Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 08 2021 22 Answers
Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 08 2021 22 Answers
Uploaded by
Chirag PatilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 08 2021 22 Answers
Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 08 2021 22 Answers
Uploaded by
Chirag PatilCopyright:
Available Formats
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER TEST 08 FOR TERM-2 EXAM (2021-22)
(ANSWERS)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE (086) MAX. MARKS : 40
CLASS : X DURATION: 2 HRS
General Instructions:
1. All questions are compulsory.
2. The question paper has three sections and 15 questions. All questions are compulsory.
3. Section–A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section–B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and
Section–C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
4. Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the
alternatives in such questions.
SECTION – A
Questions 1 to 7 carry 2 marks each.
1. (a) What is meant by vegetative propagation?
(b) How will a plant be benefitted if it reproduces by this method?
Ans: (a) Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction that occur in plants in which
new plants are produced by vegetative parts such as the roots, stems and leaves.
(b) Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those
produced from seeds. Such method also makes possible the propagation of plants that have lost
the capacity to produce seeds.
2. Consider a metal M with electronic configuration: 2, 8, 3.
(a) To which group and period of periodic table does M belong?
(b) Write the formulae of its sulphate and phosphate.
Ans: (a) As, there are 3 electrons in valence shell hence M belongs to group 13. Also, as
electrons are filled in 3 shells, (K, L, M) thus ‘M’ belongs to 3rd period.
(b) As, ‘M’ has 3 electrons in its valence shell, thus it contributes 3 electrons in bonding.
Formulae for sulphate and phosphate are M2(SO4)3 and MPO4 respectively.
3. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties,
regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each
other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. Write the names of functional group of
the compounds given below:
(a) CH3−COOH
(b) CH3−CH2−CH2−OH
Ans: (a) –COOH group: Carboxylic acid 1
(b) –OH group: Alcohol
4. Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water, but multiply in sugar solution. Give one reason for
this.
Ans: Yeast multiplies by the process of budding. It requires energy for sustaining all its life
activities. Sugar provides energy to yeast whereas water does not provide energy, so it fails to
multiply in water because of inadequate energy.
5. The following organisms form a food chain.
Insect, Hawk, Grass, Snake, Frog
Which of these organisms will have the highest concentration of non-biodegradable chemicals?
Name the phenomenon.
Ans: Highest concentration of harmful nonbiodegradable chemicals are found in top consumer
hawk. The phenomenon exhibited here is biomagnification.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1-
OR
From the following groups of living things:
(a) Create a food chain which is the most advantageous for human being in terms of energy.
(b) Construct a food web using the living things mentioned above.
Ans: (a) Short food chains are more efficient in terms of energy. The shorter the food chain is,
more is the available amount of energy for human beings to utilize.
Cereal plant → Human being
(b)
6. Can you think of magnetic field configuration with three poles?
Ans: Magnetic poles always exist in pairs. However one can imagine magnetic field
configuration with three poles - when North poles of two magnets are glued together or South
poles of two magnets are glued together to provide three field configuration.
OR
In the given diagram, crosses ⨂ represent a uniform magnetic field directed into the paper. A
conductor XY moves in the field toward right side.
(a) Find the direction of induced current in the conductor.
(b) Name the rule applicable here. Justify your answer.
Ans: (a) The direction will be from Y to X. By Fleming's right hand rule the current will be
induced in the upward direction (Y to X).
(b) Fleming's right hand rule: Hold the thumb, the fore finger and the middle finger of right hand
at right angles to each other. If the forefinger is in the direction of magnetic field and the thumb
points in the direction of motion of conductor, then the direction of induced current is indicted by
middle finger.
7. In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50 : 50.
Justify.
Ans: Human females are homogametic (44 + XX), that is they produce only one type of ova (22
+ X). Human males are heterogametic. They produce two types of sperms : (22 + X) and (22 +
Y) in equal proportion that is 50 : 50 ratio. The chance of getting male or female child is also 50 :
50, as there is equal chance of androsperm (22 + Y) or gynosperm (22 + X) fertilising an ovum.
OR
How do Mendel’s experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2-
Ans: (i) When a cross was made between a tall pea plant with round seeds and a short pea plant
with wrinkled seeds, the F1 progeny plants were all tall with round seeds. This indicates that tall
and round seeds are the dominant traits.
(ii) When the F1 plants are self-pollinated, the F2 progeny consist of some tall plants with round
seeds and some short plants with wrinkled seeds which are the parental traits.
(iii) There were also some new combinations like tall plants with wrinkled seeds and short plants
with round seeds.
(iv) Thus, it may be concluded that tall and short traits and round and wrinkled seed traits have
been inherited independently.
SECTION – B
Questions 8 to 13 carry 3 marks each.
8. An element ‘M’ has atomic number 12.
(a) Write its electronic configuration and valency.
(b) Is ‘M’ a metal or a non-metal? Give reason in support of your answer.
(c) Write the formula and nature (acidic/basic) of the oxide of M.
Ans: (a) Electronic Configuration – 2, 8, 2
Valency – 2
(b) There are two electrons in the outermost shell of M and it easily loses them to form a positive
ion. Thus, element M is a metal.
(c) M = 2, O = 2
Chemical formula M2O2 = MO
It is a basic oxide.
OR
Four elements A, B, C and D along with their configurations are given below :
Element A – 2, 1; Element B – 2, 8; Element C – 2, 8, 1; Element D – 2, 8, 8.
(i) Which two elements belong to the same period?
(ii) Which two elements belong to the same group?
(iii) Which element out of A and C is more reactive and why?
(iv) Which element out of A and B forms more number of compounds?
Ans: (i) Elements in a period have same number of shells. Thus, elements A and B belong to the
second period while C and D belong to the third period.
(ii) Elements in a group have same number of valence electrons. Thus, elements A and C belong
to the same group 1, and elements B and D belong to the same group 18.
(iii) Element C is more reactive than element A due to its bigger size and weaker force of
attraction of the nucleus on the valence electrons.
(iv) Elements B, being a noble gas does not form compounds. Hence, element A forms more
number of compounds than element B.
9. Define the following compounds:
(a) Alkanes
(b) Alkenes
(c) Alkynes
Ans: (a) Alkane: Saturated hydrocarbon with C – C single bond with molecular formula CnH2n + 2.
(b) Alkene: Unsaturated hydrocarbon with double bond in C = C with molecular formula CnH2n.
(c) Alkyne: Unsaturated hydrocarbon with triple bond in C ≡ C with molecular formula CnH2n – 2.
10. Mendel performed several experiments that include monohybrid, dihybrid and trihybrid crosses.
On the basis of these experiments, mendel formulated laws of heredity. How do Mendel’s
experiment shows that traits are inherited independently?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3-
Ans: In a dihybrid cross given by Mendel, it was observed that when two pairs of traits or
characters were considered, each trait expressed independent of the other. Thus, Mendel was able
to propose the Law of Independent Assortment, which state that pair of genes separate
independently of each other during gamete formation. This could be explained clearly from the
given cross:
F2 generation ratio : 9 (Round-yellow) : 3 (Round-green) : 3 (Wrinkled-yellow) : 1 (Wrinkled-
green)
11. In a house 4 bulbs of 100 watt each are lighted for 5 hours daily, 2 fans of 50 watt each are used
for 10 hours daily and a refrigerator of 1.00 kW is used for half an hour daily. Calculate the total
energy consumed in a month of January and its cost at the rate of ` 3.60 per kWh.
Ans: Power of each bulb = 100 watt
Total power of 4 bulbs, P1 = 4 × 100 = 400 watt
Energy consumed by bulbs in 1 day, E1 = P1 × t = 400 watt × 5 hours = 2000 Wh = 2 kWh
Power of each fan = 50 watt
Total power of 2 fans = 2 × 50 watt P2 = 100 watt
Energy consumed by fans in 1 day, E2 = P2 × t = 100 watt × 10 hours = 1000 watt hour = 1 kWh
Energy consumed by refrigerator, E3 = 1 kW × 1/2 h = 0.5 kWh
Total energy consumed in one day
E = E1 + E2 + E3 = (2 + 1 + 0.5) kWh = 3.5 kWh
Total energy consumed in a month of January (31 days)
= E × 31 = (3.5 × 31) kWh = 108.5 kWh
Cost of energy consumed = Rs. (108.5 × 3.60) = Rs. 390.6
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4-
OR
(a) Define electrical resistivity.
(b) Calculate the resistance of 1 km long copper wire of cross-section area 2 × 10–2 cm2.
[Resistivity of copper = 1.62 × 10–8 Ω m]
Ans: (a) Electrical resistivity of the material of a conductor is the resistance offered by the
conductor of length 1 m and area of cross-section 1m2.
l
(b) Resistance, R where, r = resistivity of copper = 1.62 × 10–8 Ω m
A
l = length of wire = 1 × 103m
A = Area of cross-section = 2 × 10–2 cm2
1.62 108 1000
∴ R ⇒ R = 0.81 × 10 Ω = 8.1 Ω
2 102 104
12. (a) State the relation correlating the electric current flowing in a conductor and the voltage
applied across it. Also, draw a graph to show this relationship.
(b) Find the resistance of a conductor if the electric current flowing through it is 0.35 A when the
potential difference across it is 1.4 V.
Ans: (a) The flow of current (I) in the conductor is directly proportional to the potential
difference (V) established across the conductor provided the physical conditions remain same.
Mathematically, V = IR, where R is resistance of the conductor.
(b) Given: Potential Difference (V) = 1.4 V
Current (I) = 0.35 A
As per Ohm's law, V = IR
V 1.4
So, R 4
I 0.35
13. The ozone layer is the common term for the high concentration of ozone that is found in the
stratosphere around 15–30 km above the earth's surface. It covers the entire planet and protects
life on earth.
(a) Explain the role of UV radiation in producing ozone layer. Mention the reaction involved.
(b) Why the amount of ozone in the atmosphere dropped sharply in the 1980's ?
Ans: (a) Ozone is formed in the upper atmosphere when solar UV radiation dissociate molecules
of oxygen (O2) and then this oxygen atom (O) combines with an oxygen molecule. Reaction
involved:
O2 → O + O
O + O2 → O3
(b) The amount of Ozone in the atmosphere began to drop sharply in the 1980s. This is due to the
increased use of synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons which are used as refrigerants and
in fire extinguishers.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5-
SECTION – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (a,
b and c). Parts a and b are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part c.
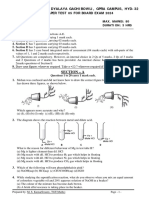
14. When current is flowing through the solenoid, the magnetic field line pattern resembles exactly
with those of a bar magnet with the fixed polarity, i.e., North and South pole at its ends and it
acquires the repulsive and attractive properties similar to bar magnet. Hence, the current carrying
solenoid behaves as a bar magnet.
(a) What are the uses of solenoid?
(b) Draw magnetic filed lines for the current carrying solenoid as shown in figure and explain
that out of three points A, B and C, at which point, magnetic field strength is maximum.
(c) How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the North and South poles of
a current carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Ans: (a) Solenoid are used to form temporary magnet called electromagnet. The electromagnet
has more advantages over permanent bar magnet as electromagnets can be turned on and off
making them effective as controls and switches.
(b) Outside the solenoid magnetic field is minimum. At the ends of solenoid, magnetic field
strength is half to that inside. So maximum field strength is at point B.
(c) When current is passed through a solenoid, it acts as a bar magnet. Suspend a bar magnet
from a support. Bring a current-carrying solenoid near the North pole of the bar magnet. Observe
if it gets attracted or repelled.
Now, perform the same action for south pole of the bar magnet.
Following the rule that opposite poles attract each other, one can identify the poles of the
solenoid.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 6-
OR
Explain the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction briefly.
Ans: To explain electromagnetic induction take two different coils of copper wire having large
number of turns (say 100 and 50 turns respectively). Insert them over a non-conducting
cylindrical roll, as shown in figure. Connect the coil-1, having large number of turns, in series
with a battery and a plug key. Also connect the other coil-2 with a galvanometer as shown.
Plug in the key. Observe the galvanometer. You will observe that the needle of the galvanometer
instantly jumps to one side and just as quickly returns to zero, indicating a momentary current in
coil-2.
Hence, the change in magnetic field lines associated with the coil-2 is the cause of induced
electric current in it.
15. Seema crossed pure breed pea plants having round-yellow seeds with wrinkled green seeds and
found that only A-B type of seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1 generation pea
plants having A-B type of seeds were cross-breed by self-pollination, then in addition to the
original round yellow and wrinkled green seeds, two new varieties A-D and C-B types of seeds
were also obtained.
(a) What type of seeds are A-B type of seeds?
(b) Which types of traits are A and B. Dominant or recessive?
(c) What type of cross is the above cross? Define the type of cross.
Ans: (a) A-B type of seeds are round in shape and yellow in colour.
(b) A-B type are dominant traits.
(c) Dihybrid cross. A cross between two plants, which differ in two pairs of contrasting
characters are called dihybrid cross.
OR
Differentiate gene and allele.
Ans: Allele (allelomorphs) refers to the alternate form of a gene pair present on the same loci in
the homologous chromosome, whereas gene is the smallest unit of an organism capable of
transmitting genetic information and expressing the same.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 7-
You might also like
- Kira + Andrew Cartagena GuideDocument20 pagesKira + Andrew Cartagena GuideKira & Andrew100% (1)
- 2021-05-12 Wynwood Design Review Committee - Full Agenda-2577Document4 pages2021-05-12 Wynwood Design Review Committee - Full Agenda-2577the next miamiNo ratings yet
- Feminism Final PaperDocument19 pagesFeminism Final PaperRubee Lee Won Ag100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 05 For Term-2 Exam (2021-22)Document12 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 05 For Term-2 Exam (2021-22)Ranjeet kumar PanditNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 05 2021 22 AnswersDocument8 pagesScience Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 05 2021 22 AnswersChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 07 2021 22Document4 pagesScience Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 07 2021 22Chirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 01 2021 22 AnswersDocument8 pagesScience Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 01 2021 22 AnswerssamridhiNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 07 2021 22 AnswersDocument7 pagesScience Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 07 2021 22 AnswersShreyans JainNo ratings yet
- 4 5848043971497956582 PDFDocument12 pages4 5848043971497956582 PDFHOORIYA FATIMANo ratings yet
- SampleDocument13 pagesSamplePritey YadavNo ratings yet
- Science Term-2 Sample PaperDocument9 pagesScience Term-2 Sample Paper[Vishal Kumar Paswan] [10 B]No ratings yet
- Click Here To Join Us On TelegramDocument14 pagesClick Here To Join Us On TelegramsugomaNo ratings yet
- Science 2013 PDFDocument19 pagesScience 2013 PDFashwaniNo ratings yet
- Science Class 10 Term 2 Sample Paper 2 SolutionDocument7 pagesScience Class 10 Term 2 Sample Paper 2 SolutionSangeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- ST 01 - Science - C X 1Document4 pagesST 01 - Science - C X 1pratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Test Paper 03 For Board Exam 2020 21 Answer 1Document15 pagesScience Class X Sample Test Paper 03 For Board Exam 2020 21 Answer 1jkc collegeNo ratings yet
- Science Sample Paper1Document4 pagesScience Sample Paper1Haresh Tripathy 2No ratings yet
- SET-A Worksheet-1 General Science (086) Term - II Question Paper Class - X General InstructionsDocument6 pagesSET-A Worksheet-1 General Science (086) Term - II Question Paper Class - X General InstructionsSnehasish MohantyNo ratings yet
- Science 3Document4 pagesScience 3Johann SoncyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2020 SET 1Document6 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2020 SET 1Purvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Delhi Public School Nacharam Sample Question Paper - 3 Science (086) Class-X, TERM IIDocument6 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Delhi Public School Nacharam Sample Question Paper - 3 Science (086) Class-X, TERM IIDeepika ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- SET-A Worksheet-1 General Science (086) Term - II: Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesSET-A Worksheet-1 General Science (086) Term - II: Marking SchemeSnehasish MohantyNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 01 For Term-2 Exam (2021-22)Document4 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 01 For Term-2 Exam (2021-22)samridhiNo ratings yet
- CBSC Class-9 Science SET-3: Section - ADocument11 pagesCBSC Class-9 Science SET-3: Section - AEliyasuddin AliNo ratings yet
- 10 Cbse Science Mock Test PaperDocument8 pages10 Cbse Science Mock Test PaperSumedha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023Document8 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023SubhaNo ratings yet
- Section-A: Physics Marks: 12Document5 pagesSection-A: Physics Marks: 12YASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument14 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023 Answershithesh365No ratings yet
- Science 2012 PDFDocument16 pagesScience 2012 PDFashwaniNo ratings yet
- Science Sample Paper Class 10 Term 2Document10 pagesScience Sample Paper Class 10 Term 2NandiniNo ratings yet
- Set 7 - Science Term 2 Sample Question PaperDocument11 pagesSet 7 - Science Term 2 Sample Question PaperkannaneastNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Test Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020 21 AnswersDocument16 pagesScience Class X Sample Test Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020 21 AnswersAjit MoteNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Mankhurd: Periodic Test (2021-22)Document2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Mankhurd: Periodic Test (2021-22)hweta173No ratings yet
- SC 22Document8 pagesSC 22mili groupNo ratings yet
- 10 Science t2 sp01Document8 pages10 Science t2 sp01adityasharma6261srNo ratings yet
- Science PaperDocument10 pagesScience PaperchiragNo ratings yet
- Science 2015 PDFDocument15 pagesScience 2015 PDFashwaniNo ratings yet
- CBSE CBSE Class 10 Science Solved Question Paper 2015Document13 pagesCBSE CBSE Class 10 Science Solved Question Paper 2015s k kumarNo ratings yet
- Class X - Science - Pre Board I - 2020-21 - Pages-DeletedDocument9 pagesClass X - Science - Pre Board I - 2020-21 - Pages-DeletedRylan DsaNo ratings yet
- X Science Term-2 Preboard-1 QPDocument5 pagesX Science Term-2 Preboard-1 QPRohail HussainNo ratings yet
- 9th Science PaperDocument7 pages9th Science PaperHIRAL SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Science Set 1Document12 pagesScience Set 1amithsabusNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Pre-Board Set 3 Question PaperDocument12 pagesClass X Science Pre-Board Set 3 Question PapertyNo ratings yet
- Science Question PaperDocument7 pagesScience Question Paperamogh biyalNo ratings yet
- Science (Term - 2), CODE - 086 Sample - Paper - 1 Class - X (2021 - 22) Chapters Covered - CH 4-Carbon and Its Compounds, CH 8 - How Do OrganismsDocument5 pagesScience (Term - 2), CODE - 086 Sample - Paper - 1 Class - X (2021 - 22) Chapters Covered - CH 4-Carbon and Its Compounds, CH 8 - How Do OrganismsSnehasish MohantyNo ratings yet
- 2nd Science Ques PaperDocument8 pages2nd Science Ques Paperfahima sunasaraNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 1Document8 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 1rmgokul78No ratings yet
- Class X Term 2 Subject: Science (086) Time: 2 Hours Max. Marks: 40 General InstructionsDocument4 pagesClass X Term 2 Subject: Science (086) Time: 2 Hours Max. Marks: 40 General InstructionsAnjali SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science Set 8Document5 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science Set 8Looa pqswNo ratings yet
- Kanaan: Sample Papers?Document14 pagesKanaan: Sample Papers?Laxmi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment-1 2014-2015 Class - IXDocument5 pagesSummative Assessment-1 2014-2015 Class - IXvidhan tiwariNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Board Class 10 March21 Science Question Paper With Solutions 2023Document26 pagesGujarat Board Class 10 March21 Science Question Paper With Solutions 2023Mere HamsafarNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (086) Term 2 (2021-22) Max. Marks:40 Time Allowed: 2 Hours General InstructionsDocument5 pagesClass X Science (086) Term 2 (2021-22) Max. Marks:40 Time Allowed: 2 Hours General InstructionslembdaNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (086) Term 2 (2021-22) Max. Marks:40 Time Allowed: 2 Hours General InstructionsDocument5 pagesClass X Science (086) Term 2 (2021-22) Max. Marks:40 Time Allowed: 2 Hours General InstructionsRAJASEKAR RAJAMANICKAMNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 37 Science (086) Class-X, Session: 2021-22Document6 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 37 Science (086) Class-X, Session: 2021-22E. Poorna AshikNo ratings yet
- Cbse 10th Science 2019 Paper Watermark 35Document39 pagesCbse 10th Science 2019 Paper Watermark 35Ghanshayam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Science PB 1 Term 1 PaperDocument5 pagesScience PB 1 Term 1 PaperMukundan PolurNo ratings yet
- Padhle Ebook - Previous 12 Year Question Papers With Solutions 2009-20 - Class 10 Science PDFDocument283 pagesPadhle Ebook - Previous 12 Year Question Papers With Solutions 2009-20 - Class 10 Science PDFSiddharth SouravNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper 2016 Science Class - X (SA - II) Time Allowed: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 90 General InstructionsDocument5 pagesSample Question Paper 2016 Science Class - X (SA - II) Time Allowed: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 90 General InstructionsAbhishek SainiNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bhai Bor Matt KarDocument2 pagesBhai Bor Matt KarChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 05 2021 22 AnswersDocument8 pagesScience Class X Term 2 Sample Paper Test 05 2021 22 AnswersChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- No SleepDocument2 pagesNo SleepChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- GugugagaDocument11 pagesGugugagaChirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Case Study On TRAUMA#1 GarlinDocument20 pagesCase Study On TRAUMA#1 Garlinanon_162719508No ratings yet
- (PDF) Johnson VictorDocument6 pages(PDF) Johnson Victorchinmay vijay100% (1)
- TSH The Sexuality Wheel Tool EnglishDocument2 pagesTSH The Sexuality Wheel Tool EnglishRita TorresNo ratings yet
- Phonetic and PhonileDocument26 pagesPhonetic and PhonilewaqasNo ratings yet
- Air Plant Care Sheet: LightDocument3 pagesAir Plant Care Sheet: LightM Mohsin ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Table SettingDocument4 pagesTable SettingBianca FormantesNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in HRMDocument7 pagesEmerging Trends in HRMBarsha ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan For Grade 10 Mapeh: Don Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High SchoolDocument3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan For Grade 10 Mapeh: Don Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High SchoolChristine Manjares - OañaNo ratings yet
- RPS Literal ReadingDocument13 pagesRPS Literal ReadingFransiska Densiana LurukNo ratings yet
- B-52245E04 System 6T Model B Maintenance 1983Document389 pagesB-52245E04 System 6T Model B Maintenance 1983Jose PerezNo ratings yet
- Final Project Imr664 (CCRM Record Center)Document25 pagesFinal Project Imr664 (CCRM Record Center)MOHD IZWANE WAHED100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Technology For Teaching and LearningNiña Mae CabsagNo ratings yet
- Eld 307 Writing Analysis DdaDocument1 pageEld 307 Writing Analysis Ddaapi-253456954No ratings yet
- O P Jindal Modern School, Hisar: Worksheet No. 3 Subject-Evs NAME: ................... ROLL NO. . Class 5Document2 pagesO P Jindal Modern School, Hisar: Worksheet No. 3 Subject-Evs NAME: ................... ROLL NO. . Class 5Raghav BansalNo ratings yet
- Application of Trigonometry Solved Board Q Paper-2Document8 pagesApplication of Trigonometry Solved Board Q Paper-2Kunal SagarNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan: Carmen National High School Carmen, San Agustin, RomblonDocument2 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan: Carmen National High School Carmen, San Agustin, RomblonVina Verdadero TomeNo ratings yet
- KET、PET不规则动词表Document2 pagesKET、PET不规则动词表kaiying zhangNo ratings yet
- May 25, 2021 Revised Chapter 1-4Document70 pagesMay 25, 2021 Revised Chapter 1-4angelo felizardoNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy in Dermatology PDFDocument5 pagesHomeopathy in Dermatology PDFlndsNo ratings yet
- Diesel Pump Clamping Device MANUALDocument61 pagesDiesel Pump Clamping Device MANUALBii NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document3 pagesActivity 4Sittie Asnile MalacoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To AccountingDocument5 pagesReviewer For CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To AccountingPatrick John AvilaNo ratings yet
- A Real Case Against The Jews - FinalDocument5 pagesA Real Case Against The Jews - Finalnofestering7255No ratings yet
- Pan New 49aDocument8 pagesPan New 49aShaik NoorshaNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis On Cadbury India LTDDocument21 pagesCost Analysis On Cadbury India LTDSurya Deepak Goud80% (20)
- Python Exception Handling - Try, Except and Finally PDFDocument1 pagePython Exception Handling - Try, Except and Finally PDFSyed Muhammad ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Account StatementDocument12 pagesAccount StatementSanjeev JoshiNo ratings yet