Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Màng Não
Màng Não
Uploaded by
minhthu05erOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Màng Não
Màng Não
Uploaded by
minhthu05erCopyright:
Available Formats
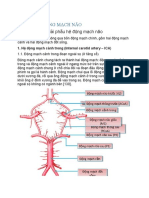
III/ Các màng não
Não bộ và tủy sống được ngăn cách với hộp sọ và ống sống bởi các màng
não tủy.
The brain and the spinal cord are separated from the brain case and spinal
tube by the meninges
Có 3 màng: màng cứng, màng nhện, màng mềm. Các màng não có tác dụng
nâng đỡ nuôi dưỡng và bảo vệ cho não - tủy.
There are 3 membranes: Dura mater, Arachnoidea, Pia mater. The
meninges have the effect of supporting, nourishing and protecting the brain
-marrow
1. Màng cứng ( Dura mater)
Khác với màn tủy gai ở một số điểm sau:
- Nằm sát thành xương, không có khoang ngoài cứng.
- Có mặt trong cho các trẻ (, liềm đại não, liềm tiểu não, hoành yên)
- Tạo nên các xoang tĩnh mạch màng cứng.
- Màng cứng bám chắc vào nền sọ hơn ở vòm sọ. Vùng dễ bóc tách Gerard
Marchant đi từ bờ sau cánh nhỏ xương bướm đến ủ chẫm thật ra không phải duy
nhất vì máu tụ ngoài màng cứng do tổn thương các mạch máu màng não có thể
lách vào giữa màn cấn và thành xương vòm sọ và một phần nền sọ.
Differs from the thorny marrow curtain in some of the following ways:
- Close to the bone wall, without a hard outer cavity.
- Present in for children (cerebral sickle, cerebellar sickle, diaphragm)
- Formation of epidural venous sinuses.
- The sclera adheres more firmly to the base of the skull than to the arch of
the skull. The Gerard Marchant dissection zone from the posterior margin
of the butterfly bone subwing to the incubation is actually not unique
because the epidural hematoma caused by damage to the meningeal
blood vessels can spleen between the curtain and the wall of the cranial
arch bone and part of the base of the skull.
- Các trẽ của màng cứng:
- Turns of the epidural:
• Liềm đại não: hình lưởi liềm, dính toàn bộ vào vòm sọ dọc theo đường giữa
và đi vào khe dọc giữa 2 bán cầu đại não, tạo nên một vách sợi. Đầu trước gắn vào
bọc lấy mõm màu gà xương sàng. Bờ trên liên tục ra sau rồi tận cùng ở ụ chẫm
trong. Bờ dưới tự do, chạy cong theo mặt trên của thể chai. Ngay sau lồi thể chai,
liềm não dính chặt vào mặt lưng lều tiểu não dọc đường giữa.
Cerebral sickle: crescent-shaped, adhering entirely to the arch of the skull
along the midline and entering the longitudinal slit between the 2 cerebral
hemispheres,forming a filamentous wall. The front end attaches to the
snout of the chicken-colored bone. The upper bank is constantly backwards
and then ends up in the inner mound. The lower bank is free, running
curved along the upper side of the bottle body. Immediately following the
bottle protrusion, the brain sickle adheres to the dorsal surface
of the cerebellar tent along the midline.
Bờ dưới liềm đại não chứa xoang tĩnh mạch dọc dưới , chạy ra sau đổ về xoang
tĩnh mạch thẳng.
The lower bank of the cerebral sickle contains the lower longitudinal
venous sinus, which flows backwards into the straight venous sinus.
• Lều tiểu não: tạo nên một mái trên hố sọ sau, ngang cắt mặt trên tiểu não,
với mặt thùy chẩm bán cầu đại não, có bờ (vòng) trong nhỏ, hợp với yên xương
bướm tạo khuyết lều tiểu não và là giới hạn trên của trung não, bờ (vòng) ngoài
lớn dính dọc theo rãnh chứa xoang tĩnh mạch ngang của xương chẩm, theo mép
rãnh dọc mặt trên phần đá xương thái dương tạo nên xoang tĩnh mạch đá trên.
Thoát vị mô não thường xảy ra tại khuyết lều tiểu não (thái dương hoặc thùy
nhông trên).
Cerebellar tent: forms a roof on the posterior cranial pit,transversely
crossing the face on the cerebellum, with the occipital lobe side of the
cerebral hemisphere, with a small inner margin (ring), fused with the
butterfly bone saddle that forms the cerebellar tent and is the upper limit
of the cerebellum, the large outer margin (ring)sticks along the groove
containing the
transverse venous sinus of the occipital bone, Following the edge of the
longitudinal groove on the upper temporal bone rock that makes up the
upper stone venous sinus. Cerebral tissue hernia usually occurs in the
cerebellar tent defect (temporal or upper iguana lobe).
• Liềm tiểu não: là một phần nhỏ của màng cứng ngay dưới ụ chẩm trong, bờ
sau dính vào mặt trong xương chẩm và chữa xoang tĩnh mạch chẩm. Bời trước
hướng vào trong, lách giữa 2 bán cầu tiểu não.
Cerebellar sickle: is a small part of the sclera just below the inner occipital
mound, the posterior bank adheres to the inner side of the occipital bone
and cures the occipital venous sinus. The anterior is directed inward,
spleen between the 2 hemispheres of the cerebellum.
• Hoành yên: hình tứ giác tạo mái hố yên, để thủng một lỗ nhỏ ở trung tâm
gọi là lỗ hoành yên để phần phễu tuyến yên đi qua.
Pituitary diaphragm: the quadrangle creates the roof of the saddle pit,
leaving a small hole in the center called the pituitary diaphragm for the
pituitary funnel to pass through
• Động mạch: cấp máu cho màng cứng, là động mạch não giữa, nhánh của
động mạch hàm và động mạch màng não sau, nhánh động mạch đốt sống.
Arterial: supplying blood to the sclera, which is the middle cerebral artery,
the branch of the jaw artery and the posterior meningeal artery, the
vertebral artery branch.
• Tĩnh mạch: là các tĩnh mạch màng não đi theo 2 hệ thống: hệ thống sau với
các hồ máu Trolard, và hệ thống nông với xoang tĩnh mạch dọc trên và đám rối
tĩnh mạch chân bướm, đảm bảo thông nối hệ tĩnh mạch nội sọ và ngoại sọ.
Veins: are meningeal veins that follow 2 systems: the posterior system with
Trolard blood pools, and the superficial system with the upper longitudinal
venous sinus and butterfly leg venous plexus, ensuring the connection of
intracranial and extracranial venous systems.
• Thần kinh của màng não là các nhánh màng não của dây sinh ba.
The nerves of the meninges are the meningeal branches of the trigeminal
cord.
2. Màng nhện (Arachnoidea)
Màng não
Tạo các bể chứa dịch não tuỷ: Creation of cerebrospinal fluid reservoirs:
Bể tiểu hành não ( Posterior cerebellomedullary)
Bể hố bên đại não (
Bể giao thoa ( Chiasmatic cistern)
Bể liên cuống não
Dịch não tuỷ đi theo các đường, đến các lạch, về các dòng, hội tụ về các bể
chứa. Khi thoát hết dịch não tuỷ, màng nhện áp sát vào màng mềm, khi đó
chỉ phân biệt được màng não cứng và mềm. Khoang dưới nhện thông với hệ
thống não thất qua các lỗ mái não thất IV và thông với các tĩnh mạch qua
các hạt nệm.
The cerebrospinal fluid follows the lines, to the creeks, about the
streams, converges about the reservoirs. When all cerebrospinal fluid
is drained, the arachnoid membrane presses against the soft
membrane, then only the hard and soft meninges are distinguished.
The subarachnoid cavity communicates with the ventricular system
through the IV ventricular roof openings and communicates with the
veins through the mattress granules.
3. Màng mềm (Pia mater)
Màng não
Bao phủ toàn bộ mặt ngoài và lách sâu vào các khe của bán cầu đại não, nó
dày lên ở quanh các não thất và tạo nên các tấm mạch mạc và cá đám rối
mạch mạc:
Đám rối màng mạch não thất IV và tấm mạch mạc não thất IV ở giữa
hành não và tiểu não.
Đám rối màng mạch não thất III liên tục với đám rối màng mạch não
thất bên qua lỗ gian não thất. Cả hai đều thuộc tấm mạch mạc não thất
III.
Covering the entire outer surface and penetrating deep into the slits
of the cerebral hemispheres, it thickens around the ventricles and
forms the vessel plates and vascular plexus:
The IV ventricular meningeal plexus and IV ventricular
meningeal vascular plate in between the cerebral cortex and
cerebellum.
The III ventricular meningeal plexus is continuous with the
lateral ventricular meningeal plexus through the ventricular
space opening. Both belong to the III ventricular meningeal
vessel plate.
You might also like
- (123doc) - Giai-Phau-He-Than-Kinh PDFDocument6 pages(123doc) - Giai-Phau-He-Than-Kinh PDFLê TuấnNo ratings yet
- 4 Mang Mach Nao Tuy GhDocument30 pages4 Mang Mach Nao Tuy Ghlamtruonghung2004No ratings yet
- Màng Não T yDocument25 pagesMàng Não T yHuyền PhạmNo ratings yet
- Giai Phau CT So NaoDocument55 pagesGiai Phau CT So NaochochetcongianNo ratings yet
- Đáp án Đề cương Giải phẫu PHẦN THAM KHẢODocument29 pagesĐáp án Đề cương Giải phẫu PHẦN THAM KHẢOキッドNo ratings yet
- giải phẫu mắtDocument10 pagesgiải phẫu mắtcamvann281003No ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP HỆ THẦN KINHDocument15 pagesÔN TẬP HỆ THẦN KINHHuỳnh Mai Thanh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Thankinhhoc p2 39 PDFDocument229 pagesThankinhhoc p2 39 PDFThanh CườngNo ratings yet
- (YhocData - Com) Noi Tru Giai PhauDocument122 pages(YhocData - Com) Noi Tru Giai PhauNgọc AnhThưNo ratings yet
- GPLS Than Nao Sau Dai Hoc Than Kinh Cap Nhat 2022 9Document145 pagesGPLS Than Nao Sau Dai Hoc Than Kinh Cap Nhat 2022 9Lê Nguyên NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Màng nhệnDocument2 pagesMàng nhệnMinh Thảo VũNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP GPDocument3 pagesÔN TẬP GPThảo NgânNo ratings yet
- Tăng ALNSDocument13 pagesTăng ALNS2051010393No ratings yet
- Giải phẫu màng não tủyDocument20 pagesGiải phẫu màng não tủyCao Thu ThủyNo ratings yet
- TỰ LUẬN GP 2Document31 pagesTỰ LUẬN GP 2Lương Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- Brain 3Document6 pagesBrain 3Cao Thu ThủyNo ratings yet
- VỊ TRÍ VÀ CẤU TẠO CỦA TỦY SỐNGDocument3 pagesVỊ TRÍ VÀ CẤU TẠO CỦA TỦY SỐNGakumawife400No ratings yet
- Giải Phẫu Động Mạch NãoDocument4 pagesGiải Phẫu Động Mạch NãoThang Tran Le Cong100% (1)
- Sinh Lý Mach Nao Tuy Mang Nao TuyDocument21 pagesSinh Lý Mach Nao Tuy Mang Nao Tuyfamthanh60No ratings yet
- Hệ thần kinh tự chủDocument8 pagesHệ thần kinh tự chủcamvann281003No ratings yet
- TEST GIẢI PHẪUDocument77 pagesTEST GIẢI PHẪUTran Thi Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- FILE - 20220902 - 112635 - Tổng hợp tự luận gp3Document7 pagesFILE - 20220902 - 112635 - Tổng hợp tự luận gp3Phạm Trần Mai AnhNo ratings yet
- Phần 1 Câu Hỏi Tự LuậnDocument10 pagesPhần 1 Câu Hỏi Tự LuậnLương Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- giải phẫu taiDocument9 pagesgiải phẫu taicamvann281003No ratings yet
- Vùng C Trư C BênDocument19 pagesVùng C Trư C Bênngocmaitn1995No ratings yet
- Bài Giảng Ngoại cơ sở 2Document113 pagesBài Giảng Ngoại cơ sở 2tung nguyenthanhNo ratings yet
- He TK TWDocument54 pagesHe TK TWThế anh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Các dây TK sọDocument57 pagesCác dây TK sọNguyen Minh TuanNo ratings yet
- Chương V - Hệ Thần KinhDocument27 pagesChương V - Hệ Thần KinhKiều DuyênNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Slide Giai Phau Sinh Ly He Than KinhDocument77 pages(123doc) Slide Giai Phau Sinh Ly He Than KinhDam Ngoc Anh100% (1)
- GIẢI PHẨU CHỨC NĂNG THẦN KINHDocument17 pagesGIẢI PHẨU CHỨC NĂNG THẦN KINHQuang NhânNo ratings yet
- Cách Đọc Ct-Scan Vùng Cổ: GVHD: PGS. TS. BS Lâm Huyền Trân Trình bày: Nhóm 2 - Lóp CK1 TMH 2020-2022Document123 pagesCách Đọc Ct-Scan Vùng Cổ: GVHD: PGS. TS. BS Lâm Huyền Trân Trình bày: Nhóm 2 - Lóp CK1 TMH 2020-2022Quang VõNo ratings yet
- CHUYÊN ĐỀ ĐỘNG MẠCH CẢNHDocument16 pagesCHUYÊN ĐỀ ĐỘNG MẠCH CẢNHNguyen NhatNo ratings yet
- LEC1.S2.8 Phôi Thai Học Hệ TK 1Document50 pagesLEC1.S2.8 Phôi Thai Học Hệ TK 1Vinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- He Than KinhDocument129 pagesHe Than KinhkieuviNo ratings yet
- Giải phẫu Màng não tủy Màng mềmDocument2 pagesGiải phẫu Màng não tủy Màng mềmMinh Thảo VũNo ratings yet
- Thanh Qu NDocument19 pagesThanh Qu Nluna tranNo ratings yet
- giải phẫu thanh quảnDocument7 pagesgiải phẫu thanh quảncamvann281003No ratings yet
- THẦN KINH TRUNG ƯƠNGDocument4 pagesTHẦN KINH TRUNG ƯƠNGTrần Quốc BảoNo ratings yet
- 12 ĐÔI DÂY THẦN KINH SỌ-FULLDocument35 pages12 ĐÔI DÂY THẦN KINH SỌ-FULLhop do thi100% (1)
- Đoan Nao Gian NaoDocument52 pagesĐoan Nao Gian Naomiumiunguyen782No ratings yet
- GP Gian Nao-Than Nao-Tieu Nao..Document34 pagesGP Gian Nao-Than Nao-Tieu Nao..Sơn LâmNo ratings yet
- Hệ TKTWDocument49 pagesHệ TKTWvngoc981No ratings yet
- ĐạihọcDuyTân 2021 BàigiảngTMH 2021F TEXTDocument86 pagesĐạihọcDuyTân 2021 BàigiảngTMH 2021F TEXTMẫn Trương100% (1)
- Giải phẫu đại nãoDocument6 pagesGiải phẫu đại nãocamvann281003No ratings yet
- Giai Phau Than - NQ-BQ-NDDocument58 pagesGiai Phau Than - NQ-BQ-NDLê Mỹ Khánh LyNo ratings yet
- GIẢI PHẪU VÙNG CỔDocument8 pagesGIẢI PHẪU VÙNG CỔDũng Hoàng Nghĩa TríNo ratings yet
- Hệ TK Trung Ương - Tuy GaiDocument31 pagesHệ TK Trung Ương - Tuy Gaianhthi22112004No ratings yet
- GP Hệ Tuần HoànDocument55 pagesGP Hệ Tuần Hoànhoàng anh hưởngNo ratings yet
- Giáo Trình Dư C Lâm Sàng - 1040526Document16 pagesGiáo Trình Dư C Lâm Sàng - 1040526Đàm HoaNo ratings yet
- phát triển phôi người tuần 4 8 bản chi tiếtDocument21 pagesphát triển phôi người tuần 4 8 bản chi tiếtvanhunghocgioiNo ratings yet
- GIẢI PHẪUDocument6 pagesGIẢI PHẪUPhạm Hoài GiangNo ratings yet
- Mô Học Hệ Tim MạchDocument13 pagesMô Học Hệ Tim Mạchnkhoa.y2022No ratings yet
- ReadDocument3 pagesReadPhạm Thành NamNo ratings yet
- BG - GP Phúc M CDocument19 pagesBG - GP Phúc M CNgọc Thẻo officalNo ratings yet
- Dịch dây thần kinh hàm dưới (V3) và thần kinh mặt (VII)Document10 pagesDịch dây thần kinh hàm dưới (V3) và thần kinh mặt (VII)26 NamB9No ratings yet
- Hệ cơ quanDocument38 pagesHệ cơ quanVi Triệu TườngNo ratings yet
- Bản Sao Của TK Y AB 31,2017Document140 pagesBản Sao Của TK Y AB 31,2017Nguyễn Thế Cường100% (1)