Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organisation QP 2
Organisation QP 2
Uploaded by
lizablatchfordCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organisation QP 2
Organisation QP 2
Uploaded by
lizablatchfordCopyright:
Available Formats
Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starch.
1.
(a) Amylase is a polymer of smaller molecules.
Name the type of smaller molecule.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(b) Name the three parts of the human digestive system that produce amylase.
1 ________________________________________________________________
2 ________________________________________________________________
3 ________________________________________________________________
(2)
(c) Explain how amylase breaks down starch.
Answer in terms of the ‘lock and key theory’.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
St Clement Danes School Page 1 of 31
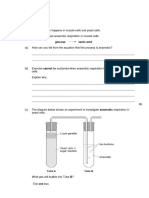
A student investigated the effect of temperature on the activity of amylase.
The figure below shows the apparatus used.
This is the method used.
1. Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure above.
2. After 5 minutes, pour the starch solution into the amylase solution and mix.
3. Remove one drop of the starch-amylase mixture and place onto a spotting tile.
4. Immediately add two drops of iodine solution to the starch-amylase mixture
on the spotting tile.
5. Record the colour of the iodine solution added to the starch-amylase mixture.
6. Repeat steps 3 to 5 every minute until the iodine solution stays yellow-brown.
7. Repeat steps 1 to 6 using water at different temperatures.
(d) Name two control variables the student used in the investigation.
1 ________________________________________________________________
2 ________________________________________________________________
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 2 of 31
(e) Why did the student leave the starch solution and amylase solution for 5 minutes before
mixing them?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
The table below shows the results of the investigation.
Time taken until iodine
Temperature in °C solution stays
yellow-brown in minutes
5 did not become yellow-brown
20 5
35 2
50 7
65 14
80 did not become yellow-brown
(f) What conclusion can be made about the effect of temperature on amylase activity between
20 °C and 65 °C?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 3 of 31
(g) Explain the results at 5 °C and at 80 °C.
Use the table above.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(5)
(h) The student investigated the effect of temperature on amylase activity.
Describe how the student could extend the investigation to determine the effect of a
different factor on amylase activity.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 17 marks)
The circulatory system is composed of the blood, blood vessels and the heart.
2.
(a) Urea is transported in the blood plasma.
Name two other substances transported in the blood plasma.
1. _________________________________________________________________
2. _________________________________________________________________
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 4 of 31
(b) Some athletes train at high altitude.
Training at high altitude increases the number of red blood cells per cm3 of blood.
Explain why having more red blood cells per cm3 of blood is an advantage to an athlete.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(c) Which two blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood?
Tick two boxes.
Aorta
Coronary artery
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Vena cava
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 5 of 31
Figure 1 shows the three types of blood vessel.
Figure 1
(d) Which type of blood vessel carries blood into the right atrium?
Tick one box.
(1)
(e) Compare the structure of an artery with the structure of a vein.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
St Clement Danes School Page 6 of 31
(f) Heart rate is controlled by a group of cells. This group of cells act as a pacemaker.
Figure 2 shows a section through the heart.
Draw an X on Figure 2 to show the position of the pacemaker.
Figure 2
(1)
(g) A patient may be fitted with an artificial pacemaker.
What condition may be treated using an artificial pacemaker?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(Total 13 marks)
St Clement Danes School Page 7 of 31
Explain how the human circulatory system is adapted to:
3.
• supply oxygen to the tissues
• remove waste products from tissues.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
(Total 6 marks)
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins.
4.
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(ii) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery in the leg and blood taken
from a vein in the leg.
Give two differences in the composition of the blood.
1. ____________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
2. ____________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 8 of 31
(b) During operations patients can lose a lot of blood. Patients often need blood transfusions to
keep them alive.
The text shows information about a new artificial blood product.
Suggest two possible advantages of using the new artificial blood, instead of using human
blood for a transfusion in humans.
1. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
2. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 6 marks)
A small animal called an axolotl lives in water. The axolotl has a double circulatory system.
5.
(a) Define the term double circulatory system.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 9 of 31
Figure 1 shows the double circulatory system of the axolotl.
Figure 1
(b) The heart of the axolotl has only one ventricle.
Label the ventricle on Figure 1.
(1)
(c) Explain why having only one ventricle makes the circulatory system less efficient than
having two ventricles.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 10 of 31
Figure 2 shows an axolotl.
Figure 2
(d) Explain why an axolotl may die in water with a low concentration of oxygen.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
If a gill of an axolotl is removed, a new gill will grow in its place.
Scientists hope to use information on how axolotls grow new gills to help with regenerating
human tissue.
(e) Name the type of cell that divides when a new gill grows.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 11 of 31
(f) Name one condition that could be treated using regenerated human tissue.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(g) Suggest one reason why an axolotl is a suitable animal for research in the laboratory.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(h) An axolotl may not be a suitable animal to study when researching regeneration in human
tissue.
Suggest one reason why.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(Total 12 marks)
The figure below shows the internal structure of the human heart.
6.
One of the heart valves is labelled.
St Clement Danes School Page 12 of 31
Sometimes a valve in the heart can start to leak.
(a) Explain why a person with a leaking heart valve has difficulty exercising.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
A patient with a leaking heart valve may have the valve replaced.
A study compared two different types of replacement heart valve:
• mechanical valves
• biological valves from pigs.
The data used in the study was collected from female patients aged 50–69.
St Clement Danes School Page 13 of 31
The following table shows the data.
Type of replacement heart valve
Mechanical Biological
Number of patients given the valve 2852 1754
Number of patients who died from heart-related
180 178
problems after valve replacement
Percentage of patients alive after 5 years 91 89
Percentage of patients needing a second valve
2.2 5.2
replacement within 6 years
Percentage of patients who had a blood clot on the brain
5.8 0.1
after surgery
(b) Give one conclusion about the death of patients from heart-related problems after a valve
replacement.
Include calculations to support your answer.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(c) One risk of mechanical valves is that blood clots can form on the surface of the valve.
Name the component of the blood that starts the process of blood clotting.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 14 of 31
(d) Evaluate the use of mechanical replacement heart valves and biological replacement heart
valves.
Use information from the table above and your own knowledge.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(6)
(Total 14 marks)
St Clement Danes School Page 15 of 31
The diagram below shows the human digestive system.
7.
(a) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram.
(1)
(b) Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called
Helicobacter pylori.
The stomach is lined with a protective lining of mucus.
Helicobacter pylori are acid-tolerant bacteria which can damage this mucus lining.
Suggest how an infection with Helicobacter pylori might result in a stomach ulcer
developing.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 16 of 31
(c) Helicobacter pylori can also cause stomach cancer.
Describe how a person infected with Helicobacter pylori could also develop liver cancer.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(d) Gluten is a form of protein found in some grains.
Describe the test you would use to find out if protein is present in food.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 17 of 31
(e) Coeliac disease is a disease of the digestive system.
It damages the lining of the small intestine when foods that contain gluten are eaten.
When people with coeliac disease eat foods that contain gluten:
1. their immune system forms antibodies to gluten
2. these antibodies attack the lining of the small intestine
3. this causes inflammation in the intestines and damages the villi.
Symptoms of coeliac disease include poor growth.
Suggest why a person with coeliac disease might have this symptom.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(Total 12 marks)
Figure 1 shows a cross section of a leaf.
8.
Figure 1
St Clement Danes School Page 18 of 31
(a) Which cell is most transparent?
✓) one box.
Tick (✓
A B C D
(1)
(b) Which cell structure in a leaf mesophyll cell is not found in a root hair cell?
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
Plants lose water through their leaves.
(c) Name the cells in a leaf that control the rate of water loss.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(d) Water is taken in by the roots, transported up the plant and lost from the leaves.
Which scientific term describes this movement of water?
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(e) Which change would decrease the rate of water loss from a plant’s leaves?
✓) one box.
Tick (✓
Increased humidity
Increased light intensity
Increased density of stomata
Increased temperature
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 19 of 31
(f) Compare the structure and function of xylem tissue and phloem tissue.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(6)
Figure 2 shows the total volume of water lost from a plant over 6 hours.
Figure 2
St Clement Danes School Page 20 of 31
(g) Determine the rate of water loss at 12:00
Use the tangent on the graph above.
Give your answer:
• in cm3 per minute
• in standard form.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Rate of water loss = _______________ cm3 per minute
(4)
(h) The rate of water loss at midnight was much lower than at 12:00
Explain why.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 17 marks)
St Clement Danes School Page 21 of 31
A student carried out an investigation using leaf epidermis.
9.
This is the method used.
1. Peel the lower epidermis from the underside of a leaf.
2. Cut the epidermis into six equal sized pieces.
3. Place each piece of lower epidermis into a different Petri dish.
4. Add 5 cm3 of salt solution to the six Petri dishes. Each Petri dish should have a different
concentration of salt solution.
5. After 1 hour, view each piece of epidermis under a microscope at ×400 magnification.
6. Count and record the total number of stomata present and the number of open stomata
that can be seen in one field of view.
The student’s results are shown in the table.
Concentration of Number of Number of open Percentage (%)
salt solution in stomata in field stomata in field of open stomata
mol / dm3 of view of view in field of view
0.0 7 7 100
0.1 8 8 100
0.2 7 6 X
0.3 9 6 67
0.4 10 4 40
0.5 9 2 22
(a) Calculate value X in the table above.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
X = ____________________ %
(1)
(b) Give one conclusion from the results in the table above.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 22 of 31
(c) How could the student find out what concentration of salt solution would result in half of the
stomata being open?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(d) The student measured the real diameter of the field of view to be 0.375 mm.
Calculate the number of open stomata per mm2 of leaf for the epidermis placed in 0.4 mol /
dm3 salt solution.
Use information from the table above.
Take π to be 3.14
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Number of open stomata = ____________________ per mm2
(3)
St Clement Danes School Page 23 of 31
(e) The diagram below shows two guard cells surrounding a closed stoma and two guard cells
surrounding an open stoma.
When light intensity is high potassium ions are moved into the guard cells.
Describe how the movement of potassium ions into the guard cells causes the stoma to
open.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(Total 10 marks)
Water moves from a plant to the atmosphere through the leaves.
10.
(a) How is the volume of water lost from the leaves controlled?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 24 of 31
(b) Describe the transport of water through a plant from the roots to the atmosphere.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
St Clement Danes School Page 25 of 31
A student investigated the volume of water lost from two plants of different species.
Both plants were kept together.
Figure 1 shows the student’s results.
Figure 1
(c) Suggest one reason for the difference in the rate of water loss from the two plants in the
first 2.5 hours.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
St Clement Danes School Page 26 of 31
Both plants were moved to a different place at 2.5 hours.
(d) Calculate the rate of water loss per hour in plant B from 2.5 hours to 3 hours.
Give your answer to 2 significant figures.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Rate of water loss = _______________________ cm3/hour
(3)
(e) Suggest two reasons why the rate of water loss in both plants changed after 2.5 hours.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
Water and carbon dioxide are exchanged between leaves and the atmosphere through pores
11. called stomata.
(a) Name the cells that control the opening and closing of the stomata.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
Water moves through a plant in the transpiration stream.
(b) Describe two differences between the transpiration stream and translocation.
1 _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
2 _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
St Clement Danes School Page 27 of 31
(c) Which environmental conditions would cause the rate of transpiration to be greatest in a
plant?
✓) one box.
Tick (✓
Cold with low humidity
Cold with high humidity
Warm with low humidity
Warm with high humidity
(1)
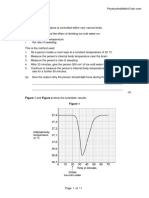
The figure below shows information about the mean width of the stomata in a plant.
St Clement Danes School Page 28 of 31
(d) The changes in the mean width of the stomata in normal conditions are an advantage to
the plant.
Explain how.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(e) The changes in the mean width of the stomata in low atmospheric carbon dioxide are
different from the changes in normal conditions.
Explain how the difference helps the plant to survive in low atmospheric carbon dioxide.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
St Clement Danes School Page 29 of 31
Plants exchange substances with the environment.
12.
(a) Plant roots absorb water mainly by osmosis.
Plant roots absorb ions mainly by active transport.
Explain why roots need to use the two different methods to absorb water and ions.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(b) What is meant by the transpiration stream?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
St Clement Danes School Page 30 of 31
(c) Students investigated the loss of water vapour from leaves.
The students:
• cut some leaves off a plant
• measured the mass of these leaves every 30 minutes for 180 minutes.
The graph shows the students’ results.
(i) The rate of mass loss in the first 30 minutes was 7 milligrams per gram of leaf per
minute.
Calculate the rate of mass loss between 30 minutes and 180 minutes.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Rate of mass loss = _______________ milligrams per gram of leaf per minute
(2)
(ii) The rate of mass loss between 0 and 30 minutes was very different from the rate of
mass loss between 30 and 180 minutes.
Suggest an explanation for the difference between the two rates.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 11 marks)
St Clement Danes School Page 31 of 31
You might also like
- Respiration I QuestionsDocument79 pagesRespiration I QuestionsAayma MunirNo ratings yet
- Triple HomeostasisDocument13 pagesTriple HomeostasisAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- 5.1.1 and 5.1.2Document10 pages5.1.1 and 5.1.2Aamina HussainNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 4Document38 pagesBio Unit 4Mei NgNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 QuestionsDocument54 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesDocument39 pagesTopic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesHayley Camenzuli100% (1)
- Set 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9Document20 pagesSet 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9tnishtalaNo ratings yet
- More Enzyme QuestionsDocument7 pagesMore Enzyme QuestionsAlNo ratings yet
- Year2guidedrevision Prac5and6Document19 pagesYear2guidedrevision Prac5and6alaynasharleezNo ratings yet
- UnknownDocument57 pagesUnknownZara KhanNo ratings yet
- Mon Omers and Polymers A LevelDocument57 pagesMon Omers and Polymers A Leveldfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis QuestionsDocument54 pagesCritical Analysis Questionsalishariz329No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Assessment Booklet: Marks 155 Time Allowed 202 MinutesDocument52 pagesTopic 3 Assessment Booklet: Marks 155 Time Allowed 202 MinutesHayley CamenzuliNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocument15 pagesA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Science Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesScience Exam QuestionscheetoNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Homeostasis QPDocument11 pages5.1 Homeostasis QPMareeb ShahNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Homeostasis QP-combinedDocument44 pages5.1 Homeostasis QP-combinedVictor BabsNo ratings yet
- 2024 3rd Year Enzymes and Digestion Test and MSDocument12 pages2024 3rd Year Enzymes and Digestion Test and MSthemathlab08No ratings yet
- AnisationDocument28 pagesAnisationStefaniya Dmitrievna “Stef” DeminetsNo ratings yet
- DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiseaseBob yuNo ratings yet
- Proteins and EnzymesDocument94 pagesProteins and Enzymesdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Organisation HTDocument17 pagesOrganisation HTjane byersNo ratings yet
- A Level Paper 1 Exams 2022 77izmgDocument69 pagesA Level Paper 1 Exams 2022 77izmgMal ChenNo ratings yet
- Set 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Document17 pagesSet 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- A01 Short Answer QuestionsDocument29 pagesA01 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- A01 Short Answer QuestionsDocument21 pagesA01 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- Week 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804Document36 pagesWeek 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Extra Q and MSDocument14 pagesCell Cycle Extra Q and MSKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- 4.1c Cell Biology HigherDocument64 pages4.1c Cell Biology HigherJayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument16 pagesWaterdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Document17 pagesSet 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741Document15 pagesWeek 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- Practical Skills QuestionsDocument62 pagesPractical Skills QuestionshftuuNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 2 Workbook - Combined HigherDocument85 pagesBiology Paper 2 Workbook - Combined Highermp2959812No ratings yet
- Membranes L4 MSDocument19 pagesMembranes L4 MSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Assessment BookletDocument36 pagesTopic 1 Assessment BookletLinNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1Document8 pagesBiology Paper 1paqurette3No ratings yet
- B 4 Revision PackDocument64 pagesB 4 Revision PackKrish SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4.1b Cell Biology Foundation HigherDocument70 pages4.1b Cell Biology Foundation Higherpzulu6774No ratings yet
- F5S Chemistry Revision Worksheet (6) - Double DecompositionDocument8 pagesF5S Chemistry Revision Worksheet (6) - Double DecompositionRaymond ChanNo ratings yet
- BiologyMock 2Document36 pagesBiologyMock 2backup14gNo ratings yet
- A03 Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- Kidneys AQADocument10 pagesKidneys AQAsfghcqrm4mNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Questions GcseDocument50 pagesBioenergetics Questions GcseDharm GajjarNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Homeostasis QP - CompressedDocument53 pages5.1 Homeostasis QP - CompressedradhaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Grade 9Document10 pagesAtomic Structure Grade 9Shalini MishraNo ratings yet
- Comb Sci Evaluate QP MS ERDocument12 pagesComb Sci Evaluate QP MS ERlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- RP - Food TestsDocument17 pagesRP - Food TestsNeel MutagiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Photosynthesis QPDocument35 pages4.1 Photosynthesis QPZaynab Ameenah KhanNo ratings yet
- ATP A Level: NameDocument38 pagesATP A Level: Namedfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- A01 3.6 Short Answer QuestionsDocument20 pagesA01 3.6 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- Exam Questions: Problem Part That Did Not Work ProperlyDocument2 pagesExam Questions: Problem Part That Did Not Work ProperlyMaria Khin YadanarNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsDocument57 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Walk and Talk MockDocument44 pagesWalk and Talk Mockalieplays117No ratings yet
- Biology Mock Paper 02 - CorrectedDocument13 pagesBiology Mock Paper 02 - CorrectedNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Formative Practice Chapter 2 (BI)Document8 pagesFormative Practice Chapter 2 (BI)suraya nazaNo ratings yet
- Homesostasis and Repsonse HigherDocument70 pagesHomesostasis and Repsonse Highermohammed fayedNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Sep Only Paper 1 QPDocument39 pagesSep Only Paper 1 QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Practice+Test+Set+7+ +Paper+1HDocument18 pagesPractice+Test+Set+7+ +Paper+1HlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Sep Only QPDocument41 pagesSep Only QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Comb Sci Evaluate QP MS ERDocument12 pagesComb Sci Evaluate QP MS ERlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Extra QPDocument23 pagesInheritance Extra QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Using Resources QPDocument22 pagesUsing Resources QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Y11 Mon BahutDocument1 pageY11 Mon BahutlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Bab IIDocument7 pagesDaftar Pustaka Bab IIWantoroNo ratings yet
- NLE Exam Drill 2 (Q Only 100)Document13 pagesNLE Exam Drill 2 (Q Only 100)Epaphras Joel MilitarNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination SummaryDocument90 pagesNeurological Examination SummaryAlida Taranu TernströmNo ratings yet
- Bleaching Part 1Document6 pagesBleaching Part 1Hamad KayaniNo ratings yet
- ESL Coronavirus Speaking TopicDocument2 pagesESL Coronavirus Speaking TopicGabriellaReneeNo ratings yet
- Constipation:: Drug Therapy For Constipation & DiarroheaDocument8 pagesConstipation:: Drug Therapy For Constipation & DiarroheaDevi Prasanna 42.No ratings yet
- Endoparasites Ectoparasites - LEC - 3Document16 pagesEndoparasites Ectoparasites - LEC - 3Medicine SWUNo ratings yet
- 2016 EUROPAEM EMF Guideline 2016 For The Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of EMF-related Health Problems and IllnessesDocument35 pages2016 EUROPAEM EMF Guideline 2016 For The Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of EMF-related Health Problems and IllnessesJessica Learmond-CriquiNo ratings yet
- 航 海 健 康 申 报 书aDocument1 page航 海 健 康 申 报 书aĐÌNH HIẾU PHẠMNo ratings yet
- Telugu Handbook For Medicos and DoctorsDocument41 pagesTelugu Handbook For Medicos and DoctorssatyaNo ratings yet
- Monotest Solution For Diagnosis Of: COVID-19Document2 pagesMonotest Solution For Diagnosis Of: COVID-19Fateh AzwiNo ratings yet
- 025c082733ea2-CLAT POST AprilDocument47 pages025c082733ea2-CLAT POST AprilHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Week 9 GM and Internship SlidesDocument75 pagesWeek 9 GM and Internship Slidesapi-235454491No ratings yet
- ST 43 PDFDocument1 pageST 43 PDFsorinNo ratings yet
- DSM Comparison ChartDocument6 pagesDSM Comparison ChartAJ commsNo ratings yet
- Cranial Ultrasound: DR Muhammad Jazib ShahidDocument43 pagesCranial Ultrasound: DR Muhammad Jazib ShahidJazib ShahidNo ratings yet
- Instruction: The Following Continuous Assessment Sheets Contain Two CategoriesDocument6 pagesInstruction: The Following Continuous Assessment Sheets Contain Two CategoriesfekaduNo ratings yet
- Standard Treatment Guidelines and Essential Medicine List For Primary Health Care 7th Edition - 2020Document626 pagesStandard Treatment Guidelines and Essential Medicine List For Primary Health Care 7th Edition - 2020Finger TladiNo ratings yet
- Ogden 5th Edition-39-48Document10 pagesOgden 5th Edition-39-48Artur Ter-BagdasarovNo ratings yet
- VPTH 121 1ST Lec ExamDocument1 pageVPTH 121 1ST Lec ExamSzarina KoNo ratings yet
- Charles University Faculty of Physical Education and SportDocument140 pagesCharles University Faculty of Physical Education and SportPaulomds1991No ratings yet
- Biosafety Levels Biological Safety Cabinets and Biosafety Laboratory ConstructionDocument64 pagesBiosafety Levels Biological Safety Cabinets and Biosafety Laboratory ConstructionAsim HussainNo ratings yet
- Taenia of HumanDocument14 pagesTaenia of HumaninnocentjeevaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Feeding After Gastrointestinal SurgeryDocument4 pagesNeonatal Feeding After Gastrointestinal SurgeryVianNo ratings yet
- ProteinuriaDocument1 pageProteinuriamutiara nurzaniNo ratings yet
- مشيناها خطى محمد فتحي عبد العال نسخة منقحة ومراجعة ومزيدة حتى نهاية 2024Document25 pagesمشيناها خطى محمد فتحي عبد العال نسخة منقحة ومراجعة ومزيدة حتى نهاية 2024mohamed fathi abdel aalNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy Asthma: Lecture # 1 by Ms. Fakhsheena AnjumDocument66 pagesClinical Pharmacy Asthma: Lecture # 1 by Ms. Fakhsheena Anjumgurrya786No ratings yet
- Module 3 Group QuizDocument6 pagesModule 3 Group QuizkasinarayananjrNo ratings yet
- IV FluidDocument28 pagesIV FluidZulfkar Latief QadrieNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Fasting For Adults To Prevent Perioperative Complications (Review)Document156 pagesPreoperative Fasting For Adults To Prevent Perioperative Complications (Review)Gor AdanNo ratings yet