Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Tooth Anatomy and Function
Human Tooth Anatomy and Function
Uploaded by
Kevin QuintanillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Tooth Anatomy and Function
Human Tooth Anatomy and Function
Uploaded by
Kevin QuintanillaCopyright:
Available Formats
*The process of teeth emerging into the
Eruption Process
mouth and becoming visible.*
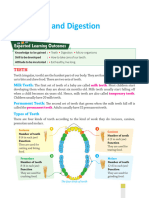
*First set of teeth, start erupting around 6 Human teeth are essential for mechanical
Primary Teeth
months.* food breakdown in the digestive system.
*Adult teeth that begin to replace primary There are four types of human teeth:
teeth around 6 years of age.*
Permanent Teeth Types of Teeth Tooth Eruption
incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
Introduction
*Stage where both primary and permanent Teeth are rooted in the upper (maxilla) and
Mixed Stage
teeth are present.* lower (mandible) jaws, covered by gums.
*One theory suggests that root development Teeth are composed of multiple tissues with
Root Development
pushes teeth into the mouth.* varying density and hardness.
Theories of Tooth Eruption
*Most widely accepted theory Role of Periodontal Ligaments
Incisors Function: Cutting food
*A factor within the tissues of the first Canines Function: Tearing food
pharyngeal arch is necessary for tooth Factor in First Pharyngeal Arch Initiation of Tooth Development Types of Teeth
development.* Premolars Function: Crushing food
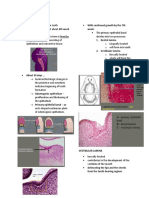
*Early stage where tooth development Molars Function: Crushing food
Bud Stage
begins.*
*Tooth development progresses with the
Cap Stage Humans are diphyodont, meaning they
formation of a cap-shaped structure.*
Stages of Tooth Development Dentition develop two sets of teeth: primary
(deciduous) and permanent (adult).
*Tooth takes on a bell shape and further
Bell Stage
develops.*
*Final stage where tooth structure matures.* Maturation Dental anatomy studies tooth structure,
development, and classification.
*Consists of various cells that produce
Enamel Organ
Tooth Development
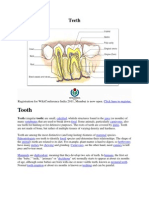
enamel.* Anatomic crown: The enamel-covered area
above the cementoenamel junction (CEJ).
*Contains cells that develop into dentin-
Dental Papilla Tooth Bud Components
Dental Anatomy
forming cells.* Anatomic root: The portion below the CEJ,
covered with cementum.
*Gives rise to various cells, including
Dental Follicle Different types of teeth have varying
cementoblasts, osteoblasts, and fibroblasts.*
Human Tooth numbers of roots.
*Hardest outer layer of the tooth, comprised
mostly of minerals.*
Enamel
Anatomy and Function
Humans typically have 20 primary (baby)
*Inner layer supporting the crown, made up teeth and 32 permanent (adult) teeth.
Dentin
of inorganic and organic materials.*
Development of Tooth Tissues Number of Teeth
Teeth are classified as incisors, canines,
*Specialized bone-like substance covering premolars, and molars.
Cementum
tooth roots.*
*Determines the shape of the tooth's root.* Hertwig's Epithelial Root Sheath
Three common systems for referring to
Tooth Notation Systems specific teeth: FDI, Universal Numbering, and
Palmer notation.
The hardest and highly mineralized
substance in the body.
Originates from oral ectoderm. 20 primary teeth, with 10 in the maxilla and
10 in the mandible.
Comprises 96% mineral, with water and
Primary Teeth (Deciduous)
Enamel Two types of incisors (centrals and laterals)
organic material making up the rest.
and two types of molars (first and second).
Normal color varies from light yellow to
grayish white.
32 permanent teeth, with 16 in the maxilla
Thickness varies across the tooth's surface. and 16 in the mandible.
Permanent Teeth
Located between enamel (or cementum) and Includes central and lateral incisors, canines,
the pulp chamber. premolars, molars, and third molars (wisdom
teeth).
Made up of inorganic materials, organic
materials, and water.
Dentin
Males tend to have larger teeth and jaws
Supports the crown of the tooth and acts as than females.
a protective layer.
Gender Differences
Differences in internal dental tissue
Contains microscopic dentinal tubules. Parts of a Tooth proportions: males have more dentin, and
females have more enamel.
Specialized bone-like substance covering
the tooth root.
Composition: inorganic material
(hydroxyapatite), organic material (collagen), Cementum
and water.
Thickest at the root apex and aids in tooth
stability.
The central part of the tooth filled with soft
connective tissue.
Contains blood vessels and nerves.
Odontoblasts initiate dentin formation. Dental Pulp
Other cell types include fibroblasts,
preodontoblasts, macrophages, and T
lymphocytes.
You might also like
- Odontopediatria MVRDocument8 pagesOdontopediatria MVRMonserrath VidalesNo ratings yet
- Ten Cates Oral Histology Development Structure and Function 9th Edition Ebook PDF VersionDocument62 pagesTen Cates Oral Histology Development Structure and Function 9th Edition Ebook PDF Versiondaniel.salazar67898% (46)
- Dental CodingDocument74 pagesDental CodingSakshi Bishnoi100% (2)
- Chapter-16 Digestion and Absorption: Important Definitions and ConceptsDocument8 pagesChapter-16 Digestion and Absorption: Important Definitions and ConceptsM JeevanNo ratings yet
- Development and Eruption of The TeethDocument5 pagesDevelopment and Eruption of The TeethZHAREIGHNEILE C. MAMOLONo ratings yet
- Poster About TeethDocument1 pagePoster About TeethNang Thanthar Aye MyaNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy Understanding The Structure and Function of TeethDocument4 pagesDental Anatomy Understanding The Structure and Function of TeethSafeer SefiNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption - L2Document82 pagesDigestion and Absorption - L2Susmita DuttaNo ratings yet
- Stephen - Teeth WorksheetDocument3 pagesStephen - Teeth Worksheetapi-348960952No ratings yet
- PRELIMS Oral PhysioDocument8 pagesPRELIMS Oral Physiobellaespeleta5No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TeethDocument17 pagesChapter 4 TeethAbegail RuizNo ratings yet
- Leaflet GigiDocument3 pagesLeaflet Gigiecha pasoNo ratings yet
- 2-Dev. To GeometriesDocument12 pages2-Dev. To GeometriesFLORENCE GERENTENo ratings yet
- 1st and 2nd - Lecture of Dental AnatomyDocument20 pages1st and 2nd - Lecture of Dental AnatomySenussi IbtisamNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroDocument17 pages1 IntroFLORENCE GERENTENo ratings yet
- Tooth Development, Eruption & Applied Aspects: Saurabh Roy 09.03.2016Document95 pagesTooth Development, Eruption & Applied Aspects: Saurabh Roy 09.03.2016reema aslamNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Eruption of Primary Teeth: Chchu, C Y YeungDocument6 pagesA Review of The Eruption of Primary Teeth: Chchu, C Y YeungBanyu علي تقويم BiruNo ratings yet
- 8&9 Preventive Orthodontics&space MaintainerDocument20 pages8&9 Preventive Orthodontics&space MaintainershawetshaebanNo ratings yet
- Sushma Development of Tooth 2nd SeminarDocument56 pagesSushma Development of Tooth 2nd SeminarDrSushma NareshNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy & Physiology: Lokender Yadav Sr-Manager Talent Development Unicorn Denmart LimitedDocument37 pagesDental Anatomy & Physiology: Lokender Yadav Sr-Manager Talent Development Unicorn Denmart LimitedLokender Yadav100% (1)
- Anatomi Gigi Geligi by TinaDocument44 pagesAnatomi Gigi Geligi by TinaTegNo ratings yet
- Oral Habits Retained Deciduous Teeth and Supernumeraries Premature LossDocument4 pagesOral Habits Retained Deciduous Teeth and Supernumeraries Premature LossGem Hanna Callano ParaguaNo ratings yet
- Primary Teeth: Transitional (Mixed) Dentition PeriodDocument2 pagesPrimary Teeth: Transitional (Mixed) Dentition PeriodGlynnis HonraNo ratings yet
- Digestion (Teeth)Document4 pagesDigestion (Teeth)OJ ICONICNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Dental AnatomyDocument16 pagesAn Overview of Dental Anatomyaimazaika1234No ratings yet
- Cleghorn2010 PDFDocument28 pagesCleghorn2010 PDFsilpayNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document7 pagesLec 4Ishtar AliNo ratings yet
- TeethDocument5 pagesTeethPradeep Arya100% (1)
- Odontogenesis NotesDocument14 pagesOdontogenesis NotesClarisse Mendoza100% (1)
- Dantotpathi FinalDocument59 pagesDantotpathi FinalGuna Soundari100% (1)
- ODONTOGENESISDocument7 pagesODONTOGENESISAngierika CorpuzNo ratings yet
- تشريح الاسنان الاولىDocument20 pagesتشريح الاسنان الاولىzainb1990355No ratings yet
- Tooth Origin and Formation - by Bugnariu Paul, Buterchi Codrut, Chit-Stinean AdonisDocument73 pagesTooth Origin and Formation - by Bugnariu Paul, Buterchi Codrut, Chit-Stinean AdonisVlad FlaviusNo ratings yet
- Tooth Development and Eruption c6Document26 pagesTooth Development and Eruption c6Wy Gnoix100% (1)
- Intro Dentistry Part-I MargvelashviliDocument16 pagesIntro Dentistry Part-I Margvelashvilirrq8cwk2gnNo ratings yet
- m1 - m2 Oral OccluDocument16 pagesm1 - m2 Oral OccluJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Endodontics 1: PrelimsDocument30 pagesEndodontics 1: PrelimsDaymon, Ma. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Anfis Gigi GeligiDocument40 pagesAnfis Gigi Geligilanoot barnabyNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Dentistry CourseDocument2 pagesOverview of The Dentistry CourseCielo DequiñaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Dental Anatomy 101 Dant PDFDocument42 pages1 - Dental Anatomy 101 Dant PDFRamez Rimez100% (1)
- Exploring Human Teeth Subtitle: An Overview of Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesExploring Human Teeth Subtitle: An Overview of Structure and FunctionzuhrakhaliddNo ratings yet
- Developmentofteeth StagesDocument45 pagesDevelopmentofteeth Stagesimi4100% (1)
- Esthetic Crowns For Primary Teeth A Review PDFDocument7 pagesEsthetic Crowns For Primary Teeth A Review PDFSan SanNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesDental Anatomy and PhysiologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Các giai đoạn phát triển của bộ răng từ sơ sinh đến trưởng thành 2023 gửi svDocument74 pagesCác giai đoạn phát triển của bộ răng từ sơ sinh đến trưởng thành 2023 gửi svAnh DũngNo ratings yet
- Oral Biology 1 Lab Manual: Faculty of DentistryDocument41 pagesOral Biology 1 Lab Manual: Faculty of DentistryMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Dental MorfologiDocument43 pagesDental MorfologiAvirna IdayantiNo ratings yet
- TeethDocument3 pagesTeethSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- CH24Document42 pagesCH24李威橙No ratings yet
- Grade4-Human BodyDocument23 pagesGrade4-Human BodyPldkNo ratings yet
- Patho Lec 4THDocument3 pagesPatho Lec 4THJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- DPP Dental Terms PDFDocument15 pagesDPP Dental Terms PDFana dizonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Dental Anatomy, Histology, Physiology, and OcclusionDocument39 pagesClinical Significance of Dental Anatomy, Histology, Physiology, and Occlusionvivi talawoNo ratings yet
- Class 4 - Teeth TypesDocument8 pagesClass 4 - Teeth Typessulagna.maitrayif24No ratings yet
- Exp SC 4 - Chapter 02Document8 pagesExp SC 4 - Chapter 02megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Kwon 2018Document11 pagesKwon 2018fatimahNo ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument20 pagesTooth DevelopmentArslan Jokhio0% (1)
- DentistryDocument1 pageDentistryKevin QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Blackboard SlidesManiaDocument23 pagesBlackboard SlidesManiaKevin QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Copia de Optical Fiber Installation Workshop by SlidesgoDocument51 pagesCopia de Optical Fiber Installation Workshop by SlidesgoKevin QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Process of ExplanationDocument5 pagesProcess of ExplanationKevin QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- VIVA Insurance GlossaryDocument23 pagesVIVA Insurance GlossaryKevin QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Ortho CaseDocument26 pagesOrtho CaseYusra ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dentistry 1 Year Lect. 1Document44 pagesIntroduction To Dentistry 1 Year Lect. 1abdulrazaqNo ratings yet
- Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerDocument3 pagesChoose The Most Appropriate AnswerMustafa S. JaberNo ratings yet
- Buccal CorridorDocument3 pagesBuccal Corridoreili1100% (1)
- Dentate PDIDocument5 pagesDentate PDIkelompok cNo ratings yet
- Arch Parameters and Dental Discrepancy (Crowding and Spacing) in A Sample of An Afro-Colombian PopulationDocument9 pagesArch Parameters and Dental Discrepancy (Crowding and Spacing) in A Sample of An Afro-Colombian PopulationnostaNo ratings yet
- Age Related Changes in Physiology of Normal Human Tooth Enamel: A ReviewDocument7 pagesAge Related Changes in Physiology of Normal Human Tooth Enamel: A ReviewHair ventionNo ratings yet
- Transverse, Vertical TpaDocument8 pagesTransverse, Vertical Tpasyaza azmanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Kanno - J Oral Rehab - 2006 CópiaDocument13 pages1 - Kanno - J Oral Rehab - 2006 CópiaYvelisse LoraNo ratings yet
- AJODO-mechanism-case ReportDocument10 pagesAJODO-mechanism-case ReportAthira JithendranathNo ratings yet
- Pulpectomy ProceduresDocument3 pagesPulpectomy ProceduresITS DENTAL COLLEGE Greater NoidaNo ratings yet
- A Harmonious Smile: Biological CostsDocument12 pagesA Harmonious Smile: Biological Costsjsjs kaknsbsNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Distal Extension Removable Partial Dentures Versus Vitallium OnesDocument4 pagesThermoplastic Distal Extension Removable Partial Dentures Versus Vitallium OnesDeasireeNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Anterior Coupling On Mandibular MovementDocument9 pagesThe Influence of Anterior Coupling On Mandibular MovementRavneet LehalNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DentistryDocument8 pagesPediatric DentistryPavleta RashkovaNo ratings yet
- Management of Fused Primary Teeth in Esthetic Zone A Case ReportDocument6 pagesManagement of Fused Primary Teeth in Esthetic Zone A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Development of Dental OcclusionDocument89 pagesDevelopment of Dental OcclusionMothi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Affect of Premature Loss in MasticationDocument6 pagesAffect of Premature Loss in MasticationAaser AhmedNo ratings yet
- Transient MalocclusionsDocument30 pagesTransient Malocclusionsdrsasi100% (1)
- Short-Term Stability of Anterior Open Bite Treatment With Clear Aligners in AdultsDocument9 pagesShort-Term Stability of Anterior Open Bite Treatment With Clear Aligners in Adultspredent230No ratings yet
- Agreement Evaluation of A Newly ProposedDocument10 pagesAgreement Evaluation of A Newly ProposedOsama GamilNo ratings yet
- Management of Impacted Canine1Document88 pagesManagement of Impacted Canine1Saumya Singh100% (1)
- Tooth EruptionDocument48 pagesTooth EruptionMohammed hisham khanNo ratings yet
- Dental Morphology & AnatomyDocument22 pagesDental Morphology & Anatomyhollerb123No ratings yet
- Cephalometric Appraisal of Nonextraction Begg Treatment of Class II MalocclusionsDocument10 pagesCephalometric Appraisal of Nonextraction Begg Treatment of Class II MalocclusionsValery V JaureguiNo ratings yet
- Ijed 2022 03 s0340CracksGerdolleBrowetDocument17 pagesIjed 2022 03 s0340CracksGerdolleBrowetkhaled emadNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Treatment PlanDocument44 pagesEndodontic Treatment Planlinh nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Use of Iowa Spaces For The Orthodontic Management of Mandibular Postsurgical Skeletal RelapseDocument6 pagesUse of Iowa Spaces For The Orthodontic Management of Mandibular Postsurgical Skeletal RelapseRamya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 LN - 10Document48 pagesGrade 4 LN - 10Annes AnthuvanNo ratings yet