Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessing The Mouth WPS Office
Assessing The Mouth WPS Office
Uploaded by
aina marie templonuevoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dental Consent FormDocument2 pagesDental Consent Formkoshimannu100% (1)
- Physical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDocument89 pagesPhysical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDeeeee100% (3)
- EO/IO Exam CriteriaDocument3 pagesEO/IO Exam CriteriaTaylor100% (1)
- Cardiac Rehabilitation ProtocolDocument5 pagesCardiac Rehabilitation Protocolmarkhabm100% (1)
- Health Assessment Skills Lecture-Midterms: Mouth and Throat Content ConditionsDocument2 pagesHealth Assessment Skills Lecture-Midterms: Mouth and Throat Content ConditionsKathryn Kathryz BeyonceNo ratings yet
- Mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeyteDocument9 pagesMouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeytePrincess AñabezaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Lecture: - Review About THE Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesHealth Assessment Lecture: - Review About THE Respiratory SystemHNo ratings yet
- Salcedo HA CU 9 ASSESSMENT of MOUTH THROAT 24 RDocument26 pagesSalcedo HA CU 9 ASSESSMENT of MOUTH THROAT 24 RshaimonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Mouth and OropharynxDocument3 pagesAssessing The Mouth and OropharynxReinell GoNo ratings yet
- 7mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus AssessmentDocument27 pages7mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus AssessmentFerocious WitNo ratings yet
- Tabular (Mouth, Heart and Neck Vessels)Document14 pagesTabular (Mouth, Heart and Neck Vessels)Kristelle Ann Irinco PajantoyNo ratings yet
- Mouth Oropharynx Nose Sinuses AseronDocument51 pagesMouth Oropharynx Nose Sinuses AseronAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Mouth and NeckDocument35 pagesMouth and NeckGabriel Almogela Jr.No ratings yet
- Ha NotesDocument12 pagesHa NotessrslytrdNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Mouth and Oropharynx Performance:: Lips and Buccal MucosaDocument3 pagesAssessing The Mouth and Oropharynx Performance:: Lips and Buccal MucosaAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Nose, Mouth, Throat and NeckDocument58 pagesNose, Mouth, Throat and NeckGloriaCoronado90% (10)
- Assessment of Nose, Sinuses, Mouth and Throat-JCCDocument43 pagesAssessment of Nose, Sinuses, Mouth and Throat-JCCEarlgerald RicafrancaNo ratings yet
- Mouth Throat Nose and Sinuses Checklist STUDENTSDocument4 pagesMouth Throat Nose and Sinuses Checklist STUDENTSRolandNo ratings yet
- Gingival Diseases in ChildrenDocument57 pagesGingival Diseases in ChildrenFourthMolar.com100% (3)
- Minor Case RASDocument41 pagesMinor Case RASNurul SufianNo ratings yet
- Nose, Mouth, Throat - Student Version 6 Slide Per PageDocument1 pageNose, Mouth, Throat - Student Version 6 Slide Per Pagegifty rathaurNo ratings yet
- Checklist EBP - Nose, Throat and MouthDocument6 pagesChecklist EBP - Nose, Throat and Mouths138140No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- #5 - A Nose, Mouth, Sinuses, ThroatDocument9 pages#5 - A Nose, Mouth, Sinuses, ThroatEsvinch EsvinchNo ratings yet
- 734common Oral Diseases Final - 4Document22 pages734common Oral Diseases Final - 4Mahmoud HassanNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Tongue LesionDocument26 pagesOral Pathology - Tongue Lesionneji_murniNo ratings yet
- תוכנית רבעונית q1 נראם גדבאןDocument84 pagesתוכנית רבעונית q1 נראם גדבאןIoana DănilăNo ratings yet
- MOUT and Oropharynx and Nose and Sinuses PRESENTATION 1Document44 pagesMOUT and Oropharynx and Nose and Sinuses PRESENTATION 1Reymart EstebanNo ratings yet
- Assessing Mouth and OropharynxDocument49 pagesAssessing Mouth and OropharynxHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Surgery: General ExamintionDocument6 pagesSurgery: General Examintionapi-3829364No ratings yet
- SodaPDF Merged Merging Result 1Document203 pagesSodaPDF Merged Merging Result 1nonelNo ratings yet
- Lec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumDocument23 pagesLec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumIRISH MANIAGONo ratings yet
- Ears, Mouth, Throat Nose, and Sinuses AssessmentDocument8 pagesEars, Mouth, Throat Nose, and Sinuses Assessmentshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Skin Hair Nail-11Document10 pagesSkin Hair Nail-11Kristine Angie RamosNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Case Profoma - AgamDocument8 pagesOphthalmology Case Profoma - AgamHarshitha ANo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology I Final ReviewDocument373 pagesOral Pathology I Final ReviewAlex ChangNo ratings yet
- 5 - Mouth - NoseDocument21 pages5 - Mouth - Nosezainahalqahtani3No ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument9 pagesHealth AssessmentJESSMAR GRACE PARMOSANo ratings yet
- Assessing The Ears 2Document4 pagesAssessing The Ears 2aina marie templonuevoNo ratings yet
- Assessing EarsDocument5 pagesAssessing EarsTeresita PunoNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument20 pagesPhysical Assessmentkylemabanta123No ratings yet
- Mouth and OropharynxDocument17 pagesMouth and OropharynxNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- Approach To Oral LesionsDocument53 pagesApproach To Oral LesionsUmut YücelNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment PDFDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment PDFsunshine jeonNo ratings yet
- (L08) Lesions of The TongueDocument7 pages(L08) Lesions of The TongueAbdullah FadhelNo ratings yet
- IPPA Physical AssxDocument4 pagesIPPA Physical Assxkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Part 2 AssignmentDocument15 pagesPhysical Assessment Part 2 AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- 10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatDocument25 pages10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatArka Ogeh100% (1)
- Pathological AnalysisDocument58 pagesPathological AnalysisAhella AlaaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Mouth and PharynxDocument4 pagesAssessing The Mouth and PharynxYudi TrigunaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Head and Neck: SurgeryDocument3 pagesExamination of Head and Neck: Surgeryapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Mouth Throat and SinusesDocument12 pagesMouth Throat and SinusesAngelo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Oral Patho Lecture Shlav BDocument65 pagesOral Patho Lecture Shlav Bشبيبةالروم الملكيين الكاثوليكNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Physical Examination: I. General SurveyDocument10 pagesConduct of Physical Examination: I. General SurveyWeng RamojalNo ratings yet
- Anu Omr Long CaseDocument29 pagesAnu Omr Long CaseAnurtha AnuNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Virus Recurrent Apthous Stomatitis Oral PathoDocument35 pagesHerpes Simplex Virus Recurrent Apthous Stomatitis Oral PathoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Physical Examination RemindersDocument23 pagesConduct of Physical Examination RemindersJazer DairoNo ratings yet
- Ha LecDocument5 pagesHa LecJulie YahnNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ChecklistDocument19 pagesHealth Assessment Checklistramzan aliNo ratings yet
- General Examination (COMPLEXION) by Dr. Rana Moustafa AlsayedDocument18 pagesGeneral Examination (COMPLEXION) by Dr. Rana Moustafa AlsayedAbdulla1999 AshrafNo ratings yet
- Ranula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandRanula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument236 pagesPharmacologyyalahopa100% (2)
- The Respiratory System: Aam Amarullah, M.PDDocument42 pagesThe Respiratory System: Aam Amarullah, M.PDUniversal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Fruit and Vegetables For HealthDocument45 pagesBenefits of Fruit and Vegetables For HealthKafid BramNo ratings yet
- CHN NotesDocument61 pagesCHN NotesAngelyn GamayaNo ratings yet
- 03 COVID Shimabukuro 508Document39 pages03 COVID Shimabukuro 508Kylie Betania Chávez VásquezNo ratings yet
- VIVENCIA PRIME All RidersDocument12 pagesVIVENCIA PRIME All RidersRalph RUzzelNo ratings yet
- Overview of Practice of Consultation Liaison.4Document10 pagesOverview of Practice of Consultation Liaison.4Sweet Memories JayaVaniNo ratings yet
- Disease Prevention and ControlDocument2 pagesDisease Prevention and Controlsudipta4321No ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology of Mother Tinctures &lower PotenciesDocument64 pagesClinical Pathology of Mother Tinctures &lower PotenciesAntony antony100% (1)
- WK 17 - Transportation and PandemicsDocument5 pagesWK 17 - Transportation and PandemicsChrissa EugenioNo ratings yet
- Psychoimmunology Essay by DR Romesh Senewiratne-Alagaratnam (MD)Document32 pagesPsychoimmunology Essay by DR Romesh Senewiratne-Alagaratnam (MD)Dr Romesh Arya Chakravarti100% (2)
- An Ancient Remedy RediscoveredDocument3 pagesAn Ancient Remedy RediscoveredVladimir ArmijosNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Examination English Class2011 1Document79 pagesNeurologic Examination English Class2011 1HieLdaJanuariaNo ratings yet
- EDUARDO ALEGRIA - Activity 1.3 - Making A DifferenceDocument3 pagesEDUARDO ALEGRIA - Activity 1.3 - Making A DifferenceLorenž SantośNo ratings yet
- (Leprosy Disease) : DefinitionDocument4 pages(Leprosy Disease) : DefinitionJulyn M SurlaNo ratings yet
- Ecq HemaDocument42 pagesEcq HemaJoezer Gumangan VeranoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal MassDocument9 pagesAbdominal Massscribd_huhuNo ratings yet
- And The Band Played On - Day 3 and 4 AnswersDocument5 pagesAnd The Band Played On - Day 3 and 4 AnswersAngelica ValmonteNo ratings yet
- A Synthesis Paper About Breast, Testicular and Cervical Cancer in The PhillipinesDocument3 pagesA Synthesis Paper About Breast, Testicular and Cervical Cancer in The Phillipinesjanna mae patriarcaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- 6th Year Final MCQ PediatricDocument10 pages6th Year Final MCQ Pediatricginaseptiani100% (6)
- SGRQ ManualDocument17 pagesSGRQ ManualParvez QuaziNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIADocument2 pagesECLAMPSIAZoe Jeanne GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Dehydration: Causes of Excessive Body Water LossesDocument4 pagesDehydration: Causes of Excessive Body Water LossesAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- NEW EDITABLE New Format New HighDocument434 pagesNEW EDITABLE New Format New Highdrsaimasaeed2No ratings yet
- MSDS Orec OzoneDocument2 pagesMSDS Orec OzoneHerni SuharniriyantiNo ratings yet
- Clinico-Etiological Spectrum of Pancytopenia in Hospitalized ChildrenDocument4 pagesClinico-Etiological Spectrum of Pancytopenia in Hospitalized ChildrenNurul Huda KowitaNo ratings yet
Assessing The Mouth WPS Office
Assessing The Mouth WPS Office
Uploaded by
aina marie templonuevoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessing The Mouth WPS Office
Assessing The Mouth WPS Office
Uploaded by
aina marie templonuevoCopyright:
Available Formats
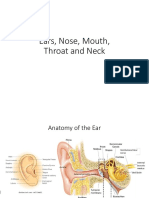
Throat
Assessing the Mouth,
Throat, Nose and
Sinuses
REVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
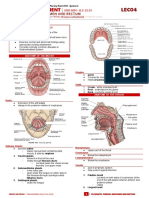
Mouth
oral cavity
From lips,cheeks, hard and soft palate, uvula,
tongue and its muscles
Sinuses
Mouth
Nose
1. Inspection of the lips
Normal:
moist, smooth, no lessions, no swelling
Abnormal
1. Dehydration - dry, cracked lips
2. Viral Infection - lesions, ulcers
3. Pallor (circumoral) - shock, anemia Cyanotic (bluish)
cold_hypoxia
5. Reddish - ketoacidosis, CO poisoning; COPD with
polycythemia
6. Edema- local/systemic allergic or anaphylactic
reaction
7. Lip cancer-squamous cell carcinoma; lower lip
2. Inspect the teeth
Normal
: 32 pearly whitish teeth, smooth surfaces,
4. Inspect Stensen ducts (parotid)
edges; 28 (4 wisdom tooth do not erupt); no Normal:
decay, no missing;jaws aligned; gums are
visible with flow of saliva; no redness, swelling, pain;
smooth, moist and no lesions
Fordyce spots(normal)
Abnormal
Abnormal
1. Yellow or Brownish teeth - smoke; drink large Reddened opening of Stensen ducts -mumps
amount or tea, caffeine or excessive intake of flouride
2. Tooth decay 5. Inspect and palpate the tongue
Normal:
3. Malocclussion
pink, moist, moderate size, with papillae; no lesions or
4. Brown or Yellow strains or White
ulcers
spots - antibiotic therapy or tooth trauma
Abnormal
5.Red, swollen gums- gingvitis., scrvy , leukemia
1. Dry, nodules, ulcers, absent papillae or fissures
6.Periodontitis-Receding red gums with loss pf teeth
are seen 2. Deep longitudinal fissures - dehydration
7.Hyperplasia ( enlarged,reddened gums) -Pregnancy, 3. Black hairy tongue - hyposalivation, heavy smoking,
pberty, leukemia use of phenytoin alcohol intake, use of mouthwash antibiotics
8. Bluish-black or gray-white line along gum - lead 4. Smooth, red, shiny tongue - Niacin or Vit.B12
poisoning deficiency
5. Enlarged tongue - hypothyroidism, acromegalyDown
3. Inspect buccal mucosa syndrome, anaphylaxis
Normal 6. Atrophied or Fasciculations - CN 12 damage
pink,moist, no lesions, ulcers, swelling
6.Assess ventral surface of tongue and
Abnormal
palpate the area.
1. Leukoplakia - chalky white raised patches; chronic
Normal:
irritation, heavy smoking,alcohol use
smooth, shiny, pink, slightly pale, with visible veins; no
2. Thrush - "Candida albicans infection whitish curd -
lesions
like patehes that scrape off over reddened mucosa and
bleed Abnormal
3. Koplik spots - measles 1. Leukoplakia, persistent lesions, ulcers, nodules -
cancer
4. Canker sores
Most common site of oral cancer nderneath the
5. Brown patches - Addison Disease
tongue
7. Inspect Wharton Ducts and observe the 4. Sulfur odor (fetor hepaticus) - End-Stage Liver
Disease
sides of the tongue
Normal: frenulum is midline; wharton ducts are visible
with salivary flow 12. Assess the uvula
Normal: fleshy, solid and hangs freely in midline
Abnormal: canker sores (chemotherapy)
Abnormal
1. asymmetrical or loss of movement - stroke/CVA
8. Check the strength of the tongue
Normal: strong resistance 2. palate fails to rise and uvula deviates - CN X
paralysis
Abnormal
1. Decreased strength - CN XIl 13. Inspect the tonsils.
Normal: Present or absent; pink, symmetric, 1+
9. Check anterior tonaue's ability to taste enlarged
Normal: can distinguish salt and sweet Abnormal Red, enlarged (2,3,4+);exudates
Abnormal: loss of taste 1+ - visible
2+ - midway between tonsillar pillars and uvula
10. Inspect the hard (anterior) and soft
3+- tonsils touch uvula
(posterior) palates and uvula
4+- tonslls touch each other
Normal:
‣ hard palate - pale or whitish. firm, transverse
rugae 14. Inspect posterior pharyngeal wall.
Normal: throat is pink, no lesions and exudates
‣ soft palate - pinkish, spongy, smooth palatine
tissues - intact
AbnomaI bright red throat with whiteor yellow
exudates - pharyngitis
Abnormal
1. Thick white plaques on hard palate'- Candidlasis
Nose
2. Deep purple, raised or flat lesion - Kaposi sarcoma
3. Yellow tint - Jaundice
1. Inspect and palpate external nose.
4. Cleft palate - opening in the hard palate Normal: color same with face; smooth, symmetric; no
tenderness
11. Note the odor Abnormal: tenderness
Normal: no unusual or foul odor
Abnormal 2 Check patency of air flow through
nostrils:
1. Fruity or acetone breathe - Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Normal: able to sniff
2. Ammonia odor - Kidney disease
Abnormal: swelling, rhinitis,obstruction
3. Fecal breath - bowel obstruction/ dental caris
3. Inspect internal nose.
Normal:
nasal mucosa - dark pink, moist, free of
exudates
nasal septum - intact turbinates - dark pink,
moist, no lesions
Abnormal
1. Nasal mucosa is swollen, bluishnand pale - allergies,
URTI
2. Epistaxis(nosebleed)
3. UIcers or perforated septum - use of cocaine, trauma,
infection,
4.Polyps
Sinuses
1. Palpate sinuses
Normal: non-tender; no crepitus
1. Tender - acute bacterial rhinosinusitis
2. (+) crepitus, exudates - Viral URI
2. Percuss sinuses
Normal: non-tender
Abnormal
1. Tender - infection or allergies
You might also like
- Dental Consent FormDocument2 pagesDental Consent Formkoshimannu100% (1)
- Physical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDocument89 pagesPhysical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDeeeee100% (3)
- EO/IO Exam CriteriaDocument3 pagesEO/IO Exam CriteriaTaylor100% (1)
- Cardiac Rehabilitation ProtocolDocument5 pagesCardiac Rehabilitation Protocolmarkhabm100% (1)
- Health Assessment Skills Lecture-Midterms: Mouth and Throat Content ConditionsDocument2 pagesHealth Assessment Skills Lecture-Midterms: Mouth and Throat Content ConditionsKathryn Kathryz BeyonceNo ratings yet
- Mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeyteDocument9 pagesMouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus Assessment: College of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeytePrincess AñabezaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Lecture: - Review About THE Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesHealth Assessment Lecture: - Review About THE Respiratory SystemHNo ratings yet
- Salcedo HA CU 9 ASSESSMENT of MOUTH THROAT 24 RDocument26 pagesSalcedo HA CU 9 ASSESSMENT of MOUTH THROAT 24 RshaimonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Mouth and OropharynxDocument3 pagesAssessing The Mouth and OropharynxReinell GoNo ratings yet
- 7mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus AssessmentDocument27 pages7mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus AssessmentFerocious WitNo ratings yet
- Tabular (Mouth, Heart and Neck Vessels)Document14 pagesTabular (Mouth, Heart and Neck Vessels)Kristelle Ann Irinco PajantoyNo ratings yet
- Mouth Oropharynx Nose Sinuses AseronDocument51 pagesMouth Oropharynx Nose Sinuses AseronAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Mouth and NeckDocument35 pagesMouth and NeckGabriel Almogela Jr.No ratings yet
- Ha NotesDocument12 pagesHa NotessrslytrdNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Mouth and Oropharynx Performance:: Lips and Buccal MucosaDocument3 pagesAssessing The Mouth and Oropharynx Performance:: Lips and Buccal MucosaAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Nose, Mouth, Throat and NeckDocument58 pagesNose, Mouth, Throat and NeckGloriaCoronado90% (10)
- Assessment of Nose, Sinuses, Mouth and Throat-JCCDocument43 pagesAssessment of Nose, Sinuses, Mouth and Throat-JCCEarlgerald RicafrancaNo ratings yet
- Mouth Throat Nose and Sinuses Checklist STUDENTSDocument4 pagesMouth Throat Nose and Sinuses Checklist STUDENTSRolandNo ratings yet
- Gingival Diseases in ChildrenDocument57 pagesGingival Diseases in ChildrenFourthMolar.com100% (3)
- Minor Case RASDocument41 pagesMinor Case RASNurul SufianNo ratings yet
- Nose, Mouth, Throat - Student Version 6 Slide Per PageDocument1 pageNose, Mouth, Throat - Student Version 6 Slide Per Pagegifty rathaurNo ratings yet
- Checklist EBP - Nose, Throat and MouthDocument6 pagesChecklist EBP - Nose, Throat and Mouths138140No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- #5 - A Nose, Mouth, Sinuses, ThroatDocument9 pages#5 - A Nose, Mouth, Sinuses, ThroatEsvinch EsvinchNo ratings yet
- 734common Oral Diseases Final - 4Document22 pages734common Oral Diseases Final - 4Mahmoud HassanNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Tongue LesionDocument26 pagesOral Pathology - Tongue Lesionneji_murniNo ratings yet
- תוכנית רבעונית q1 נראם גדבאןDocument84 pagesתוכנית רבעונית q1 נראם גדבאןIoana DănilăNo ratings yet
- MOUT and Oropharynx and Nose and Sinuses PRESENTATION 1Document44 pagesMOUT and Oropharynx and Nose and Sinuses PRESENTATION 1Reymart EstebanNo ratings yet
- Assessing Mouth and OropharynxDocument49 pagesAssessing Mouth and OropharynxHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Surgery: General ExamintionDocument6 pagesSurgery: General Examintionapi-3829364No ratings yet
- SodaPDF Merged Merging Result 1Document203 pagesSodaPDF Merged Merging Result 1nonelNo ratings yet
- Lec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumDocument23 pagesLec04 - Assessing Mouth, Throat, Abdomen and RectumIRISH MANIAGONo ratings yet
- Ears, Mouth, Throat Nose, and Sinuses AssessmentDocument8 pagesEars, Mouth, Throat Nose, and Sinuses Assessmentshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Skin Hair Nail-11Document10 pagesSkin Hair Nail-11Kristine Angie RamosNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Case Profoma - AgamDocument8 pagesOphthalmology Case Profoma - AgamHarshitha ANo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology I Final ReviewDocument373 pagesOral Pathology I Final ReviewAlex ChangNo ratings yet
- 5 - Mouth - NoseDocument21 pages5 - Mouth - Nosezainahalqahtani3No ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument9 pagesHealth AssessmentJESSMAR GRACE PARMOSANo ratings yet
- Assessing The Ears 2Document4 pagesAssessing The Ears 2aina marie templonuevoNo ratings yet
- Assessing EarsDocument5 pagesAssessing EarsTeresita PunoNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument20 pagesPhysical Assessmentkylemabanta123No ratings yet
- Mouth and OropharynxDocument17 pagesMouth and OropharynxNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- Approach To Oral LesionsDocument53 pagesApproach To Oral LesionsUmut YücelNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment PDFDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment PDFsunshine jeonNo ratings yet
- (L08) Lesions of The TongueDocument7 pages(L08) Lesions of The TongueAbdullah FadhelNo ratings yet
- IPPA Physical AssxDocument4 pagesIPPA Physical Assxkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Part 2 AssignmentDocument15 pagesPhysical Assessment Part 2 AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- 10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatDocument25 pages10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatArka Ogeh100% (1)
- Pathological AnalysisDocument58 pagesPathological AnalysisAhella AlaaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Mouth and PharynxDocument4 pagesAssessing The Mouth and PharynxYudi TrigunaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Head and Neck: SurgeryDocument3 pagesExamination of Head and Neck: Surgeryapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Mouth Throat and SinusesDocument12 pagesMouth Throat and SinusesAngelo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Oral Patho Lecture Shlav BDocument65 pagesOral Patho Lecture Shlav Bشبيبةالروم الملكيين الكاثوليكNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Physical Examination: I. General SurveyDocument10 pagesConduct of Physical Examination: I. General SurveyWeng RamojalNo ratings yet
- Anu Omr Long CaseDocument29 pagesAnu Omr Long CaseAnurtha AnuNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Virus Recurrent Apthous Stomatitis Oral PathoDocument35 pagesHerpes Simplex Virus Recurrent Apthous Stomatitis Oral PathoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Conduct of Physical Examination RemindersDocument23 pagesConduct of Physical Examination RemindersJazer DairoNo ratings yet
- Ha LecDocument5 pagesHa LecJulie YahnNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ChecklistDocument19 pagesHealth Assessment Checklistramzan aliNo ratings yet
- General Examination (COMPLEXION) by Dr. Rana Moustafa AlsayedDocument18 pagesGeneral Examination (COMPLEXION) by Dr. Rana Moustafa AlsayedAbdulla1999 AshrafNo ratings yet
- Ranula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandRanula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument236 pagesPharmacologyyalahopa100% (2)
- The Respiratory System: Aam Amarullah, M.PDDocument42 pagesThe Respiratory System: Aam Amarullah, M.PDUniversal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Fruit and Vegetables For HealthDocument45 pagesBenefits of Fruit and Vegetables For HealthKafid BramNo ratings yet
- CHN NotesDocument61 pagesCHN NotesAngelyn GamayaNo ratings yet
- 03 COVID Shimabukuro 508Document39 pages03 COVID Shimabukuro 508Kylie Betania Chávez VásquezNo ratings yet
- VIVENCIA PRIME All RidersDocument12 pagesVIVENCIA PRIME All RidersRalph RUzzelNo ratings yet
- Overview of Practice of Consultation Liaison.4Document10 pagesOverview of Practice of Consultation Liaison.4Sweet Memories JayaVaniNo ratings yet
- Disease Prevention and ControlDocument2 pagesDisease Prevention and Controlsudipta4321No ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology of Mother Tinctures &lower PotenciesDocument64 pagesClinical Pathology of Mother Tinctures &lower PotenciesAntony antony100% (1)
- WK 17 - Transportation and PandemicsDocument5 pagesWK 17 - Transportation and PandemicsChrissa EugenioNo ratings yet
- Psychoimmunology Essay by DR Romesh Senewiratne-Alagaratnam (MD)Document32 pagesPsychoimmunology Essay by DR Romesh Senewiratne-Alagaratnam (MD)Dr Romesh Arya Chakravarti100% (2)
- An Ancient Remedy RediscoveredDocument3 pagesAn Ancient Remedy RediscoveredVladimir ArmijosNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Examination English Class2011 1Document79 pagesNeurologic Examination English Class2011 1HieLdaJanuariaNo ratings yet
- EDUARDO ALEGRIA - Activity 1.3 - Making A DifferenceDocument3 pagesEDUARDO ALEGRIA - Activity 1.3 - Making A DifferenceLorenž SantośNo ratings yet
- (Leprosy Disease) : DefinitionDocument4 pages(Leprosy Disease) : DefinitionJulyn M SurlaNo ratings yet
- Ecq HemaDocument42 pagesEcq HemaJoezer Gumangan VeranoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal MassDocument9 pagesAbdominal Massscribd_huhuNo ratings yet
- And The Band Played On - Day 3 and 4 AnswersDocument5 pagesAnd The Band Played On - Day 3 and 4 AnswersAngelica ValmonteNo ratings yet
- A Synthesis Paper About Breast, Testicular and Cervical Cancer in The PhillipinesDocument3 pagesA Synthesis Paper About Breast, Testicular and Cervical Cancer in The Phillipinesjanna mae patriarcaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- 6th Year Final MCQ PediatricDocument10 pages6th Year Final MCQ Pediatricginaseptiani100% (6)
- SGRQ ManualDocument17 pagesSGRQ ManualParvez QuaziNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIADocument2 pagesECLAMPSIAZoe Jeanne GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Dehydration: Causes of Excessive Body Water LossesDocument4 pagesDehydration: Causes of Excessive Body Water LossesAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- NEW EDITABLE New Format New HighDocument434 pagesNEW EDITABLE New Format New Highdrsaimasaeed2No ratings yet
- MSDS Orec OzoneDocument2 pagesMSDS Orec OzoneHerni SuharniriyantiNo ratings yet
- Clinico-Etiological Spectrum of Pancytopenia in Hospitalized ChildrenDocument4 pagesClinico-Etiological Spectrum of Pancytopenia in Hospitalized ChildrenNurul Huda KowitaNo ratings yet