Professional Documents
Culture Documents
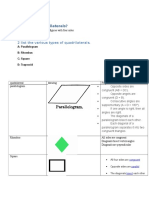
2D Shapes
2D Shapes
Uploaded by
Thủy Lê ThuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2D Shapes
2D Shapes
Uploaded by
Thủy Lê ThuCopyright:
Available Formats
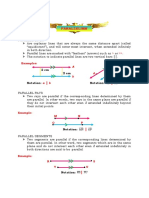
A. 5. iii 1. 4 equal sides; 4 right i.
angles; opposite sides are P = 2(a + b)
parallel; the diagonals of a A = ah
square are equal in length, here, a and b are the sides,
are perpendicular and
h = height
bisect each other.
A rhombus
B. 2. v 2. One pair of parallel ii.
sides; in a isosceles, the
P = 2(a + b)
two non-parallel sides are
equal; the diagonals in the
A = ab
isosceles are equal. here, a = width, b = length
A trapezium
C. 6. iv 3. 4 right angles; opposite iii.
sides are equal and P = 4a
parallel; the diagonals are d d
A= 1 2
equal and bisect each 2
other.
here, a = side, d1 and d 2 are the
A kite diagonals
D. 1. vi 4. Opposite sides are iv.
parallel and equal in P = 2(a + b)
length; opposite angles d1 d 2
are equal; the diagonals A=
2
bisect each other.
here, a and b are the sides, d1
and d 2 are the diagonals
A square
E. 4. i 5. 4 equal sides; opposite v.
sides are parallel; opposite P = a+b+c+d
angles are equal; the 1
A = h ( a + b)
diagonals are 2
perpendicular and bisect
A parallelogram here, a is the long base, b is the
each other.
short base, h = height, c and
d are the non-parallel sides
F. 3. ii 6. 2 pairs of equal, vi.
adjacent sides; one pair of P = 4a
opposite angles are
A = a2
equals; the diagonals are
perpendicular. here, a = side
A rectangle
You might also like
- Maths Formula Sheet For CSECDocument6 pagesMaths Formula Sheet For CSECjae jaeNo ratings yet
- 2021 Aamc 10aDocument4 pages2021 Aamc 10aNadiaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Reasoning Notes For Year 7Document5 pagesGeometric Reasoning Notes For Year 7api-291565828100% (1)
- Citizen S Charter SecondaryDocument2 pagesCitizen S Charter Secondaryapi-266482375100% (5)
- Functions (Domain and Range)Document5 pagesFunctions (Domain and Range)Dileep NaraharasettyNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Maths NotesDocument5 pagesCh-8 Maths NotesJsjn NNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 3rd QuarterDocument13 pagesGrade 9 3rd QuarterElija Fernan De JesusNo ratings yet
- 1what Are Quadrilaterals?: 2 List The Various Types of QuadrilateralsDocument2 pages1what Are Quadrilaterals?: 2 List The Various Types of QuadrilateralsAnonymous 91DuJv1pNo ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry (2014)Document12 pagesAnalytical Geometry (2014)Reitumetse MolefeNo ratings yet
- (457760) Answers 14Document2 pages(457760) Answers 14JaniceNo ratings yet
- Transformations PDFDocument42 pagesTransformations PDFJahanzaib SufyaanNo ratings yet
- Quadrangles 1Document2 pagesQuadrangles 1Rohul SibiNo ratings yet
- 3.b MeasurementsDocument23 pages3.b MeasurementsAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Math 9-Q3-Module-1Document11 pagesMath 9-Q3-Module-1Jeanette Agumbay AgunosNo ratings yet
- Z QuadrilateralDocument2 pagesZ QuadrilateralaBu HaTeMNo ratings yet
- Congruent Triangles: Stage 4 - Year 9Document12 pagesCongruent Triangles: Stage 4 - Year 9mihaiagacheNo ratings yet
- Angles and Constructions: SampleDocument21 pagesAngles and Constructions: SamplePooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- G-9 QuadrilateralsNotesDocument23 pagesG-9 QuadrilateralsNotesNysee Tamayo FerrerNo ratings yet
- CSEC Maths Revision SheetDocument6 pagesCSEC Maths Revision SheetVictoria Ram100% (1)
- Plane GeometryDocument4 pagesPlane GeometryPENDON, JORELLENo ratings yet
- Properties of Quadrilaterals WorksheetDocument4 pagesProperties of Quadrilaterals WorksheetWhitney Garnai0% (1)
- SLHT Math9 Q3 Wk1aDocument7 pagesSLHT Math9 Q3 Wk1aErica BecariNo ratings yet
- Teaching TheoremsDocument50 pagesTeaching TheoremsMuhammad Ali SidhuNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 FDocument5 pagesExercise 5 FStanleyNo ratings yet
- Select The Class Required Then Click Mouse Key To View ClassDocument50 pagesSelect The Class Required Then Click Mouse Key To View ClassAbhishek PatraNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralDocument2 pagesQuadrilateralvijiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formula Sheet-4B1CEDocument6 pagesMathematics Formula Sheet-4B1CEJelicia EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Summative Test Math 9Document2 pages3rd Quarter Summative Test Math 9Joebel Regnim Roblo100% (1)
- Quadrilateral 2024 (1)Document41 pagesQuadrilateral 2024 (1)Yonela MquqwanaNo ratings yet
- Topic F. Angles and Construction of DiagramsDocument18 pagesTopic F. Angles and Construction of Diagramslikad9730No ratings yet
- GRADE9 - MATH-0417 - Solve Problem On QuadrilateralDocument17 pagesGRADE9 - MATH-0417 - Solve Problem On QuadrilateralJea HestiaNo ratings yet
- P 6 B TextbookDocument18 pagesP 6 B TextbookThoonNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration VAbhDocument4 pagesSolid Mensuration VAbhcontridasclaireann23No ratings yet
- Rectangle, Rhombus, Parallelogram, Isosceles TrapeziumDocument20 pagesRectangle, Rhombus, Parallelogram, Isosceles TrapeziumĐặng Nhật MinhNo ratings yet
- Alternate & Corresponding AnglesDocument2 pagesAlternate & Corresponding AnglesHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Aesl June KB Class-8Document38 pagesAesl June KB Class-8Rinki SinghNo ratings yet
- Solid GeometryDocument4 pagesSolid GeometryPENDON, JORELLENo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Exam 2021-2022Document4 pagesThird Periodical Exam 2021-2022ChriS TianNo ratings yet
- Basic-Geometry FinalDocument29 pagesBasic-Geometry FinalAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- Csec Maths Revision SheetDocument7 pagesCsec Maths Revision SheetAlayna ChauharjasinghNo ratings yet
- Angles 9 (Between Parallels)Document24 pagesAngles 9 (Between Parallels)Mohammed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11 Memo Euclidean Geometry Grade 10 MathematicsDocument5 pagesWorksheet 11 Memo Euclidean Geometry Grade 10 MathematicsUmiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math v-50957225Document14 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math v-50957225Mstër DhiňgNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremDocument2 pagesCircle TheoremBunga NoionlaNo ratings yet
- Shape 4 MathsDocument2 pagesShape 4 Mathstranthihuong205No ratings yet
- Plane Figures (Repaired)Document9 pagesPlane Figures (Repaired)Mark Danniel AgtangNo ratings yet
- Parallelograms TheoremsDocument42 pagesParallelograms TheoremsEstepanie GopetNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math V: I. ObjectivesDocument14 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math V: I. ObjectivesLauren may VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Line & AnglesDocument33 pagesLine & AnglesAarushNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Geometric FiguresDocument10 pagesPlane and Solid Geometric FiguresClare PerezNo ratings yet
- Basic Geometiric Formulas and PropertiesDocument5 pagesBasic Geometiric Formulas and PropertiesPoppy HowellNo ratings yet
- Items Object Name Draw: Is It A Parallelogram Yes / NoDocument21 pagesItems Object Name Draw: Is It A Parallelogram Yes / NoErika PangilinanNo ratings yet
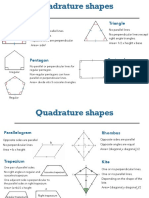
- Quadrature Shapes: Square TriangleDocument2 pagesQuadrature Shapes: Square TriangleAyah FNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document43 pagesUnit 6Game GeeksNo ratings yet
- Alternate & Corresponding Angles FinalDocument4 pagesAlternate & Corresponding Angles FinalHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Parallel LinesDocument14 pagesParallel LinesMa. Francia100% (1)
- Basic Geometiric Formulas and PropertiesDocument5 pagesBasic Geometiric Formulas and Propertiesknight gamerNo ratings yet
- Basic Geometiric Formulas and PropertiesDocument5 pagesBasic Geometiric Formulas and PropertiesRayden TanNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralsDocument35 pagesQuadrilateralsBEVERLY DOMINGONo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math VDocument14 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math VMARJUN BARTOLONo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 4 CXCDocument7 pagesFormula Sheet 4 CXCJ'zara AdamsNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Analysis of CAMS PDFDocument25 pagesUnit 4 Analysis of CAMS PDFPradeepkumar ChikkamathNo ratings yet
- 51 10th Maths All Chapter Unit Exercise Solutions English MediumDocument31 pages51 10th Maths All Chapter Unit Exercise Solutions English Mediumvadivel.km1527No ratings yet
- Medina Newsletteroct21Document2 pagesMedina Newsletteroct21api-235532287No ratings yet
- Rules - Guidelines On Private School - Edited June 19Document40 pagesRules - Guidelines On Private School - Edited June 19Julius Mey Ballecer100% (1)
- Patterns & Triggers For UCAT Abstract ReasoningDocument2 pagesPatterns & Triggers For UCAT Abstract ReasoningSamiha SaidNo ratings yet
- Vitruvian Man and Squaring of CircleDocument7 pagesVitruvian Man and Squaring of CirclememfilmatNo ratings yet
- SBM Level of PracticeDocument12 pagesSBM Level of PracticeFelcie SardidoNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 7Document33 pagesMath Grade 7api-2325119360% (1)
- Maths-Class-X - Paper - 3 PDFDocument7 pagesMaths-Class-X - Paper - 3 PDFPrabha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Pythagoras and SimilarityDocument3 pagesUnit 11 - Pythagoras and SimilarityRaffaella LaxaldeNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 7 Math Chapter 10 Practical GeometryDocument18 pagesNcert Solutions Class 7 Math Chapter 10 Practical GeometrySatvik Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Chap 04 Solutions Ex 4 2 CalculusDocument9 pagesChap 04 Solutions Ex 4 2 Calculusasghar786023No ratings yet
- IB REVIEW - Integration 2012Document6 pagesIB REVIEW - Integration 2012makunjapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Mathematics XIIDocument10 pagesChapter 9 Mathematics XIIKashif ShahNo ratings yet
- IMO Sample Paper-1Document4 pagesIMO Sample Paper-1Bhargav ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document27 pagesDay 2Adrianne Aldrin AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Angle PairsDocument14 pagesLesson 1 - Angle PairsLawrenceNo ratings yet
- Bonnie Maddox: Education Master of Arts in Elementary EducationDocument2 pagesBonnie Maddox: Education Master of Arts in Elementary Educationapi-239677720No ratings yet
- The Good Times Schools' Newspaper, South Africa, December 2013Document20 pagesThe Good Times Schools' Newspaper, South Africa, December 2013JessMorganNo ratings yet
- Imp CDF Points Maths-1bDocument13 pagesImp CDF Points Maths-1bkyathamvinaykumar41No ratings yet
- Garden Gate: Parent HandbookDocument27 pagesGarden Gate: Parent Handbookmcgraw_cherylNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Muhammad HanifNo ratings yet
- Your Turn 2: Mathematics Problem Book For JEE Chapter 2 - Trigonometric Ratios and IdentitiesDocument50 pagesYour Turn 2: Mathematics Problem Book For JEE Chapter 2 - Trigonometric Ratios and Identitiessanjayb1976gmailcomNo ratings yet
- PMR 2003-2007 Fatimah MarsalDocument62 pagesPMR 2003-2007 Fatimah MarsalMia SheraNo ratings yet
- KV JMO 2015 SolutionsDocument8 pagesKV JMO 2015 SolutionsPremMehtaNo ratings yet
- CAT 2023 Batch 3 Complete ScheduleDocument12 pagesCAT 2023 Batch 3 Complete Schedulevamsi chinnuNo ratings yet