Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JR Chemistry Day-05
JR Chemistry Day-05
Uploaded by
Harsha .0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
Jr Chemistry Day-05
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageJR Chemistry Day-05
JR Chemistry Day-05
Uploaded by
Harsha .Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
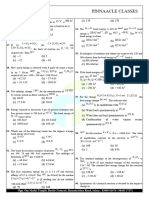
JR CHEMISTRY HOLIDAY WORKSHEET DAY: 05
41. If liquids 𝐴 and 𝐵 from an ideal solution, the:
a) Enthalpy of mixing is zero
b) Entropy of mixing is zero
c) Free energy of mixing is zero
d) Free energy as well as the entropy of mixing are each zero
42. In which of the following cases entropy decreases?
a) Solid changing to liquid
b) Expansion of a gas
c) Crystals dissolve
d) Polymerisation
43. For the reaction N + 3H ⇌ 2NH : ∆𝐻 is
a) ∆𝐸 − 2𝑅𝑇 b) ∆𝐸 − 𝑅𝑇 c) ∆𝐸 + 𝑅𝑇 d) ∆𝐸 + 2𝑅𝑇
44. When one mole of monoatomic ideal gas at 𝑇 temperature undergoes adiabatic change under a constant
external pressure of 1 atm change in volume is from 1 L to 2 L, the final temperature in Kelvin would be
𝑇 2 2
a) ( / ) b) 𝑇 + c) 𝑇 d) 𝑇 −
2 3 × 0.0821 3 × 0.0821
45. In the combustion of 2.0 g of methane, 25 kcal heat is liberated. Heat of combustion of methane would be
a) 150 kcal b) 200 kcal c) 250 kcal d) 350 kcal
46. 1 mole of an ideal gas at 25℃ is subjected to expand reversibly ten times of its initial volume. The change in
entropy of expansion is:
a) 19.15 JK mol b) 16.15 JK mol c) 22.15 JK mol d) None of these
47. The heat of formation (∆𝐻 ) of H O(𝑙) is equal to:
a) Zero
b) Molar heat of combustion of H (𝑙)
c) Molar heat of combustion of H (g)
d) Sum of heat of formation of H O(g) and O (g)
48. The entropy change for the reaction given below,
2H (g) + O (g) → 2H O(𝑙)
Is…at 300 K. Standard entropies of H (g), O (g) and H O(𝑙) are 126.6, 201.20 and 68.0 JK mol
respectively.
a) −318.4 JK mol b) 318.4 JK mol c) 31.84 JK mol d) None of these
49. Heat of combustion ∆𝐻 for C(𝑠), H (g) and CH (g) are −94, −68 and −213 kcal/mole then ∆𝐻 for C(𝑠) +
2H (g) → CH (g)i𝑠 ∶
a) −17 kcal b) −111 kcal c) −170 kcal d) −85 kcal
50. A positive change in enthalpy occurs in :
1
a) H (g) + O (g) ⟶ H O(g)
2
b) N (g) + 3H (g) ⟶ 2NH (g)
c) MgCO (𝑠) ⟶ MgO(𝑠) + CO (g)
1
d) H (g) + O (g) ⟶ H O(𝑙)
2
KEY:
41) A 42) D 43) A 44) D 45) B 46) A 47) C 48) A 49) A 50) C
You might also like
- The Relay Testing Handbook-Generator Relay Protection Testing TOC-ToF-BibDocument36 pagesThe Relay Testing Handbook-Generator Relay Protection Testing TOC-ToF-BibMartin Goodnough100% (1)
- R 200ia ManualDocument11 pagesR 200ia Manualbhanu6212No ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1-ThermochemistryDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1-ThermochemistrysyazaNo ratings yet
- PROSPER CompleteDocument1,471 pagesPROSPER Completehamidahaku100% (1)
- DPD-1 ThermodynamicDocument2 pagesDPD-1 ThermodynamicDeepNo ratings yet
- DPP 1Document2 pagesDPP 1rajeev sekhriNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry (CG)Document2 pagesPhysical Chemistry (CG)dipak20611216No ratings yet
- 3 - Chemical Thermodynamics and ThermochemistryDocument3 pages3 - Chemical Thermodynamics and ThermochemistryYawn D ArtistNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesWorksheet Thermodynamicsrahulsoorya2001No ratings yet
- DPP 2Document3 pagesDPP 2rajeev sekhriNo ratings yet
- Xi Iit-Neet Che DPT 25.12.2023 ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesXi Iit-Neet Che DPT 25.12.2023 ThermodynamicsQamar JavedNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: CH (G) 5O (G) 3CO (G) 4H O (L) + ® +Document5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: CH (G) 5O (G) 3CO (G) 4H O (L) + ® +Abhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Final Touch (RCC Do / Die Questions) Chapter: ThermodynamicsDocument17 pagesFinal Touch (RCC Do / Die Questions) Chapter: Thermodynamicsharita shindeNo ratings yet
- 03 - 9TH Co-Iit - P-B - Chemistry - Thermodynamics AssignmentDocument10 pages03 - 9TH Co-Iit - P-B - Chemistry - Thermodynamics AssignmentramkarthikeyareddyNo ratings yet
- Test Bank-CH-6 Final +Document4 pagesTest Bank-CH-6 Final +miku nakanoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Assignment)Document1 pageThermodynamics (Assignment)Nishtha100% (1)
- Answer Key TEST-1 Paper 1 11th PCMB CHEMISTRY (19-01-2024)Document10 pagesAnswer Key TEST-1 Paper 1 11th PCMB CHEMISTRY (19-01-2024)9C Jagmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Assignment)Document10 pagesThermodynamics (Assignment)Mudit KNo ratings yet
- Exercise Unit 401Document18 pagesExercise Unit 4014q7m2pmrc5No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics WorkbookDocument40 pagesThermodynamics Workbookagrimsinghal28No ratings yet
- QWQWDocument6 pagesQWQWmaduenofurtawzib.c6.1.33No ratings yet
- 2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotesDocument12 pages2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotesZa Evolution ClanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Document18 pagesChemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Sanjeeb KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry II CHM2046 Test 1, Johnston and Figueroa, University of South FloridaDocument7 pagesChemistry II CHM2046 Test 1, Johnston and Figueroa, University of South FloridaAnhvinhDoanvoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 101 Final Exam-B Fall 2014Document13 pagesChemistry 101 Final Exam-B Fall 2014Kristopher Park SolivenNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChallengeDocument9 pagesThermo ChallengeMeowCat123456789No ratings yet
- Final RevisionnnDocument28 pagesFinal Revisionnnyoyomhmdsalah2008No ratings yet
- Thermo Holiday AssignmentDocument4 pagesThermo Holiday Assignmentashray2493No ratings yet
- WPT Centre XiDocument3 pagesWPT Centre XiDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- II IIT IRP Chemistry Worksheet - 13 PDFDocument7 pagesII IIT IRP Chemistry Worksheet - 13 PDFAshwin KumarNo ratings yet
- CH1Document6 pagesCH1chittaranjan paniNo ratings yet
- C1 Ipl Mains PaperDocument4 pagesC1 Ipl Mains PaperNIVEDITA CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- Energetics Q + MSDocument32 pagesEnergetics Q + MSmamta2111No ratings yet
- Sharp Edge Question Bank at NEET - 2024Document10 pagesSharp Edge Question Bank at NEET - 20242005sahuankitaNo ratings yet
- Ambedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarDocument2 pagesAmbedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Physics Thermodynamics: GgliveDocument12 pagesPhysics Thermodynamics: GgliveChinmaya VastradNo ratings yet
- 2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocDocument10 pages2 Quizizz 2019 ptVIIIe DocKM Tsang Ka ManNo ratings yet
- CY2301Document11 pagesCY2301Prarabdha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-02 (Exercise)Document36 pagesThermodynamics-02 (Exercise)hppavilion597No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics IInd Law PC EDocument14 pagesThermodynamics IInd Law PC Eb72hbapqiNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICSDocument6 pagesTHERMODYNAMICSsujalsuhaas2007No ratings yet
- Ap Unit6 Worksheet AnswersDocument5 pagesAp Unit6 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: Fill in The BlanksDocument13 pagesChemical Energetics: Fill in The BlanksAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentAfthirah AmiraNo ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry Full Portion One Marks 1Document3 pagesXi Chemistry Full Portion One Marks 1ssanthoshjs47No ratings yet
- Adv Thermochemistry PDFDocument18 pagesAdv Thermochemistry PDFSanjanaNo ratings yet
- U W W Ve W Ve: - (Chemistry)Document6 pagesU W W Ve W Ve: - (Chemistry)ajaybolarNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit6 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit6 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- ChenDocument3 pagesChen5133.stpeterschdNo ratings yet
- Phy CheDocument2 pagesPhy CheGela EcalNo ratings yet
- CC Physical Chem Test PaperDocument4 pagesCC Physical Chem Test PaperLight MayNo ratings yet
- PhychemDocument7 pagesPhychemChrystylyn VictorioNo ratings yet
- Honors Chem Final - Review - KEY PDFDocument12 pagesHonors Chem Final - Review - KEY PDFRohith GudatiNo ratings yet
- Xi Chem 13.01.24Document2 pagesXi Chem 13.01.24faraazahmed70058No ratings yet
- JEE - Chemistry - Chemical KineticsDocument27 pagesJEE - Chemistry - Chemical Kineticsdaiwikchilukuri321No ratings yet
- Section 6-8 Test Sri VagheeshaDocument10 pagesSection 6-8 Test Sri VagheeshavishwasgharNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry WorkbookDocument36 pagesThermochemistry Workbookagrimsinghal28No ratings yet
- CHM213 TUTORIAL3 - Chemical Equilibrium - Sept 2017Document5 pagesCHM213 TUTORIAL3 - Chemical Equilibrium - Sept 2017mijaniallNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Practice Test Answer KeyDocument3 pagesCH 6 Practice Test Answer KeyLead Ferrer100% (1)
- Arjuna JEE Main Test 01 - ChemistryDocument6 pagesArjuna JEE Main Test 01 - Chemistrymriitian56No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- What To Consider When Welding Dissimilar MaterialsDocument8 pagesWhat To Consider When Welding Dissimilar MaterialsWeldPulse100% (2)
- Claims Fidic IndonesiaDocument14 pagesClaims Fidic IndonesiacemilagirmanNo ratings yet
- AbrilDocument11 pagesAbrilWilfrido Escobar ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- APMT Berth PlanningDocument1 pageAPMT Berth PlanningMaguli LagvilavaNo ratings yet
- Shell PHD ProgramDocument6 pagesShell PHD ProgramVikasRedduNo ratings yet
- TM 10-3930-237-35 Mhe-192Document104 pagesTM 10-3930-237-35 Mhe-192AdvocateNo ratings yet
- Eng CSBDocument8 pagesEng CSBivanchi888No ratings yet
- Fluid Power 1Document25 pagesFluid Power 1Ziad TarekNo ratings yet
- Advance Tech Guide - Power MV GearDocument48 pagesAdvance Tech Guide - Power MV GearNiraj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Uniflair LE TDAV - Technical Specifications PDFDocument52 pagesUniflair LE TDAV - Technical Specifications PDFtyberius7No ratings yet
- Type MVAW: Interposing RelaysDocument20 pagesType MVAW: Interposing Relaysrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Techdoc Print Page PDFDocument7 pagesTechdoc Print Page PDFSuharto ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Magneto-Optic Current TransformerDocument20 pagesMagneto-Optic Current TransformerSalil Kumar Gautam100% (1)
- JMechE Template v2023Document4 pagesJMechE Template v2023Miguel Angel Palacio NovaNo ratings yet
- 100608410Document136 pages100608410umairNo ratings yet
- TOP 250+ Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers 07 August 2021 - Thermodynamics Interview Questions - Wisdom Jobs IndiaDocument23 pagesTOP 250+ Thermodynamics Interview Questions and Answers 07 August 2021 - Thermodynamics Interview Questions - Wisdom Jobs IndiaHELL RIDERNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter: Santana NoeliaDocument2 pagesCover Letter: Santana NoeliaNoelia Dayana Santana BaldeonNo ratings yet
- Services PPT Dupont Plaza Hotel and CasinoDocument20 pagesServices PPT Dupont Plaza Hotel and CasinoShivangi Shankar100% (1)
- Planta Electrica de 152kva 120kw Motor Fawde Tipo Stamford Cabinada Abierta GSFX 120 PDFDocument6 pagesPlanta Electrica de 152kva 120kw Motor Fawde Tipo Stamford Cabinada Abierta GSFX 120 PDFSebastián Fernández LópezNo ratings yet
- Ingersoll RandDocument41 pagesIngersoll RandВиктор Мушкин100% (1)
- 6 Combustion and FlameDocument17 pages6 Combustion and Flamedian100% (1)
- Neelum Jehlum ProjectDocument89 pagesNeelum Jehlum ProjectJamman Shahid ShiblyNo ratings yet
- Active Front End Topology Based Three Phase InverterDocument6 pagesActive Front End Topology Based Three Phase InverterPoornima SNo ratings yet
- Water-Cooled Chillers With High Speed Centrifugal CompressorDocument19 pagesWater-Cooled Chillers With High Speed Centrifugal CompressorDavid PerisNo ratings yet
- Ata Chapter ListDocument1 pageAta Chapter ListFrancois FajardoNo ratings yet
- Mod. REC1/EV Mod. REC1c/EV Mod. REC1a/EV: Continuous Reaction (CSTR) Pilot PlantDocument2 pagesMod. REC1/EV Mod. REC1c/EV Mod. REC1a/EV: Continuous Reaction (CSTR) Pilot Plantcgjp120391No ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect QuestionsDocument4 pagesGreenhouse Effect QuestionsSayed Daniyal AliNo ratings yet