Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Virtual Machine 9608
Virtual Machine 9608
Uploaded by
d hkCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Financial Time Series Analysis and Prediction With Feature Engineering and Support Vector Machines - Newton - LinchenDocument5 pagesFinancial Time Series Analysis and Prediction With Feature Engineering and Support Vector Machines - Newton - LinchenNewton Linchen100% (1)
- Tardiness: Its Effects To The Academic Performance of The Grade 10 Students of Sjsfi Enrolled in S.Y. 2019-2020Document24 pagesTardiness: Its Effects To The Academic Performance of The Grade 10 Students of Sjsfi Enrolled in S.Y. 2019-2020Alyana Linog99% (86)
- Virtual Machine SeminarDocument15 pagesVirtual Machine SeminarChuks Abanum0% (2)
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual Machinec583706No ratings yet
- Final Report On VirtualizationDocument27 pagesFinal Report On VirtualizationMukesh BuradkarNo ratings yet
- NumerologyDocument24 pagesNumerologyphani60% (5)
- Cambridge International AS and A Level Computer Science: Topic Support GuideDocument13 pagesCambridge International AS and A Level Computer Science: Topic Support GuideDeewas PokhNo ratings yet
- Ameya Abhay Khedkar PPT 2021Document19 pagesAmeya Abhay Khedkar PPT 2021Shubham JoshiNo ratings yet
- OS Assignment 1Document5 pagesOS Assignment 1Usama Nasir GillNo ratings yet
- VirtualDocument9 pagesVirtualOsaigbovo TimothyNo ratings yet
- Virtual Machine SeminarDocument37 pagesVirtual Machine SeminarVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument28 pagesChapter ThreeUrgessa GedefaNo ratings yet
- CPU VirtualizationDocument6 pagesCPU VirtualizationHEMALAKSHMI DNo ratings yet
- Ac 2007-904: A Virtual Machine Environment For Real-Time Systems LaboratoriesDocument19 pagesAc 2007-904: A Virtual Machine Environment For Real-Time Systems LaboratoriesJahanzaib ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document36 pagesUnit 5AmudariaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Virtualization BasicsDocument12 pagesUnit II Virtualization Basicsgtrajasekaran1No ratings yet
- Intro To VirtualizationDocument452 pagesIntro To VirtualizationHackerman42100% (8)
- Virtual MachinesDocument2 pagesVirtual MachinesSunithaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Virtual Machines Implementation and ApplicationsDocument47 pagesAn Introduction To Virtual Machines Implementation and ApplicationsSiri chandana MannavaNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is A Virtual Machine?Document2 pages1) What Is A Virtual Machine?Beatriz GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Virtual MachineDocument8 pagesVirtual MachineSrinivas Rapelli0% (1)
- Virtual Machine (VM) : Assignment OnDocument7 pagesVirtual Machine (VM) : Assignment OnMd FurquanNo ratings yet
- Cs3451 Os Unit 5 Notes EduenggDocument25 pagesCs3451 Os Unit 5 Notes EduenggMENAGANo ratings yet
- Lab - Installing The Cyberops Workstation Virtual Machine: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLab - Installing The Cyberops Workstation Virtual Machine: ObjectivesdweekendwandererNo ratings yet
- 3-1-Installing Virtual Machine - Docx JunioDocument5 pages3-1-Installing Virtual Machine - Docx JuniodweekendwandererNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFDocument4 pages3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFBlessed Endibye KanyembaNo ratings yet
- Final Presenation On Virtual SystemsDocument13 pagesFinal Presenation On Virtual SystemsSamprit PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microsoft Dynamics® AX 2009 - Virtual PC Setup GuideDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Microsoft Dynamics® AX 2009 - Virtual PC Setup GuideGopala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineMochamad Arief Ferdiansyah NurNo ratings yet
- Virtual IzationDocument92 pagesVirtual IzationnkNo ratings yet
- Virtual Ization 3545Document40 pagesVirtual Ization 3545dhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Installing and Using XenDocument52 pagesInstalling and Using Xensushants_49151525No ratings yet
- 19 Virtualizationppt 2550Document45 pages19 Virtualizationppt 2550RohnikiNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab Solutions - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument6 pages1.1.1.4 Lab Solutions - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineAshIru Mohammed UmarNo ratings yet
- Leni Andriani - 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pagesLeni Andriani - 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineLeni AndrianiNo ratings yet
- 1.1.5 Lab - Installing The Virtual MachinesDocument4 pages1.1.5 Lab - Installing The Virtual MachinesMuharramNo ratings yet
- Virtual System Mids Short QuestionDocument4 pagesVirtual System Mids Short Questionmu70832No ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual Machine - ILMDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual Machine - ILMAna Lucia Alves dos SantosNo ratings yet
- CST423 M2 Ktunotes - inDocument15 pagesCST423 M2 Ktunotes - inRRNo ratings yet
- 1114 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pages1114 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachinesetyabudhiNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS)Document12 pagesInfrastructure As A Service (IAAS)userdemo12334No ratings yet
- Virtual MachineDocument16 pagesVirtual Machineapi-19854229No ratings yet
- Tugas 1Document14 pagesTugas 1JOSUA MARTINUS BARNABAS SAMBOUWNo ratings yet
- Assignment of OSDocument3 pagesAssignment of OSshamza hanifNo ratings yet
- Revised Tle As CSS10 Q3 WK3Document5 pagesRevised Tle As CSS10 Q3 WK3Jonald SalinasNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineHerdian MpNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To VirtualizationDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To VirtualizationCấn HùngNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineAayuliii100% (4)
- TV TheoryDocument33 pagesTV TheoryKrithika VenkatanathNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineRizky Gumelar AtmajaNo ratings yet
- Csc322 Assignment 1csc322Document3 pagesCsc322 Assignment 1csc322Anabia JanetNo ratings yet
- Comp Application 1 SampleDocument21 pagesComp Application 1 Samplelolmingani saipanyuNo ratings yet
- MoteView Users Manual 7430-0008-04 BDocument64 pagesMoteView Users Manual 7430-0008-04 BAnushree RastogiNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Authentication Authorization AccountingDocument30 pagesLab 2 - Authentication Authorization AccountingPhạm Trọng KhanhNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument6 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineGeka Shikamaru100% (1)
- Computer SoftwareDocument9 pagesComputer SoftwareZA IDNo ratings yet
- CC Unit 2Document6 pagesCC Unit 2Dharu DharaniNo ratings yet
- Mak Ing VPN Client Modules Platform IndependentDocument56 pagesMak Ing VPN Client Modules Platform IndependentAtinus VadayNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. - 1 - Virtualization 1. Objective(s)Document7 pagesExperiment No. - 1 - Virtualization 1. Objective(s)Jong FrancoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 VirtualizationDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Virtualizationarunkrishnas.21No ratings yet
- Cs3451 Ios Unit 5 NotesDocument21 pagesCs3451 Ios Unit 5 NotesspartansheikNo ratings yet
- CS8711 - Cloud Computing RecordDocument79 pagesCS8711 - Cloud Computing RecordELAKIYA RNo ratings yet
- How To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationFrom EverandHow To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument15 pagesDatabased hkNo ratings yet
- Karnaugh Maps 9608Document10 pagesKarnaugh Maps 9608d hkNo ratings yet
- Database NormalisationDocument8 pagesDatabase Normalisationd hkNo ratings yet
- DATABASE DDL and DMLDocument5 pagesDATABASE DDL and DMLd hkNo ratings yet
- Final DKSSKDocument79 pagesFinal DKSSKSarita Latthe100% (2)
- Selection of Fuses For The Protection of TransformersDocument14 pagesSelection of Fuses For The Protection of Transformersgalaxyebn100% (11)
- Subcontracting ProcedureDocument36 pagesSubcontracting Procedureswaroopreddyp100% (3)
- Ca-Cw106451-Mat-098 - Manga Termocontraible WoerDocument5 pagesCa-Cw106451-Mat-098 - Manga Termocontraible WoerJhoel Ipanaque AlarconNo ratings yet
- Fin542 Individual AssignmentDocument10 pagesFin542 Individual AssignmentAliff FarhanNo ratings yet
- Competiveness of Sri Lankan Apparel IndustryDocument9 pagesCompetiveness of Sri Lankan Apparel IndustryDanuNo ratings yet
- Kirk Summers Clinical Field Experience A Program Leader Interview Summary and ReflectionDocument4 pagesKirk Summers Clinical Field Experience A Program Leader Interview Summary and ReflectionKirk Summers100% (1)
- LSS Benefits of Kaizen To Business Excellence Evidence From A Case Study 2169 0316 1000251 (3197)Document15 pagesLSS Benefits of Kaizen To Business Excellence Evidence From A Case Study 2169 0316 1000251 (3197)Dasa ShelkNo ratings yet
- Fizika RadiologijaDocument9 pagesFizika RadiologijaBorislav TapavičkiNo ratings yet
- Week 10 RPH ENGLISHDocument4 pagesWeek 10 RPH ENGLISHAin HazirahNo ratings yet
- Pioneering Urban Practices in Transition SpacesDocument10 pagesPioneering Urban Practices in Transition SpacesFloorin OlariuNo ratings yet
- FPM Brochur 2016-17Document56 pagesFPM Brochur 2016-17Rithima SinghNo ratings yet
- CBC TMDocument108 pagesCBC TMChryz SantosNo ratings yet
- David RohlDocument3 pagesDavid RohlPhil CaudleNo ratings yet
- Std12 IndCulture TMDocument201 pagesStd12 IndCulture TMTholkappiyan GanesanNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Worksheet DypisDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Worksheet DypisPehel MehtaNo ratings yet
- Activation of Bacterial Spores. A Review': I G RminaDocument7 pagesActivation of Bacterial Spores. A Review': I G RminaJunegreg CualNo ratings yet
- TGDocument180 pagesTGavikram1984No ratings yet
- 5db83ef1f71e482 PDFDocument192 pages5db83ef1f71e482 PDFRajesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Matrices of Violence: A Post-Structural Feminist Rendering of Nawal El Saadawi's Woman at Point Zero and Lola Soneyin's The Secrets of Baba Segi's WivesDocument6 pagesMatrices of Violence: A Post-Structural Feminist Rendering of Nawal El Saadawi's Woman at Point Zero and Lola Soneyin's The Secrets of Baba Segi's WivesIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- 1000mm BOPP Tape Coating Machine Two Color Printing 40 Speed TangerangDocument6 pages1000mm BOPP Tape Coating Machine Two Color Printing 40 Speed TangerangJaja JamaludinNo ratings yet
- The Sabbath As FreedomDocument14 pagesThe Sabbath As Freedomapi-232715913No ratings yet
- Book Reviews: Supplemental Damping and Seismic Isolation by C. ChristopoulosDocument1 pageBook Reviews: Supplemental Damping and Seismic Isolation by C. ChristopoulosLuca AcetoNo ratings yet
- Cases NATRES Batch1Document113 pagesCases NATRES Batch1Leo Mark LongcopNo ratings yet
- Mock Trial Task CardsDocument8 pagesMock Trial Task CardsVitaliy Fedchenko0% (1)
- 2.06 Correlation Is Not CausationDocument2 pages2.06 Correlation Is Not CausationKavya GopakumarNo ratings yet
- Ple New Entry Codes 2024Document93 pagesPle New Entry Codes 2024luqmanluqs2No ratings yet
Virtual Machine 9608
Virtual Machine 9608
Uploaded by
d hkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Virtual Machine 9608
Virtual Machine 9608
Uploaded by
d hkCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic Support Guide
Cambridge International AS & A Level
Computer Science
9608
For examination from 2017
Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine
Cambridge International Examinations retains the copyright on all its publications.
Registered Centres are permitted to copy material from this booklet for their own
internal use. However, we cannot give permission to Centres to photocopy any
material that is acknowledged to a third party even for internal use within a Centre.
© Cambridge International Examinations 2016
Version 1.1
Updated: 10.03.16
Contents
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 2
How to use this guide .................................................................................................................. 2
Learning objectives ..................................................................................................................... 2
Prior knowledge........................................................................................................................... 2
1. Key terms ................................................................................................................................ 3
2. Theory ..................................................................................................................................... 4
2.1 What is a virtual machine?..................................................................................................... 4
2.2 Types of virtual machine ........................................................................................................ 4
2.3 Virtual machines within virtual machines ............................................................................... 6
2.4 Running virtual machines simultaneously .............................................................................. 6
2.5 The Java Virtual Machine ...................................................................................................... 7
2.6 Benefits and limitations of virtual machines ........................................................................... 8
3. Online resources...................................................................................................................... 9
3.1 Websites ............................................................................................................................... 9
4. Class and homework activities ............................................................................................... 10
4.1 Quiz ..................................................................................................................................... 10
4.2 Homework questions ........................................................................................................... 11
Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine 1
Introduction
Introduction
How to use this guide
The aim of this guide is to facilitate your teaching of Cambridge International AS and A Level
Computer Science topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine, part of the advanced theory topic 3.4 System
software. The guidance and activities in this resource are designed to help teachers devise
programmes of study which provide teaching time devoted to theory work as well as activities that
consolidate learning.
Section 1 lists some key terms used in this topic and their definitions. Section 2 introduces virtual
machines, gives examples of how they are used and lists some benefits and limitations. Section 3
lists some online resources that you or your learners may find useful. Section 4 gives ideas for
class and homework activities.
Learning objectives
Using this document should help you guide learners in the following syllabus learning objectives:
show understanding of the concept of a virtual machine
give examples of the role of virtual machines
show understanding of the benefits and limitations of virtual machines.
Prior knowledge
Before you begin teaching this topic you should:
understand what virtual machines are and what they do, including the difference
between system and process virtual machines
be familiar with different ways in which virtual machines are used
be familiar with how the Java Virtual Machine works
understand some benefits and limitations of virtual machines.
2 Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine
Key terms
1. Key terms
Word/phrase Meaning
byte code intermediate code that a virtual machine converts into machine code
compiler a program that converts source code into machine code
emulator software that runs a virtual machine
guest the emulated system/program
host the computer that runs the emulated virtual machine
machine code code written as instructions that the processor understands
process virtual an emulation of a single process
machine
source code code written in a high-level language
system virtual an emulation of a complete computer system/operating system
machine
virtualisation the process of creating and running a virtual machine
virtual software emulation of another computer/program/operating system
machine
Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine 3
Theory
2. Theory
2.1 What is a virtual machine?
Computers vary in the hardware they use, and run different programs and operating systems.
Sometimes we might want to have the functionality and capability of another computer system
running on our own computer. It may be that the hardware for the other system no longer exists or
is unavailable, or we may wish to have several versions of a computer running simultaneously on
one hardware system.
We can use software to emulate the other computer system so that our computer can behave like
that system. This emulation is known as a virtual machine.
The process of creating and running a virtual machine is known as virtualisation. The computer
that runs the virtual machine is known as the host. The virtualised system is known as a guest.
Virtualisation software, known as an emulator, creates a virtual implementation of the guest
system on the host computer, providing the host with the functions and programs of the guest. The
emulator translates the instructions of the guest computer so that the host computer can
understand them.
The emulator also provides a bridge that allows the virtual machine to use the user interface, via
the host operating system (I/O – input/output), allowing the user to interact with the software
running on the virtual machine.
Host operating system
I/O request
Hardware User
(including
Virtual machine I/O)
2.2 Types of virtual machine
2.2.1 System virtual machines
System virtual machines emulate the software of another computer system completely. They allow
the host computer to have all the software functionality of the guest system. System virtual
machines run the operating system of the guest system within the operating system of the host,
4 Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine
Theory
allowing programs supported by the guest operating system to be run on the host computer. As a
result, system virtual machines are often used to allow the host computer to run an operating
system written for another hardware platform.
Users running Apple operating systems often use a Microsoft Windows virtual machine to run the
Windows operating system on Apple computers. Similarly, users of Apple- or Windows-based
computers often run Linux as a virtual machine. The system virtual machine allows full use of the
guest computer operating system and the programs that run on it.
Another use of system virtual machines is to provide access to programs that current operating
systems no longer support. Many old DOS and Windows 3.1, 95 and 98 programs are not
supported in Windows 8 and 10. Through using a system virtual machine for these old operating
systems, such programs can still be run.
System virtual machines often require substantial processing power and memory. This is
inevitable, as many modern operating systems require fast processors and plenty of memory.
When emulating these operating systems, the more capable a host computer is, the faster and
more capable the guest operating system will be. A host computer with limited resources may still
be able to run a system virtual machine but it may have degraded performance.
A Windows 10 system virtual machine running in an Apple OS X environment.
2.2.2 Process virtual machines
Process virtual machines emulate a single program. They are often used to support a
programming language, allowing programs created in that language to run on a variety of systems.
They are frequently used to emulate old video game systems and arcade games.
Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine 5
Theory
2.3 Virtual machines within virtual machines
It is possible to run one virtual machine within another. For example, a user wanting to play an
emulated old arcade game could run the arcade game process virtual machine, within a Windows
system virtual machine, on an Apple-based computer. The host computer’s operating system
provides an interface to the guest virtual machine, which in turn provides an interface to the
process virtual machine within it.
Host computer environment
(Apple)
System virtual machine
(Windows) User
Process virtual
machine
(arcade game)
within the
virtual machine
The number of virtual machines within virtual machines is limited only by the hardware’s
performance and available memory of the host computer.
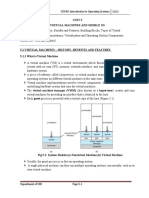
2.4 Running virtual machines simultaneously
Host server
Domain name server
virtual machine
Web server virtual
machine
Print server virtual
machine
6 Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine
Theory
If a host system is powerful enough, several virtual machines can be run side-by-side on one
computer. A good example of this is the increasing use of virtual machines to run several virtual
servers, such as a domain name server, web server and print server, on one physical server. The
host server maintains the virtual machines and allows them to act as though they are all separate
computers.
2.5 The Java Virtual Machine
Many programs are written in high-level languages such as Visual Basic, C++, Python and Java.
Before these programs can be run they need compiling. A compiler takes the high-level language
source code and converts it into machine code. This machine code is a set of instructions
specific to the processor architecture that the compiler is running on. As a result, this code can only
be run on processors that share the same instruction set.
The Java compiler does not convert a high-level language into machine code, but into an
intermediate language called byte code. This still needs translating into machine code before it
can be run on a processor.
The Java Virtual Machine is a virtual machine that reads and translates byte code into different
machine codes for many different processor architectures and operating systems. This means that
Java programs can be run on any computer that has this virtual machine, including desktop PCs,
laptops, tablets, smartphones and smart TVs.
Desktop with
Java Virtual
Machine
Tablet with
Java program Java byte code Java Virtual
Machine
Smartphone
with Java
Virtual
Machine
Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine 7
Theory
2.6 Benefits and limitations of virtual machines
Using virtual machines brings several benefits:
They allow modern systems to use programs that run on obsolete or unsupported platforms
They allow platform-independent programs to run on multiple platforms
They allow one computer to behave as several computers simultaneously
They can be easily backed up, copied and re-installed. This has particular benefits in corporate
environments where network downtime can lead to loss of revenue. The virtual machines can
be installed on another computer and be up and running again quickly.
Virtual machines also have limitations:
They emulate software, not hardware. Users trying to get the full functionality from software for
another platform may find that they still cannot use the software correctly. For example, an
emulation of a driving video game that requires a steering wheel might not be able to operate
the game correctly
Emulation requires processing power and memory. Running a virtual machine may take a
substantial amount of these resources, resulting in reduced performance from the host
computer
If the host system lacks sufficient resources, the virtual machine will also suffer from poor
performance and be difficult to use.
8 Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine
Online resources
3. Online resources
The following are useful resources for understanding virtual machines.
The content of websites is dynamic and constantly changing. Schools are strongly advised to check
each site for content and accessibility prior to using it with learners. Cambridge International
Examinations is not responsible for the accuracy or content of information contained in these sites.
The inclusion of a link to an external website should not be understood to be an endorsement of
that website or the site's owners (or their products/services).
3.1 Websites
BBC Bitesize GCSE Computer Science – basic description of the types of virtual machine; the
previous page describes the hierarchy of software languages and codes:
www.bbc.co.uk/education/guides/zgmpr82/revision/3
BBC Bitesize Higher Computing Science – virtual machines and emulators:
www.bbc.co.uk/education/guides/zsnbr82/revision/15
Introduction to virtual machines from National Instruments, including the benefits of virtualisation,
particularly for engineering:
www.ni.com/white-paper/8708/en/
Description of the Java Virtual Machine:
www.careerbless.com/java/basics/JavaArchitecture.php
Slides from Michigan Technology University – useful mainly for diagrams of system and process
virtual machines:
www.cs.mtu.edu/~zlwang/virtualmachines/slides/Introduction.ppt
Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine 9
Class and homework activities
4. Class and homework activities
4.1 Quiz
1. A virtual machine is:
a. a hardware emulation of another system
b. a software emulation of another system or program*
c. a method of backing up data
2. Virtualisation software provides:
a. a bridge between the host computer’s hardware and the emulated software*
b. a bridge between the guest computer’s hardware and software
c. a bridge between the host computer’s operating system and the emulated software
3. A system virtual machine emulates:
a. a single program
b. the hardware and software of a guest system
c. the operating system of a guest system*
4. A process virtual machine:
a. emulates a single program*
b. tells the operating system which processes to handle next
c. emulates the operating system of a guest system
5. The Java Virtual Machine translates:
a. source code into object code
b. source code into byte code
c. byte code into machine code*
10 Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine
Class and homework activities
4.2 Homework questions
1. Give three situations where a user might wish to use a virtual machine
2. Describe three advantages of using virtual machines
3. Explain how the use of virtual machines may allow software to run on multiple platforms
without alteration
4. Describe a situation where using virtual machines might not be a good idea
5. A network manager is considering using virtual machines to host his network – explain the
benefits of doing this
Topic support guide 9608 Topic 3.4.2 Virtual machine 11
You might also like
- Financial Time Series Analysis and Prediction With Feature Engineering and Support Vector Machines - Newton - LinchenDocument5 pagesFinancial Time Series Analysis and Prediction With Feature Engineering and Support Vector Machines - Newton - LinchenNewton Linchen100% (1)
- Tardiness: Its Effects To The Academic Performance of The Grade 10 Students of Sjsfi Enrolled in S.Y. 2019-2020Document24 pagesTardiness: Its Effects To The Academic Performance of The Grade 10 Students of Sjsfi Enrolled in S.Y. 2019-2020Alyana Linog99% (86)
- Virtual Machine SeminarDocument15 pagesVirtual Machine SeminarChuks Abanum0% (2)
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual Machinec583706No ratings yet
- Final Report On VirtualizationDocument27 pagesFinal Report On VirtualizationMukesh BuradkarNo ratings yet
- NumerologyDocument24 pagesNumerologyphani60% (5)
- Cambridge International AS and A Level Computer Science: Topic Support GuideDocument13 pagesCambridge International AS and A Level Computer Science: Topic Support GuideDeewas PokhNo ratings yet
- Ameya Abhay Khedkar PPT 2021Document19 pagesAmeya Abhay Khedkar PPT 2021Shubham JoshiNo ratings yet
- OS Assignment 1Document5 pagesOS Assignment 1Usama Nasir GillNo ratings yet
- VirtualDocument9 pagesVirtualOsaigbovo TimothyNo ratings yet
- Virtual Machine SeminarDocument37 pagesVirtual Machine SeminarVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument28 pagesChapter ThreeUrgessa GedefaNo ratings yet
- CPU VirtualizationDocument6 pagesCPU VirtualizationHEMALAKSHMI DNo ratings yet
- Ac 2007-904: A Virtual Machine Environment For Real-Time Systems LaboratoriesDocument19 pagesAc 2007-904: A Virtual Machine Environment For Real-Time Systems LaboratoriesJahanzaib ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document36 pagesUnit 5AmudariaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Virtualization BasicsDocument12 pagesUnit II Virtualization Basicsgtrajasekaran1No ratings yet
- Intro To VirtualizationDocument452 pagesIntro To VirtualizationHackerman42100% (8)
- Virtual MachinesDocument2 pagesVirtual MachinesSunithaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Virtual Machines Implementation and ApplicationsDocument47 pagesAn Introduction To Virtual Machines Implementation and ApplicationsSiri chandana MannavaNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is A Virtual Machine?Document2 pages1) What Is A Virtual Machine?Beatriz GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Virtual MachineDocument8 pagesVirtual MachineSrinivas Rapelli0% (1)
- Virtual Machine (VM) : Assignment OnDocument7 pagesVirtual Machine (VM) : Assignment OnMd FurquanNo ratings yet
- Cs3451 Os Unit 5 Notes EduenggDocument25 pagesCs3451 Os Unit 5 Notes EduenggMENAGANo ratings yet
- Lab - Installing The Cyberops Workstation Virtual Machine: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLab - Installing The Cyberops Workstation Virtual Machine: ObjectivesdweekendwandererNo ratings yet
- 3-1-Installing Virtual Machine - Docx JunioDocument5 pages3-1-Installing Virtual Machine - Docx JuniodweekendwandererNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFDocument4 pages3.4.2 Virtual Machine PDFBlessed Endibye KanyembaNo ratings yet
- Final Presenation On Virtual SystemsDocument13 pagesFinal Presenation On Virtual SystemsSamprit PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microsoft Dynamics® AX 2009 - Virtual PC Setup GuideDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Microsoft Dynamics® AX 2009 - Virtual PC Setup GuideGopala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineMochamad Arief Ferdiansyah NurNo ratings yet
- Virtual IzationDocument92 pagesVirtual IzationnkNo ratings yet
- Virtual Ization 3545Document40 pagesVirtual Ization 3545dhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Installing and Using XenDocument52 pagesInstalling and Using Xensushants_49151525No ratings yet
- 19 Virtualizationppt 2550Document45 pages19 Virtualizationppt 2550RohnikiNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab Solutions - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument6 pages1.1.1.4 Lab Solutions - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineAshIru Mohammed UmarNo ratings yet
- Leni Andriani - 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pagesLeni Andriani - 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineLeni AndrianiNo ratings yet
- 1.1.5 Lab - Installing The Virtual MachinesDocument4 pages1.1.5 Lab - Installing The Virtual MachinesMuharramNo ratings yet
- Virtual System Mids Short QuestionDocument4 pagesVirtual System Mids Short Questionmu70832No ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual Machine - ILMDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual Machine - ILMAna Lucia Alves dos SantosNo ratings yet
- CST423 M2 Ktunotes - inDocument15 pagesCST423 M2 Ktunotes - inRRNo ratings yet
- 1114 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pages1114 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachinesetyabudhiNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS)Document12 pagesInfrastructure As A Service (IAAS)userdemo12334No ratings yet
- Virtual MachineDocument16 pagesVirtual Machineapi-19854229No ratings yet
- Tugas 1Document14 pagesTugas 1JOSUA MARTINUS BARNABAS SAMBOUWNo ratings yet
- Assignment of OSDocument3 pagesAssignment of OSshamza hanifNo ratings yet
- Revised Tle As CSS10 Q3 WK3Document5 pagesRevised Tle As CSS10 Q3 WK3Jonald SalinasNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineHerdian MpNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To VirtualizationDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To VirtualizationCấn HùngNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument4 pages1.1.1.4 Lab Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineAayuliii100% (4)
- TV TheoryDocument33 pagesTV TheoryKrithika VenkatanathNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument5 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineRizky Gumelar AtmajaNo ratings yet
- Csc322 Assignment 1csc322Document3 pagesCsc322 Assignment 1csc322Anabia JanetNo ratings yet
- Comp Application 1 SampleDocument21 pagesComp Application 1 Samplelolmingani saipanyuNo ratings yet
- MoteView Users Manual 7430-0008-04 BDocument64 pagesMoteView Users Manual 7430-0008-04 BAnushree RastogiNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Authentication Authorization AccountingDocument30 pagesLab 2 - Authentication Authorization AccountingPhạm Trọng KhanhNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineDocument6 pages1.1.1.4 Lab - Installing The CyberOps Workstation Virtual MachineGeka Shikamaru100% (1)
- Computer SoftwareDocument9 pagesComputer SoftwareZA IDNo ratings yet
- CC Unit 2Document6 pagesCC Unit 2Dharu DharaniNo ratings yet
- Mak Ing VPN Client Modules Platform IndependentDocument56 pagesMak Ing VPN Client Modules Platform IndependentAtinus VadayNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. - 1 - Virtualization 1. Objective(s)Document7 pagesExperiment No. - 1 - Virtualization 1. Objective(s)Jong FrancoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 VirtualizationDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Virtualizationarunkrishnas.21No ratings yet
- Cs3451 Ios Unit 5 NotesDocument21 pagesCs3451 Ios Unit 5 NotesspartansheikNo ratings yet
- CS8711 - Cloud Computing RecordDocument79 pagesCS8711 - Cloud Computing RecordELAKIYA RNo ratings yet
- How To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationFrom EverandHow To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument15 pagesDatabased hkNo ratings yet
- Karnaugh Maps 9608Document10 pagesKarnaugh Maps 9608d hkNo ratings yet
- Database NormalisationDocument8 pagesDatabase Normalisationd hkNo ratings yet
- DATABASE DDL and DMLDocument5 pagesDATABASE DDL and DMLd hkNo ratings yet
- Final DKSSKDocument79 pagesFinal DKSSKSarita Latthe100% (2)
- Selection of Fuses For The Protection of TransformersDocument14 pagesSelection of Fuses For The Protection of Transformersgalaxyebn100% (11)
- Subcontracting ProcedureDocument36 pagesSubcontracting Procedureswaroopreddyp100% (3)
- Ca-Cw106451-Mat-098 - Manga Termocontraible WoerDocument5 pagesCa-Cw106451-Mat-098 - Manga Termocontraible WoerJhoel Ipanaque AlarconNo ratings yet
- Fin542 Individual AssignmentDocument10 pagesFin542 Individual AssignmentAliff FarhanNo ratings yet
- Competiveness of Sri Lankan Apparel IndustryDocument9 pagesCompetiveness of Sri Lankan Apparel IndustryDanuNo ratings yet
- Kirk Summers Clinical Field Experience A Program Leader Interview Summary and ReflectionDocument4 pagesKirk Summers Clinical Field Experience A Program Leader Interview Summary and ReflectionKirk Summers100% (1)
- LSS Benefits of Kaizen To Business Excellence Evidence From A Case Study 2169 0316 1000251 (3197)Document15 pagesLSS Benefits of Kaizen To Business Excellence Evidence From A Case Study 2169 0316 1000251 (3197)Dasa ShelkNo ratings yet
- Fizika RadiologijaDocument9 pagesFizika RadiologijaBorislav TapavičkiNo ratings yet
- Week 10 RPH ENGLISHDocument4 pagesWeek 10 RPH ENGLISHAin HazirahNo ratings yet
- Pioneering Urban Practices in Transition SpacesDocument10 pagesPioneering Urban Practices in Transition SpacesFloorin OlariuNo ratings yet
- FPM Brochur 2016-17Document56 pagesFPM Brochur 2016-17Rithima SinghNo ratings yet
- CBC TMDocument108 pagesCBC TMChryz SantosNo ratings yet
- David RohlDocument3 pagesDavid RohlPhil CaudleNo ratings yet
- Std12 IndCulture TMDocument201 pagesStd12 IndCulture TMTholkappiyan GanesanNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Worksheet DypisDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Worksheet DypisPehel MehtaNo ratings yet
- Activation of Bacterial Spores. A Review': I G RminaDocument7 pagesActivation of Bacterial Spores. A Review': I G RminaJunegreg CualNo ratings yet
- TGDocument180 pagesTGavikram1984No ratings yet
- 5db83ef1f71e482 PDFDocument192 pages5db83ef1f71e482 PDFRajesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Matrices of Violence: A Post-Structural Feminist Rendering of Nawal El Saadawi's Woman at Point Zero and Lola Soneyin's The Secrets of Baba Segi's WivesDocument6 pagesMatrices of Violence: A Post-Structural Feminist Rendering of Nawal El Saadawi's Woman at Point Zero and Lola Soneyin's The Secrets of Baba Segi's WivesIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- 1000mm BOPP Tape Coating Machine Two Color Printing 40 Speed TangerangDocument6 pages1000mm BOPP Tape Coating Machine Two Color Printing 40 Speed TangerangJaja JamaludinNo ratings yet
- The Sabbath As FreedomDocument14 pagesThe Sabbath As Freedomapi-232715913No ratings yet
- Book Reviews: Supplemental Damping and Seismic Isolation by C. ChristopoulosDocument1 pageBook Reviews: Supplemental Damping and Seismic Isolation by C. ChristopoulosLuca AcetoNo ratings yet
- Cases NATRES Batch1Document113 pagesCases NATRES Batch1Leo Mark LongcopNo ratings yet
- Mock Trial Task CardsDocument8 pagesMock Trial Task CardsVitaliy Fedchenko0% (1)
- 2.06 Correlation Is Not CausationDocument2 pages2.06 Correlation Is Not CausationKavya GopakumarNo ratings yet
- Ple New Entry Codes 2024Document93 pagesPle New Entry Codes 2024luqmanluqs2No ratings yet