Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise 2 and Long Quiz 1
Exercise 2 and Long Quiz 1
Uploaded by
AthanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 2 and Long Quiz 1
Exercise 2 and Long Quiz 1
Uploaded by
AthanCopyright:
Available Formats
TUP CAVITE PHYSICS FOR ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGISTS (LECTURE)
Carlos Q. Trinidad Avenue, Brgy. Salawag, Dasmariñas, Cavite
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCES
S.Y. 2023-2024 2nd SEMESTER
CU 2: Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions
Name: Date: Score in Exercise 2: Score in L. Quiz 1:
Section: Room:
Teacher:
Instructions for Exercise 2: Read the problem below. At the back of this paper, kindly write your pertinent solution following
our format for the problem set. (5 points)
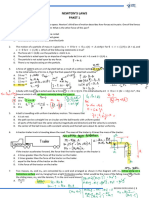
Two blocks A & B move toward each other on a frictionless horizontal surface. Before the collision, block A moves
to the right at 5 m/s while block B to the left at 10 m/s. If the masses of blocks A & B are 7 kg and 5 kg, respectively, find (a)
the velocities of blocks after the collision if the collision is inelastic with e = 0.60, (b) the total kinetic energy before and after
the collision, & (c) the energy loss.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Instructions for Long Quiz 1:
I. Conceptual Questions. Choose the best answer for each given item. Write the letter of your choice beside each item.
1. Two identical cars are traveling at the same speed toward each other. Treating them as isolated systems, do they
have the same momentum? Why or why not? (1 point)
a. Yes, because they have the same mass.
b. Yes, because they have the same speed.
c. No, because they are moving towards each other.
d. No, because they are treated as isolated systems.
2. Softer landing after a high jump tends to ____________. (1 point)
a. increase collision time. b. increase impact. c. increase momentum. d. increase force.
3. Balls A and B have equal masses. They collided observing a perfectly inelastic collision on a horizontal surface. If A
has a velocity of v and collides with B which is at rest, with what velocity will they move after the collision? (3 points)
a. v b. v/2 c. v/4 d. v/8
II. Problem-Solving. Choose the best answer for each given item. To gain the maximum point, write your pertinent
computation at the back of this following our format for the problem set. (5 points each)
4. A 1.0-kg ball is dropped vertically onto the floor at a rate of 25 m/s. It rebounds at 10 m/s. What is the impulse on
the ball during the impact?
a. 15 N•s b. 25 N•s c. 35 N•s d. 45 N•s
5. Two 10-kg inelastic spheres move with velocities of 15 m/s and 5 m/s in the same direction. Determine the energy
loss when they collide.
a. 0 J b. 250 J c. 500 J d. 1000 J
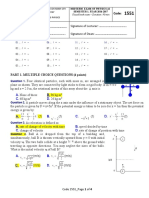
For items 6 and 7. Two balls A and B are approaching each other with velocities of 4.5 m/s, E, and 7.2 m/s, W respectively.
The mass of ball A is 3.2 kg, while that of ball B is 5.6 kg. Assuming the collision is elastic. Find:
6. the velocity of A after impact.
a. 1.31 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝐸 b. 1.31 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝑊 c. 10.39 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝐸 d. 10.39 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝑊
7. the velocity of B after impact.
a. 10.39 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝐸 b. 10.39 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝑊 c. 1.31 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝐸 d. 1.31 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 𝑊
8. A 1 500-kg car traveling east with a speed of 25.0 m/s collides at an intersection with a 2,500-kg truck traveling
north at a speed of 20.0 m/s. Find the direction and magnitude of the velocity of the wreckage after the collision,
assuming the vehicles stick together after the collision.
a. 𝑣⃑𝑓 = 12.50 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 53.13° 𝑁 𝑜𝑓𝐸 c. 𝑣⃑𝑓 = 15.63 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 53.13° 𝑁 𝑜𝑓𝐸
𝑚
b. 𝑣⃑𝑓 = 12.50 ⁄𝑠 , 36.87° 𝑁 𝑜𝑓𝐸 d. 𝑣⃑𝑓 = 15.63 𝑚⁄𝑠 , 36.87° 𝑁 𝑜𝑓𝐸
You might also like
- Unit 5 ExercisesDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Four Pillars of Sex - WorthinessDocument5 pagesFour Pillars of Sex - WorthinessVagner VagnerNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 ch09 Test Bank陳禹誌No ratings yet
- MomentumDocument16 pagesMomentumΝίκος ΕλληνοκαστρίτηςNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 and Long Quiz 1Document1 pageExercise 2 and Long Quiz 1casseyshane.bayosNo ratings yet
- AP Phys 1 Quiz MomentumDocument10 pagesAP Phys 1 Quiz MomentumWenyang LiNo ratings yet
- Ap Phys1 - Momentum Multiple Choice - 2019 01 09Document10 pagesAp Phys1 - Momentum Multiple Choice - 2019 01 09黃吏維No ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 1 Summative ExamDocument4 pagesPHYSICS 1 Summative ExamLeizel MundoNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa City Administration Education Bureau Addis Abeba Grade 12 Physics Model Examinations GINBOT 2013/MAY 2021Document9 pagesAddis Ababa City Administration Education Bureau Addis Abeba Grade 12 Physics Model Examinations GINBOT 2013/MAY 2021dmc constructionNo ratings yet
- 6 - Lecture Examples - Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument9 pages6 - Lecture Examples - Linear Momentum and CollisionsMojery MohauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Momentum Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Momentum Multiple Choicejayson albarracinNo ratings yet
- Practice Momentum TestDocument5 pagesPractice Momentum TestKinalPatelNo ratings yet
- HW7.2 ConservationofMomentumWSDocument4 pagesHW7.2 ConservationofMomentumWSmaalmeida85No ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13Document18 pagesAP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13YazaanNo ratings yet
- Ap Phys1 - Test Momentum v3 - 2017 12 21Document5 pagesAp Phys1 - Test Momentum v3 - 2017 12 21yooh9814No ratings yet
- Part A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPart A - Multiple Choice QuestionsBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Momentum MCQDocument3 pagesMomentum MCQFaeequa nasrahNo ratings yet
- DMCM 2713 Revision Questions (Chapter 4: Kinetics of A Particle: Impulse and Momentum)Document4 pagesDMCM 2713 Revision Questions (Chapter 4: Kinetics of A Particle: Impulse and Momentum)zul hilmiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Model 2014 G12Document11 pagesPHYSICS Model 2014 G12Kedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- NAIS Final Exam 2020-2021 Semester 2: Subject: G9 PhysicsDocument7 pagesNAIS Final Exam 2020-2021 Semester 2: Subject: G9 PhysicsHoracio FerrándizNo ratings yet
- Phys 1D03 Test 2 Online F20 Ave PDFDocument5 pagesPhys 1D03 Test 2 Online F20 Ave PDFMarc YorkNo ratings yet
- College Physics 10th Edition Serway Test BankDocument18 pagesCollege Physics 10th Edition Serway Test Bankrussellarnoldmbgzcoqiyd100% (27)
- Ebook College Physics 10Th Edition Serway Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesEbook College Physics 10Th Edition Serway Test Bank Full Chapter PDFalberttuyetrcpk100% (15)
- College Physics 10th Edition Serway Test BankDocument37 pagesCollege Physics 10th Edition Serway Test Bankdoraphillipsooeot100% (19)
- Summative Test in Grade 9 ScienceDocument3 pagesSummative Test in Grade 9 ScienceApolonio Pamittan Jr.No ratings yet
- PHYSICS Assignment SA1 Class 9 CBSEDocument5 pagesPHYSICS Assignment SA1 Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- PHYSICS Revision Assignment SA1Document5 pagesPHYSICS Revision Assignment SA1gurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 4th Q - ReviewerDocument1 pageSCIENCE 9 4th Q - ReviewerJonel RuleNo ratings yet
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Document5 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Q4 Summative-1Document4 pagesQ4 Summative-1artNo ratings yet
- Ce2a 105 f08Document5 pagesCe2a 105 f08jessieNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines College of ScienceDocument10 pagesUniversity of The Philippines College of SciencecrizwiseNo ratings yet
- Energy in A Collision Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesEnergy in A Collision Practice Questionsrana elshaNo ratings yet
- Ex3mech 2019Document8 pagesEx3mech 2019Nasim RazaviNo ratings yet
- FR MomentumDocument22 pagesFR MomentumJanel Edwards0% (1)
- Physics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1Document8 pagesPhysics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1abdiasfaw7152No ratings yet
- Full College Physics 10Th Edition Serway Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument41 pagesFull College Physics 10Th Edition Serway Test Bank Online PDF All Chapterkammaeromanaa100% (3)
- PhysicsLAB - 2006 Physics Quiz Bowl (Part 1)Document6 pagesPhysicsLAB - 2006 Physics Quiz Bowl (Part 1)Bishoy AkmalNo ratings yet
- Physics Set I PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Set I PDFAdityaSinghNo ratings yet
- AsdfDocument22 pagesAsdfSylvia Amanda SiregarNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Physics C Mechanics 2023 AP Daily Practice SessionsDocument5 pagesSession 1 Physics C Mechanics 2023 AP Daily Practice SessionsMelba CuervoNo ratings yet
- Ce2a 105 f08Document5 pagesCe2a 105 f08Mona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 11 Unit 4 WorksheetDocument14 pagesPhysics Grade 11 Unit 4 Worksheetsample nameNo ratings yet
- Momentum Worksheet PacketDocument10 pagesMomentum Worksheet PacketsmexiiloriNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter - Science 9Document7 pages4TH Quarter - Science 9MARIA THERESA TULALINo ratings yet
- Physics SolvedDocument16 pagesPhysics SolvedAbhijeet Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Phy G11 - PQ2Document5 pagesPhy G11 - PQ2RonaldNo ratings yet
- OAPT - Grade 11 Physics Contest - 2018 OAPT Grade 11 Physics Contest ANSWER KEY PDFDocument10 pagesOAPT - Grade 11 Physics Contest - 2018 OAPT Grade 11 Physics Contest ANSWER KEY PDFAmana Alam100% (1)
- Phys 1011 Final SAMPLEDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 Final SAMPLEJonah the mixerNo ratings yet
- Cantidad de MovimientoDocument6 pagesCantidad de MovimientoSebastianNo ratings yet
- Physics An Algebra Based Approach 1st Edition Mcfarland Test BankDocument38 pagesPhysics An Algebra Based Approach 1st Edition Mcfarland Test Bankloganyjl9th100% (15)
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument5 pagesKinematicsHamza YareNo ratings yet
- Force, Motion and EnergyDocument18 pagesForce, Motion and EnergyTushitaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam ANSWERKEYDocument6 pagesFinal Exam ANSWERKEYFiel Ericson SolaresNo ratings yet
- Physics End of Term 3 ExamDocument7 pagesPhysics End of Term 3 Examkakaleclement303No ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- Introductory Physics Classwork Over Chapters 06 and 07Document4 pagesIntroductory Physics Classwork Over Chapters 06 and 07SamanthaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 2016-2017-01Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 2016-2017-01Gia Hân EmiNo ratings yet
- 6.4 - Quadratic Functions & Graphs of FunctionsDocument39 pages6.4 - Quadratic Functions & Graphs of FunctionsGabriel PrisecariuNo ratings yet
- Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) : Overview and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesCross Laminated Timber (CLT) : Overview and DevelopmentDevansh KhareNo ratings yet
- Panic Iphone X 64Document252 pagesPanic Iphone X 64misku75No ratings yet
- EBVF4103 (Chapter 4) Fluid Mechanics For Civil EngineeringDocument30 pagesEBVF4103 (Chapter 4) Fluid Mechanics For Civil EngineeringSaurabh SumanNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document3 pagesTask 1SITI MAHARANI 2020No ratings yet
- Quarter Plan: Division of Negros OccidentalDocument3 pagesQuarter Plan: Division of Negros OccidentalShairel GesimNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Kellert - The - Practice - of - Biophilic - Design - 240528 - 234119Document27 pages2015 - Kellert - The - Practice - of - Biophilic - Design - 240528 - 234119sindyartiNo ratings yet
- Multimodals and It's ElementsDocument27 pagesMultimodals and It's ElementsJosie PabloNo ratings yet
- GB-4540 Rev1Document42 pagesGB-4540 Rev1Алексей ХоролецNo ratings yet
- Gas Cylinders Tracking2021Document37 pagesGas Cylinders Tracking2021Gourav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fueling Progress, Pakistan Iran Gas PipelineDocument4 pagesFueling Progress, Pakistan Iran Gas PipelineJunaid SaqibNo ratings yet
- Ansys Fluent 12.0 Text Command List: April 2009Document79 pagesAnsys Fluent 12.0 Text Command List: April 2009baghaliNo ratings yet
- MGT 30525 - Organizational BehaviorDocument19 pagesMGT 30525 - Organizational BehaviorNaveen PragashNo ratings yet
- BS 4346 - 2 Joints and FittingsDocument17 pagesBS 4346 - 2 Joints and FittingsPD AWSSIESPNo ratings yet
- The Historical HebdomadDocument5 pagesThe Historical HebdomadDark JaperNo ratings yet
- Vibro-Acoustic Response of An Infinite, Rib-Stiffened, Thick-Plate Assembly Using Finite-Element AnalysisDocument8 pagesVibro-Acoustic Response of An Infinite, Rib-Stiffened, Thick-Plate Assembly Using Finite-Element Analysisaurora borealissNo ratings yet
- 614-Article Text-1092-2-10-20190708Document8 pages614-Article Text-1092-2-10-20190708Petrus BageNo ratings yet
- MATLAB For Iteration Hydraulic Modeling For Environmental Engineering StudentsDocument5 pagesMATLAB For Iteration Hydraulic Modeling For Environmental Engineering StudentsEngr Hafiz Qasim AliNo ratings yet
- HR Interview Questions Quick GuideDocument19 pagesHR Interview Questions Quick GuidePradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- DMAIC-Measuring The PVC Pipe Manufacturing Process: January 2015Document12 pagesDMAIC-Measuring The PVC Pipe Manufacturing Process: January 2015Ahua WangNo ratings yet
- Ielts Task 1Document10 pagesIelts Task 1Jana Shamseldin AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer With Chemical Reaction in Multiphase Systems 1983 PDFDocument1,079 pagesMass Transfer With Chemical Reaction in Multiphase Systems 1983 PDFMark Herring100% (1)
- Delta DOP A User ManualDocument53 pagesDelta DOP A User Manualخطاب الشاميNo ratings yet
- Psychology of Success Finding Meaning in Work and Life 6th Edition Denis Waitley Test BankDocument25 pagesPsychology of Success Finding Meaning in Work and Life 6th Edition Denis Waitley Test BankJamesGonzalezwbpg100% (37)
- Implementation Plan: Limited Face-to-Face Learning ModalityDocument48 pagesImplementation Plan: Limited Face-to-Face Learning ModalityimpromtouNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal FinalDocument9 pagesProject Proposal FinalVillamor CathleenNo ratings yet
- Basic GIS 1 CUDE6011: The Structure of Geographic DataDocument19 pagesBasic GIS 1 CUDE6011: The Structure of Geographic DataCephas Ben JesusNo ratings yet
- AI-based Chatbot For Skin Disease Prediction Using CNN and ID3 Decision TreeDocument46 pagesAI-based Chatbot For Skin Disease Prediction Using CNN and ID3 Decision TreeChumma SpamNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1, - 2 Enviro Chem 1Document38 pagesLesson-1, - 2 Enviro Chem 1JoudNo ratings yet