 1ali jabbar100% (1)
- Heavy Metal DetoxDocument20 pagesHeavy Metal DetoxJon SmithNo ratings yet
- Portions For Grade 10 Preliminary Examination-1Document6 pagesPortions For Grade 10 Preliminary Examination-1BBBBNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Modified True or False: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesActivity 1: Modified True or False: Page 1 of 2Shiela Joy JuralbalNo ratings yet
- Oltec Coat 98 Fds Vers 8 - enDocument8 pagesOltec Coat 98 Fds Vers 8 - enGrégory EcalleNo ratings yet
- Calibration Curve: Concentration Absorbance (MG/L) F (X) 0.0374290909x R 0.9996352674 AbsorbanceDocument16 pagesCalibration Curve: Concentration Absorbance (MG/L) F (X) 0.0374290909x R 0.9996352674 Absorbanceprmahajan18No ratings yet
- Toxic Substances Containment TankDocument272 pagesToxic Substances Containment Tanktobeykim1No ratings yet
- Tds Turbo Fuse 170 1500Document1 pageTds Turbo Fuse 170 1500JuanManuelPerillaNo ratings yet
- M-I Drilling Fluids Material Safety Data Sheet: Pipelax WDocument4 pagesM-I Drilling Fluids Material Safety Data Sheet: Pipelax WHunterNo ratings yet
Organic Chemistry PDF
Organic Chemistry PDF
Uploaded by
Zeyad OsamaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry PDF
Organic Chemistry PDF
Uploaded by
Zeyad OsamaCopyright:
Available Formats
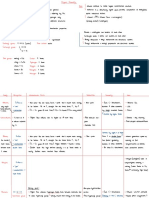
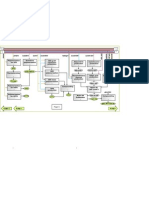
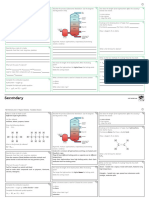
alkene
hydrocarbons
alkane
Classification Carboxylic acid
alcohol
ester
glucose
Catalogs raw materials
yeast
C=C___-C=C-
Addition polymerization
Polymers Anaerobic
Drawing the repeating unit
maufacturing conditions 37℃
dicarboxylic acid&diamine polyamide e.g. nylon
Condensation polymerization Catalyst: Enzymes(yest)
dicarboxylic acid&diol polyester e.g. PET Fermentation
renewability
Warm&normal temperature(37℃)
Structural isomer
Advantages
Isomers
low pressure(1 atm)
Position isomer
C-C only Saturation
Definitions small amount of energy required
pros and cons
C=C or more requried Addition reastions Unsaturation Organic Chemistry More labor required
slow
Producing ethanol Drawbacks
meth impure(with by-products) separated by
eth atch(when a reaction stops another one has
b
to begin within a relatively long time period)
prop
naming the substances ethene
but raw materials
steam
pent
300℃
hex
Naming Hydration conditions 60 atm
methyl
Catalyst: concentrated phrosphoric acid
ethyl
AD
propyl
pros and cons In comparison to those of fermentation
naming the groups
DisAD
butyl
ethanol
pentyl raw materials
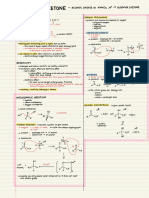
acidified potassium manganate
hexyl Reaction&manufacture Producing ethanoic acid
Observation: purple solution turns colorless
carboxylic acid
raw materials
alcohol
catalyst: concentrated sulfuric acid
Conditions
Heat applied
Esterification
Acid gives off its -OH
Principle
Alcohol gives off its -H
based on acid
Naming group name from alcohol
suffix: noic--oate
long chains into short chains
catalyst: aluminium oxide&silica
Cracking Conditions 500℃
huge reactor
when the temperature is high enough, hydrogen can be produced
You might also like
- Business English Leaving A MessageDocument2 pagesBusiness English Leaving A MessageZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- CRODA Surfactants and Alkoxylated Polyols Overview FEB 2013Document8 pagesCRODA Surfactants and Alkoxylated Polyols Overview FEB 2013Maria Eugenia CiveiraNo ratings yet
- Petrochemicals Flowchart (ICIS)Document1 pagePetrochemicals Flowchart (ICIS)Guido BerdinaNo ratings yet
- ICIS-Petrochemicals Poster Online v7Document2 pagesICIS-Petrochemicals Poster Online v7remedali100% (1)
- Refinery ConfigurationDocument1 pageRefinery Configurationriverlife88100% (1)
- SSPC-SP 1 Solvent Cleaning PDFDocument2 pagesSSPC-SP 1 Solvent Cleaning PDFbhadresh_prajapati_188% (8)
- Cellular Transport Lab. Rep. (Bio. 100)Document16 pagesCellular Transport Lab. Rep. (Bio. 100)Jericho CarenaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry G Homologous & Denaturing To: CarbonylDocument7 pagesChemistry G Homologous & Denaturing To: CarbonyljfdhkskfNo ratings yet
- ICIS - Petchems FlowchartDocument2 pagesICIS - Petchems Flowchartxibs2009No ratings yet
- Crude Oil QPDocument12 pagesCrude Oil QPBethNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil QPDocument10 pagesCrude Oil QPSreeja Sen Year 10No ratings yet
- Equation (G) Nitrogen: HydrogenDocument1 pageEquation (G) Nitrogen: HydrogenMUHAMMAD LUQMAN HAKIMI MOHD ZAMRINo ratings yet
- ET Complete Chemistry GuideDocument18 pagesET Complete Chemistry GuideCesar BarretoNo ratings yet
- 02 Feedstocks & ProductsDocument135 pages02 Feedstocks & ProductsciclointermedioNo ratings yet
- Carpenter Carpol BrochureDocument3 pagesCarpenter Carpol Brochureimran_espana4968No ratings yet
- Chemical Compatability Complex PDFDocument4 pagesChemical Compatability Complex PDFArvind MohanramNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemAnnu AkNo ratings yet
- Main 6Document1 pageMain 6susCitiesNo ratings yet
- Hydroprocessing: Hydrocracking & HydrotreatingDocument45 pagesHydroprocessing: Hydrocracking & HydrotreatingRobin ZwartNo ratings yet
- CBEN409 07 Catalytic CrackingDocument37 pagesCBEN409 07 Catalytic Crackingrameshkarthik810No ratings yet
- 07 Catalytic Cracking PDFDocument37 pages07 Catalytic Cracking PDFjeedanNo ratings yet
- 239 Albert Replacement Cladding PanelsDocument4 pages239 Albert Replacement Cladding PanelsmeghadurganNo ratings yet
- Blending OptimizationDocument37 pagesBlending OptimizationAle Sanz100% (1)
- Periodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Elements W Chemical Group Block PubChemClick LinkNo ratings yet
- Mon Nov 26 13:05:35 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Document1 pageMon Nov 26 13:05:35 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Hardika BayuNo ratings yet
- Data Ganryo 05Document3 pagesData Ganryo 05Ashesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Default FolderDocument6 pagesDefault FolderAtharva SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 13 - fcc1Document28 pages13 - fcc1ananth2012No ratings yet
- C8 Pre StudyDocument2 pagesC8 Pre Studyxnqt5n8q89No ratings yet
- 02 Feedstocks & Products PDFDocument124 pages02 Feedstocks & Products PDFdimasNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument2 pagesLipid MetabolismsnxuNo ratings yet
- טבלה מחזוריתDocument2 pagesטבלה מחזוריתorosipovNo ratings yet
- Frac Moa Poster 2007Document1 pageFrac Moa Poster 2007David PanézNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets - UpdatedDocument267 pagesData Sheets - Updateddurgesh82338114100% (1)
- Comparison - Modeling1Document5 pagesComparison - Modeling1davidNo ratings yet
- Scan 29 Apr 2024Document1 pageScan 29 Apr 2024pwishnutama11No ratings yet
- 05 Delayed CokingDocument52 pages05 Delayed CokingRobin ZwartNo ratings yet
- Respiration SummaryDocument1 pageRespiration SummaryXyrex XNo ratings yet
- Mon Nov 26 13:09:22 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Document1 pageMon Nov 26 13:09:22 2018 Case: D:/BENZENE222.HSC Flowsheet: Case (Main)Hardika BayuNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-05-04 at 22.38.50Document1 pageScreenshot 2024-05-04 at 22.38.50frazervibezNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document14 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2Tiên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Refinery Fundamentals-60-60Document1 pageRefinery Fundamentals-60-60Prem Preetham DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Zero Gasolene Refinery Configuration With SDA (Solvent Deashphaltene)Document9 pagesZero Gasolene Refinery Configuration With SDA (Solvent Deashphaltene)s k kumarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatHồng Ngọc VõNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble PolymersDocument9 pagesWater Soluble Polymers顾云飞No ratings yet
- Cargo Chart Sample PDFDocument1 pageCargo Chart Sample PDFRGCNo ratings yet
- Cargo Compatibility Chart: Reactive GroupsDocument1 pageCargo Compatibility Chart: Reactive GroupsRGCNo ratings yet
- 06 Delayed Coking PDFDocument34 pages06 Delayed Coking PDFsureshmechanical86No ratings yet
- 03 - Crude - Destillation Units PDFDocument35 pages03 - Crude - Destillation Units PDFRodrigo Goyzueta FloresNo ratings yet
- DQ of Biomolecules by Bharat Panchal SirDocument3 pagesDQ of Biomolecules by Bharat Panchal SirsashankkotaNo ratings yet
- Se Que Te Arrepentiras 2do TrombonDocument1 pageSe Que Te Arrepentiras 2do TrombonTutoriales De PercusionNo ratings yet
- Additives For Lubricants Product OverviewDocument5 pagesAdditives For Lubricants Product Overviewgaurav chauhanNo ratings yet
- CARMEN FANTASIA Per Flauto 1Document3 pagesCARMEN FANTASIA Per Flauto 1Giuseppe Di BenedettoNo ratings yet
- 06 Delayed CokingDocument36 pages06 Delayed CokingMilan TrengovskiNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 2, Core Pure Year 2 PDFDocument1 pageEverything You Need To Memorise - Part 2, Core Pure Year 2 PDFhanasilver96No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 14, 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan Jul 14, 2023horikyosuke24No ratings yet
- Denah Site Plan GFDocument1 pageDenah Site Plan GFRafiqi Faris SNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 10Th Edition Spencer L Seager Full ChapterDocument51 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 10Th Edition Spencer L Seager Full Chapterevelyn.whatley794100% (17)
- Everything SummarisedDocument2 pagesEverything SummarisedAryan GovenderNo ratings yet
- IMSLP772451-PMLP558152-02 - C. Ph. E. Bach - Flute Concerto in D Minor - FluteDocument11 pagesIMSLP772451-PMLP558152-02 - C. Ph. E. Bach - Flute Concerto in D Minor - Fluteluis lopezNo ratings yet
- Pieghevole Icap Sira Woodcoating Settembre 2022Document2 pagesPieghevole Icap Sira Woodcoating Settembre 2022kingkb58No ratings yet
- Esquema Elétrico NGD 9.3 PDFDocument2 pagesEsquema Elétrico NGD 9.3 PDFluiskovalchukNo ratings yet
- LKLKLDocument1 pageLKLKLZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Exercises MSDocument9 pagesQuadratic Equations Exercises MSZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document4 pagesChapter 8Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Novel 1Document13 pagesNovel 1Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Main Words: Tags CreatedDocument12 pagesMain Words: Tags CreatedZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Book Review2Document4 pagesBook Review2Zeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- HackingDocument5 pagesHackingZeyad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Document4 pagesSorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 2Bryan Philip BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Adsorption in Packed Bed: Experiment No-3Document7 pagesAdsorption in Packed Bed: Experiment No-3Harsh DuttaNo ratings yet
- Cables and Wires CatalogueDocument16 pagesCables and Wires CatalogueVENITHA KNo ratings yet
- Using Chitosan To Extend Shelf Life Research Proposal MantillasDocument7 pagesUsing Chitosan To Extend Shelf Life Research Proposal MantillasTristan Jay AranasNo ratings yet
- Infor LN 10.5 Live CompanyDocument13 pagesInfor LN 10.5 Live CompanyMohamed SameerNo ratings yet
- Wbi11 01 Rms 20240307Document25 pagesWbi11 01 Rms 20240307ashfairfan30No ratings yet
- UY, BENITO PortfolioBio 4thQrtrDocument16 pagesUY, BENITO PortfolioBio 4thQrtrArlen Mae RayosNo ratings yet
- Adhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsDocument50 pagesAdhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsFatema86100% (2)
- Final ExamDocument11 pagesFinal Exammalak hilalNo ratings yet
- MSDS Novec 3MDocument9 pagesMSDS Novec 3MJun AntonioNo ratings yet
- 2016 IOGPGas Oil Industry NORMreport 412Document69 pages2016 IOGPGas Oil Industry NORMreport 412WrodolfoEPNNo ratings yet
- X Ray Films and Its TypesDocument41 pagesX Ray Films and Its TypespradeepNo ratings yet
- Product Presentation - Sony Energy Storage Station PDFDocument15 pagesProduct Presentation - Sony Energy Storage Station PDFCARLOS ANDRES SARMIENTO CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Ship Hull Coatings PDFDocument36 pagesShip Hull Coatings PDFBranko BrezecNo ratings yet
- Controlled Release Pellets: An Effective Tool in Chronic TherapyDocument26 pagesControlled Release Pellets: An Effective Tool in Chronic TherapyfakhriNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument6 pagesAromatic CompoundsSANIA FAJAR KHANNo ratings yet
- Palatihan ISCC 2023Document15 pagesPalatihan ISCC 2023imran.teknikkimiaNo ratings yet
- Roto Foodgrade Certificat NSF 2021Document1 pageRoto Foodgrade Certificat NSF 2021Erwan Le GuenNo ratings yet
- Ek-4-C Yurt Dişi İlaç Fi̇yat Li̇stesi̇Document3 pagesEk-4-C Yurt Dişi İlaç Fi̇yat Li̇stesi̇Ebru MeltemNo ratings yet
- Iwcf Exercise STC 1Document149 pagesIwcf Exercise STC 1ali jabbar100% (1)
- Heavy Metal DetoxDocument20 pagesHeavy Metal DetoxJon SmithNo ratings yet
- Portions For Grade 10 Preliminary Examination-1Document6 pagesPortions For Grade 10 Preliminary Examination-1BBBBNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Modified True or False: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesActivity 1: Modified True or False: Page 1 of 2Shiela Joy JuralbalNo ratings yet
- Oltec Coat 98 Fds Vers 8 - enDocument8 pagesOltec Coat 98 Fds Vers 8 - enGrégory EcalleNo ratings yet
- Calibration Curve: Concentration Absorbance (MG/L) F (X) 0.0374290909x R 0.9996352674 AbsorbanceDocument16 pagesCalibration Curve: Concentration Absorbance (MG/L) F (X) 0.0374290909x R 0.9996352674 Absorbanceprmahajan18No ratings yet
- Toxic Substances Containment TankDocument272 pagesToxic Substances Containment Tanktobeykim1No ratings yet
- Tds Turbo Fuse 170 1500Document1 pageTds Turbo Fuse 170 1500JuanManuelPerillaNo ratings yet
- M-I Drilling Fluids Material Safety Data Sheet: Pipelax WDocument4 pagesM-I Drilling Fluids Material Safety Data Sheet: Pipelax WHunterNo ratings yet