Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KOM Definition
KOM Definition
Uploaded by
capicaspCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Smart Plant Monitoring SystemDocument31 pagesSmart Plant Monitoring SystemTejeshwini100% (1)
- Kinematics of MechanicsDocument34 pagesKinematics of MechanicsErasmo Israel Garcia Ochoa100% (1)
- Unit 1Document44 pagesUnit 1Prabal SinghNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery NotesDocument25 pagesKinematics of Machinery Notesnishanth87No ratings yet
- SSC-Theory of MachineDocument75 pagesSSC-Theory of MachineSteph Dela MujerNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument33 pagesUnit IThe sky BlueNo ratings yet
- Note 1440423033Document17 pagesNote 1440423033Siva GaneshNo ratings yet
- Pimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismDocument43 pagesPimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismNarendra ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I TomDocument37 pagesUnit-I TomBandi KumarreddyNo ratings yet
- Kom NotesDocument15 pagesKom NoteselangandhiNo ratings yet
- Theory of MechanismsDocument51 pagesTheory of Mechanismsduraiprakash83No ratings yet
- Theory of MachineDocument21 pagesTheory of MachineVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine-1 - PPTDocument224 pagesTheory of Machine-1 - PPTHabib A BtooshNo ratings yet
- Me6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulDocument64 pagesMe6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulkjsdjsdaNo ratings yet
- KOM 2 Marks - Edition 3Document24 pagesKOM 2 Marks - Edition 3rajeshNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument10 pagesAssignmentABDULREHMAN RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Introduction To KinematicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Kinematicsdhilip_sacetNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Using Crank and Slotted Link MechanismDocument3 pagesAir Compressor Using Crank and Slotted Link MechanismPatel NikhilNo ratings yet
- Asif Rahaman TOMDocument10 pagesAsif Rahaman TOMAsif RahamanNo ratings yet
- Inversion of MechanismDocument38 pagesInversion of MechanismMudit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basics of Mechanisms: 1. What Is Kinematics?Document18 pagesUnit 1 - Basics of Mechanisms: 1. What Is Kinematics?VENKATESHNo ratings yet
- Kom Notes555Document9 pagesKom Notes555Nagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Basics of MechanismsNagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- Question and AnswerDocument12 pagesQuestion and AnswerDeni -No ratings yet
- Question 1 OLDocument12 pagesQuestion 1 OLDeni -No ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument23 pagesHeat Exchangertekitech443No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Week One Kinematics of Mechanism 1Document10 pagesLecture Notes For Week One Kinematics of Mechanism 1John KimaniNo ratings yet
- Mmodule-1 INTRODUCTION To Kinematics of MachineDocument85 pagesMmodule-1 INTRODUCTION To Kinematics of MachineVinayak VernekarNo ratings yet
- KOM Unit-1 PDFDocument18 pagesKOM Unit-1 PDFpuneethNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument64 pagesKinematics of MachineryStar SathishNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFDocument40 pagesUNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFAravind MuddebihalNo ratings yet
- 機動學CH1 Basic ConceptsDocument98 pages機動學CH1 Basic Concepts王祥任No ratings yet
- Mechanism 69869Document28 pagesMechanism 69869Abi DemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theory of Machines: June 2015Document9 pagesIntroduction To Theory of Machines: June 2015ADIPESHNo ratings yet
- Mechaism 1Document47 pagesMechaism 1Tsegaye AbayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingDocument40 pagesCHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingdanielNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Using Crank and Slotted MechanismDocument2 pagesAir Compressor Using Crank and Slotted MechanismbalaNo ratings yet
- 20 - 1-Linkage MechanismDocument6 pages20 - 1-Linkage MechanismNishant DeyNo ratings yet
- Aim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryDocument6 pagesAim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryAvinash RNo ratings yet
- Tom Two Mark QuestionDocument23 pagesTom Two Mark QuestionTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- I Unit NotesDocument40 pagesI Unit NotesThirumalai RNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 MerchDocument66 pagesLecture 3 MerchMuhammad Amir TajNo ratings yet
- Simple MechanismDocument15 pagesSimple MechanismPrabal SinghNo ratings yet
- introductionto-theoryof-machinesDocument10 pagesintroductionto-theoryof-machinesashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- Machine Dynamics - I Lecture Note: (Assist. Prof. Mechanical Engineering Department, VSSUT, Burla, Orissa, India)Document70 pagesMachine Dynamics - I Lecture Note: (Assist. Prof. Mechanical Engineering Department, VSSUT, Burla, Orissa, India)phb1986No ratings yet
- Theory of Machine ReportDocument10 pagesTheory of Machine ReportABDULREHMAN RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument64 pagesKinematics of MachineryarulmuruganNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument8 pagesMechanismsJai BhavaniNo ratings yet
- Eme 305-1-1Document114 pagesEme 305-1-1DanielNo ratings yet
- Tomdwdwdqwed RVGRVVDocument14 pagesTomdwdwdqwed RVGRVVBijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Simple MechanismDocument18 pagesSimple MechanismRufi RizwanNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Notes - Kinematics of MachineryDocument65 pagesLecturer Notes - Kinematics of Machineryehsan_shameli100% (1)
- INVERSIONS of MECHANISMSDocument39 pagesINVERSIONS of MECHANISMSDibakar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Full Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?From EverandFull Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?No ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- STM29 - Lower Half Martinito, John Patrick Eldwin Recto, Jan Ralph Yanga, Nicole Francine BDocument2 pagesSTM29 - Lower Half Martinito, John Patrick Eldwin Recto, Jan Ralph Yanga, Nicole Francine BJan Ralph RectoNo ratings yet
- English MONTHDocument6 pagesEnglish MONTHSoliman Micaela M.No ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Social SciencesDocument18 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Social SciencesArjane Grace SullanoNo ratings yet
- Calbayog City Athletic Association (CCAA)Document14 pagesCalbayog City Athletic Association (CCAA)LindsayNo ratings yet
- Measurement Sheet For Installetion of Utility BridgeDocument3 pagesMeasurement Sheet For Installetion of Utility BridgeNewaz KabirNo ratings yet
- Idioms CSS by PreparationPointDocument20 pagesIdioms CSS by PreparationPointBilal AliNo ratings yet
- HALSEY - Bad at Love (Ver. 2) Guitar Chords - Guitar Chords ExplorerDocument5 pagesHALSEY - Bad at Love (Ver. 2) Guitar Chords - Guitar Chords ExplorerManuNo ratings yet
- L1 Random Variables and Probability Distribution PDFDocument7 pagesL1 Random Variables and Probability Distribution PDFVicky C. GaleraNo ratings yet
- Sleep: Are You A Lark or An Owl?Document3 pagesSleep: Are You A Lark or An Owl?ხათუნა ტრაპაიძეNo ratings yet
- Model: AGB2518ZKZ (TAG2522Z) : Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageModel: AGB2518ZKZ (TAG2522Z) : Technical Data SheetZikko Firmansyah100% (2)
- Apple Airpods Max Complete Features Instructions ManualDocument7 pagesApple Airpods Max Complete Features Instructions ManualIlaria iudiceNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Teaching PDFDocument6 pagesCoordination Compounds Teaching PDFNeel PatelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Software PDFDocument12 pagesElectrical Engineering Software PDFAkd Deshmukh50% (2)
- Amphibians: Class AmphibiaDocument33 pagesAmphibians: Class Amphibiaisfi farihaNo ratings yet
- Social Anxiety DisorderDocument12 pagesSocial Anxiety DisorderhafiznaveedNo ratings yet
- MA1101R Chapter1Document54 pagesMA1101R Chapter1le trung hieuNo ratings yet
- I Cannot Live With You PoemsDocument4 pagesI Cannot Live With You PoemsDaeng ArifNo ratings yet
- Computer System ServicingDocument11 pagesComputer System ServicingArman Santiago100% (1)
- Damodar Leela Kath ADocument35 pagesDamodar Leela Kath Aanshumanbiswal2319No ratings yet
- Data Book de BombaDocument7 pagesData Book de BombaSharon Botiny100% (1)
- Vegan Mayonnaise - Simple Vegan Blog PDFDocument2 pagesVegan Mayonnaise - Simple Vegan Blog PDFjkoiluNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Road: By: Rivas, Ghail F. Bsce 5-B To: Arch. Marlon C. Solloso InstructorDocument14 pagesKinetic Road: By: Rivas, Ghail F. Bsce 5-B To: Arch. Marlon C. Solloso InstructorGhail Rivas Gha ILNo ratings yet
- Iso 1328-Agma - Parte 1Document35 pagesIso 1328-Agma - Parte 1bernaldoarnaoNo ratings yet
- OLine FRP Cable Ladder - TrayDocument5 pagesOLine FRP Cable Ladder - TrayTeknik produksi wikonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, The World, From AbhidharmakosabhasyamDocument202 pagesChapter 3, The World, From Abhidharmakosabhasyamoceanic23No ratings yet
- Low-Loss Power Splitters - Multi-Band 800 - 2500 MHZ 860 10017, 860 10018, 860 10019Document1 pageLow-Loss Power Splitters - Multi-Band 800 - 2500 MHZ 860 10017, 860 10018, 860 10019Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Curly Arrow Worksheet Homework 39495Document2 pagesCurly Arrow Worksheet Homework 39495Edward FrazerNo ratings yet
- M400 M600 M800 M880 Manual A5Document101 pagesM400 M600 M800 M880 Manual A5Hoff ZhangNo ratings yet
- Degremont WTP MBRDocument29 pagesDegremont WTP MBRCHIN FelleNo ratings yet
KOM Definition
KOM Definition
Uploaded by
capicaspCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KOM Definition
KOM Definition
Uploaded by
capicaspCopyright:
Available Formats
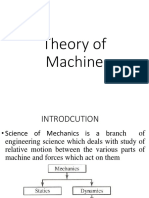
Definition : Each part of a machine which has relative motion to some other part of the machine is
known as kinematic link or an element.
Definition : A machine is an assemblage of a links or mechanisms which are used to transmit both the
required motion and forces.
Definition : Structure is an assemblage of resistant bodies without any relative motion between the
links.
Definition : When two kinematic links are connected in such a way that their motion is either completely
or successfully constrained, these two links are said to form a kinematic pair.
Definition : Kinematic chain is defined as the combination of kinematic pairs in which each link forms a
part of two kinematic pairs and the relative motion between the links is either completely constrained
or successfully constrained.
Definition of Mechanism : A “mechanism” is a kinematic chain with any one link fixed which is used to
transmit the required motion.
Definition : It should be noted that in case the different links of a kinematic chain are fixed, the result is
a different mechanism. Such mechanisms obtained are called inversion of a mechanism. These will be
discussed in subsequent section.
Definition : The behaviour and appearance of such mechanism are different. Each mechanism thus
obtained is called an inversion of kinematic chain.
Grashof’s law states that for a planer four bar chain mechanism, the sum of the length of shortest and
longest links should not be greater than the sum of the remaining two link lengths if there is to be a
continuous relative rotation between two links.
Definition : When two links which are equal in lengths are adjacent to each other then mechanism is
called as deltoid four bar linkage.
If we apply the kutzbach criterion to planer mechanism, then Equation (1.15.1) will be modified and that
modified equation is known as Grubler’s Criterion for planer mechanism
Definition : The component of acceleration in the direction of vector in the direction parallel to link OP
and its direction towards the centre of rotation O is called centripetal acceleration.
Definition : The sum of the relative position vectors for the links forming a closed loop in the given
mechanism is always zero. This is called as loop closure equation.
A Hooke’s joint, commonly known as Universal coupling, is used to connect two non-parallel and
intersecting shafts. It is also used for transmission of motion and power four shafts with angular
misalignment where flexible coupling does not serve the purpose.
Definition : The diagram showing the variation of speed of driven shaft 2 with respect to driven shaft is
called polar diagram
Definition : Degree of freedom (DOF) of a point is the number of independent coordinates required to
define the position and orientation of a point.
You might also like
- Smart Plant Monitoring SystemDocument31 pagesSmart Plant Monitoring SystemTejeshwini100% (1)
- Kinematics of MechanicsDocument34 pagesKinematics of MechanicsErasmo Israel Garcia Ochoa100% (1)
- Unit 1Document44 pagesUnit 1Prabal SinghNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery NotesDocument25 pagesKinematics of Machinery Notesnishanth87No ratings yet
- SSC-Theory of MachineDocument75 pagesSSC-Theory of MachineSteph Dela MujerNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument33 pagesUnit IThe sky BlueNo ratings yet
- Note 1440423033Document17 pagesNote 1440423033Siva GaneshNo ratings yet
- Pimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismDocument43 pagesPimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismNarendra ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I TomDocument37 pagesUnit-I TomBandi KumarreddyNo ratings yet
- Kom NotesDocument15 pagesKom NoteselangandhiNo ratings yet
- Theory of MechanismsDocument51 pagesTheory of Mechanismsduraiprakash83No ratings yet
- Theory of MachineDocument21 pagesTheory of MachineVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine-1 - PPTDocument224 pagesTheory of Machine-1 - PPTHabib A BtooshNo ratings yet
- Me6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulDocument64 pagesMe6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulkjsdjsdaNo ratings yet
- KOM 2 Marks - Edition 3Document24 pagesKOM 2 Marks - Edition 3rajeshNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument10 pagesAssignmentABDULREHMAN RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Introduction To KinematicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Kinematicsdhilip_sacetNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Using Crank and Slotted Link MechanismDocument3 pagesAir Compressor Using Crank and Slotted Link MechanismPatel NikhilNo ratings yet
- Asif Rahaman TOMDocument10 pagesAsif Rahaman TOMAsif RahamanNo ratings yet
- Inversion of MechanismDocument38 pagesInversion of MechanismMudit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basics of Mechanisms: 1. What Is Kinematics?Document18 pagesUnit 1 - Basics of Mechanisms: 1. What Is Kinematics?VENKATESHNo ratings yet
- Kom Notes555Document9 pagesKom Notes555Nagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Basics of MechanismsNagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- Question and AnswerDocument12 pagesQuestion and AnswerDeni -No ratings yet
- Question 1 OLDocument12 pagesQuestion 1 OLDeni -No ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument23 pagesHeat Exchangertekitech443No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Week One Kinematics of Mechanism 1Document10 pagesLecture Notes For Week One Kinematics of Mechanism 1John KimaniNo ratings yet
- Mmodule-1 INTRODUCTION To Kinematics of MachineDocument85 pagesMmodule-1 INTRODUCTION To Kinematics of MachineVinayak VernekarNo ratings yet
- KOM Unit-1 PDFDocument18 pagesKOM Unit-1 PDFpuneethNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument64 pagesKinematics of MachineryStar SathishNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFDocument40 pagesUNIT 1. Introduction To KOM PDFAravind MuddebihalNo ratings yet
- 機動學CH1 Basic ConceptsDocument98 pages機動學CH1 Basic Concepts王祥任No ratings yet
- Mechanism 69869Document28 pagesMechanism 69869Abi DemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theory of Machines: June 2015Document9 pagesIntroduction To Theory of Machines: June 2015ADIPESHNo ratings yet
- Mechaism 1Document47 pagesMechaism 1Tsegaye AbayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingDocument40 pagesCHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingdanielNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Using Crank and Slotted MechanismDocument2 pagesAir Compressor Using Crank and Slotted MechanismbalaNo ratings yet
- 20 - 1-Linkage MechanismDocument6 pages20 - 1-Linkage MechanismNishant DeyNo ratings yet
- Aim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryDocument6 pagesAim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryAvinash RNo ratings yet
- Tom Two Mark QuestionDocument23 pagesTom Two Mark QuestionTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- I Unit NotesDocument40 pagesI Unit NotesThirumalai RNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 MerchDocument66 pagesLecture 3 MerchMuhammad Amir TajNo ratings yet
- Simple MechanismDocument15 pagesSimple MechanismPrabal SinghNo ratings yet
- introductionto-theoryof-machinesDocument10 pagesintroductionto-theoryof-machinesashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- Machine Dynamics - I Lecture Note: (Assist. Prof. Mechanical Engineering Department, VSSUT, Burla, Orissa, India)Document70 pagesMachine Dynamics - I Lecture Note: (Assist. Prof. Mechanical Engineering Department, VSSUT, Burla, Orissa, India)phb1986No ratings yet
- Theory of Machine ReportDocument10 pagesTheory of Machine ReportABDULREHMAN RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument64 pagesKinematics of MachineryarulmuruganNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument8 pagesMechanismsJai BhavaniNo ratings yet
- Eme 305-1-1Document114 pagesEme 305-1-1DanielNo ratings yet
- Tomdwdwdqwed RVGRVVDocument14 pagesTomdwdwdqwed RVGRVVBijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Simple MechanismDocument18 pagesSimple MechanismRufi RizwanNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Notes - Kinematics of MachineryDocument65 pagesLecturer Notes - Kinematics of Machineryehsan_shameli100% (1)
- INVERSIONS of MECHANISMSDocument39 pagesINVERSIONS of MECHANISMSDibakar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Full Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?From EverandFull Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?No ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- STM29 - Lower Half Martinito, John Patrick Eldwin Recto, Jan Ralph Yanga, Nicole Francine BDocument2 pagesSTM29 - Lower Half Martinito, John Patrick Eldwin Recto, Jan Ralph Yanga, Nicole Francine BJan Ralph RectoNo ratings yet
- English MONTHDocument6 pagesEnglish MONTHSoliman Micaela M.No ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Social SciencesDocument18 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Social SciencesArjane Grace SullanoNo ratings yet
- Calbayog City Athletic Association (CCAA)Document14 pagesCalbayog City Athletic Association (CCAA)LindsayNo ratings yet
- Measurement Sheet For Installetion of Utility BridgeDocument3 pagesMeasurement Sheet For Installetion of Utility BridgeNewaz KabirNo ratings yet
- Idioms CSS by PreparationPointDocument20 pagesIdioms CSS by PreparationPointBilal AliNo ratings yet
- HALSEY - Bad at Love (Ver. 2) Guitar Chords - Guitar Chords ExplorerDocument5 pagesHALSEY - Bad at Love (Ver. 2) Guitar Chords - Guitar Chords ExplorerManuNo ratings yet
- L1 Random Variables and Probability Distribution PDFDocument7 pagesL1 Random Variables and Probability Distribution PDFVicky C. GaleraNo ratings yet
- Sleep: Are You A Lark or An Owl?Document3 pagesSleep: Are You A Lark or An Owl?ხათუნა ტრაპაიძეNo ratings yet
- Model: AGB2518ZKZ (TAG2522Z) : Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageModel: AGB2518ZKZ (TAG2522Z) : Technical Data SheetZikko Firmansyah100% (2)
- Apple Airpods Max Complete Features Instructions ManualDocument7 pagesApple Airpods Max Complete Features Instructions ManualIlaria iudiceNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds Teaching PDFDocument6 pagesCoordination Compounds Teaching PDFNeel PatelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Software PDFDocument12 pagesElectrical Engineering Software PDFAkd Deshmukh50% (2)
- Amphibians: Class AmphibiaDocument33 pagesAmphibians: Class Amphibiaisfi farihaNo ratings yet
- Social Anxiety DisorderDocument12 pagesSocial Anxiety DisorderhafiznaveedNo ratings yet
- MA1101R Chapter1Document54 pagesMA1101R Chapter1le trung hieuNo ratings yet
- I Cannot Live With You PoemsDocument4 pagesI Cannot Live With You PoemsDaeng ArifNo ratings yet
- Computer System ServicingDocument11 pagesComputer System ServicingArman Santiago100% (1)
- Damodar Leela Kath ADocument35 pagesDamodar Leela Kath Aanshumanbiswal2319No ratings yet
- Data Book de BombaDocument7 pagesData Book de BombaSharon Botiny100% (1)
- Vegan Mayonnaise - Simple Vegan Blog PDFDocument2 pagesVegan Mayonnaise - Simple Vegan Blog PDFjkoiluNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Road: By: Rivas, Ghail F. Bsce 5-B To: Arch. Marlon C. Solloso InstructorDocument14 pagesKinetic Road: By: Rivas, Ghail F. Bsce 5-B To: Arch. Marlon C. Solloso InstructorGhail Rivas Gha ILNo ratings yet
- Iso 1328-Agma - Parte 1Document35 pagesIso 1328-Agma - Parte 1bernaldoarnaoNo ratings yet
- OLine FRP Cable Ladder - TrayDocument5 pagesOLine FRP Cable Ladder - TrayTeknik produksi wikonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, The World, From AbhidharmakosabhasyamDocument202 pagesChapter 3, The World, From Abhidharmakosabhasyamoceanic23No ratings yet
- Low-Loss Power Splitters - Multi-Band 800 - 2500 MHZ 860 10017, 860 10018, 860 10019Document1 pageLow-Loss Power Splitters - Multi-Band 800 - 2500 MHZ 860 10017, 860 10018, 860 10019Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Curly Arrow Worksheet Homework 39495Document2 pagesCurly Arrow Worksheet Homework 39495Edward FrazerNo ratings yet
- M400 M600 M800 M880 Manual A5Document101 pagesM400 M600 M800 M880 Manual A5Hoff ZhangNo ratings yet
- Degremont WTP MBRDocument29 pagesDegremont WTP MBRCHIN FelleNo ratings yet