Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Web Development Notes
Web Development Notes
Uploaded by
deydsagnik32Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Web Development Notes
Web Development Notes
Uploaded by
deydsagnik32Copyright:
Available Formats
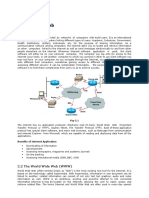
Working of the Internet
When we open our favourite web app on our device and we’re
instantly connected to the world. This is all made possible
because two devices connect and communicate via a wired or
wireless connection, forming something called a network. We
can connect multiple devices to this network. But this becomes
very complicated very quickly, as each device needs to connect to
every other device to communicate effectively. This problem is
solved by something called a Network Switch that connects
multiple devices and allows them to communicate with each
other. The network switch can connect to other network
switches, and now two networks can connect. These network
switches then connect to more network switches until we have
something called an interconnected network. This
interconnected network has another name that we might be
familiar with. It's called the Internet. When we use websites or
video streaming services on the Internet, these are provided by
computers called servers. Our devices are called clients. This is
known as the client-server model. Internet connects the entire
world. If we ever had a video call with someone on another
continent that video data travel through large undersea cables
connecting the world's networks. These cables can transfer huge
volumes of data per second. There are a lot more technical
details that go into making the Internet possible.
Webserver & Its Working
A web server is a software application or hardware device that
stores, processes, and delivers web content (such as web pages,
images, and files) to users' web browsers over the internet. It
listens for incoming requests, handles these requests, and sends
the requested data back to the user's browser, enabling users to
access websites and web applications hosted on the server.
A web server operates by listening for incoming requests from
users' web browsers. When a user enters a website's URL or
clicks a link, their browser sends a request to the web server
hosting that site. The server identifies the requested content,
whether it's a webpage, image, or file, and retrieves it from its
storage. It then generates an HTTP response containing the
requested data, along with metadata. This response is sent back
to the user's browser, which renders the web content. This
process repeats for each user request, enabling users worldwide
to access and interact with websites and web applications hosted
on the server.
Websites & Webpages
Websites are collections of web pages and digital content that are
accessible over the internet through a specific domain name or
URL (Uniform Resource Locator). They can include text, images,
videos, and interactive elements, serving various purposes such
as information dissemination, e-commerce, entertainment, or
communication.
Webpages are individual documents or files on the internet that
are written in HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) and are
designed to be displayed in web browsers. They contain text,
images, links, and multimedia elements, providing information
or interactive content to users when accessed through a web
browser. Webpages are the building blocks of websites.
You might also like
- Flexbox Cheatsheet PDFDocument1 pageFlexbox Cheatsheet PDFEwketbirhan AlemuNo ratings yet
- DNN Platform 8 0 0 Administrator Manual PDFDocument551 pagesDNN Platform 8 0 0 Administrator Manual PDFXavier PiratovaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 IntroductionDocument14 pagesCh1 Introductionpriyanimbhorepatil20No ratings yet
- Cabataña, Mart D. Unit 4. DOMT 3-1Document1 pageCabataña, Mart D. Unit 4. DOMT 3-1Mart CabatañaNo ratings yet
- Web Technology Study Material GTU - 23042016 - 032646AM PDFDocument82 pagesWeb Technology Study Material GTU - 23042016 - 032646AM PDFVikalp Panseriya100% (1)
- Concept of WWW.: J.B.Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument110 pagesConcept of WWW.: J.B.Institute of Engineering and TechnologyjayaraoNo ratings yet
- Front EndDocument20 pagesFront Endheidijemini1No ratings yet
- Unit-2 (Client Server Architecture) - 1Document6 pagesUnit-2 (Client Server Architecture) - 1Jatin NandalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document29 pagesUnit 5drgurungr18No ratings yet
- World Wide WebDocument23 pagesWorld Wide WebJoyce TenorioNo ratings yet
- Internet TechDocument19 pagesInternet Techmarkusfavour05No ratings yet
- WT Unit 1 Notes.@omiDocument29 pagesWT Unit 1 Notes.@omiat8709742No ratings yet
- Question Bank SolutionDocument87 pagesQuestion Bank SolutionPATEL POOJANNo ratings yet
- E-Notes PDF All-Units IWTDocument82 pagesE-Notes PDF All-Units IWTmysadidvd009No ratings yet
- World Wide WebDocument2 pagesWorld Wide Websonukaushik7717No ratings yet
- HTML 1Document22 pagesHTML 1gayatripophale4No ratings yet
- 2 Chepter 2Document40 pages2 Chepter 2pankajusbNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: An Introduction To The World Wide WebDocument23 pagesChapter-1: An Introduction To The World Wide WebSameer MittalNo ratings yet
- Basics of InternetDocument23 pagesBasics of InternetRambir SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 WadDocument30 pagesUnit 1 WadWe TogetherNo ratings yet
- Chapter (1) Fundamental of Web TechnologyDocument103 pagesChapter (1) Fundamental of Web TechnologyPhone PyaeNo ratings yet
- HTML Is A Language of /WEB.: InternetDocument28 pagesHTML Is A Language of /WEB.: InternetRohit_Dubey_350No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Internet and WebDocument34 pagesIntroduction To The Internet and WebRenzogcNo ratings yet
- What Is Internet?: EmailDocument20 pagesWhat Is Internet?: EmailHossain Bahalul RifatNo ratings yet
- The Internet History1.1Document28 pagesThe Internet History1.1akki0rockeyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Subtopic: Introduction To World Wide Web - Internet OperationDocument17 pagesUnit 1: Subtopic: Introduction To World Wide Web - Internet OperationNiketa Govind KhalkhoNo ratings yet
- Web TECH NOTESDocument87 pagesWeb TECH NOTESupdeshroy816No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document9 pagesUnit 3AjmalNo ratings yet
- Web DesignDocument20 pagesWeb DesignShine InstituteNo ratings yet
- Web Technology NotesDocument13 pagesWeb Technology NotesAnkit TalwarNo ratings yet
- Itwd Unit 1Document11 pagesItwd Unit 1ayushsingh96510No ratings yet
- It Sivapadidapu PDFDocument130 pagesIt Sivapadidapu PDFAnonymous 0f4b6SNo ratings yet
- Web Application DevelopmentDocument114 pagesWeb Application DevelopmentramuappalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document46 pagesUnit 1عبدالرحيم اودينNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document51 pagesUnit 1Super heroNo ratings yet
- WEB PROGRAMMING Unit 1 NotesDocument15 pagesWEB PROGRAMMING Unit 1 Notesbaby100% (1)
- Web - Quick Guide Web - Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesWeb - Quick Guide Web - Basic Conceptsgajus87No ratings yet
- CSC 318Document13 pagesCSC 318Rosmos GlobalNo ratings yet
- Basic Internet TerminologyDocument4 pagesBasic Internet TerminologyAbi Abinaya100% (1)
- Web TechnologiesDocument121 pagesWeb Technologiesvenkatagayathri069No ratings yet
- Client and Server ArchitectureDocument11 pagesClient and Server Architectureksuresh8No ratings yet
- Web Systems and Tech.Document61 pagesWeb Systems and Tech.Arnold ColancolanNo ratings yet
- Web ClientDocument44 pagesWeb ClientAnvesh MagantiNo ratings yet
- 1Document51 pages1Vinod ReddyNo ratings yet
- Web Engineering: Engr. Muhammad Umer HaroonDocument56 pagesWeb Engineering: Engr. Muhammad Umer HaroonBabar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Basic Internet & ProtocolsDocument48 pagesBasic Internet & Protocolsgunasundar choppaNo ratings yet
- Internet NotesDocument21 pagesInternet Notesmiamimorris1966No ratings yet
- Internet NotesDocument20 pagesInternet NotesKadima ChitechiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WWWDocument36 pagesIntroduction To WWWjohnhaile23No ratings yet
- Web Architecture and ComponentsDocument3 pagesWeb Architecture and Componentsapi-297232544No ratings yet
- Types of Server: What Is Server Platform?Document4 pagesTypes of Server: What Is Server Platform?Bala MurugamNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Basics of InternetDocument20 pagesChapter-1 Basics of InternetRudransh singhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part1Document20 pagesUnit 1 Part1Ashish BhoyeNo ratings yet
- Applications of Internet: Computer Networks Internet Protocol SuiteDocument4 pagesApplications of Internet: Computer Networks Internet Protocol SuiteankurlalaNo ratings yet
- Comp II.... Unit 1Document31 pagesComp II.... Unit 1theanuuradha1993gmaiNo ratings yet
- Web Infrastructure DesignDocument9 pagesWeb Infrastructure Designgoogle sharingNo ratings yet
- 12-IP NotesDocument3 pages12-IP NotesParasNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument7 pagesComputer NotesGaming HardyNo ratings yet
- Computer 5th UnitDocument7 pagesComputer 5th UnitSakshi chouhanNo ratings yet
- Semantc Web and Social NetworksDocument63 pagesSemantc Web and Social NetworksANCY THOMASNo ratings yet
- Web Applications using JSP (Java Server Page): Develop a fully functional web applicationFrom EverandWeb Applications using JSP (Java Server Page): Develop a fully functional web applicationNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineFrom EverandComputer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineNo ratings yet
- Holistic Seo: Yoast Seo For Wordpress Training - Lesson 1.1Document16 pagesHolistic Seo: Yoast Seo For Wordpress Training - Lesson 1.1Mohit RuhalNo ratings yet
- CodeSchool CrackingTheCaseWithFlexboxDocument83 pagesCodeSchool CrackingTheCaseWithFlexboxJuan Arturo Bravo AguinagaNo ratings yet
- Computer Class FilesDocument36 pagesComputer Class FilesGeorgia GrantNo ratings yet
- Search Engine Optimization: Abhilash Patel Ranklab Interactive, Recovery Brands, LLC @mistabhilashDocument31 pagesSearch Engine Optimization: Abhilash Patel Ranklab Interactive, Recovery Brands, LLC @mistabhilashapi-62303070No ratings yet
- My Life Sux NowDocument9 pagesMy Life Sux NowDanyCaissyNo ratings yet
- Web CrawlingDocument26 pagesWeb CrawlingHimanshu Agrawal100% (1)
- A Technical Report ON Student Industrial Work Experience Scheme (Siwes)Document16 pagesA Technical Report ON Student Industrial Work Experience Scheme (Siwes)Aidy SaxNo ratings yet
- Google Tag Manager / Cookie Consent IntegrationDocument3 pagesGoogle Tag Manager / Cookie Consent IntegrationManeaNo ratings yet
- SEO ClassDocument26 pagesSEO ClassNesla SherinNo ratings yet
- How To Perfectly Fit An SVG's ViewBox To Its Contents Using JavaScript - DEV CommunityDocument8 pagesHow To Perfectly Fit An SVG's ViewBox To Its Contents Using JavaScript - DEV CommunitywalidabbasNo ratings yet
- Jon Cooper - Modern Day Link Building PDFDocument44 pagesJon Cooper - Modern Day Link Building PDFMariaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Java ScriptDocument24 pagesInternship Report Java ScriptAbhishek GautamNo ratings yet
- Session AffinityDocument2 pagesSession AffinityRahul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Nginx Security Hardening GuideDocument12 pagesNginx Security Hardening Guidescrib_nokNo ratings yet
- HTML NotesDocument30 pagesHTML NotesSudheer Reddy PothuraiNo ratings yet
- Fblog2021 04 06Document3 pagesFblog2021 04 06indah rambeNo ratings yet
- Research Paper HTTP 3.0Document8 pagesResearch Paper HTTP 3.0akash DroliaNo ratings yet
- Payload Hasil SniffDocument3 pagesPayload Hasil SniffEniie Endthoonk Cta'a PezegNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 CSE1007 ETH VL2021220104880 Reference Material I 22-Oct-2021 1. Java ServletsDocument40 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 CSE1007 ETH VL2021220104880 Reference Material I 22-Oct-2021 1. Java Servletsakshata bhatNo ratings yet
- NISR The PHISHING GuideDocument42 pagesNISR The PHISHING GuidesedimbiNo ratings yet
- Wapka TagDocument32 pagesWapka Tagalokraj4uuNo ratings yet
- 5 FC 88Document107 pages5 FC 88sanjay sharmaNo ratings yet
- Openlayers Workshop: Follow Along With The Demos atDocument36 pagesOpenlayers Workshop: Follow Along With The Demos atrachid_lhissouNo ratings yet
- Web Page Credibility ChecklistDocument8 pagesWeb Page Credibility Checklistapi-463461471No ratings yet
- Assessment Event Written 01 03Document9 pagesAssessment Event Written 01 03ZahidNo ratings yet
- TOFFS API USER MANUAL v1.0Document70 pagesTOFFS API USER MANUAL v1.0Freddie ChanNo ratings yet
- CSS TheoryDocument21 pagesCSS TheoryG.Chaitanya KiranNo ratings yet
- Forcing HTTPS Redirection and Cloudflare's Flexible SSL - GomahDocument6 pagesForcing HTTPS Redirection and Cloudflare's Flexible SSL - GomahPradyumna Singh RathoreNo ratings yet