Professional Documents
Culture Documents
About Bangladesh
About Bangladesh
Uploaded by
tanhahossain29302930Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
About Bangladesh
About Bangladesh
Uploaded by
tanhahossain29302930Copyright:
Available Formats
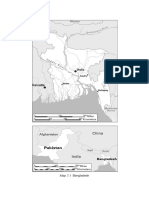
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia.
It is the
eighth-most populous country in the world and is among the most densely populated countries
with a population of nearly 170 million in an area of 148,460 square kilometers (57,320 sq. mi).
Bangladesh shares land borders with India to the west, north, and east, and Myanmar to the
southeast; to the south, it has a coastline along the Bay of Bengal. It is narrowly separated from
Bhutan and Nepal by the Siliguri Corridor and from China by the Indian state of Sikkim in the
north. Dhaka, the capital and largest city, is the nation's political, financial, and cultural center.
Chittagong, the second-largest city, is the busiest port on the Bay of Bengal. The official
language is Bengali.
Bangladesh forms the sovereign part of the historic and ethno linguistic region of Bengal, which
was divided during the Partition of India in 1947.The country, has a Bengali Muslim majority.
Ancient Bengal was known as Gangaridai and was a bastion of pre-Islamic kingdoms. Muslim
conquests after 1204 heralded the sultanate and Mughal periods, during which an independent
Bengal Sultanate and a wealthy Mughal Bengal transformed the region into an important
center of regional affairs, trade, and diplomacy. After 1757, Bengal's administrative jurisdiction
reached its greatest extent under the Bengal Presidency of the British Empire. In 1940, the first
Prime Minister of Bengal, A. K. Fazlul Huq, supported the Lahore Resolution. Before the
partition of Bengal, a Bengali sovereign state was first proposed by Premier H. S. Suhrawardy.
In 1947, East Bengal became the most populous province in the Dominion of Pakistan. It was
renamed as East Pakistan, with Dhaka becoming the country's legislative capital. The Bengali
Language Movement in 1952; the East Bengali legislative election in 1954; the six point
movement of 1966; and the 1970 Pakistani general election resulted in the rise of Bengali
nationalism and pro-democracy movements. The refusal of the Pakistani military junta to
transfer power to the Awami League, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, led to the Bangladesh
Liberation War in 1971. The Mukti Bahini, aided by India, waged a successful armed revolution.
The conflict saw the Bangladesh genocide and the massacre of pro-independence Bengali
civilians, including intellectuals. The new state of Bangladesh became the first constitutionally
secular state in South Asia in 1972. Islam was declared the state religion in 1988.In 2010, the
Bangladesh Supreme Court reaffirmed secular principles in the constitution.
It maintains the third-largest military in the region and is the largest contributor of personnel to
UN peacekeeping operations. Bangladesh is a unitary parliamentary republic based on the
Westminster system. Bengalis make up 99% of the total population. The country consists of
eight divisions, 64 districts and 495 sub districts, as well as the world's largest mangrove forest.
It hosts one of the largest refugee populations in the world due to the Rohingya genocide. It
hosts the headquarters of BIMSTEC. It is a founding member of the SAARC, as well as a member
of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation and the Commonwealth of Nations.
You might also like
- The Girl Who Ate A Death God (All Volumes)Document627 pagesThe Girl Who Ate A Death God (All Volumes)Yassine AourhanNo ratings yet
- BangladeshDocument1 pageBangladeshplayingpiano2100No ratings yet
- Bangladesh (Republic of Bangladesh, Is A Country In: PronouncedDocument2 pagesBangladesh (Republic of Bangladesh, Is A Country In: PronouncedRajib KhanNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh: History and GeographyDocument22 pagesBangladesh: History and GeographySenouiiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh (: Rāmāyana MahābhārataDocument2 pagesBangladesh (: Rāmāyana Mahābhāratadivya kashyapNo ratings yet
- 100 Years History of BangladeshDocument9 pages100 Years History of BangladeshTonmoy Dey100% (1)
- The Emergence of The Independent BangladeshDocument4 pagesThe Emergence of The Independent BangladeshShahriwar RikNo ratings yet
- 100 Years History of BangladeshDocument10 pages100 Years History of BangladeshTonmoy DeyNo ratings yet
- BangladeshDocument52 pagesBangladeshBotol MalayaNo ratings yet
- Green BanglaDocument5 pagesGreen BanglaAnonymous C9ZNFkrb6No ratings yet
- About BDDocument3 pagesAbout BDNn TusharNo ratings yet
- Indo Pak WarDocument7 pagesIndo Pak WarJANVI GUPTANo ratings yet
- FSA Pakistan-Bangladesh RelationsDocument17 pagesFSA Pakistan-Bangladesh RelationsM Adnan AzizNo ratings yet
- Student Name: Sumaiya Zaman Mohima Student Id: 211010003Document2 pagesStudent Name: Sumaiya Zaman Mohima Student Id: 211010003Anas RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Partition of BengalDocument10 pagesThe Partition of BengalSadaf Nazir100% (1)
- National Textile University Faisalabad: Assignment No: 1 Title of AssignmentDocument20 pagesNational Textile University Faisalabad: Assignment No: 1 Title of AssignmentAbid SarwarNo ratings yet
- Social Science Major 5 - BangladeshDocument2 pagesSocial Science Major 5 - BangladeshFredrich RamaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan An OverviewDocument8 pagesPakistan An Overviewt a khanNo ratings yet
- HIstoryDocument16 pagesHIstoryborglingchompersNo ratings yet
- Causes of Seperation of EPakistanDocument12 pagesCauses of Seperation of EPakistanAMAN ABDUL QADEERNo ratings yet
- Musammat Mahzebin: Lecturer Department of Humanities Khulna University of Engineering and Technology (KUET)Document35 pagesMusammat Mahzebin: Lecturer Department of Humanities Khulna University of Engineering and Technology (KUET)ShabbirAhamed DharusSalamNo ratings yet
- Separation of East Pakistan-1Document7 pagesSeparation of East Pakistan-1hmuzammal105No ratings yet
- The Liberation War of Bangladesh Assign Main1Document19 pagesThe Liberation War of Bangladesh Assign Main1Ssilent Ssoul100% (3)
- Pak Study U-13Document15 pagesPak Study U-13borglingchompersNo ratings yet
- Post-Partition (1947-Present) : IndiaDocument17 pagesPost-Partition (1947-Present) : IndiaPiyush RanjanNo ratings yet
- Republic of IndiaDocument17 pagesRepublic of IndiaEnal GodilNo ratings yet
- History of Bangladesh WarDocument17 pagesHistory of Bangladesh WarSariputta AnandNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Info of FlagDocument3 pagesBangladesh Info of Flagdmitriytorpedo1924No ratings yet
- Genesis of BangladeshDocument33 pagesGenesis of BangladeshgdapbbbsybsuusrgnwNo ratings yet
- North South University Department of History HIS103Document7 pagesNorth South University Department of History HIS103Ahanaf FaminNo ratings yet
- Geo-Political History of BangladeshDocument6 pagesGeo-Political History of Bangladeshxeo zeoNo ratings yet
- Report On Bangladesh Constitution - FinalDocument31 pagesReport On Bangladesh Constitution - FinalAl Hossain HossainNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh WikipediaDocument15 pagesBangladesh WikipediaAamir HussainNo ratings yet
- The Partition of BengalDocument22 pagesThe Partition of BengalhurairaNo ratings yet
- Separation of East Pakistan 1971Document3 pagesSeparation of East Pakistan 1971Muhammad Abu Turab YeetNo ratings yet
- Slide - Session 19Document39 pagesSlide - Session 19Abdullah JayedNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh: People's Republic of BangladeshDocument5 pagesBangladesh: People's Republic of BangladeshMehediBahadurNo ratings yet
- Bengali NationalismDocument2 pagesBengali NationalismAdiba Ahamed0% (1)
- 1971 Genocide in BangladeshDocument30 pages1971 Genocide in BangladeshAbir Mahmud ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Division of PakistanDocument14 pagesDivision of PakistanMohtashim Farfelu GhufraniNo ratings yet
- West BengalDocument13 pagesWest BengalPriya Pandey100% (1)
- Lecture 11Document29 pagesLecture 11Sajid Rahman EvanNo ratings yet
- Gen 226 2019-1-10-258Document13 pagesGen 226 2019-1-10-258Kazi Shariat UllahNo ratings yet
- India Contribution FinalDocument5 pagesIndia Contribution FinalkinjorkhanNo ratings yet
- History of East Pakistan - WikipediaDocument11 pagesHistory of East Pakistan - WikipediazubaerjewelNo ratings yet
- EMB AssignmentDocument7 pagesEMB AssignmentShuvro RoyNo ratings yet
- Emergence of BangladeshDocument11 pagesEmergence of BangladeshNerdBoy 619No ratings yet
- 1971 Liberation WarDocument12 pages1971 Liberation Warraisaalam0411No ratings yet
- Zubair Ayoub PST FinalDocument15 pagesZubair Ayoub PST Finalganok balochNo ratings yet
- Pak Study Assigment 2Document5 pagesPak Study Assigment 2maroofjahanaziziNo ratings yet
- Political and Constitutional Development SalmaDocument12 pagesPolitical and Constitutional Development SalmaKhan Ume Salma Danish100% (1)
- Mcom304 Adopt A CountryDocument7 pagesMcom304 Adopt A Countryapi-719874719No ratings yet
- FINAL SLIDE Bangladesh StudyDocument35 pagesFINAL SLIDE Bangladesh StudyShafrid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Libeation War of BangladeshDocument50 pagesLibeation War of BangladeshAvee EmersonNo ratings yet
- Why Nation Building For Pakistan?Document8 pagesWhy Nation Building For Pakistan?hinaNo ratings yet
- GoruDocument2 pagesGoruEmadul BasharNo ratings yet
- East Pakistan and The Emancipation of BangladeshDocument2 pagesEast Pakistan and The Emancipation of Bangladeshacurciojunior23No ratings yet
- Sayeedi Full Verdict - War CrimeDocument120 pagesSayeedi Full Verdict - War CrimeUllash JayedNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: The Liberation War of Bangladesh "The Peoples War"Document9 pagesTerm Paper: The Liberation War of Bangladesh "The Peoples War"Mashukur Rahman100% (1)
- History AssignmentDocument6 pagesHistory AssignmentSadia Tasnim 1721783No ratings yet
- Dusk, Dawn and Liberation: A Historical Fiction on the Liberation Struggle of BangladeshFrom EverandDusk, Dawn and Liberation: A Historical Fiction on the Liberation Struggle of BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ottoman EmpireDocument4 pagesAssignment Ottoman EmpireRobert BrookeNo ratings yet
- Patrimoine CulturelDocument5 pagesPatrimoine CulturelislemmonkiNo ratings yet
- African StatsDocument48 pagesAfrican StatsNana AsantewaNo ratings yet
- Faulty Coodination (Lesson) Group 1Document5 pagesFaulty Coodination (Lesson) Group 1Alexis MüllerNo ratings yet
- Đính Kèm 2 Sơ Đ T CH C EVN - QT1Document2 pagesĐính Kèm 2 Sơ Đ T CH C EVN - QT1Doan Ngoc DucNo ratings yet
- Conflict, Change and Conflict ResolutionDocument26 pagesConflict, Change and Conflict ResolutionF M Tunvir ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Ace Milan - Dec - LuaDocument8 pagesAce Milan - Dec - Luazakirachi200219No ratings yet
- Was Fhere A Caribou Killed in Apocolypse Now - Google SearchDocument1 pageWas Fhere A Caribou Killed in Apocolypse Now - Google SearchcharlenemybeanNo ratings yet
- PAC3 Vietnam Operations Chart Livingrules 021122Document2 pagesPAC3 Vietnam Operations Chart Livingrules 021122Peter McGloneNo ratings yet
- All Quiet On The Western Front: Novel Study UnitDocument7 pagesAll Quiet On The Western Front: Novel Study UnitSahar HaidaryNo ratings yet
- On Translating Arabic and English Media Texts (Part 1)Document9 pagesOn Translating Arabic and English Media Texts (Part 1)mw6559010No ratings yet
- OM - P08 - Planning ControlDocument19 pagesOM - P08 - Planning ControlEnzo TrigueirosNo ratings yet
- A Movie Review of Heneral Luna by Jerrold TarogDocument2 pagesA Movie Review of Heneral Luna by Jerrold TarogLoraine TubigNo ratings yet
- Solo Play For Warcry: One-Off Solo BattlesDocument3 pagesSolo Play For Warcry: One-Off Solo BattlesБогдан БуркаNo ratings yet
- Nazi Germany Dissertation IdeasDocument5 pagesNazi Germany Dissertation IdeasPaperWritingCompanyCanada100% (1)
- Danh Sách Phòng ĐoànDocument1 pageDanh Sách Phòng ĐoànNghĩa TrầnNo ratings yet
- Finnish Pistols and RevolversDocument91 pagesFinnish Pistols and RevolversRenato SpinelliNo ratings yet
- The French Revolutionary Tradition in Russian and Soviet Politics Political Thought and Culture Jay Bergman Full ChapterDocument67 pagesThe French Revolutionary Tradition in Russian and Soviet Politics Political Thought and Culture Jay Bergman Full Chaptercrystal.jimerson169100% (6)
- Mechanical Properties of WaterDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of WaterBindu MenonNo ratings yet
- Kobelco Hydraulic Excavator Sk400 IV Sk400lc IV Operators ManualDocument23 pagesKobelco Hydraulic Excavator Sk400 IV Sk400lc IV Operators Manualemilyclements220382sqj100% (65)
- 1st Neapolitan Infantry Regiment 1806 1815Document14 pages1st Neapolitan Infantry Regiment 1806 1815pcojediNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Blockchain Based Smart Grids 1St Edition Miadreza Shafie Khah Editor Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Blockchain Based Smart Grids 1St Edition Miadreza Shafie Khah Editor Online Ebook All Chapter PDFsusan.brazil584100% (12)
- Naufragia Procter v2.1Document1 pageNaufragia Procter v2.1sigurdhartNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi AssassinationDocument5 pagesRajiv Gandhi AssassinationAryan JakharNo ratings yet
- Genealogy On FacebookDocument166 pagesGenealogy On Facebookmoonswings100% (8)
- The International History ReviewDocument21 pagesThe International History ReviewNidhi PrakritiNo ratings yet
- Failure of United NationDocument21 pagesFailure of United NationFarhana Firoz MeemNo ratings yet
- Indian Maritime Doctrine 2009 UpdatedDocument188 pagesIndian Maritime Doctrine 2009 Updatedankitpanda0% (1)
- Anti Fascism MovementDocument22 pagesAnti Fascism MovementSYED ABDULLAH UMAR HASHMINo ratings yet