Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Draft Soal Ktof Agustus 2020
Draft Soal Ktof Agustus 2020
Uploaded by
Yogesh KhatriCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Heat TransferDocument21 pagesHeat TransferSuzanne Sarsuelo100% (3)
- Mp3003tut07 08sem1Document18 pagesMp3003tut07 08sem1Feeling_so_flyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ia Voltaic Cells Year 11Document12 pagesChemistry Ia Voltaic Cells Year 11Jaemin KimNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Physics - Version 2Document12 pagesIIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Physics - Version 2Sumit SahaNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 Test 4Document4 pagesPhase 2 Test 4Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Physics Model QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhysics Model QuestionsQuantum HeatNo ratings yet
- Section 6 - General Physics 2 With SolutionsDocument15 pagesSection 6 - General Physics 2 With SolutionspaimoNo ratings yet
- Heat Equation Analysis of Defrosting A Roll of Frozen Ground BeefDocument3 pagesHeat Equation Analysis of Defrosting A Roll of Frozen Ground BeefJuan José Leiva AlegreNo ratings yet
- Jee 2020 JanDocument13 pagesJee 2020 Jankruthika karraNo ratings yet
- Physics Model QuestionsDocument23 pagesPhysics Model QuestionsQuantum HeatNo ratings yet
- MIT3 044S13 Pset1Document5 pagesMIT3 044S13 Pset1Dak KaizNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document29 pagesLecture 08kamran bhatNo ratings yet
- Physics TempDocument8 pagesPhysics TemprenNo ratings yet
- Problems 2017Document2 pagesProblems 2017Adith SaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Transient Heat Conduction & Heisler ChartDocument40 pagesLecture 5 - Transient Heat Conduction & Heisler ChartMonkey D. LuffyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 PDFDocument11 pagesTutorial 4 PDFHelmi HayaziNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Approach To Physics by DR TimothyDocument18 pagesLast Minute Approach To Physics by DR Timothyfavouramara188No ratings yet
- B-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiDocument3 pagesB-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiNhật Thanh TôNo ratings yet
- 2021hy3p - SolutionDocument2 pages2021hy3p - SolutionEndi WongNo ratings yet
- Heater Temperature Sensor Ti Nano-Disk Thermal Bridge: R V Rbe/MDocument2 pagesHeater Temperature Sensor Ti Nano-Disk Thermal Bridge: R V Rbe/MTest EmailNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2Document11 pagesTutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2JoserineNo ratings yet
- Me Acv 18 QPDocument30 pagesMe Acv 18 QPHarshit TejraNo ratings yet
- Quals 2012 Sec 1Document15 pagesQuals 2012 Sec 1puput123No ratings yet
- PHY1032S ClassTest3-2020Document2 pagesPHY1032S ClassTest3-2020lukhanyisojikela12No ratings yet
- 22.01 Fall 2015, Problem Set 7 (Normal Version) : 1 Conceptual/Analytical QuestionsDocument8 pages22.01 Fall 2015, Problem Set 7 (Normal Version) : 1 Conceptual/Analytical QuestionsDANIELA FORERO RAMÍREZNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1이동근No ratings yet
- Motion and Recombination of Electrons and HolesDocument24 pagesMotion and Recombination of Electrons and HolesFlor EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document27 pagesChapter 07Libyan KnightNo ratings yet
- Experimental Verification of Landauer's Principle Linking Information and ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesExperimental Verification of Landauer's Principle Linking Information and ThermodynamicsDavid Jiménez GarzónNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Equivalent of Heat: C T Constant T C C CDocument3 pagesThe Mechanical Equivalent of Heat: C T Constant T C C CSerajNo ratings yet
- We M5Document14 pagesWe M5knyogishNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 5 Sem Heat and Mass Transfer Rme502 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesBtech Me 5 Sem Heat and Mass Transfer Rme502 2020 PDFSuryaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsPandyaNo ratings yet
- 13.Heat Transfer and Thermal Expansion_vikas ProofreadDocument5 pages13.Heat Transfer and Thermal Expansion_vikas ProofreadShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document9 pagesPs 1Maulana ArifNo ratings yet
- Black BodyDocument36 pagesBlack BodyAamir AliNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-01 ME502 IntroductionDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet-01 ME502 IntroductionDebjyoti DeyNo ratings yet
- Phys 213 ExamDocument12 pagesPhys 213 ExamJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Heat TransferDocument7 pagesHomework 2 Heat TransferGonzalo Salfate MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS To Mock Exam June 2022 CSECDocument21 pagesSOLUTIONS To Mock Exam June 2022 CSECJayda JosephNo ratings yet
- EGF4053 Chapter 2Document35 pagesEGF4053 Chapter 2hanis izzatiNo ratings yet
- Class X Full Mock Physics Hari Sir 9064194423Document2 pagesClass X Full Mock Physics Hari Sir 9064194423physicshari.bwnNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Examination in Dynamics: p (t) =Asinω t) that inducesDocument35 pagesPreliminary Examination in Dynamics: p (t) =Asinω t) that inducesAS asNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Radiation in Class Exercises IIDocument2 pages3.1 Radiation in Class Exercises IIPabloNo ratings yet
- Radiation Practice QuestionDocument66 pagesRadiation Practice QuestionPranshu MahajanNo ratings yet
- February 14 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 375 Heat TransferDocument5 pagesFebruary 14 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 375 Heat TransferYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyNo ratings yet
- Comment On The SelfDocument2 pagesComment On The Selfrobert hookNo ratings yet
- IISc Internship ReportDocument16 pagesIISc Internship ReportvivishekNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics 2017Document28 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics 2017FrancisNo ratings yet
- Ii Pu Physics Answerkeys SRS Pu College PDFDocument11 pagesIi Pu Physics Answerkeys SRS Pu College PDFSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- 2 - Thermochemistry in FireDocument68 pages2 - Thermochemistry in FirepaulNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7roxy8marie8chanNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument115 pagesStructure of AtomHarshtej Singh MakkarNo ratings yet
- CHM092 Chapter 2 Atoms-Ions-PeriodicDocument240 pagesCHM092 Chapter 2 Atoms-Ions-PeriodicNUrLinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument21 pagesAtomic StructureShahriar ShafiNo ratings yet
- KF 3 PDFDocument27 pagesKF 3 PDFmifNo ratings yet
- 16 Atomic Structure SheetDocument43 pages16 Atomic Structure SheetVINOD JINo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Class 11spiral - 2020-21Document71 pagesChemistry - Class 11spiral - 2020-21NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Test # 10 - Atoms - Bottom of PyramidDocument4 pagesTest # 10 - Atoms - Bottom of PyramidGautam AryaNo ratings yet
- QB Topic 4 SHMDocument5 pagesQB Topic 4 SHMmarufinoNo ratings yet
- Cour Complet Et TD Mecanique Quantique Relativiste 2 BatnaDocument106 pagesCour Complet Et TD Mecanique Quantique Relativiste 2 BatnazeraouliaabdelhamidNo ratings yet
- CP3 Exam 1 Study Guide 20103Document7 pagesCP3 Exam 1 Study Guide 20103guitarguybs07100% (1)
- Atoms: Chapter TwelveDocument16 pagesAtoms: Chapter TwelveBhoomika VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 38 - Zeeman Effect and Electron SpinDocument17 pagesLecture 38 - Zeeman Effect and Electron SpinLesterNo ratings yet
- ISV SM Ch39Document58 pagesISV SM Ch39손은결No ratings yet
- 02 Atomic Structure-Solved Example-1Document24 pages02 Atomic Structure-Solved Example-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument7 pagesChemistry AssignmentYASH GOSAVINo ratings yet
- MSR Assignment PH6011 Feb 13Document2 pagesMSR Assignment PH6011 Feb 13Overloaded SenseNo ratings yet
- I WV5 A4 B4 Ark FADr 6 PJP JDocument43 pagesI WV5 A4 B4 Ark FADr 6 PJP Jaafiyaasad123No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry IIDocument22 pagesPhysical Chemistry IIJamaica FielNo ratings yet
- Vedantu Neet Ug Material Part 2Document41 pagesVedantu Neet Ug Material Part 2PrateekNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom DPP 6 SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesStructure of Atom DPP 6 SOLUTIONiitmohakNo ratings yet
- Bohr Sommerfeld ModelDocument10 pagesBohr Sommerfeld ModelKrishna Sai NNo ratings yet
- 3DSchrodinger Hydrogen PDFDocument9 pages3DSchrodinger Hydrogen PDFLdvdMiixNo ratings yet
- A Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumDocument3 pagesA Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- S3511PG - General Physics Assignment 3Document2 pagesS3511PG - General Physics Assignment 3Hambeleleleni NgotipeniNo ratings yet
- 16 - 1 - Part I Angular Momentum - Explicit SolutionsDocument4 pages16 - 1 - Part I Angular Momentum - Explicit SolutionsLeon DobrzinskyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Barton Zwiebach MITDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 Barton Zwiebach MITJhon FlorezNo ratings yet
- Virial TheoremDocument1 pageVirial Theoremgo9uNo ratings yet
- Phy 142 Practice Questions: AluminumDocument5 pagesPhy 142 Practice Questions: AluminumAbdulganeey Horlarmilekan MuheezNo ratings yet
- Ats 2 (Csir Net) PDFDocument17 pagesAts 2 (Csir Net) PDFAayushi VermaNo ratings yet
Draft Soal Ktof Agustus 2020
Draft Soal Ktof Agustus 2020
Uploaded by
Yogesh KhatriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Draft Soal Ktof Agustus 2020
Draft Soal Ktof Agustus 2020
Uploaded by
Yogesh KhatriCopyright:
Available Formats
Machine Translated by Google
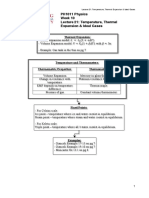
QUESTION
Physics Olympiad Open Contest
August 2020
Machine Translated by Google
PHYSICS OLYMPIC OPEN CONTEST
Friday, 21 August 2020
Processing time: 72 hours
1. Needle
An igloo or igloo is a house or temporary residence, dome-shaped and built
from blocks of snow. Although igloos are synonymous with Inuit dwellings, there are many igloos
built by Canadians living in the Central Arctic and the Thule region of Greenland. Snow is suitable
used as an insulator (insulating material) from cold weather. The room temperature inside the igloo is way off
warmer, and allows humans to live even though the outside temperature can reach -46 °C.
In this problem we will review the thermal properties of igloo ice walls as insulators.
Consider a hemispherical igloo whose walls are made of solid snow with radii.
inner radius = 2 and outer radius = 2.5 . Thermal conductivity of dense snow =
0.25 ÿ1 ÿ1 ÿ1 .
In polar coordinates, the rate of heat flowing per unit area or also called
The heat flux can be expressed as:
= ÿmr
Where is the thermal conductivity of the material, is the temperature, and is the distance to the center
coordinate. The negative sign indicates that heat flows from high temperature to low temperature.
Assume atmospheric pressure is the same as at sea level, 1.01 × 105 , homogeneous environmental temperature
and there is no wind. The air is dry and there is not much water vapor.
a. When it is known that the temperature difference inside the igloo and outside is ÿ = 40 ° (temperature
in the igloo is higher than the ambient temperature), determine the total calories wasted to
environment per unit time. Assume the internal wall temperature is below 0° .
b. This temperature difference is maintained by a petromax lamp that emits light
homogeneous in all directions. Assume that the rays that hit the ground are completely absorbed. When wide
2
axis surface 7 , and the emissivity of the flame in a perfect petromax lamp, determine the temperature
the axis! The petromax lamp is located in the center of the igloo.
Now the flame of the lamp is enlarged, so that its power is doubled.
Assume the ambient temperature outside the igloo is ÿ30° .
c. In this case, the inner walls of the igloo will melt. Determine the radius of the new igloo when the wall
inside no longer melts. Assume that the melted water immediately condenses again at the bottom of the igloo,
so that it does not form a layer of water vapor on the inner wall surface.
d. What is the rate of increase when the initial lamp is replaced? Use the heat of melting ice =
334000 ÿ1 3
, dense snow density 900 / .
Indonesian Physics Olympiad Community Page 1 of 4
Machine Translated by Google
PHYSICS OLYMPIC OPEN CONTEST
Friday, 21 August 2020
Processing time: 72 hours
2. Cube in a Foggy Room
Two cubes of identical mass and side are moving in a foggy room. Fog
In the room it has a homogeneous density and the constituent particles do not interact
one another. Both boxes move in the same direction and initial speed 0. Cube 1 is wrong
one side is directly facing the direction of motion, while cube 2 is like cube 1 but rotated by
450 (the system is illustrated in the figure to the side). Calculate the ratio of the speed of cube 1 to
cube 2 after both have moved for unit time! Collisions between fog particles and
The cube is perfectly elastic.
3. Memristor
In general, the electrical circuit components that are often encountered are resistors, capacitors,
and inductor. However, in 1971, Leon Chua proposed a new circuit component
which, he argued, completes the family of electrical circuit components. these components
called memristor, short for memory resistor. Memristors are components of electrical circuits
which can store a magnetic field flux ÿ (similar to an inductor) if a charge difference is applied
(similar to a capacitor) on both legs of the memristor. Memristancy (symbolized by )
defined via the equation ÿ = , where ÿ is the change in magnetic field flux
which occurs if the charge on the memristor leg changes by . In this question, we will review
one type of memristor, proposed by Strukov et al. (2008).
The memristor that will be used in this problem has memristance as a charge function
electricity in both legs as follows
( ) = [1 ÿ ( )]
where ( ) is the electric charge stored in the memristor leg, and
=
2 (1 ÿ )
Mathematically, a memristor is equivalent to a non-constant resistor, so
the following relationship applies
()=()()
where ( ) and ( ) respectively are the voltage and current on this memristor. Note that
The unit of memristance is Ohm, the same as the unit of resistor.
a. Consider a memristor connected to an AC current source with a current ( ) =
0 sin . There are no other components except the memristor and AC current source. If the initial conditions
is = 0 when = 0, determine the voltage across the memristor as a function of time.
b. Define parameter = 0 ÿ . Prove that in this case, the voltage ( ) as
The current function ( ) on the memristor can be written as
Indonesian Physics Olympiad Community Page 2 of 4
Machine Translated by Google
PHYSICS OLYMPIC OPEN CONTEST
Friday, 21 August 2020
Processing time: 72 hours
()=
0
)
[1 ÿ ± ÿ1 ÿ ( 2]
c. Now, change the AC current source to an AC voltage source with voltage ( ) =
0
sin . If the initial condition is = 0 when = 0, determine the current in the memristor as
time function. Use the = parameter 0 ÿ if needed.
d. Based on the results in sub-problem c), determine the relationship between current as a function of voltage
( ) on the memristor. Also determine the relationship that must be satisfied by the function ( )
can always be well defined.
4. Electrons and Protons
In a negatively charged hydrogen atom, there is a proton in the middle.
middle surrounded by two electrons in the first outer shell. In quantum mechanics
It is stated that electrons have a constant amount of angular momentum in the same shell.
For example, in this problem, the angular momentum in the first shell is , the atomic radius is , pasta
electrons are , and the mass of the proton is . Determine the angular velocities of all modes
Electron oscillations when given a very small deviation in the radial direction! (Assume that electrons
always in front of other electrons because the oscillation deviation is very small.
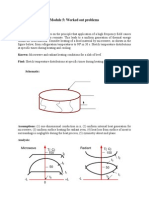
5. Pendulum Oscillations in a Rotating Frame
Consider a system as shown in the figure. Assume the entire mass of the pendulum is centered at
end of the pendulum load with total mass and the length of the pendulum is . Moment of inertia
the pendulum about the axis of rotation is . The pendulum is attached to a spring with constant and
natural length. The wheel on which the pendulum-spring system is attached is connected to the regulator
the speed of the axle through its center of mass so that the wheel can rotate without friction
purely without translation. The radius of the wheel is where > and ignore the mass of the wheel. On
each part of the question, the regulator is moved in such a way that the system is in a state
steady-state ( = constant) and the rope remains tense as long as the condition lasts. At steady state-
the angular state between the pendulum and the spring is . The plane of movement of the system is vertical (Terrain
2
gravity pointing vertically downwards). Use coordinates as in the picture and for
To make the work easier, please use a frame that rotates with the wheels because of the coordinates
which is used to move with the wheel.
a. Determine ÿ so that the system is in dynamic equilibrium, then explain it positionally
this equilibrium! (State in , , , , , )
b. Define the terms so that this equilibrium position can occur! (State in
, , , , )
Indonesian Physics Olympiad Community Page 3 of 4
Machine Translated by Google
PHYSICS OLYMPIC OPEN CONTEST
Friday, 21 August 2020
Processing time: 72 hours
c. From equilibrium, the pendulum is deflected radially (Remember that the angle ÿ is the position
pendulum to the vertical line according to the wheel frame which is non-inertial and angular as well
seen in a non-inertial frame rotating with the wheels).
i. Determine the frequency of oscillation of the pendulum for small deviations (Express in , , , , ,
and ÿ)
ii. Under what conditions can the angular frequency of oscillations be achieved? This condition has consequences
on the one you got before, what was it?
System Image
Indonesian Physics Olympiad Community Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Heat TransferDocument21 pagesHeat TransferSuzanne Sarsuelo100% (3)
- Mp3003tut07 08sem1Document18 pagesMp3003tut07 08sem1Feeling_so_flyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ia Voltaic Cells Year 11Document12 pagesChemistry Ia Voltaic Cells Year 11Jaemin KimNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Physics - Version 2Document12 pagesIIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Physics - Version 2Sumit SahaNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 Test 4Document4 pagesPhase 2 Test 4Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Physics Model QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhysics Model QuestionsQuantum HeatNo ratings yet
- Section 6 - General Physics 2 With SolutionsDocument15 pagesSection 6 - General Physics 2 With SolutionspaimoNo ratings yet
- Heat Equation Analysis of Defrosting A Roll of Frozen Ground BeefDocument3 pagesHeat Equation Analysis of Defrosting A Roll of Frozen Ground BeefJuan José Leiva AlegreNo ratings yet
- Jee 2020 JanDocument13 pagesJee 2020 Jankruthika karraNo ratings yet
- Physics Model QuestionsDocument23 pagesPhysics Model QuestionsQuantum HeatNo ratings yet
- MIT3 044S13 Pset1Document5 pagesMIT3 044S13 Pset1Dak KaizNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document29 pagesLecture 08kamran bhatNo ratings yet
- Physics TempDocument8 pagesPhysics TemprenNo ratings yet
- Problems 2017Document2 pagesProblems 2017Adith SaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Transient Heat Conduction & Heisler ChartDocument40 pagesLecture 5 - Transient Heat Conduction & Heisler ChartMonkey D. LuffyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 PDFDocument11 pagesTutorial 4 PDFHelmi HayaziNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Approach To Physics by DR TimothyDocument18 pagesLast Minute Approach To Physics by DR Timothyfavouramara188No ratings yet
- B-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiDocument3 pagesB-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiNhật Thanh TôNo ratings yet
- 2021hy3p - SolutionDocument2 pages2021hy3p - SolutionEndi WongNo ratings yet
- Heater Temperature Sensor Ti Nano-Disk Thermal Bridge: R V Rbe/MDocument2 pagesHeater Temperature Sensor Ti Nano-Disk Thermal Bridge: R V Rbe/MTest EmailNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2Document11 pagesTutorial 2 - Statistical Thermodynamics 2JoserineNo ratings yet
- Me Acv 18 QPDocument30 pagesMe Acv 18 QPHarshit TejraNo ratings yet
- Quals 2012 Sec 1Document15 pagesQuals 2012 Sec 1puput123No ratings yet
- PHY1032S ClassTest3-2020Document2 pagesPHY1032S ClassTest3-2020lukhanyisojikela12No ratings yet
- 22.01 Fall 2015, Problem Set 7 (Normal Version) : 1 Conceptual/Analytical QuestionsDocument8 pages22.01 Fall 2015, Problem Set 7 (Normal Version) : 1 Conceptual/Analytical QuestionsDANIELA FORERO RAMÍREZNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1이동근No ratings yet
- Motion and Recombination of Electrons and HolesDocument24 pagesMotion and Recombination of Electrons and HolesFlor EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document27 pagesChapter 07Libyan KnightNo ratings yet
- Experimental Verification of Landauer's Principle Linking Information and ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesExperimental Verification of Landauer's Principle Linking Information and ThermodynamicsDavid Jiménez GarzónNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Equivalent of Heat: C T Constant T C C CDocument3 pagesThe Mechanical Equivalent of Heat: C T Constant T C C CSerajNo ratings yet
- We M5Document14 pagesWe M5knyogishNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 5 Sem Heat and Mass Transfer Rme502 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesBtech Me 5 Sem Heat and Mass Transfer Rme502 2020 PDFSuryaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsPandyaNo ratings yet
- 13.Heat Transfer and Thermal Expansion_vikas ProofreadDocument5 pages13.Heat Transfer and Thermal Expansion_vikas ProofreadShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document9 pagesPs 1Maulana ArifNo ratings yet
- Black BodyDocument36 pagesBlack BodyAamir AliNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-01 ME502 IntroductionDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet-01 ME502 IntroductionDebjyoti DeyNo ratings yet
- Phys 213 ExamDocument12 pagesPhys 213 ExamJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Heat TransferDocument7 pagesHomework 2 Heat TransferGonzalo Salfate MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS To Mock Exam June 2022 CSECDocument21 pagesSOLUTIONS To Mock Exam June 2022 CSECJayda JosephNo ratings yet
- EGF4053 Chapter 2Document35 pagesEGF4053 Chapter 2hanis izzatiNo ratings yet
- Class X Full Mock Physics Hari Sir 9064194423Document2 pagesClass X Full Mock Physics Hari Sir 9064194423physicshari.bwnNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Examination in Dynamics: p (t) =Asinω t) that inducesDocument35 pagesPreliminary Examination in Dynamics: p (t) =Asinω t) that inducesAS asNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Radiation in Class Exercises IIDocument2 pages3.1 Radiation in Class Exercises IIPabloNo ratings yet
- Radiation Practice QuestionDocument66 pagesRadiation Practice QuestionPranshu MahajanNo ratings yet
- February 14 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 375 Heat TransferDocument5 pagesFebruary 14 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 375 Heat TransferYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyNo ratings yet
- Comment On The SelfDocument2 pagesComment On The Selfrobert hookNo ratings yet
- IISc Internship ReportDocument16 pagesIISc Internship ReportvivishekNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics 2017Document28 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics 2017FrancisNo ratings yet
- Ii Pu Physics Answerkeys SRS Pu College PDFDocument11 pagesIi Pu Physics Answerkeys SRS Pu College PDFSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- 2 - Thermochemistry in FireDocument68 pages2 - Thermochemistry in FirepaulNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7roxy8marie8chanNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument115 pagesStructure of AtomHarshtej Singh MakkarNo ratings yet
- CHM092 Chapter 2 Atoms-Ions-PeriodicDocument240 pagesCHM092 Chapter 2 Atoms-Ions-PeriodicNUrLinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument21 pagesAtomic StructureShahriar ShafiNo ratings yet
- KF 3 PDFDocument27 pagesKF 3 PDFmifNo ratings yet
- 16 Atomic Structure SheetDocument43 pages16 Atomic Structure SheetVINOD JINo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Class 11spiral - 2020-21Document71 pagesChemistry - Class 11spiral - 2020-21NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Test # 10 - Atoms - Bottom of PyramidDocument4 pagesTest # 10 - Atoms - Bottom of PyramidGautam AryaNo ratings yet
- QB Topic 4 SHMDocument5 pagesQB Topic 4 SHMmarufinoNo ratings yet
- Cour Complet Et TD Mecanique Quantique Relativiste 2 BatnaDocument106 pagesCour Complet Et TD Mecanique Quantique Relativiste 2 BatnazeraouliaabdelhamidNo ratings yet
- CP3 Exam 1 Study Guide 20103Document7 pagesCP3 Exam 1 Study Guide 20103guitarguybs07100% (1)
- Atoms: Chapter TwelveDocument16 pagesAtoms: Chapter TwelveBhoomika VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 38 - Zeeman Effect and Electron SpinDocument17 pagesLecture 38 - Zeeman Effect and Electron SpinLesterNo ratings yet
- ISV SM Ch39Document58 pagesISV SM Ch39손은결No ratings yet
- 02 Atomic Structure-Solved Example-1Document24 pages02 Atomic Structure-Solved Example-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument7 pagesChemistry AssignmentYASH GOSAVINo ratings yet
- MSR Assignment PH6011 Feb 13Document2 pagesMSR Assignment PH6011 Feb 13Overloaded SenseNo ratings yet
- I WV5 A4 B4 Ark FADr 6 PJP JDocument43 pagesI WV5 A4 B4 Ark FADr 6 PJP Jaafiyaasad123No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry IIDocument22 pagesPhysical Chemistry IIJamaica FielNo ratings yet
- Vedantu Neet Ug Material Part 2Document41 pagesVedantu Neet Ug Material Part 2PrateekNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom DPP 6 SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesStructure of Atom DPP 6 SOLUTIONiitmohakNo ratings yet
- Bohr Sommerfeld ModelDocument10 pagesBohr Sommerfeld ModelKrishna Sai NNo ratings yet
- 3DSchrodinger Hydrogen PDFDocument9 pages3DSchrodinger Hydrogen PDFLdvdMiixNo ratings yet
- A Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumDocument3 pagesA Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- S3511PG - General Physics Assignment 3Document2 pagesS3511PG - General Physics Assignment 3Hambeleleleni NgotipeniNo ratings yet
- 16 - 1 - Part I Angular Momentum - Explicit SolutionsDocument4 pages16 - 1 - Part I Angular Momentum - Explicit SolutionsLeon DobrzinskyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Barton Zwiebach MITDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 Barton Zwiebach MITJhon FlorezNo ratings yet
- Virial TheoremDocument1 pageVirial Theoremgo9uNo ratings yet
- Phy 142 Practice Questions: AluminumDocument5 pagesPhy 142 Practice Questions: AluminumAbdulganeey Horlarmilekan MuheezNo ratings yet
- Ats 2 (Csir Net) PDFDocument17 pagesAts 2 (Csir Net) PDFAayushi VermaNo ratings yet