Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment Re
Assignment Re
Uploaded by
tongshie77Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment Re
Assignment Re
Uploaded by
tongshie77Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: Francine Kate A.
Ukat Course: BS Accountancy-1
Day and Time of Class: Monday (1:30-4:30 pm)
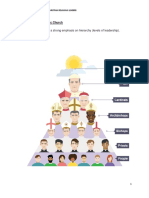
POPE
The Leader of Catholic Church
The Pope, often referred to as the Bishop of Rome and the spiritual leader of the Catholic Church, holds a position of immense
influence and responsibility. With millions of followers worldwide, the Pope plays a crucial role in guiding the faithful,
shaping church doctrine, and representing Catholicism on the global stage. At the core of the Pope's responsibilities is their
role as the supreme authority in matters of faith, morals, and church governance within the Catholic Church. As the Vicar of
Christ on Earth, the Pope is considered the successor of Saint Peter, to whom Jesus entrusted the keys of the Kingdom of
Heaven according to Catholic tradition.
One of the primary functions of the Pope is to interpret and uphold the teachings of the Catholic Church. Through encyclicals,
apostolic exhortations, and other pronouncements, the Pope articulates the Church's stance on theological, ethical, and social
issues. This guidance is based on the Scriptures, sacred tradition, and the Magisterium, which comprises the teaching authority
of the Church. The Pope also serves as a unifying figure for Catholics worldwide, fostering communion and solidarity among
diverse communities of believers. Through pastoral visits, papal audiences, and apostolic journeys, the Pope connects with the
faithful, offering spiritual guidance, encouragement, and pastoral care.
The selection of a new Pope occurs within the framework of a papal conclave, a centuries-old tradition steeped in prayer,
deliberation, and discernment. When a Pope dies or resigns, the College of Cardinals convenes in Vatican City to elect a
successor. Cardinals eligible to participate in the conclave gather in the Sistine Chapel, where they engage in prayer and
reflection. The election process is governed by strict protocols to ensure confidentiality and impartiality. Cardinals cast ballots
in multiple rounds until a candidate receives a two-thirds majority. Once a consensus is reached, the chosen cardinal becomes
the new Pope. The announcement is made with the traditional Latin phrase "Habemus Papam" ("We have a Pope"), followed
by the introduction of the newly elected Pope to the world from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica.
The Pope's influence extends beyond the Catholic Church, resonating in global affairs, interfaith dialogue, and social advocacy.
As a moral authority, the Pope addresses pressing issues such as poverty, human rights, environmental stewardship, and
peacebuilding. Papal encyclicals, letters, and speeches convey the Pope's teachings and perspectives on contemporary
challenges. For instance, Pope Francis has emphasized themes of mercy, compassion, and social justice, urging Catholics to
embrace inclusivity, care for the marginalized, and protect the planet. The Pope's diplomatic engagements and visits to
different nations foster dialogue, understanding, and collaboration among religious communities and governments. These
efforts contribute to promoting peace, reconciliation, and intercultural exchange on a global scale. Furthermore, the Pope's
symbolic presence and pastoral outreach inspire hope, unity, and solidarity among Catholics worldwide. Papal initiatives, such
as World Youth Day, synods, and charitable endeavors, engage believers in spiritual renewal, evangelization, and service to
others.
In conclusion, the Pope's role as the spiritual leader of the Catholic Church encompasses doctrinal authority, pastoral care, and
global advocacy. The papal election process reflects the Church's tradition of discernment and continuity. Through their
teachings, outreach, and engagement, Popes exert a profound impact on individuals, communities, and societies, shaping the
course of Catholicism and contributing to broader conversations on faith, ethics, and human dignity.
You might also like
- (1996) Malachi Martin - Windswept HouseDocument1,340 pages(1996) Malachi Martin - Windswept HouseIred Owlet84% (31)
- The Rule of The Templars by J.M. Upton-WardDocument424 pagesThe Rule of The Templars by J.M. Upton-WardRui Sequeira100% (1)
- Augustine Came To KentDocument1 pageAugustine Came To KentChris Shanahan0% (1)
- If Today You Hear His Voice (Fr. Roch Kereszty)Document46 pagesIf Today You Hear His Voice (Fr. Roch Kereszty)Iggy yeoNo ratings yet
- II. 3. - Pastoral Care and Counselling in The Reformation TraditionsDocument6 pagesII. 3. - Pastoral Care and Counselling in The Reformation TraditionsKross Lnza KhiangteNo ratings yet
- The Banished Heart. Origins of Heteropraxis in The Catholic ChurchDocument9 pagesThe Banished Heart. Origins of Heteropraxis in The Catholic ChurchQuo PrimumNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of The Catholic ChurchDocument4 pagesHierarchy of The Catholic ChurchCJ Usares100% (1)
- Diocesan Spirituality: Response of Catholic Schools To The Challenges of The New EvangelizationDocument15 pagesDiocesan Spirituality: Response of Catholic Schools To The Challenges of The New EvangelizationKevin T. Onaro100% (2)
- PopesDocument2 pagesPopesJEFFERSONNo ratings yet
- Roman Catholic Church HierarchyDocument5 pagesRoman Catholic Church HierarchyHarly Joe Ellazo BagunaNo ratings yet
- Catholism ReportDocument8 pagesCatholism ReportAbdurahman AdilNo ratings yet
- Pope Benedict XVI and The ChurchDocument5 pagesPope Benedict XVI and The ChurchAlvi ViadoyNo ratings yet
- Pope FrancisDocument3 pagesPope FrancisPatricia SusckindNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy Catholic Church 1Document5 pagesHierarchy Catholic Church 1Mary Jane TadeoNo ratings yet
- Thoughts From FR Alberione 2Document47 pagesThoughts From FR Alberione 2MargaretKerryfsp100% (2)
- The Priesthood of the Faithful: A Theology of Hope for the ChurchFrom EverandThe Priesthood of the Faithful: A Theology of Hope for the ChurchNo ratings yet
- Holy Spirit, Its Soul, We Can Never Get To Know It Completely. The Church Is Mystery by Reason Of: Its Origin in The Father'sDocument4 pagesHoly Spirit, Its Soul, We Can Never Get To Know It Completely. The Church Is Mystery by Reason Of: Its Origin in The Father'sJohn Christian MacanNo ratings yet
- How The Patristic Fathers Can Help Us Strengthen Liturgical Catechesis For The NonesDocument12 pagesHow The Patristic Fathers Can Help Us Strengthen Liturgical Catechesis For The NonesLauren StamperNo ratings yet
- The Pocket Guide to the Popes: The Pontiffs from St. Peter to John PaulFrom EverandThe Pocket Guide to the Popes: The Pontiffs from St. Peter to John PaulRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Quiet Revolution of Pope Francis: A Synodal Catholic Church in Ireland Revised EditionFrom EverandThe Quiet Revolution of Pope Francis: A Synodal Catholic Church in Ireland Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Azusa, Rome, and Zion: Pentecostal Faith, Catholic Reform, and Jewish RootsFrom EverandAzusa, Rome, and Zion: Pentecostal Faith, Catholic Reform, and Jewish RootsNo ratings yet
- Living the Gospel of Jesus Christ: Orthodox and Evangelical Approaches to Discipleship and Christian FormationFrom EverandLiving the Gospel of Jesus Christ: Orthodox and Evangelical Approaches to Discipleship and Christian FormationMark OxbrowNo ratings yet
- The History and Beliefs of Old Catholicism and the Old Catholic Church of North AmericaFrom EverandThe History and Beliefs of Old Catholicism and the Old Catholic Church of North AmericaNo ratings yet
- Eastern Orthodox Christian ChurchDocument11 pagesEastern Orthodox Christian ChurchNicu Carlig100% (1)
- 1 Sacred TraditionDocument12 pages1 Sacred TraditionmargarettebeltranNo ratings yet
- Primacy PDFDocument25 pagesPrimacy PDFJeremiah Clemente dC TorresNo ratings yet
- THISONeDocument4 pagesTHISONeCarmel VassalloNo ratings yet
- Religions Within The Municipality of OtonDocument8 pagesReligions Within The Municipality of OtonJennifer Dapilmoto MandalNo ratings yet
- Christianity Depth Study - Syllabus Notes - Daniel WilsonDocument5 pagesChristianity Depth Study - Syllabus Notes - Daniel Wilsonstudent2407No ratings yet
- Lesson 5. The Hierarchy of The ChurchDocument5 pagesLesson 5. The Hierarchy of The ChurchRose DepistaNo ratings yet
- Church in Dialogue With Non-Christians in The Light of NADocument9 pagesChurch in Dialogue With Non-Christians in The Light of NAHan Zaw HtunNo ratings yet
- Robert McElroy AUSCP Presentation June 26, 2018Document6 pagesRobert McElroy AUSCP Presentation June 26, 2018National Catholic Reporter100% (1)
- Christian Unity — the Next Step: 'That They May All Be One'From EverandChristian Unity — the Next Step: 'That They May All Be One'No ratings yet
- The Orthodox Missionary EthosDocument9 pagesThe Orthodox Missionary EthosLinekerosNo ratings yet
- Religious Studies ReviewerDocument3 pagesReligious Studies ReviewerJanica SamsonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Summary Theo 12Document7 pagesMidterm Summary Theo 12MJ GabrilloNo ratings yet
- Roman Catholicism Is A Worldwide Religious Tradition of Some 1.1 Billion Members. It Traces ItsDocument5 pagesRoman Catholicism Is A Worldwide Religious Tradition of Some 1.1 Billion Members. It Traces Itsaybi pearlNo ratings yet
- Charismatic Group in Catholic ChurchDocument6 pagesCharismatic Group in Catholic ChurchEverything newNo ratings yet
- Mission in the Spirit / Ma and Ma: Towards a Pentecostal/Charismatic MissiologyFrom EverandMission in the Spirit / Ma and Ma: Towards a Pentecostal/Charismatic MissiologyNo ratings yet
- 25 de Agosto 2020 Theology of The Laity PDFDocument22 pages25 de Agosto 2020 Theology of The Laity PDFJesús SecaNo ratings yet
- 224-That - All - May - Be - One - by Walter Veith PDFDocument18 pages224-That - All - May - Be - One - by Walter Veith PDFDikapsNo ratings yet
- Collegiality &ecumenim - Rayan Lobo, SJDocument7 pagesCollegiality &ecumenim - Rayan Lobo, SJRayan Joel Lobo100% (1)
- Glossary of Terms E28093 Pope John Xxiii and Vatican IIDocument2 pagesGlossary of Terms E28093 Pope John Xxiii and Vatican IIRuthHansellNo ratings yet
- ALH January 2019 TimesDocument69 pagesALH January 2019 TimesMaria Paz CastellanoNo ratings yet
- The Apostolic FathersDocument178 pagesThe Apostolic Fathersludwig9No ratings yet
- Introduction EcclesologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction Ecclesologyaudrey barcelonaNo ratings yet
- MagisteriumDocument6 pagesMagisteriumboomonyouNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12-Wit Soc PDFDocument11 pagesLesson 12-Wit Soc PDFNaffea PeligrinoNo ratings yet
- Mission of The Church CatholicDocument14 pagesMission of The Church CatholicMichael_Carpen_85870% (1)
- Church Leaders AND System OF AuthorityDocument23 pagesChurch Leaders AND System OF AuthoritySharmin ReulaNo ratings yet
- Church Leaders AND System OF AuthorityDocument23 pagesChurch Leaders AND System OF AuthoritySharmin ReulaNo ratings yet
- Preaching Written Report - Trent To Enlightenment ConsolidatedDocument20 pagesPreaching Written Report - Trent To Enlightenment ConsolidatedRoger Ryan AlbaNo ratings yet
- An Open Letter To Confused Cath - Archbishop Marcel Lefebvre - PD PDFDocument81 pagesAn Open Letter To Confused Cath - Archbishop Marcel Lefebvre - PD PDFDiogo BorgesNo ratings yet
- The Role of Christian LeadersDocument11 pagesThe Role of Christian LeaderskiatatgaNo ratings yet
- The New Directory for Catechesis: Highlights and Summaries for Catechists and Pastoral LeadersFrom EverandThe New Directory for Catechesis: Highlights and Summaries for Catechists and Pastoral LeadersNo ratings yet
- Benefaction and Patronage in Leadership: A Socio-Historical Exegesis of the Pastoral EpistlesFrom EverandBenefaction and Patronage in Leadership: A Socio-Historical Exegesis of the Pastoral EpistlesNo ratings yet
- Charism and CST Pfeil 2007Document17 pagesCharism and CST Pfeil 2007Makoy MarkozNo ratings yet
- JOHN PAUL II IN RELATION WITH OTHER GROUPSDocument31 pagesJOHN PAUL II IN RELATION WITH OTHER GROUPSRamir SimbreNo ratings yet
- Catholic Reformati ON: Prepare By: Group 3Document12 pagesCatholic Reformati ON: Prepare By: Group 3Kezia CanutoNo ratings yet
- Binongko - Pemilih TMS Dan Pemilih Baru Dalam DPTHP2Document192 pagesBinongko - Pemilih TMS Dan Pemilih Baru Dalam DPTHP2SuparmanNo ratings yet
- Diaconate Ordination HomilyDocument2 pagesDiaconate Ordination HomilyLloyd MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ad Audiendas Confessiones Review & ExamDocument2 pagesAd Audiendas Confessiones Review & ExamNguyen Anh HuyNo ratings yet
- Mary, Tower of David Cardinal NewmanDocument21 pagesMary, Tower of David Cardinal NewmanJoao OssolaNo ratings yet
- PDS QuestionnaireDocument54 pagesPDS QuestionnaireIoannes PaulusNo ratings yet
- Sacraments and God's Presence Reflection PaperDocument1 pageSacraments and God's Presence Reflection PaperShannin MaeNo ratings yet
- 1-2nd Synod of LucenaDocument2 pages1-2nd Synod of LucenaLavander BlushNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument336 pagesDocumentccopresearchNo ratings yet
- The Canterbury Tales As Microcosm of Middle English SocietyDocument4 pagesThe Canterbury Tales As Microcosm of Middle English SocietyJett RoyNo ratings yet
- Rizal NolimetangereDocument6 pagesRizal Nolimetangereruth bulawinNo ratings yet
- TudorsDocument18 pagesTudorsLasc EmilianNo ratings yet
- Holy OrdersDocument13 pagesHoly OrdersVJ VENICE NICOLE SILVANo ratings yet
- Martin Luther Thesis 32Document8 pagesMartin Luther Thesis 32afktgoaaeynepd100% (2)
- Rites Holy Week McManus 1952Document157 pagesRites Holy Week McManus 19521culture100% (1)
- The Antiquities of The Christian Church by Bingham V.4 PDFDocument550 pagesThe Antiquities of The Christian Church by Bingham V.4 PDFMarwa Saied100% (1)
- Syriac Catholic ChurchDocument10 pagesSyriac Catholic Churchgoodie038No ratings yet
- Dhaka University: Department of EnglishDocument6 pagesDhaka University: Department of EnglishKamrul Islam1996No ratings yet
- The Holy Office On Worship With Non-CatholicsDocument4 pagesThe Holy Office On Worship With Non-CatholicsRon LawsonNo ratings yet
- Life of ST John BoscoDocument6 pagesLife of ST John BoscoKernyuy ClovisNo ratings yet
- Compassionate Pastor Dec 2009Document48 pagesCompassionate Pastor Dec 2009RFC MascarenhasNo ratings yet
- Retraction of Rizal - Pascual - Part 2Document50 pagesRetraction of Rizal - Pascual - Part 2karl IgniciaNo ratings yet
- Rel Ed 4 - Module 6 - Holy Eucharist - Part 2-MergedDocument35 pagesRel Ed 4 - Module 6 - Holy Eucharist - Part 2-MergedCatherine AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Phys1488 2904Document4 pagesPhys1488 2904Muhammad rafi Insan FillahNo ratings yet
- Church Teaching: Course Learning Packets Saint Louis University School of Teacher Education and Liberal ArtsDocument6 pagesChurch Teaching: Course Learning Packets Saint Louis University School of Teacher Education and Liberal Artsmark sarteNo ratings yet
- 01 The Birth of The Modern WorldDocument8 pages01 The Birth of The Modern WorldDadal 12No ratings yet