Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 7
Class 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 7
Uploaded by
1445800Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 7
Class 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 7
Uploaded by
1445800Copyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT NO.
7
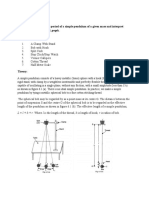
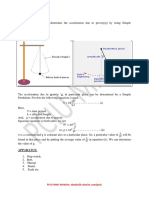
SIMPLE PENDULUM
Aim: To find the acceleration due to gravity at the place using a simple pendulum and
plotting a graph between l and T2
Apparatus: A simple pendulum, stop watch, meter scale.
Theory: A simple pendulum is made by tying a metallic bob to a fine thread.
Time period of a simple pendulum is given by :
𝒍
𝑻 = 𝟐 l – length of the pendulum
𝒈
T – Time period.
𝟒 𝝅𝟐 𝒍
𝒈=
𝑻𝟐
Procedure:
1. Take the cotton thread and tie its one end to the bob
2. Pass the thread through the two split parts of the cork with the thread coming
out just 40 cm
3. Tighten the two halves of the cork between the clamp.
4. Fix the clamp in a stand kept on a table at such a height that the bob doesn’t
touch anywhere while swinging.
5. Find the least count & zero error of the stop watch.
6. Find the time taken for 20 oscillations and thus find the time taken for 1
oscillation
7. Repeat the experiment for different lengths, say 50cm, 60cm, 70cm & 80 cm.
8. Plot a graph between the length (l) and square of the time period (T2).
9. From the graph, find the value of l/T2. Substitute the value in equation (2) and
find the value of g
Result: The acceleration due to gravity at the place is m/s2
Precautions: i) The thread should be weightless and inextensible.
ii) Care should be taken while measuring the time for 20 oscillations
Sources of Error: i) The bob may spin while oscillating
ii) The stop watch may be inaccurate.
T2
Observations :
Time for 1
Time for 20 T2
Sr. No Length (l) (cm) Oscillation (T)
Oscillations (s) (s2)
(s)
1 40
2 50
3 60
4 70
5 80
𝒍
From the graph, = ms-2
𝑻𝟐
Calculations :
𝟒 𝝅𝟐 𝒍
𝒈=
𝑻𝟐
You might also like
- Lab 13 Compound PendulumDocument4 pagesLab 13 Compound PendulumWaqas Muneer Khan100% (1)
- Physics Project (XI)Document13 pagesPhysics Project (XI)Tanaya Biswas78% (18)
- MPEG Poster LowrezDocument1 pageMPEG Poster Lowrezhalansuresh100% (1)
- 11 Steps For GMATDocument4 pages11 Steps For GMATfazlayNo ratings yet
- XIIth Manual 2010Document22 pagesXIIth Manual 2010kiranpatel0100% (1)
- Physics Project XIDocument10 pagesPhysics Project XIanishkadiyalaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual - Class 11 Experiment No. 4Document4 pagesPhysics Lab Manual - Class 11 Experiment No. 4masterjedi1008No ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument14 pagesPHYSICSAshish Shejith100% (2)
- Exp 5 Simple PendulumDocument2 pagesExp 5 Simple PendulumPriti UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Pick Out Information You Deem To Be Necessary From The Excerpt BelowDocument3 pagesPick Out Information You Deem To Be Necessary From The Excerpt Belowcrampersad100No ratings yet
- D.K.Pandey: Acceleration Due To Gravity G' by Bar PendulumDocument2 pagesD.K.Pandey: Acceleration Due To Gravity G' by Bar PendulumVirender RanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Grade 11Document4 pagesExperiment 7 Grade 11Varnit MehraNo ratings yet
- Physics EXPERIMENTs Term2Document6 pagesPhysics EXPERIMENTs Term2cutuNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesSimple PendulumReshan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Pdfa1 5Document1 pagePdfa1 5aizat100% (1)
- The Simple Pendulum TotalDocument5 pagesThe Simple Pendulum TotalMEXI EVYNo ratings yet
- The Simple Pendulum (Ver2)Document8 pagesThe Simple Pendulum (Ver2)Abigail ProctorNo ratings yet
- Phy 11Document11 pagesPhy 11workforadynamichamingNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument1 pageSimple PendulumASNNo ratings yet
- Problem StatementDocument2 pagesProblem Statementlonely scorpioNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum ExperimentDocument5 pagesSimple Pendulum ExperimentrezzmanNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Engg Phy Practical Manual PDFDocument36 pagesB.Tech Engg Phy Practical Manual PDFAshim BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Materials RequiredDocument5 pagesMaterials Requiredzeeshan ahmadNo ratings yet
- Eee 102 - Exp-3 - 233001310Document6 pagesEee 102 - Exp-3 - 233001310nahianrahman0011No ratings yet
- Experiment 1.1 (FZ F4)Document2 pagesExperiment 1.1 (FZ F4)Izzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Modulus of RigidityDocument3 pagesModulus of RigiditySourav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesSimple PendulumTapajit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Python BasicsDocument2 pagesPython BasicsNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Week4 Simple PendulumDocument7 pagesPhys2 Week4 Simple PendulumSahirNo ratings yet
- Lab Report M2Document6 pagesLab Report M2Safin Rafin HaqNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Simple Pendulum LabDocument2 pagesExperiment 3 - Simple Pendulum LabElizabeth LizNo ratings yet
- Practical No 4Document5 pagesPractical No 4Mahin SarkarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Simple Pendulum: Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 Simple Pendulum: Learning Outcomes翁绍棠No ratings yet
- Experiment Apparatus Used: Theory:: Coefficient of Damping (B)Document2 pagesExperiment Apparatus Used: Theory:: Coefficient of Damping (B)amitNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document11 pagesExp 10Jay-ar BensOnNo ratings yet
- 2223 Level NS Core Physics BGT Questions Solutions (Relativity)Document5 pages2223 Level NS Core Physics BGT Questions Solutions (Relativity)Michael HajjNo ratings yet
- Practical WorkDocument14 pagesPractical WorkEzhilarasiPazhanivelNo ratings yet
- PendulumDocument4 pagesPendulumAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Physics ResonanceColumn1Document2 pagesHsslive XI Physics ResonanceColumn1Saajan MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Exp - 4 Simple Pendulum PDFDocument4 pagesExp - 4 Simple Pendulum PDFyaswanthNo ratings yet
- Determine G by Using Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesDetermine G by Using Simple PendulumMohammad Sahedul MarufNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To GravityDocument4 pagesAcceleration Due To GravitySahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vibration Engineering: ExperimentDocument3 pagesVibration Engineering: ExperimentSonu SainiNo ratings yet
- Anikar LabdocxDocument10 pagesAnikar Labdocxnahianrahman0011No ratings yet
- EEE - MPE - IPE Lab ManualDocument44 pagesEEE - MPE - IPE Lab Manualfisherman.psychNo ratings yet
- Dynamic MethodDocument5 pagesDynamic MethodMASTER PIECENo ratings yet
- Physics (1), English 1, IP 1Document15 pagesPhysics (1), English 1, IP 1fahadjubayer49No ratings yet
- Phy Prac Solved - Iv PDFDocument90 pagesPhy Prac Solved - Iv PDFJuma mnandiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration Lab ManualDocument5 pagesMechanical Vibration Lab Manualanon_390081062No ratings yet
- Physics Elastic Constant by Searle's ApparatusDocument1 pagePhysics Elastic Constant by Searle's ApparatusPooja GautamNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 11th 2021-22Document5 pagesEXPERIMENT 11th 2021-22Dolly ParmarNo ratings yet
- Maxwell NeedleDocument10 pagesMaxwell NeedleKlinsmannJanujajJurgenNo ratings yet
- Experiment-4 (Compound Pendulum)Document7 pagesExperiment-4 (Compound Pendulum)Redwanul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Indian School of Physics: The Goal of Education Is The Advancement of Knowledge and The Dissemination of TruthDocument63 pagesIndian School of Physics: The Goal of Education Is The Advancement of Knowledge and The Dissemination of TruthPrashant GargNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 4 - Bar Pendulum and Kater's PendulumDocument20 pagesExperiment - 4 - Bar Pendulum and Kater's PendulumDev HalvawalaNo ratings yet
- EXP2 Bar Pendulum 1637863083559 1647488088751Document2 pagesEXP2 Bar Pendulum 1637863083559 1647488088751Abhishek SainiNo ratings yet
- 2.rigidity ModulusDocument4 pages2.rigidity Modulusmanas100% (1)
- Https:olympiads Hbcse Tifr Res in:wp-content:uploads:2022:03:IOQP2022-PartII-Questions-enDocument4 pagesHttps:olympiads Hbcse Tifr Res in:wp-content:uploads:2022:03:IOQP2022-PartII-Questions-enjimlee.borahNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum ExperimentDocument7 pagesSimple Pendulum ExperimenthmahammeNo ratings yet
- Crocheted Scoodies: 20 Gorgeous Hooded Scarves and Cowls to CrochetFrom EverandCrocheted Scoodies: 20 Gorgeous Hooded Scarves and Cowls to CrochetNo ratings yet
- Oversize Fashion Crochet: 6 Cozy Cardigans, Pullovers & Wraps Designed with Maximum Style and EaseFrom EverandOversize Fashion Crochet: 6 Cozy Cardigans, Pullovers & Wraps Designed with Maximum Style and EaseNo ratings yet
- 17373class XiiDocument7 pages17373class XiiKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- 1.electric Charges FieldsDocument18 pages1.electric Charges FieldsKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- 11.dual NatureDocument5 pages11.dual NatureKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Motion in A Straight Line Practice Sheet No. Questions AnswersDocument3 pagesCH 3 - Motion in A Straight Line Practice Sheet No. Questions AnswersKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Literary Device EnglishDocument5 pagesLiterary Device EnglishKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Bbet-2020-C-Xi (Paper-2) - Pcm-Sample PaperDocument22 pagesBbet-2020-C-Xi (Paper-2) - Pcm-Sample PaperKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Units, Dimensions and MeasurementDocument11 pagesUnits, Dimensions and MeasurementKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Note Making WorksheetDocument2 pagesNote Making WorksheetKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Note Making WorksheetDocument2 pagesNote Making WorksheetKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- 3.motion Straight LineDocument12 pages3.motion Straight LineKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Letter To ComplaintDocument9 pagesLetter To ComplaintKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- No. Questions Answers: CH 2 - Units & Measurements Practice Sheet - 1Document2 pagesNo. Questions Answers: CH 2 - Units & Measurements Practice Sheet - 1Krish PatelNo ratings yet
- Formula Tutorial1Document84 pagesFormula Tutorial1Krish PatelNo ratings yet
- The Tiger in The ZOODocument3 pagesThe Tiger in The ZOOKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Research ProjectDocument1 pageResearch ProjectKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Offshore Structures and Ship Impact Analysis MRT 608Document17 pagesOffshore Structures and Ship Impact Analysis MRT 608Emmanuel Olisa Umenwa100% (2)
- Casting DefectsDocument27 pagesCasting DefectsRitik PatelNo ratings yet
- CNS Unit IDocument135 pagesCNS Unit IDarshan rocky KNo ratings yet
- What Statistical Analysis Should I Use?: Sunday, June 4, 2017 04:22 AMDocument364 pagesWhat Statistical Analysis Should I Use?: Sunday, June 4, 2017 04:22 AMAnonymous 3fDD3BNo ratings yet
- Consumer Choice: ECON1005 Principles of Economics I (Microeconomics)Document33 pagesConsumer Choice: ECON1005 Principles of Economics I (Microeconomics)Daniel SarchaevNo ratings yet
- UACE Physics Paper 1 Set1Document5 pagesUACE Physics Paper 1 Set1Ed Molson100% (1)
- Research Methodology SyllabusDocument1 pageResearch Methodology SyllabusYogeshRavalNo ratings yet
- Prashanth BN Assistant Professor Department Mechanical Engineering Amrita School of EngineeringDocument12 pagesPrashanth BN Assistant Professor Department Mechanical Engineering Amrita School of EngineeringPrashanth BnNo ratings yet
- LIFTDocument37 pagesLIFTNek ManNo ratings yet
- Live Aircraft Detection With Mode-S Transponder Using RTL-SDRDocument7 pagesLive Aircraft Detection With Mode-S Transponder Using RTL-SDRatalasa-1No ratings yet
- Tesis Flipped ClassroomDocument63 pagesTesis Flipped ClassroomEdward David Caté100% (1)
- Guitar Riffer Manual: Beijing Ample Sound Technology Co. LTDDocument13 pagesGuitar Riffer Manual: Beijing Ample Sound Technology Co. LTDPalanisamy BalasubramaniNo ratings yet
- Peran CAD Dalam Industri 4.0Document59 pagesPeran CAD Dalam Industri 4.0Rinaldi PraharsamahasiswaNo ratings yet
- 20174-C Using Gill WindSonic Sensor With RX3000 StationDocument10 pages20174-C Using Gill WindSonic Sensor With RX3000 StationjuokadNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test Form 1B PDFDocument2 pagesChapter Test Form 1B PDFAlen CaldeoNo ratings yet
- 05.01.23 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A&B) - Jee - Main - GTM-2 - QPDocument21 pages05.01.23 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A&B) - Jee - Main - GTM-2 - QPkasalachinuNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument42 pagesFunctionsRonit BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- SW 7 2 Installation and Configuration Guide DV 3 0Document145 pagesSW 7 2 Installation and Configuration Guide DV 3 0hacker_05No ratings yet
- Cedes Gls 126 Manual enDocument3 pagesCedes Gls 126 Manual enDenis RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Brick MasonryDocument32 pagesBrick MasonryBalaji vNo ratings yet
- Shielded Loop Aerials Rev 0Document27 pagesShielded Loop Aerials Rev 0jaynoweNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarDocument6 pagesFiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarVivek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kelayakan Bisnis Kedai Kopi (Studi Kasus Pada Agrowisata N8 Malabar, Pangalengan, Kabupaten Bandung)Document12 pagesAnalisis Kelayakan Bisnis Kedai Kopi (Studi Kasus Pada Agrowisata N8 Malabar, Pangalengan, Kabupaten Bandung)Gafa GafaNo ratings yet
- Angle Between Two LinesDocument4 pagesAngle Between Two LinesKashifNo ratings yet
- PC F50det 04Document61 pagesPC F50det 04Oracio GaitanNo ratings yet
- OAS351 SPACE SCIENCE Unit 2 NotesDocument18 pagesOAS351 SPACE SCIENCE Unit 2 NotessubramaninandhakishoreNo ratings yet
- Verilog Testbench For Spi ProtocolDocument5 pagesVerilog Testbench For Spi Protocolarivalagan13No ratings yet
- Reference Charts For Controlled Extraoral Application To Maxillary MolarsDocument6 pagesReference Charts For Controlled Extraoral Application To Maxillary MolarsSrishti SyalNo ratings yet